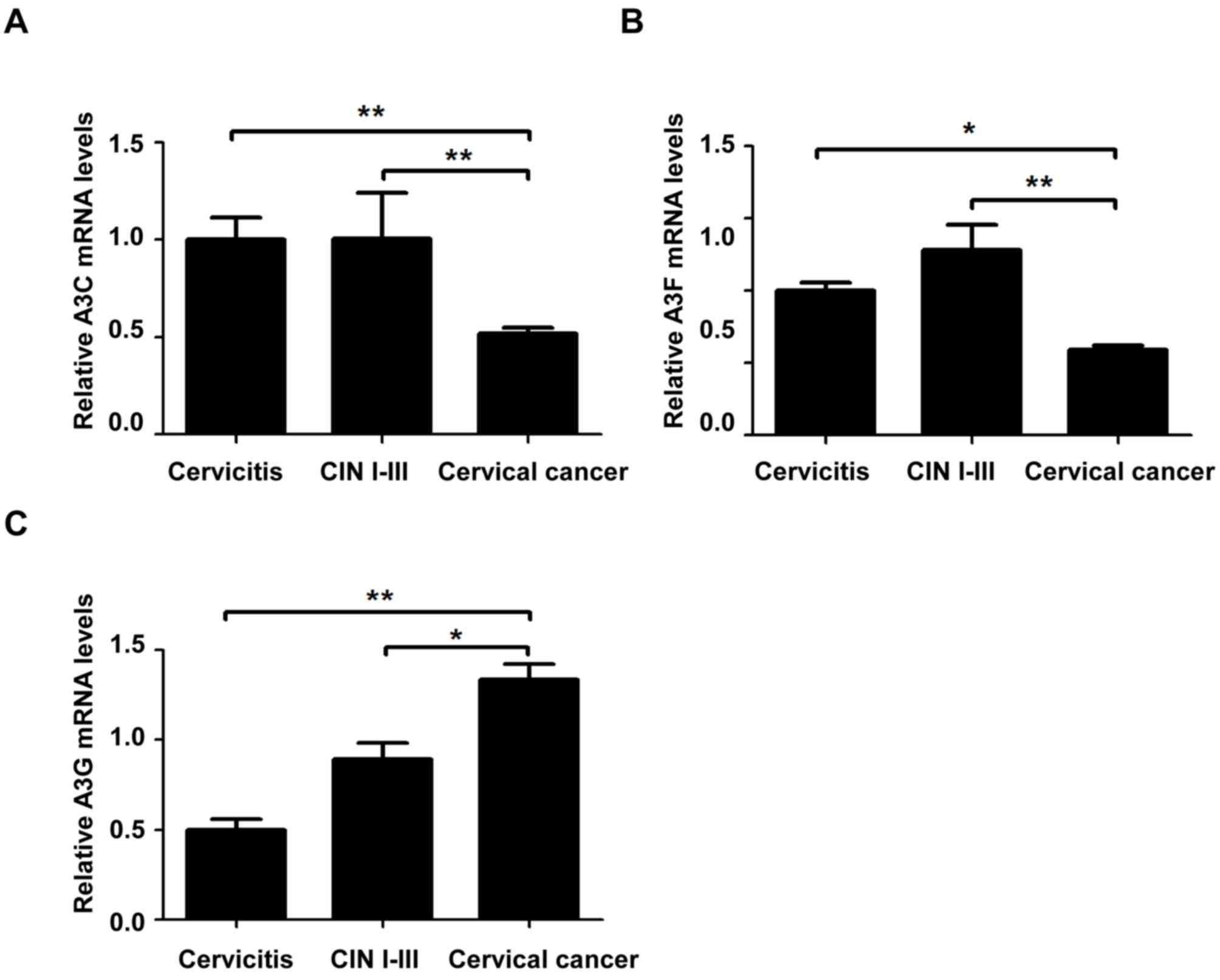
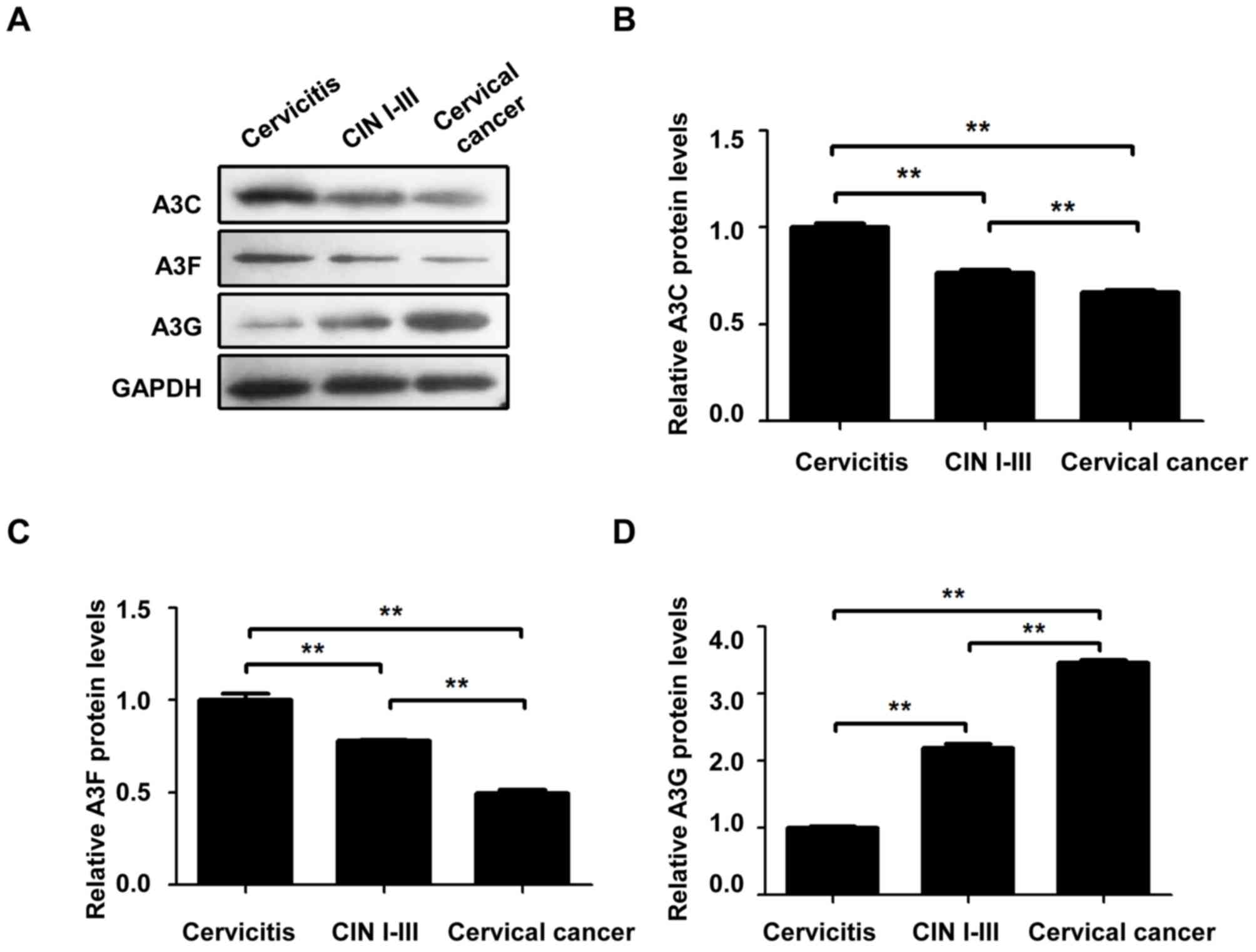
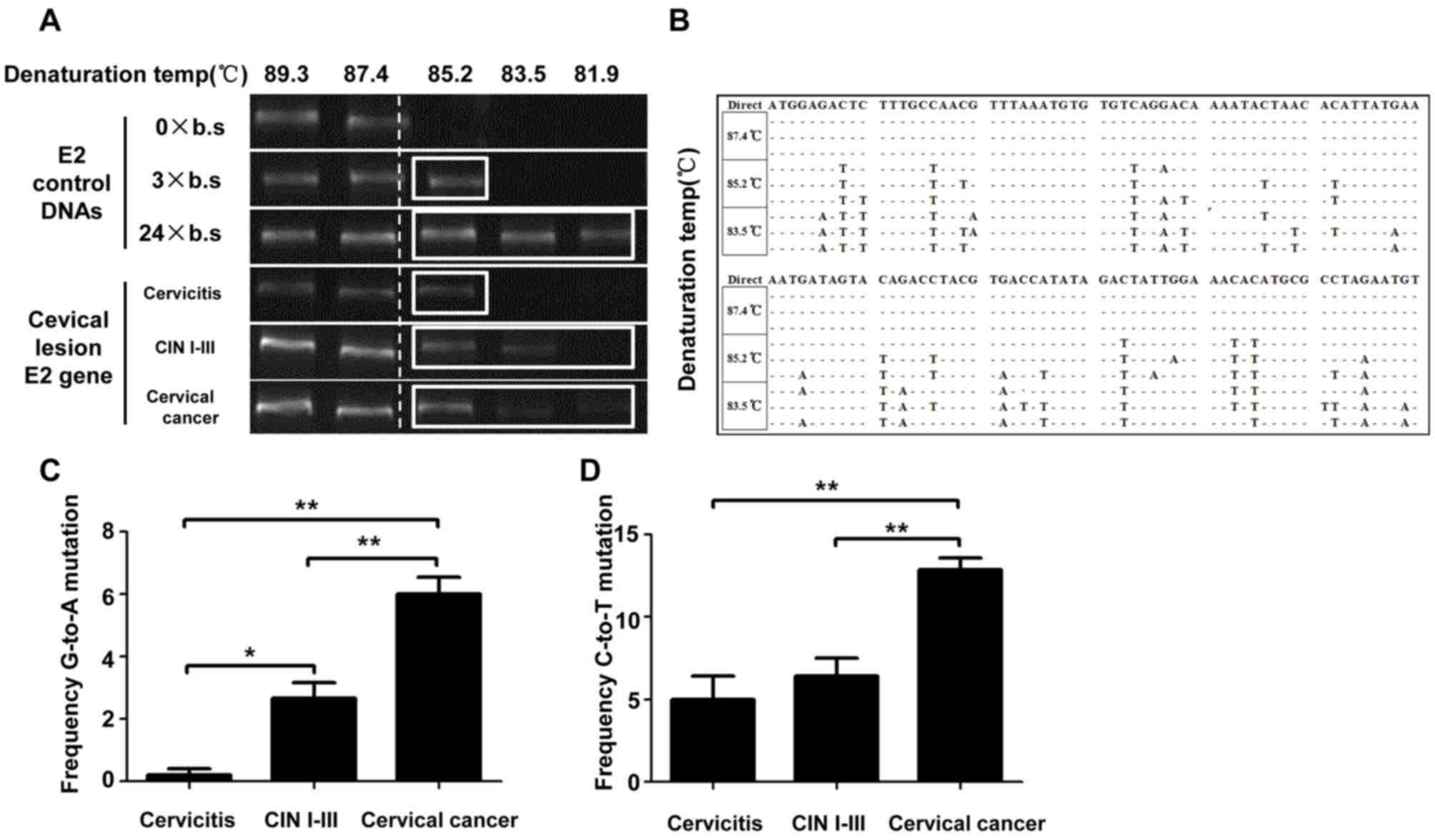
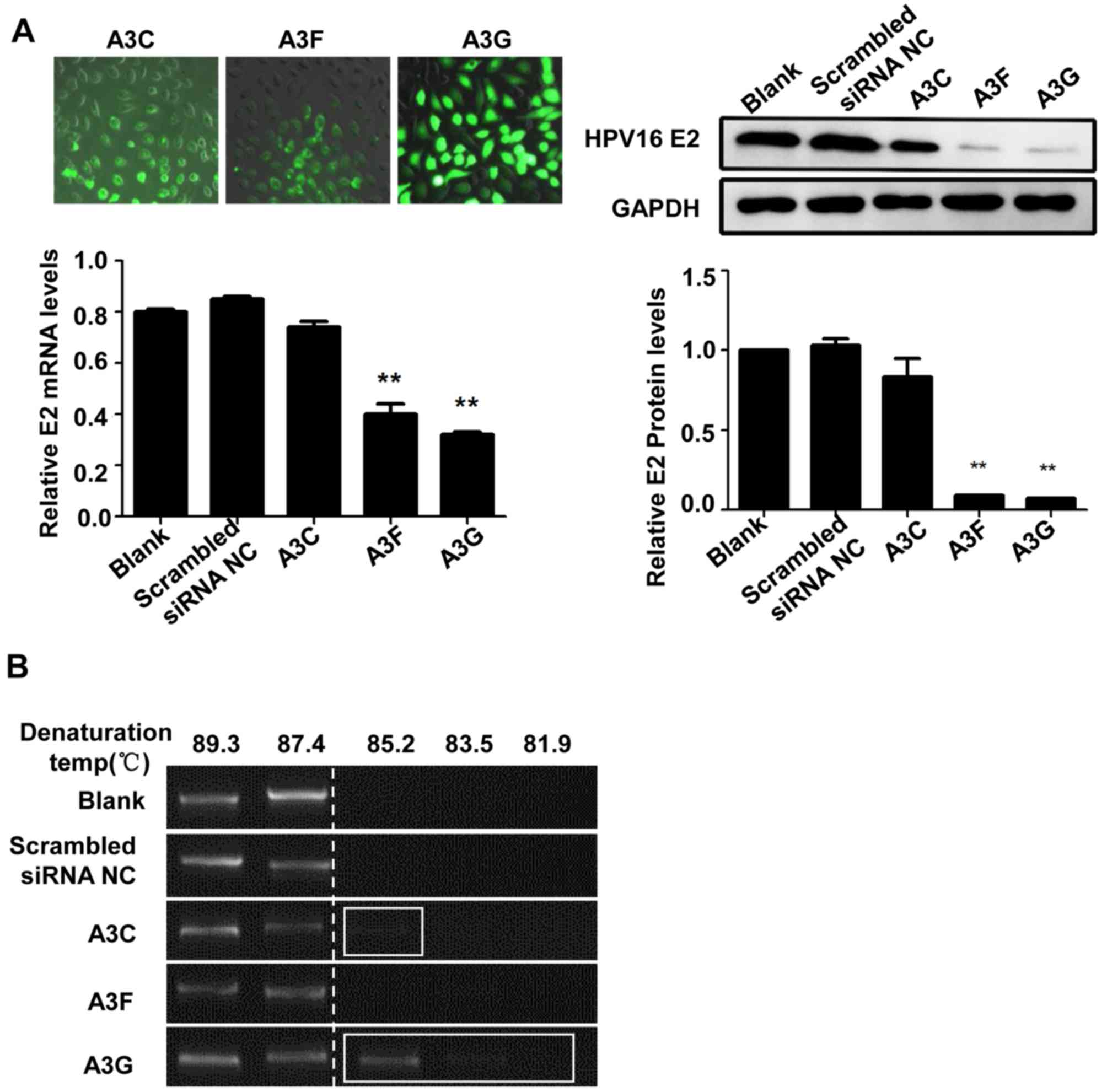
|
1
|
Warren CJ, Westrich JA, Doorslaer KV and
Pyeon D: Roles of APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B in human papillomavirus
infection and disease progression. Viruses. 9:E2332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Salter JD, Bennett RP and Smith HC: The
APOBEC protein family: United by structure, divergent in function.
Trends Biochem Sci. 41:578–594. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ikeda T, Symeonides M, Albin JS, Li M,
Thali M and Harris RS: HIV-1 adaptation studies reveal a novel
Env-mediated homeostasis mechanism for evading lethal hypermutation
by APOBEC3G. PLoS Pathog. 14:e10070102018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ebrahimi D, Richards CM, Carpenter MA,
Wang J, Ikeda T, Becker JT, Cheng AZ, McCann JL, Shaban NM,
Salamango DJ, et al: Genetic and mechanistic basis for APOBEC3H
alternative splicing, retrovirus restriction, and counteraction by
HIV-1 protease. Nat Commun. 9:41372018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Anderson BD, Ikeda T, Moghadasi SA, Martin
AS, Brown WL and Harris RS: Natural APOBEC3C variants can elicit
differential HIV-1 restriction activity. Retrovirology. 15:782018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim EY, Lorenzo-Redondo R, Little SJ,
Chung YS, Phalora PK, Maljkovic Berry I, Archer J, Penugonda S,
Fischer W, Richman DD, et al: Human APOBEC3 induced mutation of
human immunodeficiency virus type-1 contributes to adaptation and
evolution in natural infection. PLoS Pathog. 10:e10042812014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Luo J: Stable expression of porcine
APOBEC3F in PK15 cells and its inhibitory effects on PERV mutation.
Guangxi University 2012.
|
|
8
|
Noguchi C, Hiraga N, Mori N, Tsuge M,
Imamura M, Takahashi S, Fujimoto Y, Ochi H, Abe H, Maekawa T, et
al: Dual effect of APOBEC3G on Hepatitis B virus. J Gen Virol.
88:432–440. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vieira VC, Leonard B, White EA, Starrett
GJ, Temiz NA, Lorenz LD, Lee D, Soares MA, Lambert PF, Howley PM
and Harris RS: Human papillomavirus E6 triggers upregulation of the
antiviral and cancer genomic DNA deaminase APOBEC3B. mBio.
5:e02234–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bulliard Y, Narvaiza I, Bertero A, Peddi
S, Röhrig UF, Ortiz M, Zoete V, Castro-Diaz N, Turelli P, Telenti
A, et al: Structure-function analyses point to a
polynucleotide-accommodating groove essential for APOBEC3A
restriction activities. J Virol. 85:1765–1776. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tsuge M, Noguchi C, Akiyama R, Matsushita
M, Kunihiro K, Tanaka S, Abe H, Mitsui F, Kitamura S, Hatakeyama T,
et al: G to A hypermutation of TT virus. Virus Res. 149:211–216.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gee P, Ando Y, Kitayama H, Yamamoto SP,
Kanemura Y, Ebina H, Kawaguchi Y and Koyanagi Y: APOBEC1-mediated
editing and attenuation of herpes simplex virus 1 DNA indicate that
neurons have an antiviral role during herpes simplex encephalitis.
J. Virol. 85:9726–9736. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Suspène R, Aynaud MM, Koch S, Pasdeloup D,
Labetoulle M, Gaertner B, Vartanian JP, Meyerhans A and Wain-Hobson
S: Genetic editing of herpes simplex virus 1 and Epstein-Barr
herpesvirus genomes by human APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases in culture
and in vivo. J Virol. 85:7594–7602. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lucifora J, Xia Y, Reisinger F, Zhang K,
Stadler D, Cheng X, Sprinzl MF, Koppensteiner H, Makowska Z, Volz
T, et al: Specifific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear
hepatitis B virus cccDNA. Science. 343:1221–1228. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hirose Y, Onuki M, Tenjimbayashi Y, Mori
S, Ishii Y, Takeuchi T, Tasaka N, Satoh T, Morisada T, Iwata T, et
al: Within-host variations of human papillomavirus reveal APOBEC
signature mutagenesis in the viral genome. J Virol. 92:e00017–18.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stenglein MD, Burns MB, Li M, Lengyel J
and Harris RS: APOBEC3 proteins mediate the clearance of foreign
DNA from human cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 17:222–229. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kondo S, Wakae K, Wakisaka N, Nakanishi Y,
Ishikawa K, Komori T, Moriyama-Kita M, Endo K, Murono S, Wang Z, et
al: APOBEC3A associates with human papillomavirus genome
integration in oropharyngeal cancers. Oncogene. 36:1687–1697. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Graham SV: Human papillomavirus: Gene
expression, regulation and prospects for novel diagnostic methods
and antiviral therapies. Future Microbiol. 5:1493–1506. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xue Y, Bellanger S, Zhang W, Lim D, Low J,
Lunny D and Thierry F: HPV16 E2 is an immediate early marker of
viral infection, preceding E7 expression in precursor structures of
cervical carcinoma. Cancer Res. 70:5316–5325. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bhatla N, Aoki D, Sharma DN and
Sankaranarayanan R: Cancer of the cervix uteri. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 143 (Suppl 2):S22–S36. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
de Sanjose S, Quint WG, Alemany L, Geraets
DT, Klaustermeier JE, Lloveras B, Tous S, Felix A, Bravo LE, Shin
HR, et al: Human papillomavirus genotype attribution in invasive
cervical cancer: A retrospective cross-sectional worldwide study.
Lancet Oncol. 11:1048–1056. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Pande S, Jain N, Prusty BK, Bhambhani S,
Gupta S, Sharma R, Batra S and Das BC: Human papillomavirus type 16
variant analysis of E6,E7, and L1 gennes and long control regin in
biopsy samples from cervical cancer patients in North India. J Clin
Microbiol. 46:1060–1066. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Franceschi S: The IARC commitment to
cancer prevention: The example of papillomavirus and cervical
cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. 166:277–297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Suspène R, Guétard D, Henry M, Sommer P,
Wain-Hobson S and Vartanian JP: Extensive editing of both hepatitis
B virus DNA strands by APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases in vitro and in
vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:8321–8326. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Noguchi C, Ishino H, Tsuge M, Fujimoto Y,
Imamura M, Takahashi S and Chayama K: G to A hypermutation of
hepatitis B virus. Hepatology. 41:626–633. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Suspène R, Henry M, Guillot S, Wain-Hobson
S and Vartanian JP: Recovery of APOBEC3-edited human
immunodeficiency virus G->A hypermutants by differential DNA
denaturation PCR. J Gen Virol. 86:125–129. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nik-Zainal S, Alexandrov LB, Wedge DC, Van
Loo P, Greenman CD, Raine K, Jones D, Hinton J, Marshall J,
Stebbings LA, et al: Mutational processes molding the genomes of 21
breast cancers. Cell. 149:979–993. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Alexandrov LB, Nik-Zainal S, Wedge DC,
Aparicio SA, Behjati S, Biankin AV, Bignell GR, Bolli N, Borg A,
Børresen-Dale AL, et al: Signatures of mutational processes in
human cancer. Nature. 500:415–421. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Malim MH: APOBEC proteins and intrinsic
resistance to HIV-1 infection. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
364:675–687. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sheehy AM, Gaddis NC, Choi JD and Malim
MH: Isolation of a human gene that inhibits HIV-1 infection and is
suppressed by the viral Vif protein. Nature. 418:646–650. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kitamura K, Wang Z, Chowdhury S, Simadu M,
Koura M and Muramatsu M: Uracil DNA glycosylase counteracts
APOBEC3G-induced hypermutation of hepatitis B viral genomes:
Excision repair of covalently closed circular DNA. PLoS Pathog.
9:e10033612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vieira VC and Soares MA: The role of
cytidine deaminases on innate immune responses against human viral
infections. Biomed Res Int. 2013:6830952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nik-Zainal S, Wedge DC, Alexandrov LB,
Petljak M, Butler AP, Bolli N, Davies HR, Knappskog S, Martin S,
Papaemmanuil E, et al: Association of a germline copy number
polymorphism of APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B with burden of putative
APOBEC-dependent mutations in breast cancer. Nat Genet. 46:487–491.
2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Roberts SA, Sterling J, Thompson C, Harris
S, Mav D, Shah R, Klimczak LJ, Kryukov GV, Malc E, Mieczkowski PA,
et al: Clustered mutations in yeast and in human cancers can arise
from damaged long single-strand DNA regions. Mol Cell. 46:424–435.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kazanov MD, Roberts SA, Polak P,
Stamatoyannopoulos J, Klimczak LJ, Gordenin DA and Sunyaev SR:
APOBEC-induced cancer mutations are uniquely enriched in
early-replicating, gene-dense, and active chromatin regions. Cell
Rep. 13:1103–1109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Roberts SA, Lawrence MS, Klimczak LJ,
Grimm SA, Fargo D, Stojanov P, Kiezun A, Kryukov GV, Carter SL,
Saksena G, et al: An APOBEC cytidine deaminase mutagenesis pattern
is widespread in human cancers. Nat Genet. 45:970–976. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Burns MB, Lackey L, Carpenter MA, Rathore
A, Land AM, Leonard B, Refsland EW, Kotandeniya D, Tretyakova N,
Nikas JB, et al: APOBEC3B is an enzymatic source of mutation in
breast cancer. Nature. 494:366–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mussil B, Suspène R, Aynaud MM, Gauvrit A,
Vartanian JP and Wain-Hobson S: Human APOBEC3A isoforms translocate
to the nucleus and induce DNA double strand breaks leading to cell
stress and death. PLoS One. 8:e736412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang Z, Wakae K, Kitamura K, Aoyama S, Liu
G, Koura M, Monjurul AM, Kukimoto I and Muramatsu M: APOBEC3
deaminases induce hypermutation in human papillomavirus 16 DNA upon
beta interferon stimulation. J Virol. 88:1308–1317. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Burns MB, Temiz NA and Harris RS: Evidence
for APOBEC3B mutagenesis in multiple human cancers. Nat Genet.
45:977–983. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|