|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
O'Connell JB, Maggard MA and Ko CY: Colon
cancer survival rates with the new American joint committee on
cancer sixth edition staging. J Natl Cancer Inst. 96:1420–1425.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hari DM, Leung AM, Lee JH, Sim MS, Vuong
B, Chiu CG and Bilchik AJ: AJCC cancer staging manual 7th edition
criteria for colon cancer: Do the complex modifications improve
prognostic assessment? J Am Coll Surg. 217:181–190. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cerottini JP, Caplin S, Pampallona S and
Givel JC: Prognostic factors in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep.
6:409–414. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Micu BV, Vesa SC, Pop TR and Micu CM:
Evaluation of prognostic factors for 5 year-survival after surgery
for colorectal cancer. Ann Ital Chir. 91:41–48. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rashtak S, Ruan X, Druliner BR, Liu H,
Therneau T, Mouchli M and Boardman LA: Peripheral neutrophil to
lymphocyte ratio improves prognostication in colon cancer. Clin
Colorectal Cancer. 16:115–123 e3. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ma C, Xie J, Luo C, Yin H, Li R, Wang X,
Xiong W, Zhang T, Jiang P, Qi W, et al: OxLDL promotes
lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis in gastric cancer by
upregulating VEGFC expression and secretion. Int J Oncol.
54:572–584. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nowak C and Ärnlöv J: A Mendelian
randomization study of the effects of blood lipids on breast cancer
risk. Nat Commun. 9:39572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Murtola TJ, Kasurinen TVJ, Talala K, Taari
K, Tammela TLJ and Auvinen A: Serum cholesterol and prostate cancer
risk in the Finnish randomized study of screening for prostate
cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 22:66–76. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Raju K, Punnayanapalya SS, Mariyappa N,
Eshwarappa SM, Anjaneya C and Kai LJ: Significance of the plasma
lipid profile in cases of carcinoma of cervix: A tertiary hospital
based study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:3779–3784. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fan TWM, Zhang X, Wang C, Yang Y, Kang WY,
Arnold S, Higashi RM, Liu J and Lane AN: Exosomal lipids for
classifying early and late stage non-small cell lung cancer. Anal
Chim Acta. 1037:256–264. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang Y, Mauldin PD, Ebeling M, Hulsey TC,
Liu B, Thomas MB, Camp ER and Esnaola NF: Effect of metabolic
syndrome and its components on recurrence and survival in colon
cancer patients. Cancer. 119:1512–1520. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peng F, Hu D, Lin X, Chen G, Liang B, Chen
Y, Li C, Zhang H, Xia Y, Lin J, et al: An in-depth prognostic
analysis of baseline blood lipids in predicting postoperative
colorectal cancer mortality: The FIESTA study. Cancer Epidemiol.
52:148–157. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Manfredi S, Bouvier AM, Lepage C, Hatem C,
Dancourt V and Faivre J: Incidence and patterns of recurrence after
resection for cure of colonic cancer in a well defined population.
Br J Surg. 93:1115–1122. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Benson AB III, Schrag D, Somerfield MR,
Cohen AM, Figueredo AT, Flynn PJ, Krzyzanowska MK, Maroun J,
McAllister P, Van Cutsem E, et al: American society of clinical
oncology recommendations on adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II
colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 22:3408–3419. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
O'Connor ES, Greenblatt DY, LoConte NK,
Gangnon RE, Liou JI, Heise CP and Smith MA: Adjuvant chemotherapy
for stage II colon cancer with poor prognostic features. J Clin
Oncol. 29:3381–3388. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A: AJCC cancer staging manual, 7th ed.
Springer. (New York, NY). 2010.
|
|
18
|
Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH and
Theise ND: WHO classification of tumours of the digestic system.
(4th). (Lyon). IARC press. 2010.
|
|
19
|
Zhou BF and Cooperative Meta-Analysis
Group of the Working Group on Obesity in China: Predictive values
of body mass index and waist circumference for risk factors of
certain related diseases in Chinese adults-study on optimal cut-off
points of body mass index and waist circumference in Chinese
adults. Biomed Environ Sci. 15:83–96. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
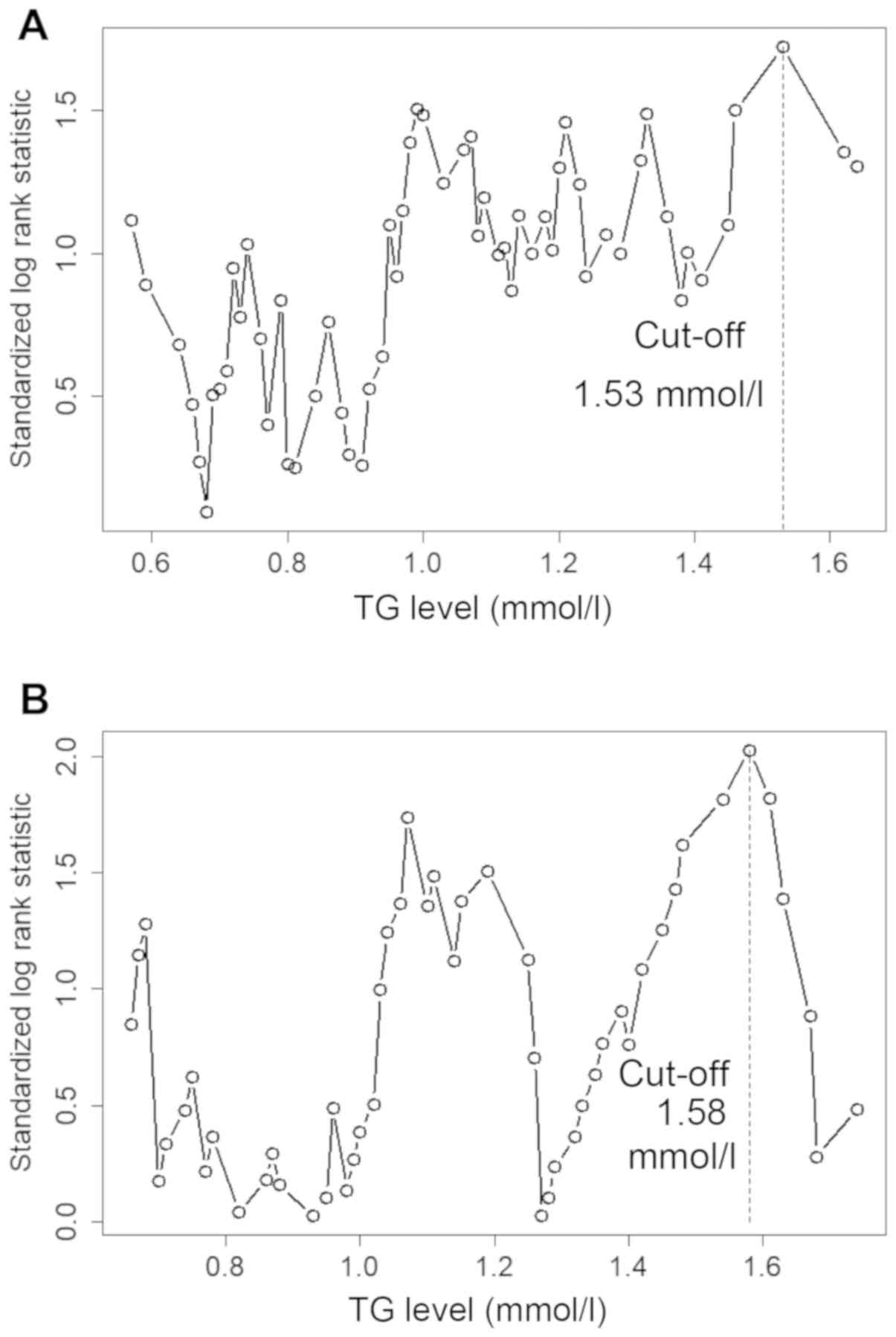
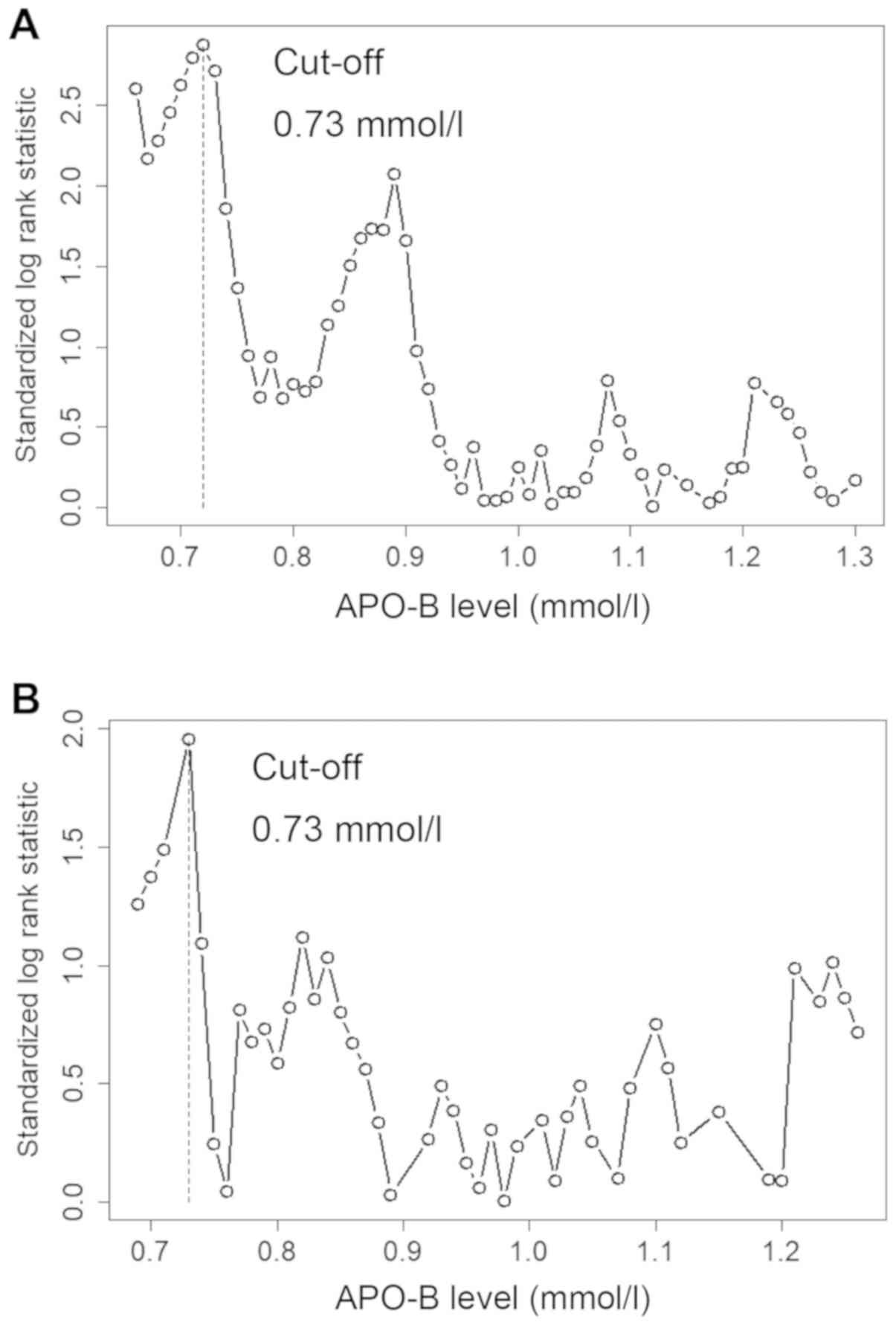
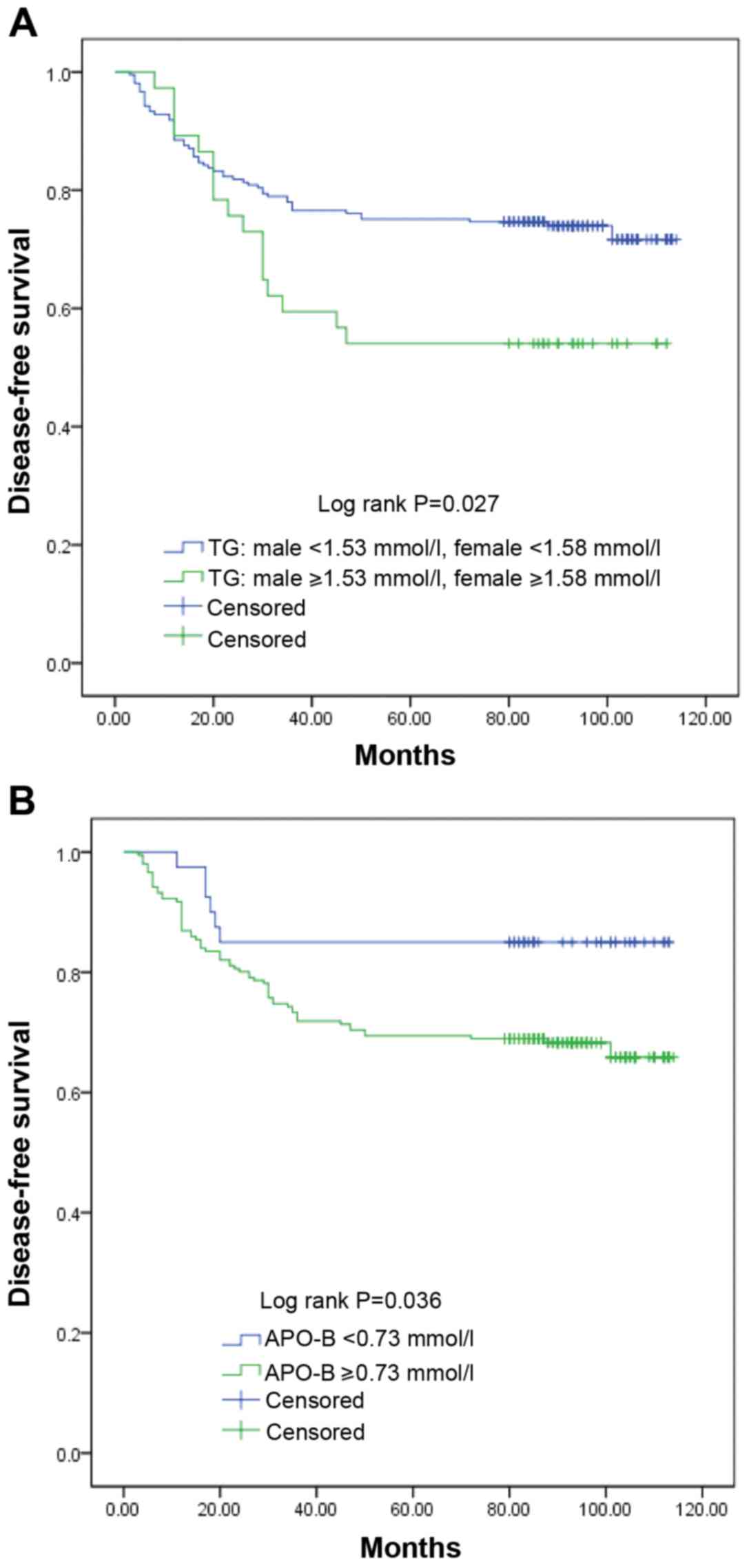
Torsten H and Berthold L: On the exact
distribution of maximally selected rank statistics. Comput Stat
Data Anal. 43:121–137. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Brown MS and Goldstein JL: A
receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science.
232:34–47. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kane JP: Apolipoprotein B: Structural and
metabolic heterogeneity. Annu Rev Physiol. 45:637–650. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Borgquist S, Butt T, Almgren P, Shiffman
D, Stocks T, Orho-Melander M, Manjer J and Melander O:
Apolipoproteins, lipids and risk of cancer. Int J Cancer.
138:2648–2656. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Katzke VA, Sookthai D, Johnson T, Kühn T
and Kaaks R: Blood lipids and lipoproteins in relation to incidence
and mortality risks for CVD and cancer in the prospective
EPIC-Heidelberg cohort. BMC Med. 15:2182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
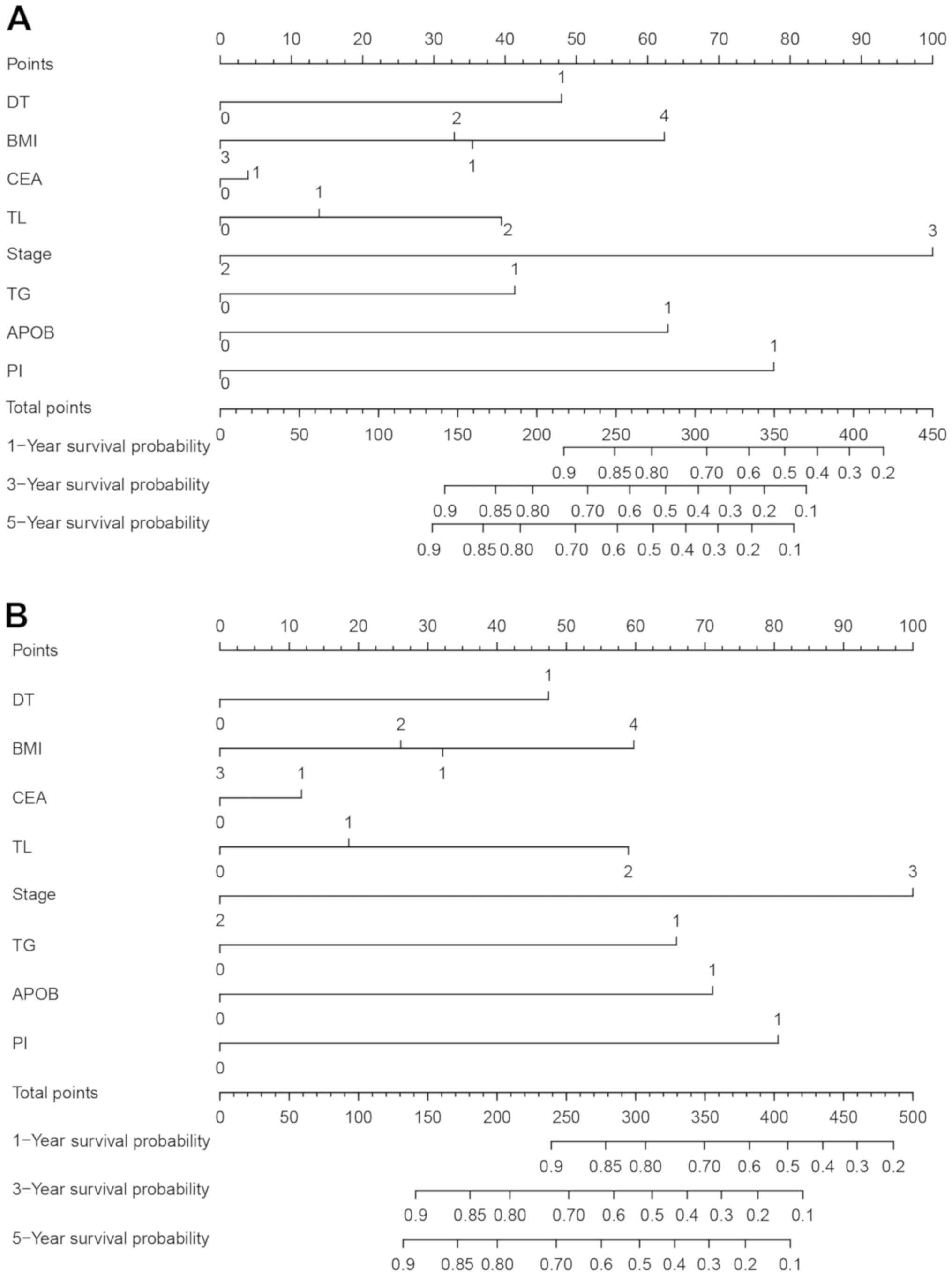
Chen S, Lai Y, He Z, Li J, He X, Shen R,
Ding Q, Chen H, Peng S and Liu W: Establishment and validation of a
predictive nomogram model for non-small cell lung cancer patients
with chronic hepatitis B viral infection. J Transl Med. 16:1162018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma MZ, Yuan SQ, Chen YM and Zhou ZW:
Preoperative apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A1 ratio: A novel
prognostic factor for gastric cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
11:2169–2176. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
National Cholesterol Education Program
(NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High
Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III), . Third
report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert
panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood
cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III) final report.
Circulation. 106:3143–3421. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Angelin B, Eriksson M and Rudling M: Bile
acids and lipoprotein metabolism: A renaissance for bile acids in
the post-statin era? Curr Opin Lipidol. 10:269–274. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fasshauer M and Paschke R: Regulation of
adipocytokines and insulin resistance. Diabetologia. 46:1594–1603.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Croft B, Reed M, Patrick C, Kovacevich N
and Voutsadakis IA: Diabetes, obesity, and the metabolic syndrome
as prognostic factors in stages I to III colorectal cancer
patients. J Gastrointest Cancer. 50:221–229. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shen Z, Ye Y, Bin L, Yin M, Yang X, Jiang
K and Wang S: Metabolic syndrome is an important factor for the
evolution of prognosis of colorectal cancer: Survival, recurrence,
and liver metastasis. Am J Surg. 200:59–63. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Melvin JC, Holmberg L, Rohrmann S, Loda M
and Van Hemelrijck M: Serum lipid profiles and cancer risk in the
context of obesity: Four meta-analyses. J Cancer Epidemiol.
2013:8238492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Esposito K, Chiodini P, Capuano A,
Bellastella G, Maiorino MI, Rafaniello C, Panagiotakos DB and
Giugliano D: Colorectal cancer association with metabolic syndrome
and its components: A systematic review with meta-analysis.
Endocrine. 44:634–647. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Borena W, Stocks T, Jonsson H, Strohmaier
S, Nagel G, Bjørge T, Manjer J, Hallmans G, Selmer R, Almquist M,
et al: Serum triglycerides and cancer risk in the metabolic
syndrome and cancer (Me-Can) collaborative study. Cancer Causes
Control. 22:291–299. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li X, Tang H, Wang J and Xie X, Liu P,
Kong Y, Ye F, Shuang Z, Xie Z and Xie X: The effect of preoperative
serum triglycerides and high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels
on the prognosis of breast cancer. Breast. 32:1–6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hayashi N, Matsushima M, Yamamoto T,
Sasaki H, Takahashi H and Egawa S: The impact of
hypertriglyceridemia on prostate cancer development in patients
aged ≥60 years. BJU Int. 109:515–519. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Stocks T, Lukanova A, Bjørge T, Ulmer H,
Manjer J, Almquist M, Concin H, Engeland A, Hallmans G, Nagel G, et
al: Metabolic factors and the risk of colorectal cancer in 580,000
men and women in the metabolic syndrome and cancer project
(Me-Can). Cancer. 117:2398–2407. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pakiet A, Kobiela J, Stepnowski P,
Sledzinski T and Mika A: Changes in lipids composition and
metabolism in colorectal cancer: A review. Lipids Health Dis.
18:292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lausen B, Hothorn T, Bretz F and
Schumacher M: Assessment of optimal selected prognostic factors.
Biom J. 46:364–374. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ridker PM: Fasting versus nonfasting
triglycerides and the prediction of cardiovascular risk: Do we need
to revisit the oral triglyceride tolerance test? Clin Chem.
54:11–13. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cramer L, Hildebrandt B, Kung T, Wichmann
K, Springer J, Doehner W, Sandek A, Valentova M, Stojakovic T,
Scharnagl H, et al: Cardiovascular function and predictors of
exercise capacity in patients with colorectal cancer. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 64:1310–1319. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim MH, Kim HN and Choi WS: The
association between subclinical inflammation and abnormal glucose
and lipid metabolisms in normal-weight Korean individuals. Nutr
Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 28:1106–1113. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
McKeown-Eyssen G: Epidemiology of
colorectal cancer revisited: Are serum triglycerides and/or plasma
glucose associated with risk? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
3:687–695. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rossi S, Graner E, Febbo P, Weinstein L,
Bhattacharya N, Onody T, Bubley G, Balk S and Loda M: Fatty acid
synthase expression defines distinct molecular signatures in
prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 1:707–715. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Flavin R, Zadra G and Loda M: Metabolic
alterations and targeted therapies in prostate cancer. J Pathol.
223:283–294. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Migita T, Ruiz S, Fornari A, Fiorentino M,
Priolo C, Zadra G, Inazuka F, Grisanzio C, Palescandolo E, Shin E,
et al: Fatty acid synthase: A metabolic enzyme and candidate
oncogene in prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 101:519–532. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Aparicio T, Ducreux M, Faroux R, Barbier
E, Manfredi S, Lecomte T, Etienne PL, Bedenne L, Bennouna J, Phelip
JM, et al: Overweight is associated to a better prognosis in
metastatic colorectal cancer: A pooled analysis of FFCD trials. Eur
J Cancer. 98:1–9. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee J, Meyerhardt JA, Giovannucci E and
Jeon JY: Association between body mass index and prognosis of
colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies.
PLoS One. 10:e01207062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|