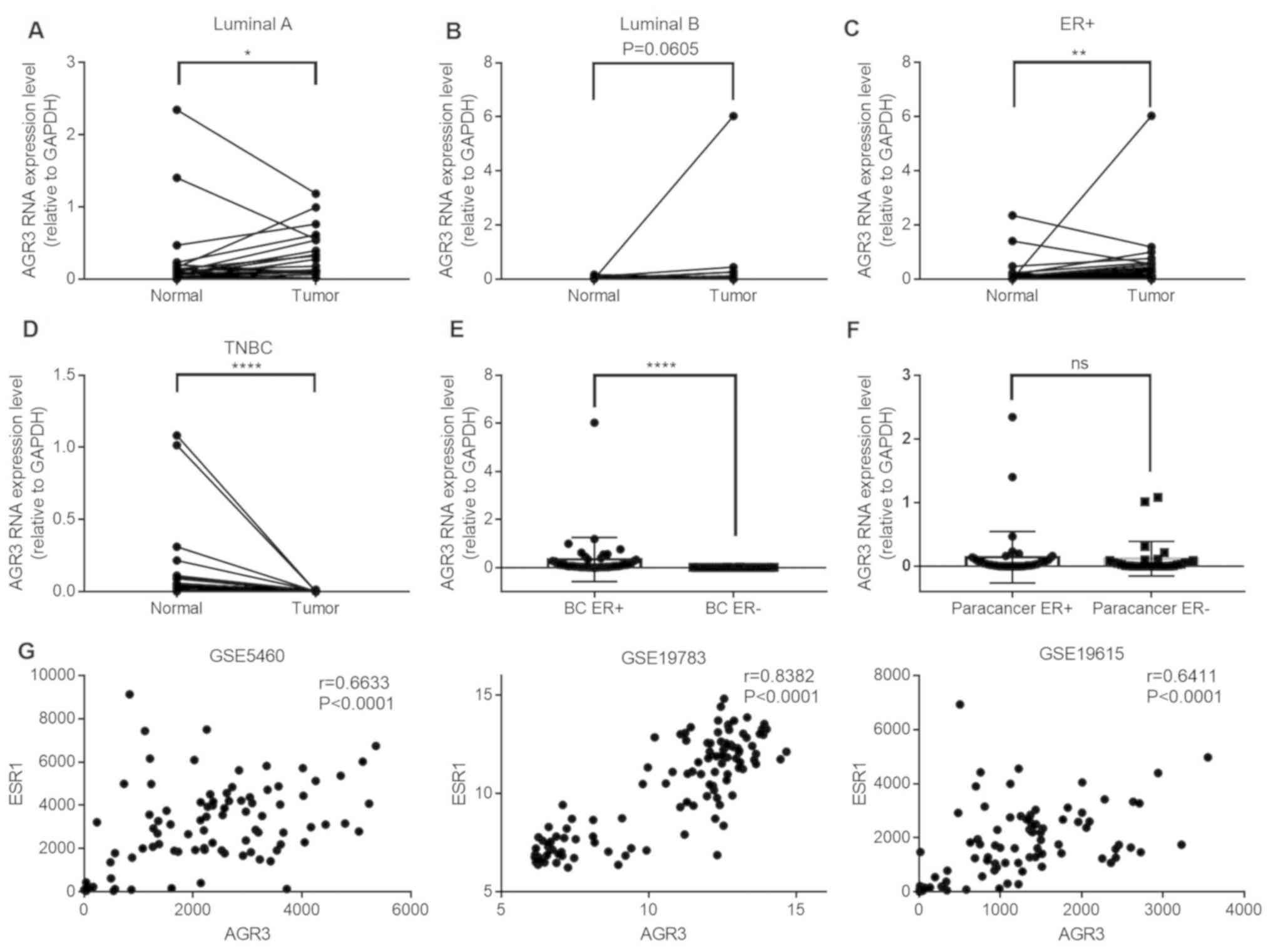
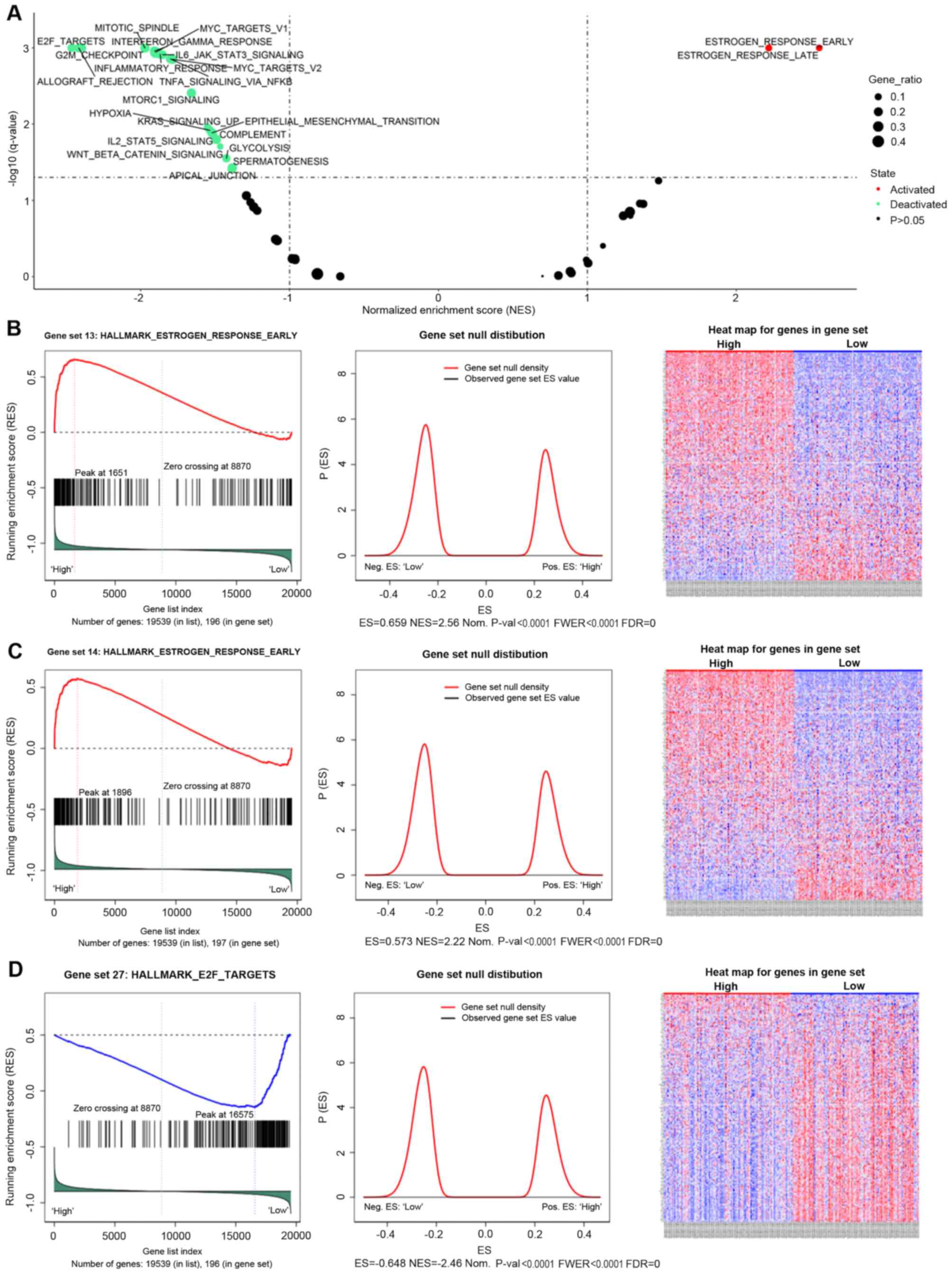
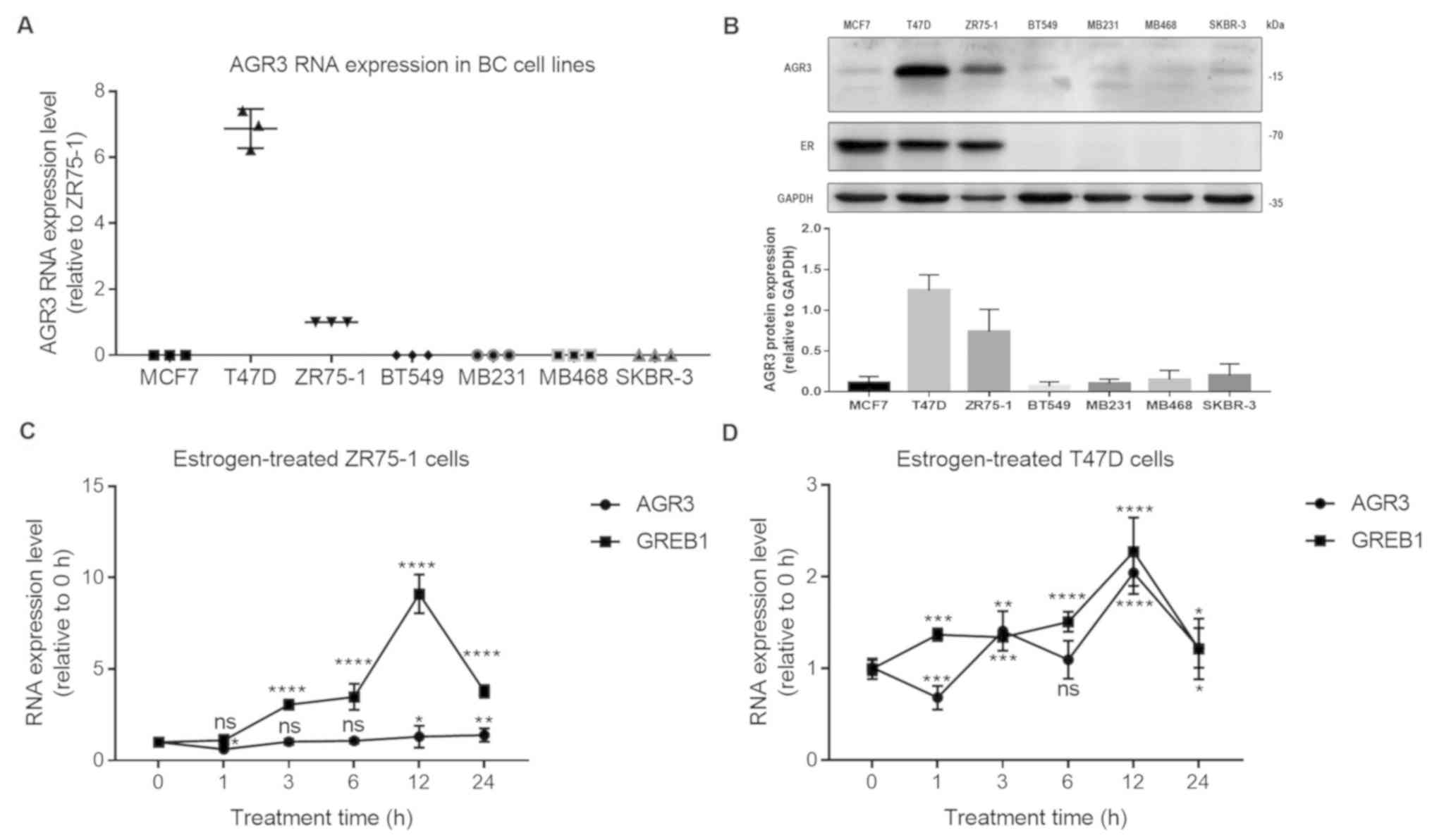
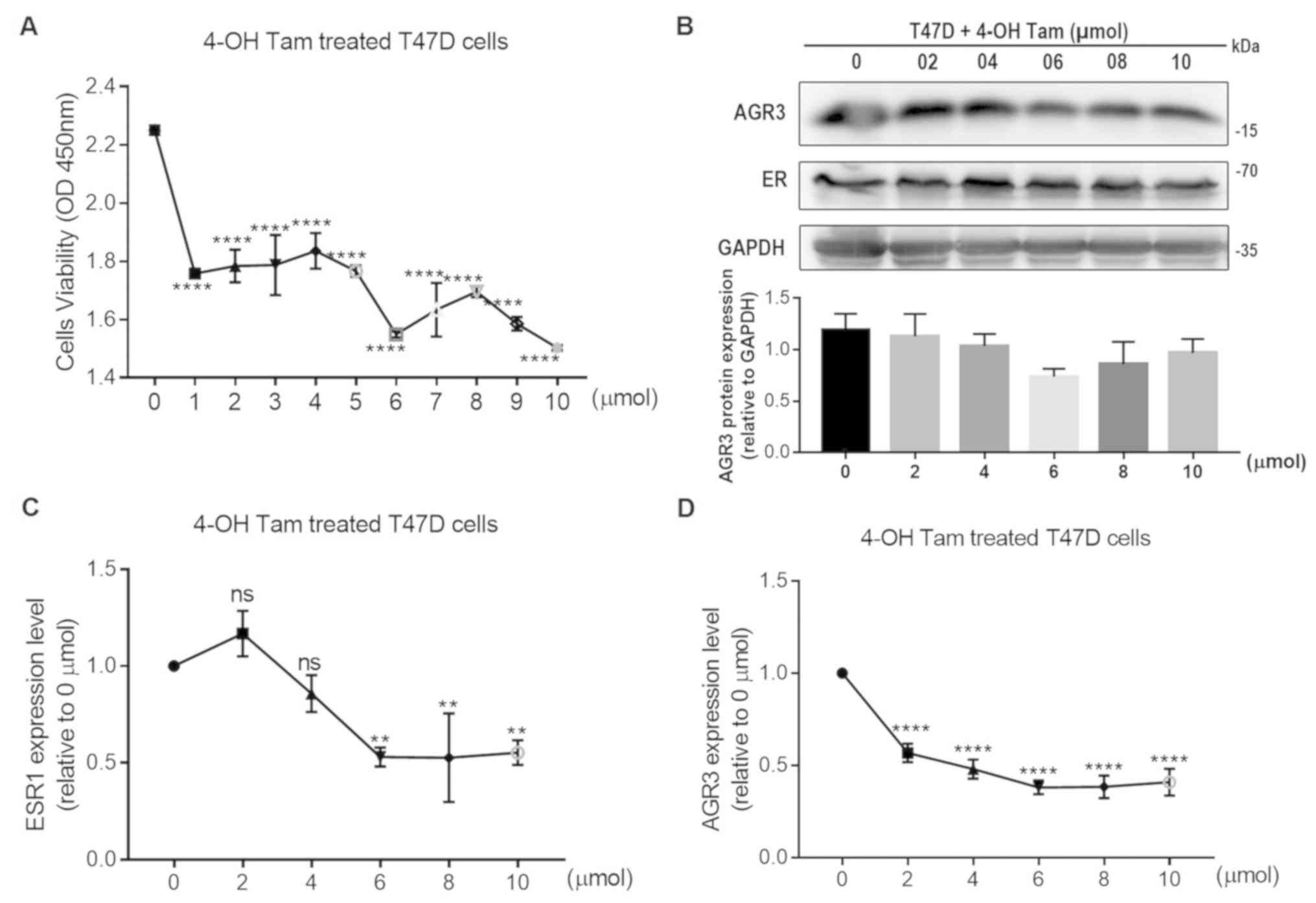
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Coates AS, Winer EP, Goldhirsch A, Gelber
RD, Gnant M, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B, Senn HJ and Panel M:
Tailoring therapies-improving the management of early breast
cancer: St gallen international expert consensus on the primary
therapy of early breast cancer 2015. Ann Oncol. 26:1533–1546. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Allred DC: Issues and updates: Evaluating
estrogen receptor- alpha, progesterone receptor, and HER2 in breast
cancer. Mod Pathol. 23 (Suppl 2):S52–S59. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bai Z and Gust R: Breast cancer, estrogen
receptor and ligands. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 342:133–149. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yue W, Yager JD, Wang JP, Jupe ER and
Santen RJ: Estrogen receptor-dependent and independent mechanisms
of breast cancer carcinogenesis. Steroids. 78:161–170. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jia M, Dahlman-Wright K and Gustafsson JA:
Estrogen receptor alpha and beta in health and disease. Best Pract
Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 29:557–568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jia M, Andreassen T, Jensen L, Bathen TF,
Sinha I, Gao H, Zhao C, Haldosen LA, Cao Y, Girnita L, et al:
Estrogen receptor α promotes breast cancer by reprogramming choline
metabolism. Cancer Res. 76:5634–5646. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Persson S, Rosenquist M, Knoblach B,
Khosravi-Far R, Sommarin M and Michalak M: Diversity of the protein
disulfide isomerase family: Identification of breast tumor induced
Hag2 and Hag3 as novel members of the protein family. Mol
Phylogenet Evol. 36:734–740. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ivanova AS, Tereshina MB, Ermakova GV,
Belousov VV and Zaraisky AG: Agr genes, missing in amniotes, are
involved in the body appendages regeneration in frog tadpoles. Sci
Rep. 3:12792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Z, Wu Z, Chen H, Zhu Q, Gao G, Hu L,
Negi H, Kamle S and Li D: Induction of anterior gradient 2 (AGR2)
plays a key role in insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1)-induced
breast cancer cell proliferation and migration. Med Oncol.
32:5772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Verma S, Salmans ML, Geyfman M, Wang H, Yu
Z, Lu Z, Zhao F, Lipkin SM and Andersen B: The estrogen-responsive
Agr2 gene regulates mammary epithelial proliferation and
facilitates lobuloalveolar development. Dev Biol. 369:249–260.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Obacz J, Takacova M, Brychtova V, Dobes P,
Pastorekova S, Vojtesek B and Hrstka R: The role of AGR2 and AGR3
in cancer: Similar but not identical. Eur J Cell Biol. 94:139–147.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
King ER, Tung CS, Tsang YT, Zu Z, Lok GT,
Deavers MT, Malpica A, Wolf JK, Lu KH, Birrer MJ, et al: The
anterior gradient homolog 3 (AGR3) gene is associated with
differentiation and survival in ovarian cancer. Am J Surg Pathol.
35:904–912. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bu H, Schweiger MR, Manke T, Wunderlich A,
Timmermann B, Kerick M, Pasqualini L, Shehu E, Fuchsberger C, Cato
AC and Klocker H: Anterior gradient 2 and 3-two prototype
androgen-responsive genes transcriptionally upregulated by
androgens and by oestrogens in prostate cancer cells. FEBS J.
280:1249–1266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brychtova V, Zampachova V, Hrstka R,
Fabian P, Novak J, Hermanova M and Vojtesek B: Differential
expression of anterior gradient protein 3 in intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol.
96:375–381. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Obacz J, Brychtova V, Podhorec J, Fabian
P, Dobes P, Vojtesek B and Hrstka R: Anterior gradient protein 3 is
associated with less aggressive tumors and better outcome of breast
cancer patients. Onco Targets Ther. 8:1523–1532. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Obacz J, Sommerova L, Sicari D, Durech M,
Avril T, Iuliano F, Pastorekova S, Hrstka R, Chevet E, Delom F and
Fessart D: Extracellular AGR3 regulates breast cancer cells
migration via Src signaling. Oncol Lett. 18:4449–4456.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu Q, Shao Y, Zhang J, Zhang H, Zhao Y,
Liu X, Guo Z, Chong W, Gu F and Ma Y: Anterior gradient 3 promotes
breast cancer development and chemotherapy response. Cancer Res
Treat. 52:218–245. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu X, Lu X, Wang ZC, Iglehart JD, Zhang X
and Richardson AL: Predicting features of breast cancer with gene
expression patterns. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 108:191–201. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Enerly E, Steinfeld I, Kleivi K, Leivonen
SK, Aure MR, Russnes HG, Rønneberg JA, Johnsen H, Navon R, Rødland
E, et al: miRNA-mRNA integrated analysis reveals roles for miRNAs
in primary breast tumors. PLoS One. 6:e169152011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li Y, Zou L, Li Q, Haibe-Kains B, Tian R,
Li Y, Desmedt C, Sotiriou C, Szallasi Z, Iglehart JD, et al:
Amplification of LAPTM4B and YWHAZ contributes to chemotherapy
resistance and recurrence of breast cancer. Nat Med. 16:214–218.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grossman RL, Heath AP, Ferretti V, Varmus
HE, Lowy DR, Kibbe WA and Staudt LM: Toward a shared vision for
cancer genomic data. N Engl J Med. 375:1109–1112. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Durbin BP, Hardin JS, Hawkins DM and Rocke
DM: A variance-stabilizing transformation for gene-expression
microarray data. Bioinformatics. 18 (Suppl 1):S105–S110. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yager JD and Davidson NE: Estrogen
carcinogenesis in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 354:270–282. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mohammed H, D'Santos C, Serandour AA, Ali
HR, Brown GD, Atkins A, Rueda OM, Holmes KA, Theodorou V, Robinson
JL, et al: Endogenous purification reveals GREB1 as a key estrogen
receptor regulatory factor. Cell Rep. 3:342–349. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fletcher GC, Patel S, Tyson K, Adam PJ,
Schenker M, Loader JA, Daviet L, Legrain P, Parekh R, Harris AL and
Terrett JA: hAG-2 and hAG-3, human homologues of genes involved in
differentiation, are associated with oestrogen receptor-positive
breast tumours and interact with metastasis gene C4.4a and
dystroglycan. Br J Cancer. 88:579–585. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hrstka R, Nenutil R, Fourtouna A, Maslon
MM, Naughton C, Langdon S, Murray E, Larionov A, Petrakova K,
Muller P, et al: The pro-metastatic protein anterior gradient-2
predicts poor prognosis in tamoxifen-treated breast cancers.
Oncogene. 29:4838–4847. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wilson CL, Sims AH, Howell A, Miller CJ
and Clarke RB: Effects of oestrogen on gene expression in
epithelium and stroma of normal human breast tissue. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 13:617–628. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|