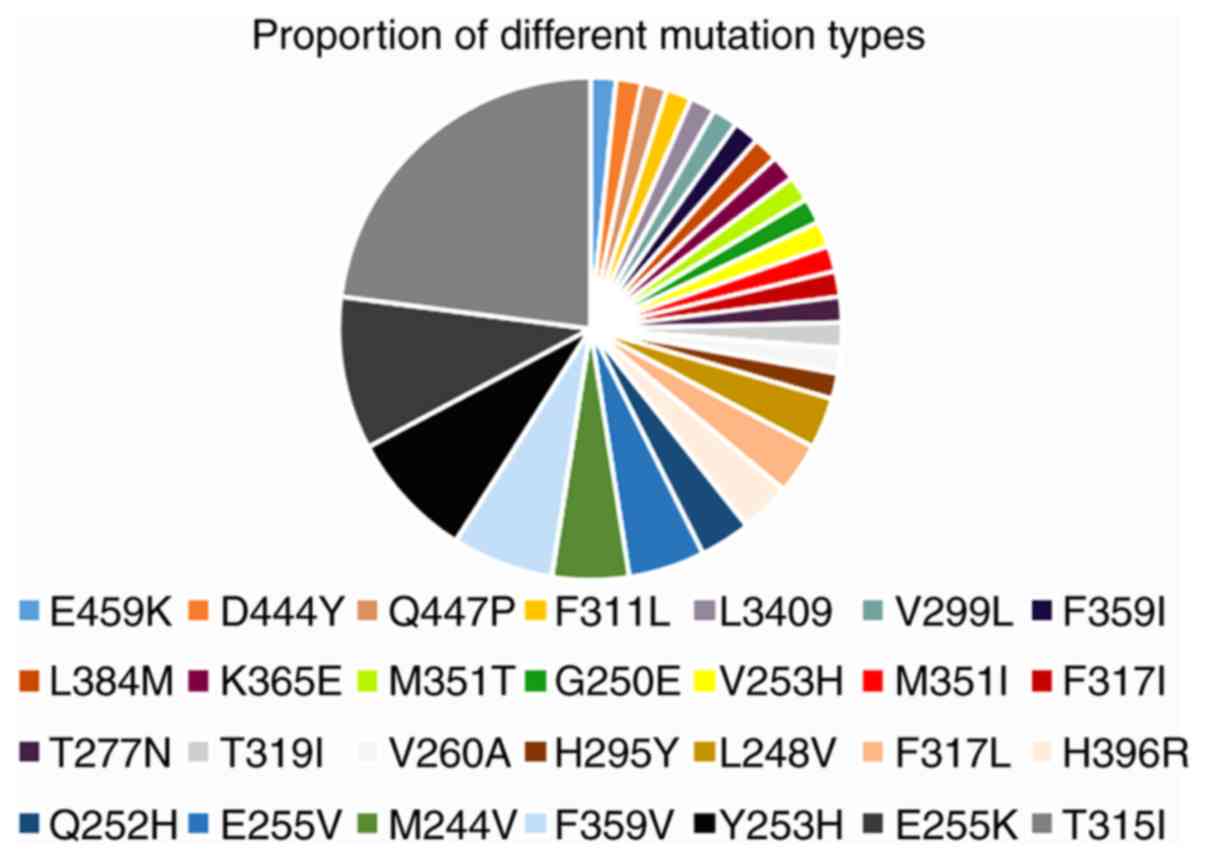
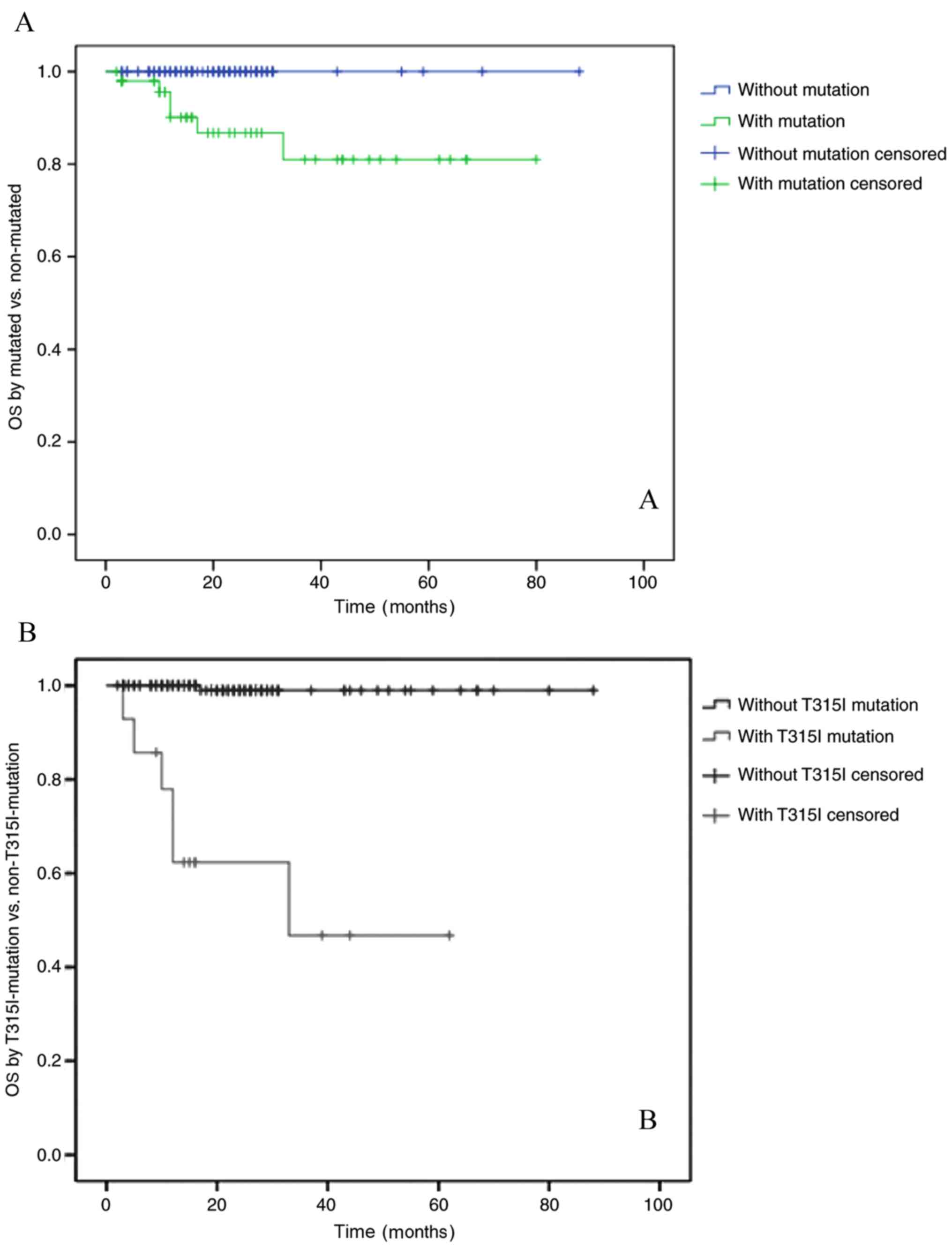
|
1
|
Machova Polakova K, Kulvait V, Benesova A,
Linhartova J, Klamova H, Jaruskova M, de Benedittis C, Haferlach T,
Baccarani M, Martinelli G, et al: Next-generation deep sequencing
improves detection of BCR-ABL1 kinase domain mutations emerging
under tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment of chronic myeloid
leukemia patients in chronic phase. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
141:887–899. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kaleem B, Shahab S, Ahmed N and Shamsi TS:
Chronic myeloid leukemia-prognostic value of mutations. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 17:7415–7423. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Apperley JF: Chronic myeloid leukaemia.
Lancet. 385:1447–1459. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Loscocco F, Visani G, Galimberti S, Curti
A and Isidori A: BCR-ABL independent mechanisms of resistance in
chronic myeloid leukemia. Front Oncol. 9:9392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pasic I and Lipton JH: Current approach to
the treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia. Leuk Res. 55:65–67.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Eide CA and O'Hare T: Chronic myeloid
leukemia: Advance in understanding disease biology and mechanisms
of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Curr Hematol Malig
Rep. 10:158–166. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Soverini S, de Benedittis C, Mancini M and
Martinelli G: Mutations in the BCR-ABL1 kinase domain and elsewhere
in chronic myeloid leukemia. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk S1.
(Suppl):S120–S128. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yang K and Fu LW: Mechanisms of resistance
to BCR-ABL TKIs and the therapeutic strategies: A review. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 93:277–292. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Balabanov S, Braig M and Brümmendorf TH:
Current aspects in resistance against tyrosine kinase inhibitors in
chronic myelogenous leukemia. Drug Discov Today Technol. 11:89–99.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baccarani M, Castagnetti F, Gugliotta G
and Rosti G: A review of the European LeukemiaNet recommendations
for the management of CML. Ann Hematol. 94 (Suppl 2):S141–S147.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Soverini S, De Benedittis C, Mancini M and
Martinelli G: Present and future of molecular monitoring in chronic
myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 173:337–349. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pagnano KB, Bendit I, Boquimpani C, De
Souza CA, Miranda EC, Zalcberg I, Larripa I, Nardinelli L, Silveira
RA, Fogliatto L, et al: BCR-ABL mutations in chronic myeloid
leukemia treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors and impact on
survival. Cancer Invest. 33:451–458. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cagnetta A, Garuti A, Marani C, Cea M,
Miglino M, Rocco I, Palermo C, Fugazza G, Cirmena G, Colombo N, et
al: Evaluating treatment response of chronic myeloid leukemia:
Emerging science and technology. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
13:779–790. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shah NP, Skaggs BJ, Branford S, Hughes TP,
Nicoll JM, Paquette RL and Sawyers CL: Sequential ABL kinase
inhibitor therapy selects for compound drug-resistant BCR-ABL
mutations with altered oncogenic potency. J Clin Invest.
117:2562–2569. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Khorashad JS, Kelley TW, Szankasi P, Mason
CC, Soverini S, Adrian LT, Eide CA, Zabriskie MS, Lange T, Estrada
JC, et al: BCR-ABL1 compound mutations in tyrosine kinase
inhibitor-resistant CML: Frequency and clonal relationships. Blood.
121:489–498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gibbons DL, Pricl S, Posocco P, Laurini E,
Fermeglia M, Sun H, Talpaz M, Donato N and Quintás-Cardama A:
Molecular dynamics reveal BCR-ABL1 polymutants as a unique
mechanism of resistance to PAN-BCR-ABL1 kinase inhibitor therapy.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:3550–3555. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miller GD, Bruno BJ and Lim CS: Resistant
mutations in CML and Ph+ALL-role of ponatinib. Biologics.
8:243–254. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Poch Martell M, Sibai H, Deotare U and
Lipton JH: Ponatinib in the therapy of chronic myeloid leukemia.
Expert Rev Hematol. 9:923–932. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kujak C and Kolesar JM: Treatment of
chronic myelogenous leukemia. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 73:113–120.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Modugno M: New resistance mechanisms for
small molecule kinase inhibitors of Abl kinase. Drug Discov Today
Technol. 11:5–10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Haznedaroglu IC: Drug therapy in the
progressed CML patient with multi-TKI failure. Mediterr J Hematol
Infect Dis. 7:e20150142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Patel AB, O'Hare T and Deininger MW:
Mechanisms of resistance to ABL kinase inhibition in chronic
myeloid leukemia and the development of next generation ABL kinase
inhibitors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 31:589–612. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Apperley JF: Part I: Mechanisms of
resistance to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia. Lancet Oncol.
8:1018–1029. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Corbin AS, La Rosée P, Stoffregen EP,
Druker BJ and Deininger MW: Several BCR-ABL kinase domain mutants
associated with imatinib mesylate resistance remain sensitive to
imatinib. Blood. 101:4611–4614. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hochhaus A, Schenk T, Erben P, Ernst T, La
Rosée P and Müller MC: Cause and management of therapy resistance.
Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 22:367–379. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hehlmann R, Saußele S, Voskanyan A and
Silver RT: Management of CML-blast crisis. Best Pract Res Clin
Haematol. 29:295–307. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Soverini S, De Benedittis C, Mancini M and
Martinelli G: Best practices in chronic myeloid leukemia monitoring
and management. Oncologist. 21:626–633. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Morozova EV, Vlasova YY, Pryanishnikova
MV, Lepik KV and Afanasyev BV: Efficacy of dasatinib in a CML
patient in blast crisis with F317L mutation: A case report and
literature review. Biomarker Insights. 10 (Suppl 3):S43–S47.
2015.
|