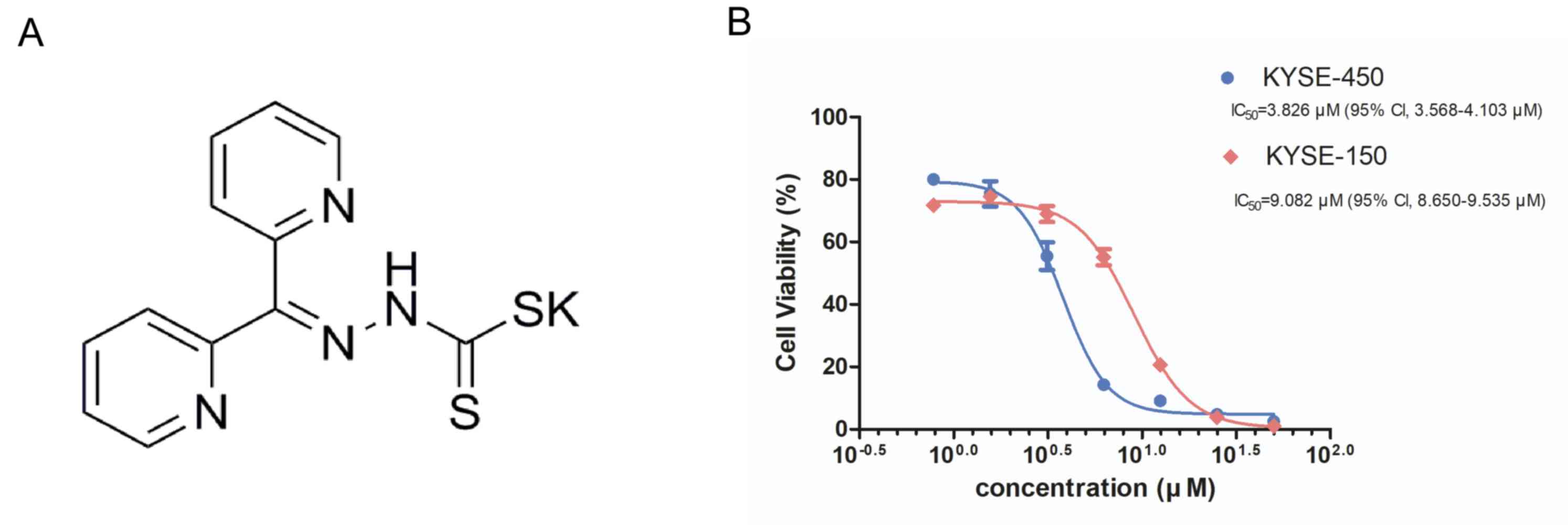
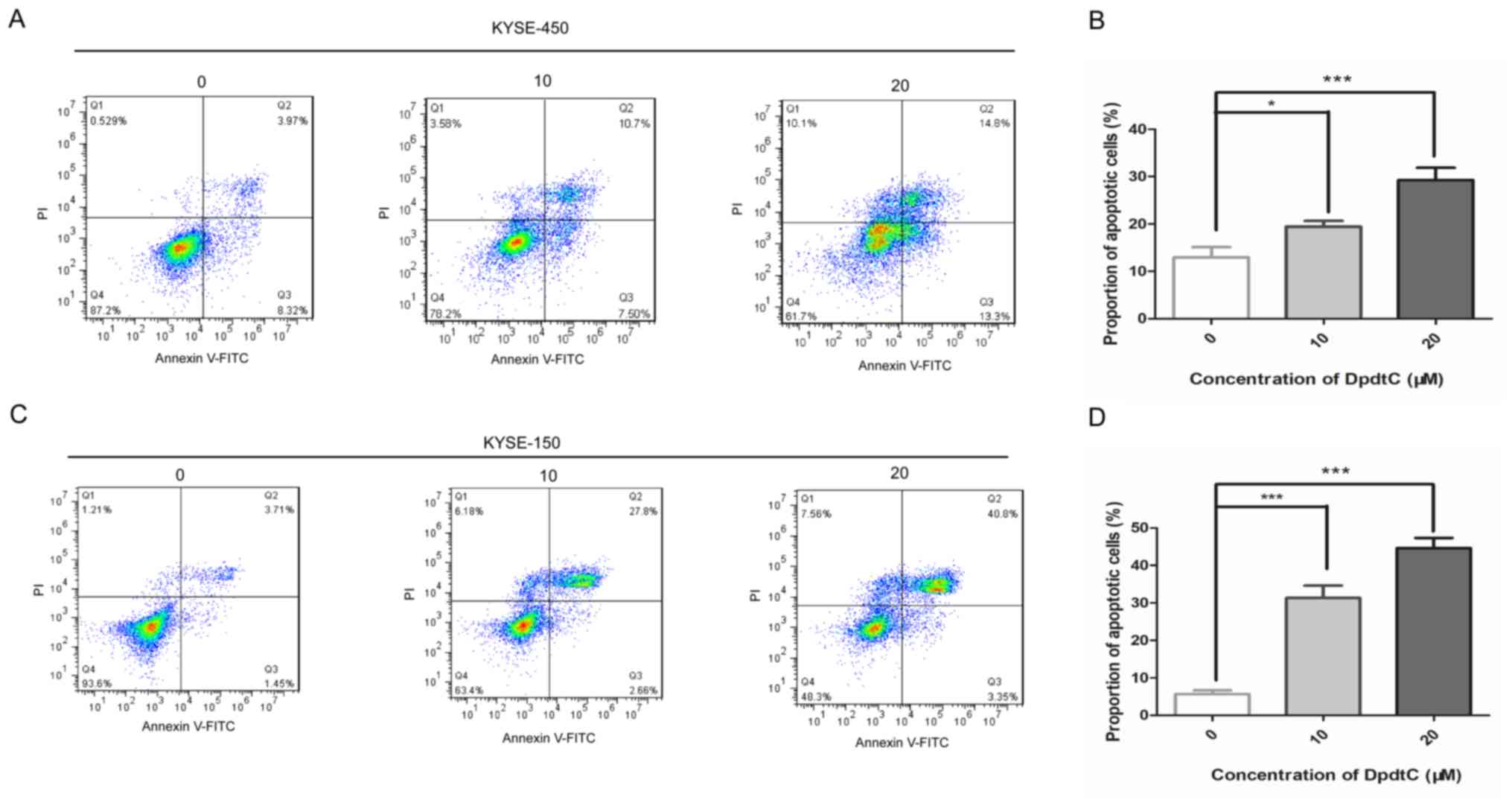
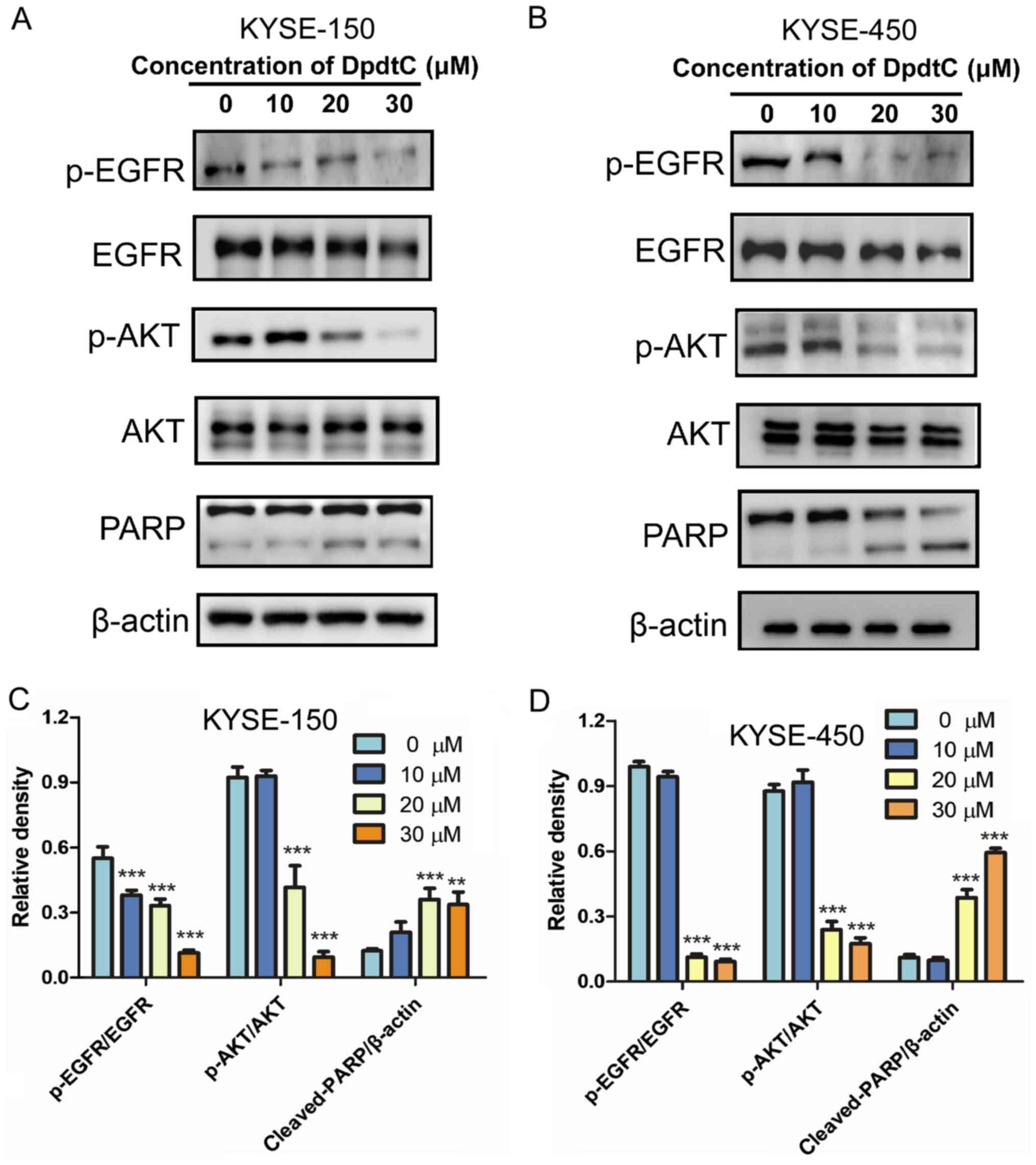
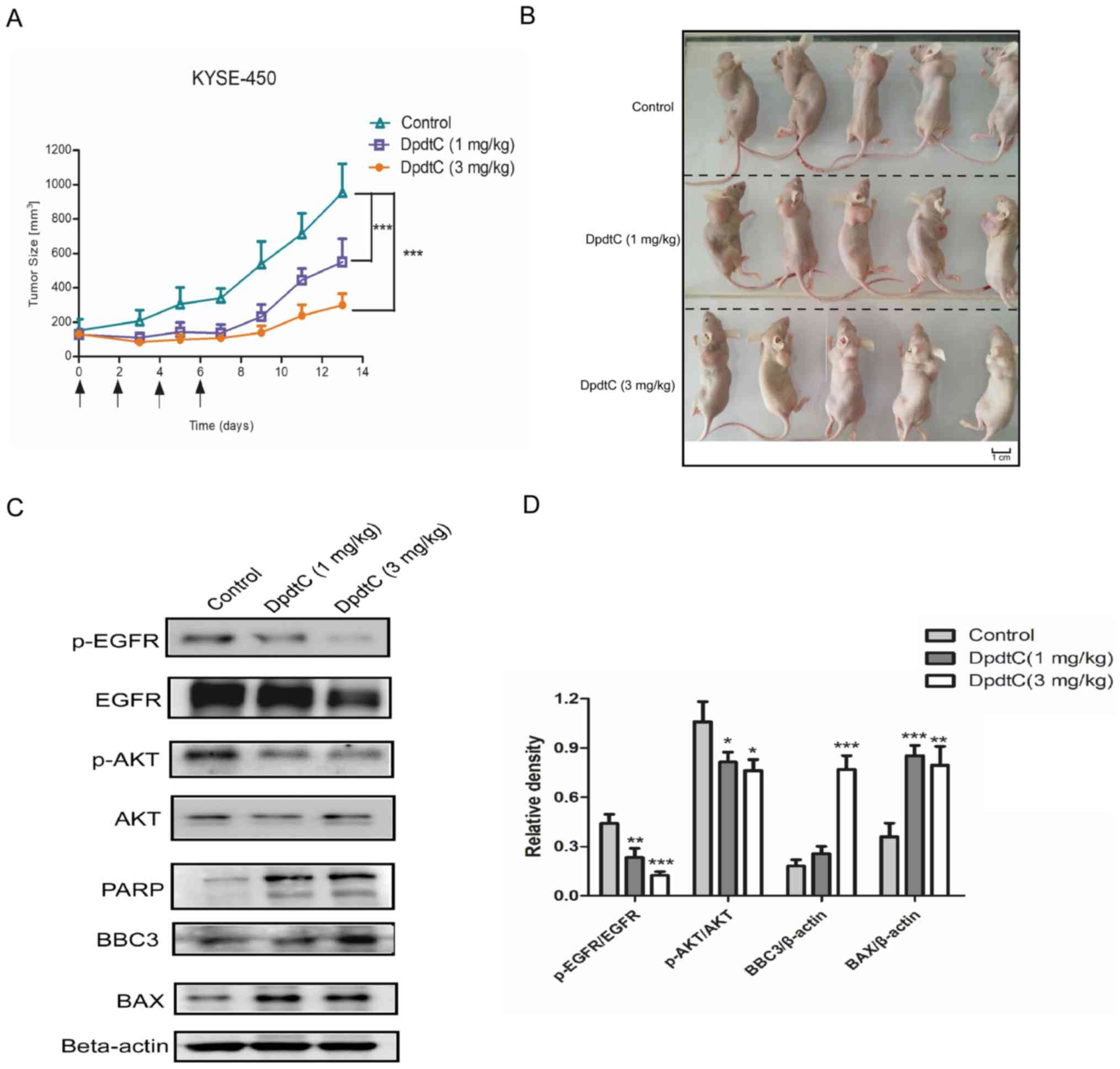
|
1
|
Wu C, Li D, Jia W, Hu Z, Zhou Y, Yu D,
Tong T, Wang M, Lin D, Qiao Y, et al: Genome-wide association study
identifies common variants in SLC39A6 associated with length of
survival in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. Nat Genet.
45:632–638. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guo XF, Zhu XF, Yang WC, Zhang SH and Zhen
YS: An EGFR/HER2-Bispecific and enediyne-energized fusion protein
shows high efficacy against esophageal cancer. PLoS One.
9:e929862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Campbell NP and Villaflor VM: Neoadjuvant
treatment of esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
16:3793–3803. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kovacevic Z, Chikhani S, Lovejoy DB and
Richardson DR: Novel thiosemicarbazone iron chelators induce
up-regulation and phosphorylation of the metastasis suppressor
N-myc down-stream regulated gene 1: A new strategy for the
treatment of pancreatic cancer. Mol Pharmacol. 80:598–609. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang J, Yin D, Xie C, Zheng T, Liang Y,
Hong X, Lu Z, Song X, Song R, Yang H, et al: The iron chelator
Dp44mT inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via N-Myc
downstream-regulated gene 2 (NDRG2)/gp130/STAT3 pathway.
Oncotarget. 5:8478–8491. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang T, Fu Y, Huang T, Liu Y, Wu M, Yuan
Y, Li S and Li C: Copper ion attenuated the antiproliferative
activity of Di-2-pyridylhydrazone dithiocarbamate derivative;
however, there was a lack of correlation between ros generation and
antiproliferative activity. Molecules. 21(pii): E10882016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fu Y, Liu Y, Wang J and Li C, Zhou S, Yang
Y, Zhou P, Lu C and Li C: Calcium release induced by
2-pyridinecarboxaldehyde thiosemicarbazone and its copper complex
contributes to tumor cell death. Oncol Rep. 37:1662–1670. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dixon KM, Lui GY, Kovacevic Z, Zhang D,
Yao M, Chen Z, Dong Q, Assinder SJ and Richardson DR: Dp44mT
targets the AKT, TGF-β and ERK pathways via the metastasis
suppressor NDRG1 in normal prostate epithelial cells and prostate
cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 108:409–419. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen Z, Zhang D, Yue F, Zheng M, Kovacevic
Z and Richardson DR: The iron chelators Dp44mT and DFO inhibit
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via up-regulation
of N-Myc downstream-regulated gene 1 (NDRG1). J Biol Chem.
287:17016–17028. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Orrenius S, Nobel CS, van den Dobbelsteen
DJ, Burkitt MJ and Slater AF: Dithiocarbamates and the redox
regulation of cell death. Biochem Soc Trans. 24:1032–1038. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Buac D, Schmitt S, Ventro G, Kona FR and
Dou QP: Dithiocarbamate-based coordination compounds as potent
proteasome inhibitors in human cancer cells. Mini Rev Med Chem.
12:1193–1201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang Y, Liu Y, Guo R, Fu Y, Zhang Z, Zhang
P, Zhou P, Wang T, Huang T, Li X and Li C: The novel
dithiocarbamate, DpdtC suppresses HER2-overexpressed cancer cells
by up-regulating NDRG1 via inactivation of HER2-ERK 1/2 signaling.
Sci Rep. 8:33982018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang Y, Tian Z, Ding Y, Li X, Zhang Z,
Yang L, Zhao F, Ren F and Guo R: EGFR-targeted immunotoxin exerts
antitumor effects on esophageal cancers by increasing ROS
accumulation and inducing apoptosis via inhibition of the
Nrf2-keap1 pathway. J Immunol Res. 2018:10902872018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jones-Bolin S: Guidelines for the care and
use of laboratory animals in biomedical research. Curr Protoc
Pharmacol Appendix 4: Appendix 4B. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yang Y, Guo R, Tian X, Zhang Z, Zhang P,
Li C and Feng Z: Synergistic anti-tumor activity of Nimotuzumab in
combination with Trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 489:523–527. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Jiang G, Yao F, He Y, Liang G,
Zhang Y, Hu B, Wu Y, Li Y and Liu H: Growth inhibition and
apoptosis induced by osthole, a natural coumarin, in hepatocellular
carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e378652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yuan J, Lovejoy DB and Richardson DR:
Novel di-2-pyridyl-derived iron chelators with marked and selective
antitumor activity: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Blood.
104:1450–1458. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Whitnall M, Howard J, Ponka P and
Richardson DR: A class of iron chelators with a wide spectrum of
potent antitumor activity that overcomes resistance to
chemotherapeutics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:14901–14906. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ohyashiki JH, Kobayashi C, Hamamura R,
Okabe S, Tauchi T and Ohyashiki K: The oral iron chelator
deferasirox represses signaling through the mTOR in myeloid
leukemia cells by enhancing expression of REDD1. Cancer Sci.
100:970–977. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Le NT and Richardson DR: Iron chelators
with high antiproliferative activity up-regulate the expression of
a growth inhibitory and metastasis suppressor gene: A link between
iron metabolism and proliferation. Blood. 104:2967–2975. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu W, Yue F, Zheng M, Merlot A, Bae DH,
Huang M, Lane D, Jansson P, Lui GY, Richardson V, et al: The
proto-oncogene c-Src and its downstream signaling pathways are
inhibited by the metastasis suppressor, NDRG1. Oncotarget.
6:8851–8874. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li C, Liu Y, Fu Y, Huang T and Kang L: The
antiproliferative activity of di-2-pyridylketone dithiocarbamate is
partly attributed to catalase inhibition: Detailing the interaction
by spectroscopic methods. Mol Biosyst. 13:1817–1826. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schreck R, Meier B, Mannel DN, Droge W and
Baeuerle PA: Dithiocarbamates as potent inhibitors of nuclear
factor kappa B activation in intact cells. J Exp Med.
175:1181–1194. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Milacic V, Chen D, Ronconi L,
Landis-Piwowar KR, Fregona D and Dou QP: A novel anticancer
gold(III) dithiocarbamate compound inhibits the activity of a
purified 20S proteasome and 26S proteasome in human breast cancer
cell cultures and xenografts. Cancer Res. 66:10478–10486. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ronconi L, Marzano C, Zanello P, Corsini
M, Miolo G, Maccà C, Trevisan A and Fregona D: Gold(III)
dithiocarbamate derivatives for the treatment of cancer: Solution
chemistry, DNA binding, and hemolytic properties. J Med Chem.
49:1648–1657. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nobel CS, Burgess DH, Zhivotovsky B,
Burkitt MJ, Orrenius S and Slater AF: Mechanism of dithiocarbamate
inhibition of apoptosis: Thiol oxidation by dithiocarbamate
disulfides directly inhibits processing of the caspase-3 proenzyme.
Chem Res Toxicol. 10:636–643. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|