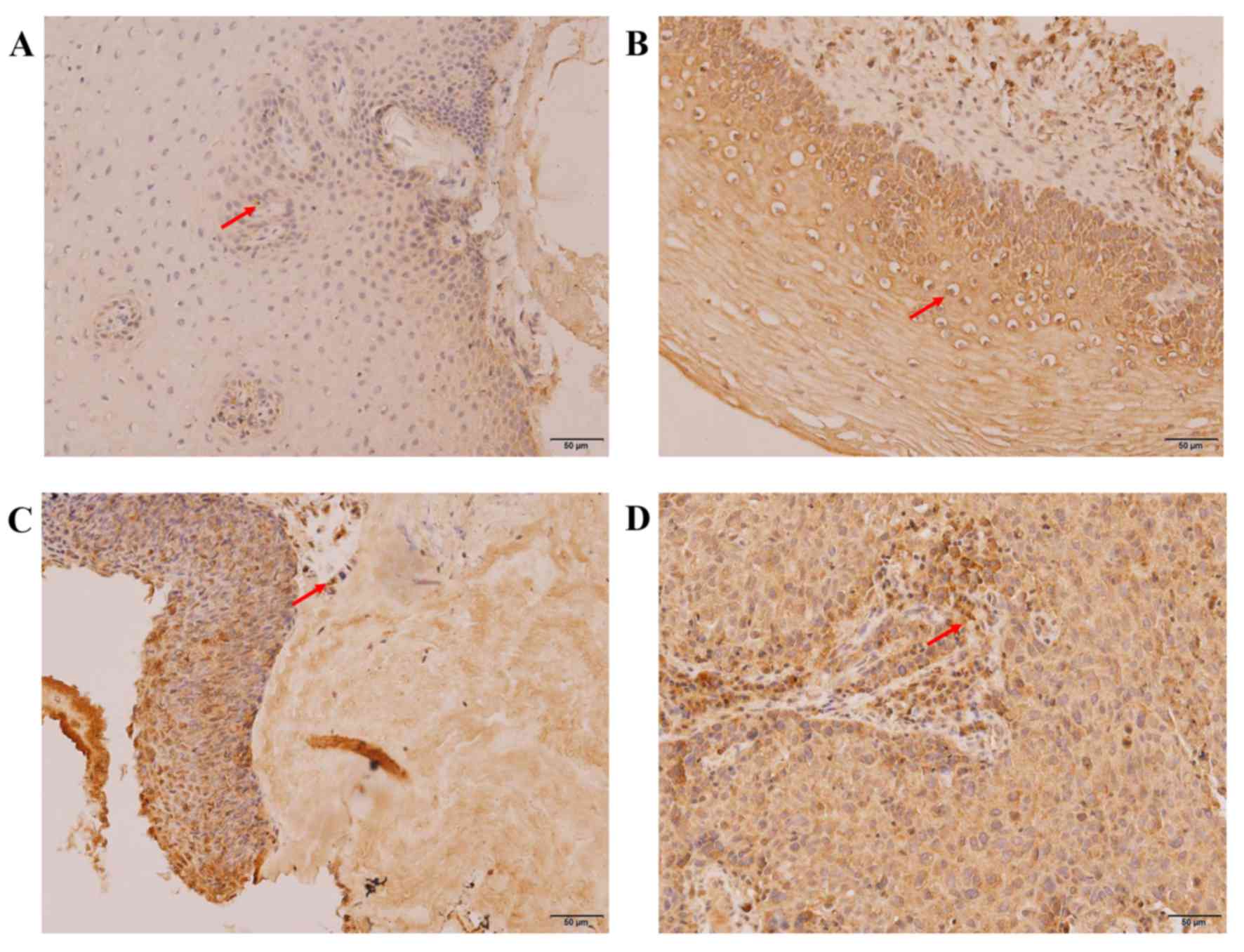
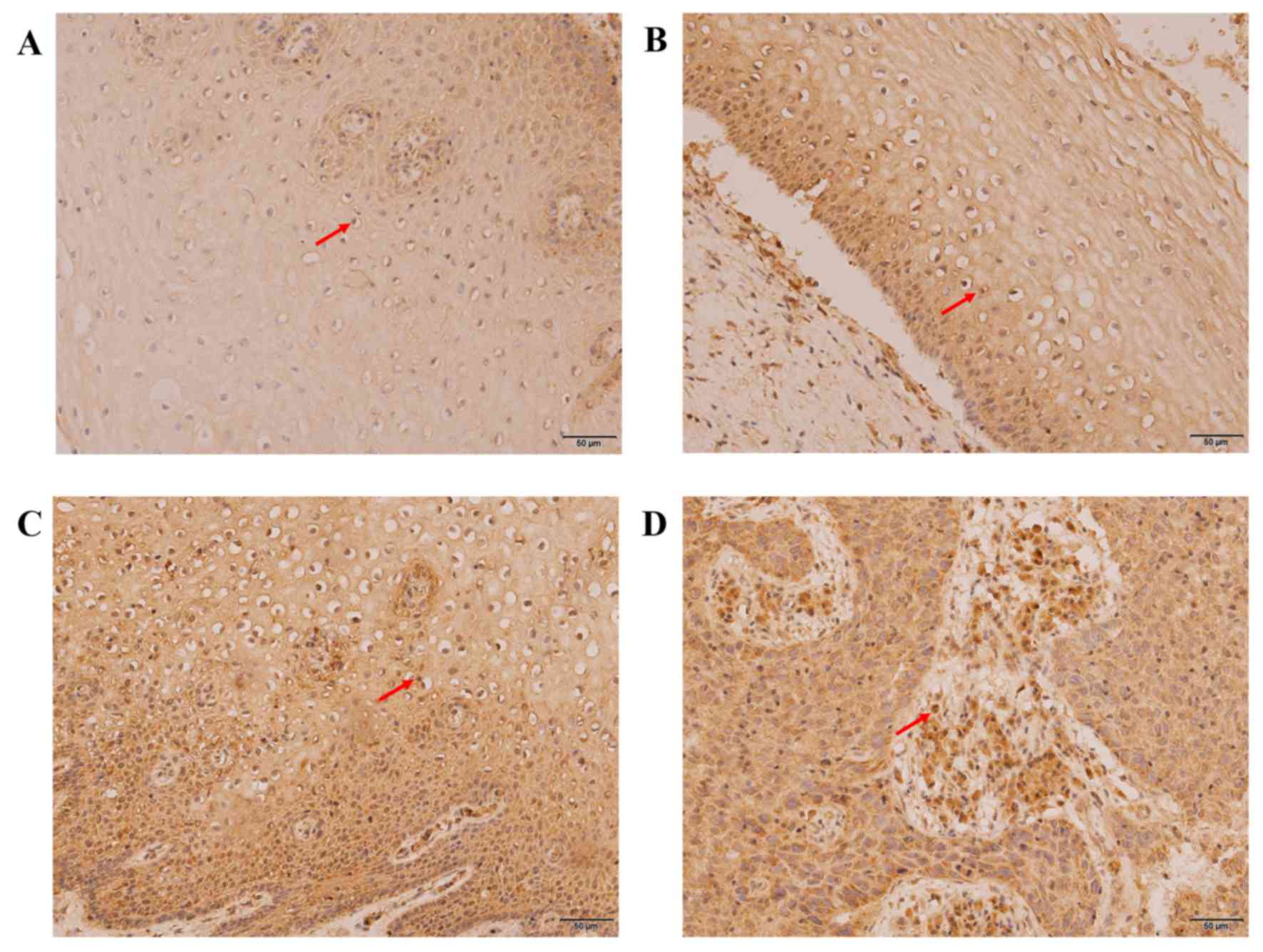
|
1
|
Arbyn M, Weiderpass E, Bruni L, de Sanjosé
S, Saraiya M, Ferlay J and Bray F: Estimates of incidence and
mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: A worldwide analysis. Lancet
Glob Health. 8:e191–e203. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Plummer M, Peto J and Franceschi S;
International Collaboration of Epidemiological Studies of Cervical
Cancer, : Time since first sexual intercourse and the risk of
cervical cancer. Int J Cancer. 130:2638–2644. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shrestha AD, Neupane D, Vedsted P and
Kallestrup P: Cervical cancer prevalence, incidence and mortality
in low and middle income countries: A systematic review. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 19:319–324. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arbyn M, Snijders PJ, Meijer CJ, Berkhof
J, Cuschieri K, Kocjan BJ and Poljak M: Which high-risk HPV assays
fulfil criteria for use in primary cervical cancer screening? Clin
Microbiol Infect. 21:817–826. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wright TC, Stoler MH, Behrens CM, Sharma
A, Zhang G and Wright TL: Primary cervical cancer screening with
human papillomavirus: End of study results from the ATHENA study
using HPV as the first-line screening test. Gynecol Oncol.
136:189–197. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dasari S, Wudayagiri R and Valluru L:
Cervical cancer: Biomarkers for diagnosis and treatment. Clin Chim
Acta. 445:7–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pozzan C, Cardin R, Piciocchi M, Cazzagon
N, Maddalo G, Vanin V, Giacomin A, Pontisso P, Cillo U and Farinati
F: Diagnostic and prognostic role of SCCA-IgM serum levels in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
29:1637–1644. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Maddalo G, Fassan M, Cardin R, Piciocchi
M, Marafatto F, Rugge M, Zaninotto G, Pozzan C, Castoro C, Ruol A,
et al: Squamous cellular carcinoma antigen serum determination as a
biomarker of barrett esophagus and esophageal cancer. J Clin
Gastroenterol. 52:401–406. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chechlinska M, Kowalewska M,
Brzoska-Wojtowicz E, Radziszewski J, Ptaszynski K, Rys J, Kaminska
J and Nowak R: Squamous cell carcinoma antigen 1 and 2 expression
in cultured normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells and in vulvar
squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 31:559–567. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
El-Rachkidy RG, Young HS, Griffiths CE and
Camp RD: Humoral autoimmune responses to the squamous cell
carcinoma antigen protein family in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol.
128:2219–2224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jeong BK, Choi DH, Huh SJ, Park W, Bae DS
and Kim BG: The role of squamous cell carcinoma antigen as a
prognostic and predictive factor in carcinoma of uterine cervix.
Radiat Oncol J. 29:191–198. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shimura K. Mabuchi S, Yokoi T, Sasano T,
Sawada K, Hamasaki T and Kimura T: Utility of serum squamous cell
carcinoma antigen levels at the time of recurrent cervical cancer
diagnosis in determining the optimal treatment choice. J Gynecol
Oncol. 24:321–329. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim BG: Squamous cell carcinoma antigen in
cervical cancer and beyond. J Gynecol Oncol. 24:291–292. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sen N, Gui B and Kumar R: Role of MTA1 in
cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
33:879–889. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yi S, Guangqi H and Guoli H: The
association of the expression of MTA1, NM23H1 with the invasion,
metastasis of ovarian carcinoma. Chin Med Sci J. 18:87–92.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guddeti RK, Bali P, Karyala P and Pakala
SB: MTA1 coregulator regulates LDHA expression and function in
breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 520:54–59. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bilikezi·Aikemu F, Min L, Xiumei Z,
Junling G, Danjin G and Qi: Expression and significance of MTA1,
MMP-2, MMP-7 in cervical cancer. Chin J Mod Med. 23:51–54.
2013.
|
|
18
|
Dannenmann C, Shabani N, Friese K, Jeschke
U, Mylonas I and Brüning A: The metastasis-associated gene MTA1 is
upregulated in advanced ovarian cancer, represses ERβ, and enhances
expression of oncogenic cytokine GRO. Cancer Biol Ther.
7:1460–1467. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rao Y, Wang H, Fan L and Chen G: Silencing
MTA1 by RNAi reverses adhesion, migration and invasiveness of
cervical cancer cells (SiHa) via altered expression of p53, and
E-cadherin/β-catenin complex. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med
Sci. 31:1–9. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Scheffner M, Werness BA, Huibregtse JM,
Levine AJ and Howley PM: The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human
papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53.
Cell. 63:1129–1136. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Moody CA and Laimins LA: Human
papillomavirus oncoproteins: Pathways to transformation. Nat Rev
Cancer. 10:550–560. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pan FP, Zhou HK, Bu HQ, Chen ZQ, Zhang H,
Xu LP, Tang J, Yu QY, Chu YQ, Pan J, et al: Emodin enhances the
demethylation by 5-Aza-CdR of pancreatic cancer cell
tumor-suppressor genes P16, RASSF1A and ppENK. Oncol Rep.
35:1941–1949. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bleotu C, Botezatu A, Goia CD, Socolov D,
Corniţescu F, Teleman S, Huică I, Iancu I and Anton G: P16INK4A-A
possible marker in HPV persistence screening. Roum Arch Microbiol
Immunol. 68:183–189. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun X and Kaufman PD: Ki-67: More than a
proliferation marker. Chromosoma. 127:175–186. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kimura M, Matsumoto T, Morizane T, Sonoue
H, Ogishima D and Kinoshita K: Histopathological study of the
spreading neoplastic cells in cervical glands and surface epithelia
in cervical intra-epithelial neoplasia and microinvasive squamous
cell carcinoma: Ki-67 immunostaining is a useful marker for
pathological diagnosis from the gland involvement site. Pathol Int.
56:428–433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Carreras R, Alameda F, Mancebo G,
García-Moreno P, Mariñoso ML, Costa C, Fusté P, Baró T and Serrano
S: A study of Ki-67, c-erbB2 and cyclin D-1 expression in CIN-I,
CIN-III and squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix. Histol
Histopathol. 22:587–592. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang D, Xu Q and Mao Q: Expression of P16,
Ki67 and HPV16/18 in cervical lesions and their clinical
implications. Int J Pathol Clin Med. 32:211–215. 2012.
|
|
28
|
Clarke MA, Cheung LC, Castle PE, Schiffman
M, Tokugawa D, Poitras N, Lorey T, Kinney W and Wentzensen N:
Five-year risk of cervical precancer following p16/ki-67 dual-stain
triage of HPV-positive women. JAMA Oncol. 5:181–186. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wentzensen N, Clarke MA, Bremer R, Poitras
N, Tokugawa D, Goldhoff PE, Castle PE, Schiffman M, Kingery JD,
Grewal KK, et al: Clinical evaluation of human papillomavirus
screening with p16/ki-67 dual stain triage in a large organized
cervical cancer screening program. JAMA Intern Med. 179:881–888.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhong P, Li J, Gu Y, Liu Y, Wang A, Sun Y
and Lu L: P16 and Ki-67 expression improves the diagnostic accuracy
of cervical lesions but not predict persistent high risk human
papillomavirus infection with CIN1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:2979–2986. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pesic A, Krings A, Hempel M, Preyer R,
Chatzistamatiou K, Agorastos T and Kaufmann AM: CIN2+ detection of
the HPV DNA array genotyping assay in comparison with the cobas
4800 HPV test and cytology. Virol J. 16:922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tang Z, Xu Y, Song N, Zou D, Liao Y, Li Q
and Pan C: A comparison of the MeltPro® HPV test with
the Cobas® HPV test for detecting and genotyping 14
high-risk human papillomavirus types. Arch Virol. 163:725–730.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brusselaers N, Shrestha S, van de Wijgert
J and Verstraelen H: Vaginal dysbiosis and the risk of human
papillomavirus and cervical cancer: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 221:9–18. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Melnikow J, Henderson JT, Burda BU, Senger
CA, Durbin SS and Weyrich MS: Screening for cervical cancer with
high-risk human papillomavirus testing. JAMA. 320:687–705. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kjær SK, Munk C, Junge J and Iftner T:
Carcinogenic HPV prevalence and age-specific type distribution in
40,382 women with normal cervical cytology, ASCUS/LSIL, HSIL, or
cervical cancer: What is the potential for prevention? Cancer
Causes Control. 25:179–189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Song SH, Park HM, Eom DW, Lee JK, Lee NW,
Kim AR, Hur JY, Lee KW, Park YK and Saw HS: The expression of p16
(INK4a) and Ki-67 in relation to high-risk human papilloma viral
load and residual disease after conization with positive margins.
Int J Gynecol Cancer. 17:858–867. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|