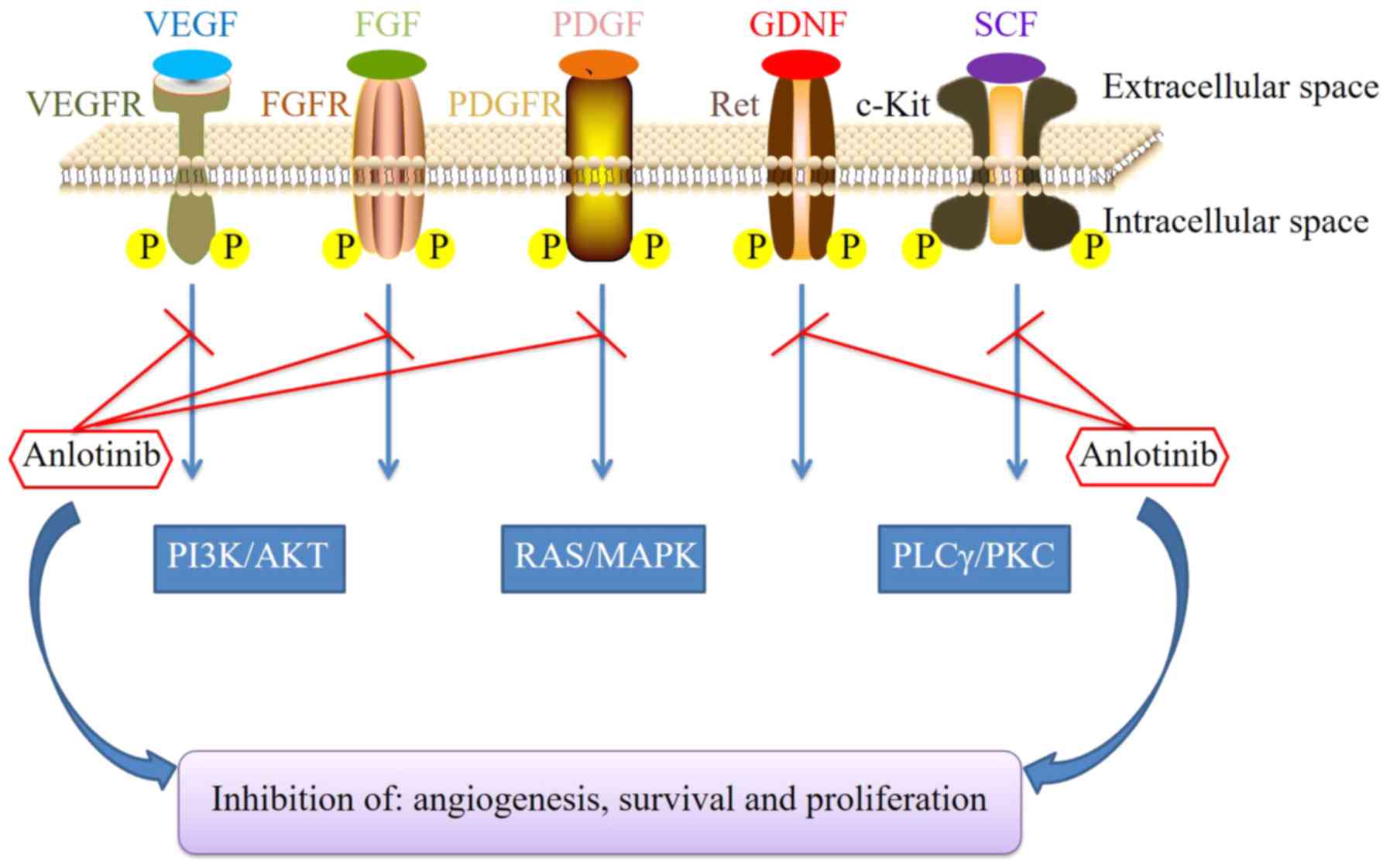
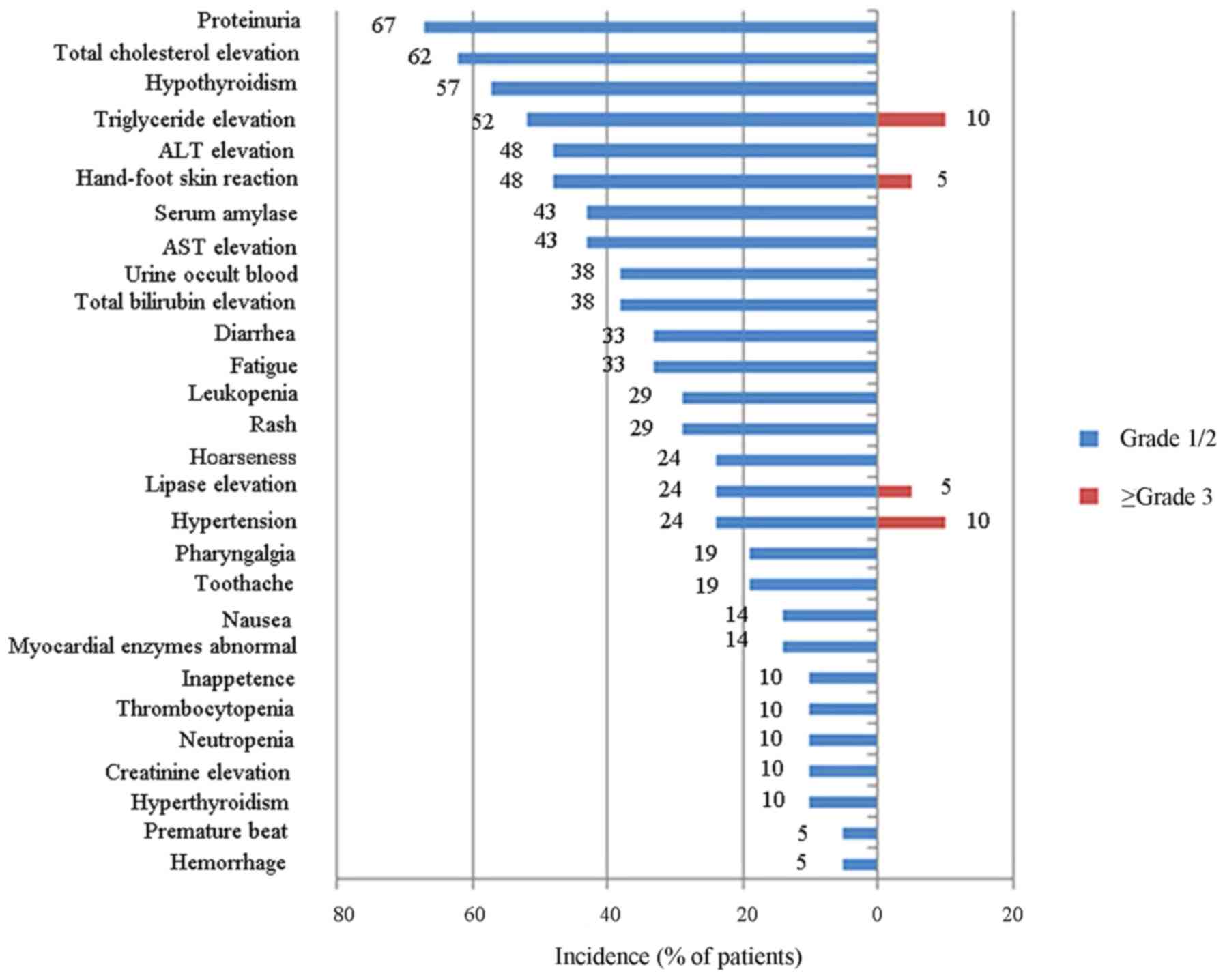
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Viallard C and Larrivée B: Tumor
angiogenesis and vascular normalization: Alternative therapeutic
targets. Angiogenesis. 20:409–426. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Voravud N and Charuruk N: Tumor
angiogenesis. J Med Assoc Thai. 82:394–404. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Regad T: Targeting RTK signaling pathways
in cancer. Cancers (Basel). 7:1758–1784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zwick E, Bange J and Ullrich A: Receptor
tyrosine kinase signalling as a target for cancer intervention
strategies. Endocr Relat Cancer. 8:161–173. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Petrelli F, Borgonovo K, Cabiddu M,
Ghilardi M and Barni S: Cetuximab and panitumumab in KRAS wild-type
colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Int J Colorectal Dis.
26:823–833. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Butti R, Das S, Gunasekaran VP, Yadav AS,
Kumar D and Kundu GC: Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) in breast
cancer: Signaling, therapeutic implications and challenges. Mol
Cancer. 17:342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Giaccone G, González-Larriba JL, van
Oosterom AT, Alfonso R, Smit EF, Martens M, Peters GJ, van der
Vijgh WJ, Smith R, Averbuch S and Fandi A: Combination therapy with
gefitinib, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor, gemcitabine and cisplatin in patients with advanced
solid tumors. Ann Oncol. 15:831–838. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Manning G, Plowman GD, Hunter T and
Sudarsanam S: Evolution of protein kinase signaling from yeast to
man. Trends Biochem Sci. 27:514–520. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Knox JJ, Barrios CH, Kim TM, Cosgriff T,
Srimuninnimit V, Pittman K, Sabbatini R, Rha SY, Flaig TW, Page RD,
et al: Final overall survival analysis for the phase II RECORD-3
study of first-line everolimus followed by sunitinib versus
first-line sunitinib followed by everolimus in metastatic RCC. Ann
Oncol. 28:1339–1345. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ogasawara S, Chiba T, Ooka Y, Suzuki E,
Maeda T, Yokoyama M, Wakamatsu T, Inoue M, Saito T, Kobayashi K, et
al: Characteristics of patients with sorafenib-treated advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma eligible for second-line treatment. Invest
New Drugs. 36:332–339. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
How J, Mann J, Laczniak AN and Baggstrom
MQ: Pulsatile erlotinib in EGFR-positive non-small-cell lung cancer
patients with leptomeningeal and brain metastases: Review of the
literature. Clin Lung Cancer. 18:354–363. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ,
Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, et al: Erlotinib vs.
chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced
EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL,
CTONG-0802): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study.
Lancet Oncol. 12:735–742. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Urata Y, Katakami N, Morita S, Kaji R,
Yoshioka H, Seto T, Satouchi M, Iwamoto Y, Kanehara M, Fujimoto D,
et al: Randomized phase III study comparing gefitinib with
erlotinib in patients with previously treated advanced lung
adenocarcinoma: WJOG 5108L. J Clin Oncol. 34:3248–3257. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liao Z, Li F, Zhang C, Zhu L, Shi Y, Zhao
G, Bai X, Hassan S, Liu X, Li T, et al: Phase II trial of VEGFR2
inhibitor apatinib for metastatic sarcoma: Focus on efficacy and
safety. Exp Mol Med. 51:1–11. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J,
Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R and Johnson DH:
Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2542–2550. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
An J and Lv W: Endostar (rh-endostatin)
versus placebo in combination with vinorelbine plus cisplatin
chemotherapy regimen in treatment of advanced non-small cell lung
cancer: A meta-analysis. Thorac Cancer. 9:606–612. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Syed YY: Anlotinib: First global approval.
Drugs. 78:1057–1062. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liang L, Hui K, Hu C, Wen Y, Yang S, Zhu
P, Wang L, Xia Y, Qiao Y, Sun W, et al: Autophagy inhibition
potentiates the anti-angiogenic property of multikinase inhibitor
anlotinib through JAK2/STAT3/VEGFA signaling in non-small cell lung
cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang G, Sun M, Jiang Y, Zhang T, Sun W,
Wang H, Yin F, Wang Z, Sang W, Xu J, et al: Anlotinib, a novel
small molecular tyrosine kinase inhibitor, suppresses growth and
metastasis via dual blockade of VEGFR2 and MET in osteosarcoma. Int
J Cancer. 145:979–993. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ruan X, Shi X, Dong Q, Yu Y, Hou X, Song
X, Wei X, Chen L and Gao M: Antitumor effects of anlotinib in
thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 26:153–164. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin B, Song X, Yang D, Bai D, Yao Y and Lu
N: Anlotinib inhibits angiogenesis via suppressing the activation
of VEGFR2, PDGFRβ and FGFR1. Gene. 654:77–86. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xie C, Wan X, Quan H, Zheng M, Fu L, Li Y
and Lou L: Preclinical characterization of anlotinib, a highly
potent and selective vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2
inhibitor. Cancer Sci. 109:1207–1219. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jang HS, Woo SR, Song KH, Cho H, Chay DB,
Hong SO, Lee HJ, Oh SJ, Chung JY, Kim JH and Kim TW: API5 induces
cisplatin resistance through FGFR signaling in human cancer cells.
Exp Mol Med. 49:e3742017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Turkington RC, Longley DB, Allen WL,
Stevenson L, McLaughlin K, Dunne PD, Blayney JK, Salto-Tellez M,
Van Schaeybroeck S and Johnston PG: Fibroblast growth factor
receptor 4 (FGFR4): A targetable regulator of drug resistance in
colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sugimoto K, Miyata Y, Nakayama T, Saito S,
Suzuki R, Hayakawa F, Nishiwaki S, Mizuno H, Takeshita K, Kato H,
et al: Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 facilitates the growth and
chemo-resistance of leukemia cells in the bone marrow by modulating
osteoblast functions. Sci Rep. 6:307792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Saito S, Morishima K, Ui T, Hoshino H,
Matsubara D, Ishikawa S, Aburatani H, Fukayama M, Hosoya Y, Sata N,
et al: The role of HGF/MET and FGF/FGFR in fibroblast-derived
growth stimulation and lapatinib-resistance of esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 15:822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cochrane DR, Spoelstra NS, Howe EN,
Nordeen SK and Richer JK: MicroRNA-200c mitigates invasiveness and
restores sensitivity to microtubule-targeting chemotherapeutic
agents. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:1055–1066. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bayraktar R and Van Roosbroeck K: miR-155
in cancer drug resistance and as target for miRNA-based
therapeutics. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 37:33–44. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang Y, Zhao M, Zhao H, Cheng S, Bai R and
Song M: MicroRNA-940 restricts the expression of
metastasis-associated gene MACC1 and enhances the antitumor effect
of Anlotinib on colorectal cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 12:2809–2822.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ma DB, Qin MM, Shi L and Ding XM:
MicroRNA-6077 enhances the sensitivity of patients-derived lung
adenocarcinoma cells to anlotinib by repressing the activation of
glucose transporter 1 pathway. Cell Signal. 64:1093912019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang L, En H, Yang L, Zhang Y, Sun B and
Gao J: miR-596 suppresses the expression of Survivin and enhances
the sensitivity of osteosarcoma cells to the molecular targeting
agent anlotinib. Onco Targets Ther. 12:6825–6838. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lu J, Xu W, Qian J, Wang S, Zhang B, Zhang
L, Qiao R, Hu M, Zhao Y, Zhao X, et al: Transcriptome profiling
analysis reveals that CXCL2 is involved in anlotinib resistance in
human lung cancer cells. BMC Med Genomics. 12 (Suppl 2):S382019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sun Y, Niu W, Du F, Du C, Li S, Wang J, Li
L, Wang F, Hao Y, Li C and Chi Y: Safety, pharmacokinetics, and
antitumor properties of anlotinib, an oral multi-target tyrosine
kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced refractory solid
tumors. J Hematol Oncol. 9:1052016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Werner TL, Kannapel E, Chen J, Chen M and
Cohen AL: Safety and PK results from a phase Ib study of AL3818
(anlotinib) hydrochloride in subjects with ovarian, cervical, and
endometrial cancers. J Clin Oncol. 35 (15 Suppl):e170712017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Reck M and Rabe KF: precision diagnosis
and treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J
Med. 377:849–861. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Han B, Li K, Zhao Y, Li B, Cheng Y, Zhou
J, Lu Y, Shi Y, Wang Z, Jiang L, et al: Anlotinib as a third-line
therapy in patients with refractory advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer: A multicentre, randomised phase II trial (ALTER0302). Br J
Cancer. 118:654–661. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cheng Y, Wang Q, Li K, Shi J, Wu L, Han B,
Chen G, He J, Wang J, Qin H and Li X: Anlotinib as third-line or
further-line treatment in relapsed SCLC: A multicentre, randomized,
doubleblind phase 2 trial. J Thorac Oncol. 13 (10 Suppl):S351–S352.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Morrison BA: Soft tissue sarcomas of the
extremities. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 16:285–290. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gatta G, van der Zwan JM, Casali PG,
Siesling S, Dei Tos AP, Kunkler I, Otter R, Licitra L, Mallone S,
Tavilla A, et al: Rare cancers are not so rare: The rare cancer
burden in Europe. Eur J Cancer. 47:2493–2511. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Meyer M and Seetharam M: First-line
therapy for metastatic soft tissue sarcoma. Curr Treat Options
Oncol. 20:62019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ryan CW, Merimsky O, Agulnik M, Blay JY,
Schuetze SM, Van Tine BA, Jones RL, Elias AD, Choy E, Alcindor T,
et al: PICASSO III: A phase III, placebo-controlled study of
doxorubicin with or without palifosfamide in patients with
metastatic soft tissue sarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 34:3898–3905. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chi Y, Fang Z, Hong X, Yao Y, Sun P, Wang
G, Du F, Sun Y, Wu Q, Qu G, et al: Safety and efficacy of
anlotinib, a multikinase angiogenesis inhibitor, in patients with
refractory metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma. Clin Cancer Res.
24:5233–5238. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yao Y, Chi Y, Fang Z, Wang S, Huang G, Cai
Q, Shang G, Wang G, Qu G, Wu Q, et al: Efficacy of anlotinib in
advanced soft tissue sarcoma by prior lines of therapy, age and
dose modification. Ann Oncol. 29 (Suppl 8):viii576–viii595. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Niu X, Wang J XB, Yu S, Zhang X, Huang Z,
Cai J, Cai Z, Chen J, Cheng X, et al: Chinese society of clinical
oncology (CSCO) guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of soft
tissue sarcoma. People's Medical Publishing House. (Beijing, China,
1st edition). 2019.
|
|
46
|
Anlotinib Hydrochloride Capsules [Package
insert]. (Lianyungang, China). ChiaTai TianQing Pharmaceutical
Group. 2019.(In Chinese).
|
|
47
|
Lim H, Devesa SS, Sosa JA, Check D and
Kitahara CM: Trends in thyroid cancer incidence and mortality in
the United States, 1974–2013. JAMA. 317:1338–1348. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Roman S, Lin R and Sosa JA: Prognosis of
medullary thyroid carcinoma: Demographic, clinical, and pathologic
predictors of survival in 1252 cases. Cancer. 107:2134–2142. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Romei C, Ciampi R and Elisei R: A
comprehensive overview of the role of the RET proto-oncogene in
thyroid carcinoma. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 12:192–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wells SA Jr, Gosnell JE, Gagel RF, Moley
J, Pfister D, Sosa JA, Skinner M, Krebs A, Vasselli J and
Schlumberger M: Vandetanib for the treatment of patients with
locally advanced or metastatic hereditary medullary thyroid cancer.
J Clin Oncol. 28:767–772. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kurzrock R, Sherman SI, Ball DW,
Forastiere AA, Cohen RB, Mehra R, Pfister DG, Cohen EE, Janisch L,
Nauling F, et al: Activity of XL184 (Cabozantinib), an oral
tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with medullary thyroid
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 29:2660–2666. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Schlumberger MJ, Elisei R, Bastholt L,
Wirth LJ, Martins RG, Locati LD, Jarzab B, Pacini F, Daumerie C,
Droz JP, et al: Phase II study of safety and efficacy of motesanib
in patients with progressive or symptomatic, advanced or metastatic
medullary thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:3794–3801. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lam ET, Ringel MD, Kloos RT, Prior TW,
Knopp MV, Liang J, Sammet S, Hall NC, Wakely PE Jr, Vasko VV, et
al: Phase II clinical trial of sorafenib in metastatic medullary
thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol. 28:2323–2330. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sun Y, Du F, Gao M, Ji Q, Li Z, Zhang Y,
Guo Z, Wang J, Chen X, Wang J, et al: Anlotinib for the treatment
of patients with locally advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid
cancer. Thyroid. 28:1455–1461. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D,
Brest A, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, et al:
SEER Cancer statistics review, 1975–2016. National Cancer
Institute. (Bethesda, MD). 2018.Updated
April 9. 2020.
|
|
56
|
Rini BI, Powles T, Atkins MB, Escudier B,
McDermott DF, Suarez C, Bracarda S, Stadler WM, Donskov F, Lee JL,
et al: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sunitinib in patients
with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma
(IMmotion151): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised
controlled trial. Lancet. 393:2404–2415. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Cella D, Reeves J,
Hawkins R, Guo J, Nathan P, Staehler M, de Souza P, Merchan JR, et
al: Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma.
N Engl J Med. 369:722–731. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lee JB, Park HS, Park S, Lee HJ, Kwon KA,
Choi YJ, Kim YJ, Nam CM, Cho NH, Kang B, et al: Temsirolimus in
Asian metastatic/recurrent non-clear cell renal carcinoma. Cancer
Res Treat. 51:1578–1588. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liu C, Cao F, Xing W, Si T, Yu H, Yang X
and Guo Z: Efficacy of cryoablation combined with sorafenib for the
treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma. Int J Hyperthermia.
36:220–228. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Schultze-Seemann W, Schulz H, Tschechne B
and Häckl M: Bevacizumab plus IFN-alpha-2a in first-line treatment
of patients with advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A
prospective german non-interventional study. Anticancer Res.
39:875–882. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhou AP, Bai YX, Song V, Li HZ, Xie XD,
Ren XB, Ye DW, Liu JY, Luo H, Bai XZ, et al: Anlotinib in
metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) with a previous anti-VEGFR
TKI: Preliminary results from a multicenter, phase II trial. J Clin
Oncol. 34 (15 Suppl):e160822016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Zhou AP, Bai Y, Song Y, Luo H, Ren XB,
Wang X, Shi B, Fu C, Cheng Y, Liu J, et al: Anlotinib versus
sunitinib as first-line treatment for metastatic renal cell
carcinoma: A randomized phase II clinical trial. Oncologist.
24:e701–e708. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Huang J, Xiao J, Fang W, Lu P, Fan Q, Shu
Y, Feng JF, Zhang S, Ba Y, Liu Y, et al: Anlotinib in
chemotherapy-refractory metastatic esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma (ESCC): A randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase II
trial. J Clin Oncol. 37 (4 Suppl):S952019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Wang L HJ, Han Y, Li Y, Fu J, Mao W, Wang
X, Chen K, Fang W, Fan Q, et al: Chinese Society of Clinical
Oncology (CSCO) guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of
esophageal cancer. People's Medical Publishing House. (Beijing,
China, 1st edition). 2019.
|
|
65
|
Han B, Li K, Wang Q, Zhang L, Shi J, Wang
Z, Cheng Y, He J, Shi Y, Zhao Y, et al: Effect of anlotinib as a
third-line or further treatment on overall survival of patients
with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: The ALTER 0303 phase 3
randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 4:1569–1575. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Haber DA, Bell DW, Sordella R, Kwak EL,
Godin-Heymann N, Sharma SV, Lynch TJ and Settleman J: Molecular
targeted therapy of lung cancer: EGFR mutations and response to
EGFR inhibitors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 70:419–426.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li K, Han BH, Wang QM, Li PC, Shi JH, Wang
ZH, Cheng Y, He JX, Shi YK, Chen WQ, et al: OS outcomes to
anlotinib in patients (pts) with refractory NSCLC of both wild-type
(WT) and mutant EGFR. J Clin Oncol. 36 (15 Suppl):e210132018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Shao L, Wang W, Song Z and Zhang Y: The
efficacy and safety of anlotinib treatment for advanced lung
cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 12:6549–6554. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gao W, He J, Jin SD, Xu J, Yu TF, Wang W,
Zhu Q, Dai H, Wu H, Liu YQ, et al: Association of initial epidermal
growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors treatment and
EGFR exon 19 deletion with frequency of the T790M mutation in
non-small cell lung cancer patients after resistance to first-line
epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Onco
Targets Ther. 12:9495–9504. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kwak EL, Sordella R, Bell DW,
Godin-Heymann N, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Driscoll DR,
Fidias P, Lynch TJ, et al: Irreversible inhibitors of the EGF
receptor may circumvent acquired resistance to gefitinib. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:7665–7670. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhou M, Chen X, Zhang H, Xia L, Tong X,
Zou L, Hao R, Pan J, Zhao X, Chen D, et al: China national medical
products administration approval summary: Anlotinib for the
treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer after two lines of
chemotherapy. Cancer Commun (Lond). 39:362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Si X, Zhang L, Wang H, Zhang X, Wang M,
Han B, Li K, Wang Q, Shi J, Wang Z, et al: Quality of life results
from a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, multi-center
phase III trial of anlotinib in patients with advanced non-small
cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 122:32–37. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Liang W, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Han X, Yang X,
He J, Li K and Han B: P2.01–01 The impact of anlotinib on brain
metastases of NSCLC: Post-hoc analysis of a phase III randomized
control trial (ALTER0303). J Thorac Oncol. 13 (10 Suppl):S6652018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Wang J, Zhao Y, Wang Q, Zhang L, Shi J,
Wang Z, Cheng Y, He J, Shi Y, Yu H, et al: Prognostic factors of
refractory NSCLC patients receiving anlotinib hydrochloride as the
third- or further-line treatment. Cancer Biol Med. 15:443–451.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Dobbin SJH, Cameron AC, Petrie MC, Jones
RJ, Touyz RM and Lang NN: Toxicity of cancer therapy: What the
cardiologist needs to know about angiogenesis inhibitors. Heart.
104:1995–2002. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Si X, Zhang L, Wang H, Zhang X, Wang M,
Han B, Li K, Wang Q, Shi J, Wang Z, et al: Management of
anlotinib-related adverse events in patients with advanced
non-small cell lung cancer: Experiences in ALTER-0303. Thorac
Cancer. 10:551–556. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Rimassa L, Danesi R, Pressiani T and Merle
P: Management of adverse events associated with tyrosine kinase
inhibitors: Improving outcomes for patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 77:20–28. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Walko CM and Grande C: Management of
common adverse events in patients treated with sorafenib: Nurse and
pharmacist perspective. Semin Oncol. 41 (Suppl 2):S17–S28. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Miura S, Fujino M, Matsuo Y, Tanigawa H
and Saku K: Nifedipine-induced vascular endothelial growth factor
secretion from coronary smooth muscle cells promotes endothelial
tube formation via the kinase insert domain-containing
receptor/fetal liver kinase-1/NO pathway. Hypertens Res.
28:147–153. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kim SY, Kim SM, Chang H, Kim BW, Lee YS,
Chang HS and Park CS: Safety of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in
patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: Real-world use of
lenvatinib and Sorafenib in Korea. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
10:3842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Nikolaou V, Syrigos K and Saif MW:
Incidence and implications of chemotherapy related hand-foot
syndrome. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 15:1625–1633. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Srinivas S, Stein D, Teltsch DY, Tao S,
Cisar L and Ramaswamy K: Real-world chart review study of adverse
events management in patients taking tyrosine kinase inhibitors to
treat metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Oncol Pharm Pract.
24:574–583. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Cheville AL, Kollasch J, Vandenberg J,
Shen T, Grothey A, Gamble G and Basford JR: A home-based exercise
program to improve function, fatigue, and sleep quality in patients
with stage IV lung and colorectal cancer: A randomized controlled
trial. J Pain Symptom Manage. 45:811–821. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Rugo HS, Di Palma JA, Tripathy D, Bryce R,
Moran S, Olek E and Bosserman L: The characterization, management,
and future considerations for ErbB-family TKI-associated diarrhea.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 175:5–15. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
McCole DF and Barrett KE: Decoding
epithelial signals: Critical role for the epidermal growth factor
receptor in controlling intestinal transport function. Acta Physiol
(Oxf). 195:149–159. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Bowen JM, Mayo BJ, Plews E, Bateman E,
Stringer AM, Boyle FM, Finnie JW and Keefe DM: Development of a rat
model of oral small molecule receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor-induced diarrhea. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:1269–1275. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Lu J, Shi Q, Zhang L, Wu J, Lou Y, Qian J,
Zhang B, Wang S, Wang H, Zhao X and Han B: Integrated transcriptome
analysis reveals KLK5 and L1CAM predict response to anlotinib in
NSCLC at 3rd line. Front Oncol. 9:8862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Liu Z, Wang J, Meng Z, Wang X, Zhang C,
Qin T, Chen J, Jiang X, Wang L, Lin L, et al: CD31-labeled
circulating endothelial cells as predictor in anlotinib-treated
non-small-cell lung cancer: Analysis on ALTER-0303 study. Cancer
Med. Jun 1–2018.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
89
|
Lu J, Zhang W, Yan B, Li H, Zhang L, Dong
Y, Qian J, Wang S, Zhang B, Wu J, et al: Tumor mutation index as a
biomarker for responsive stratification on multi-targeted TKI
anlotinib: An ALTER-0303 companion diagnostic study. Ann Oncol. 29
(Suppl 9):ix1132018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Lu J, Zhong H, Wu J, Chu T, Zhang L, Li H,
Wang Q, Li R, Zhao Y, Gu A, et al: Circulating DNA-based sequencing
guided anlotinib therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Adv Sci
(Weinh). 6:19007212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Chen D, Xu J, Zhao Y, Chu T, Zhong H, Han
B and Zhong R: Prognostic value of tumor cavitation in
extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer patients treated with
anlotinib. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 146:401–406. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Ohm JE and Carbone DP: VEGF as a mediator
of tumor-associated immunodeficiency. Immunol Res. 23:263–272.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Garber K: Promising early results for
immunotherapy-antiangiogenesis combination. J Natl Cancer Inst.
106(pii): dju3922014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Rizvi NA, Antonia SJ, Shepherd FA, Chow
LQ, Goldman J, Shen Y, Chen AC and Gettinger S: Nivolumab
(Anti-PD-1; BMS-936558, ONO-4538) maintenance as monotherapy or in
combination with bevacizumab (BEV) for non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC) previously treated with chemotherapy: Metastatic non-small
cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol. 90 (5 Suppl):S322014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Ahn MJ, Sun JM, Lee SH, Ahn JS and Park K:
EGFR TKI combination with immunotherapy in non-small cell lung
cancer. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 16:465–469. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|