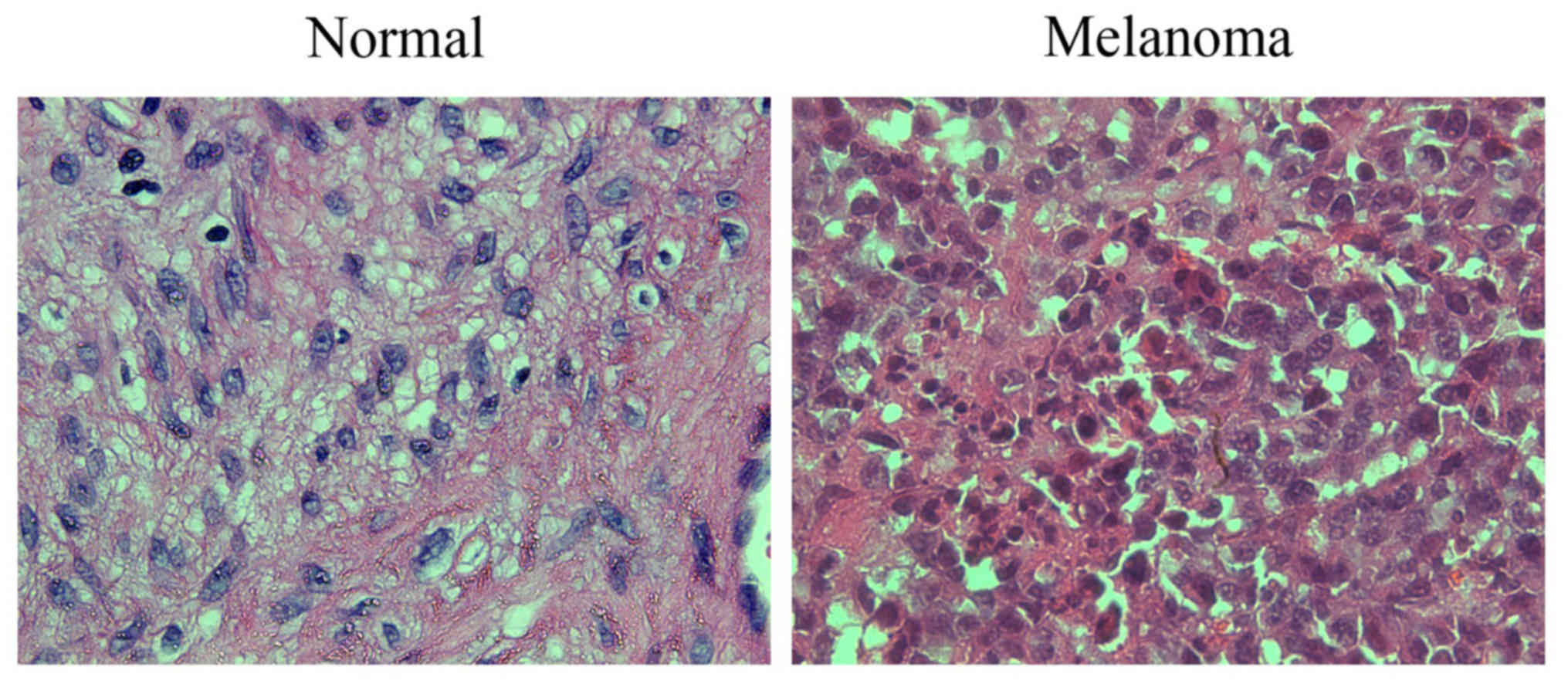
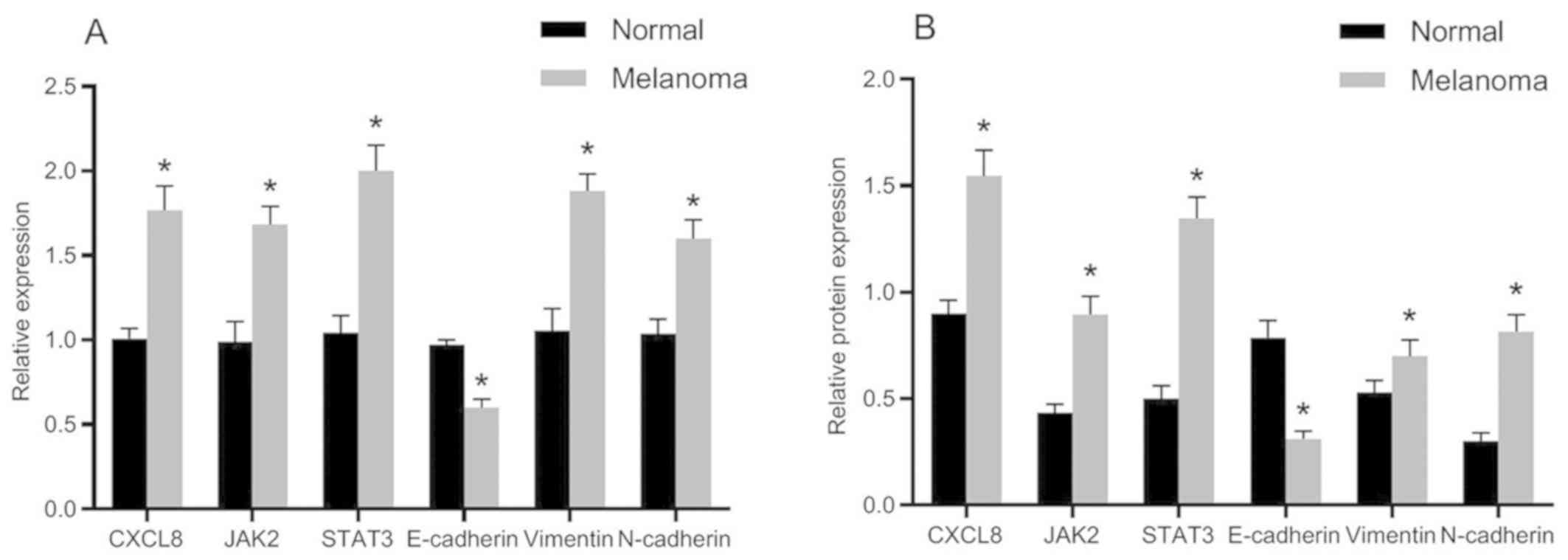
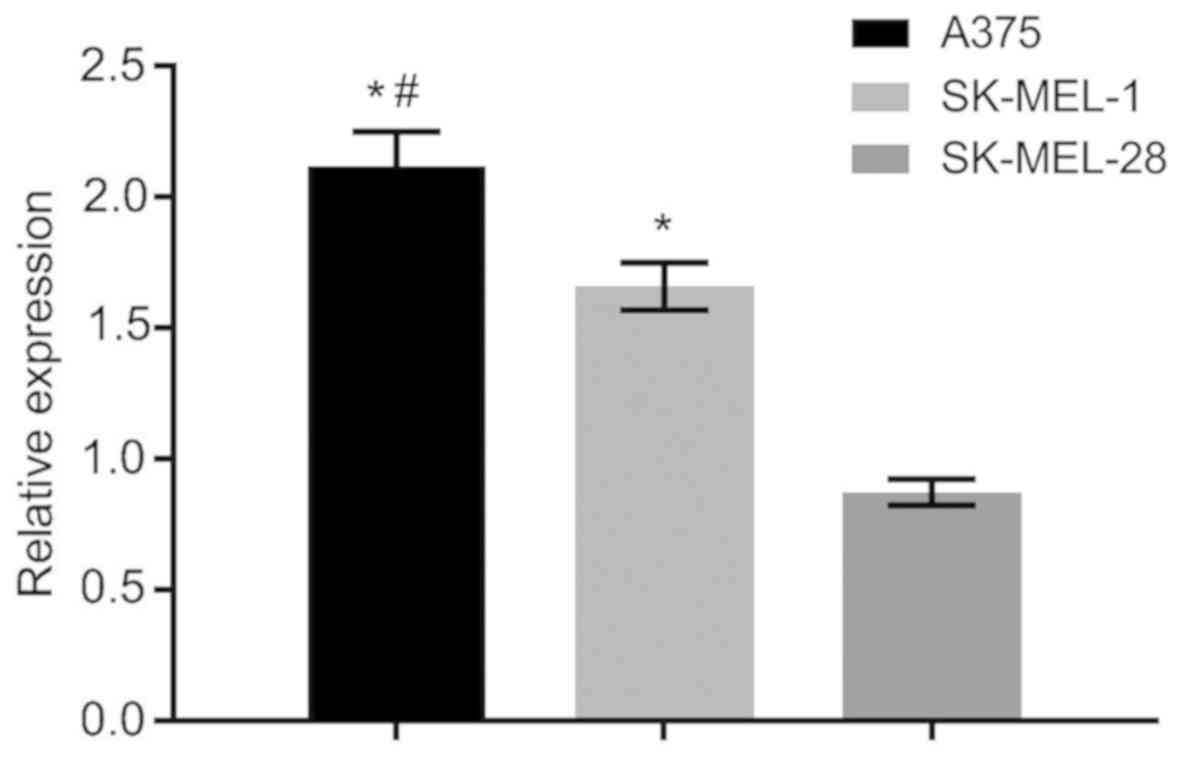
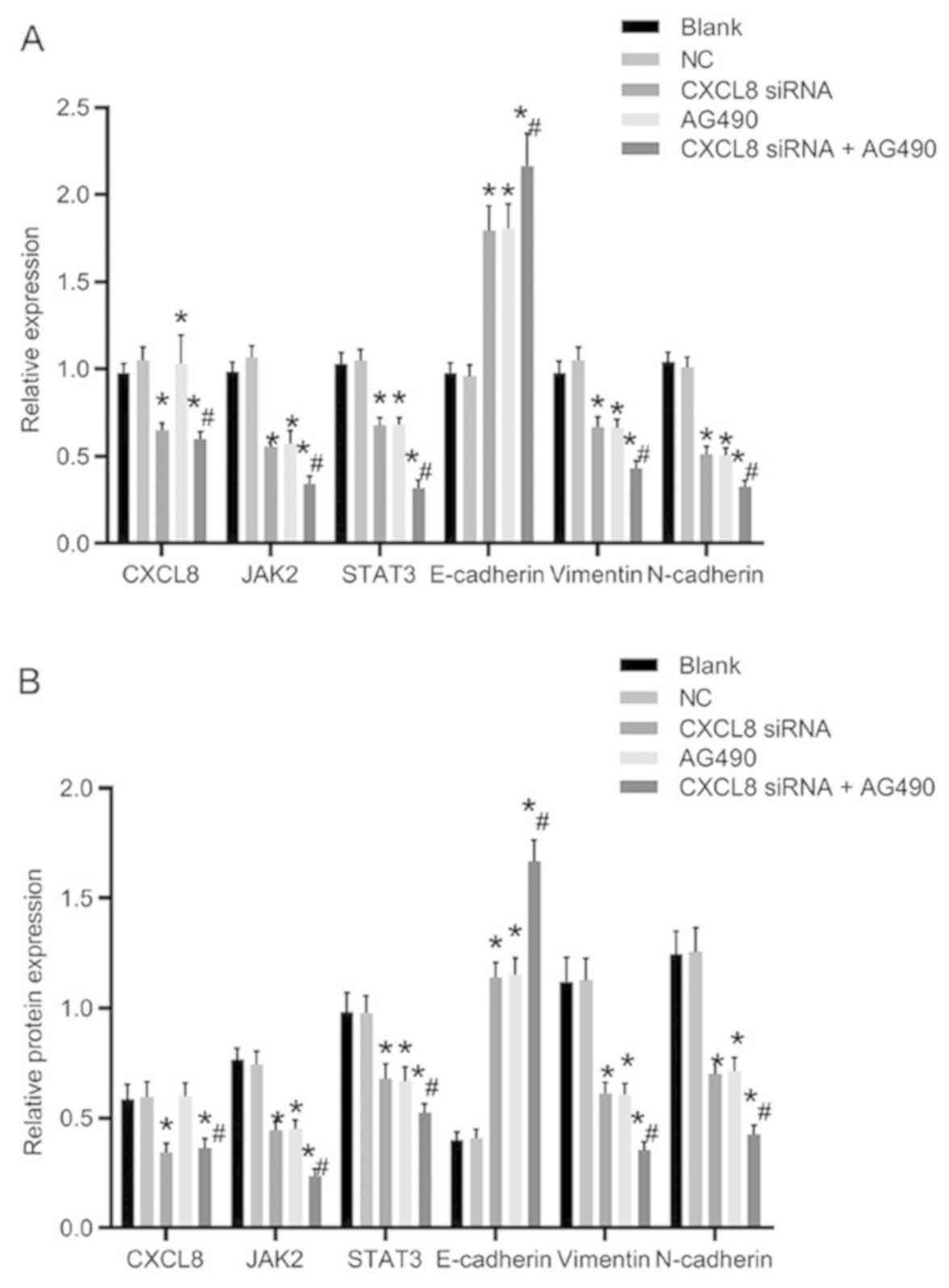
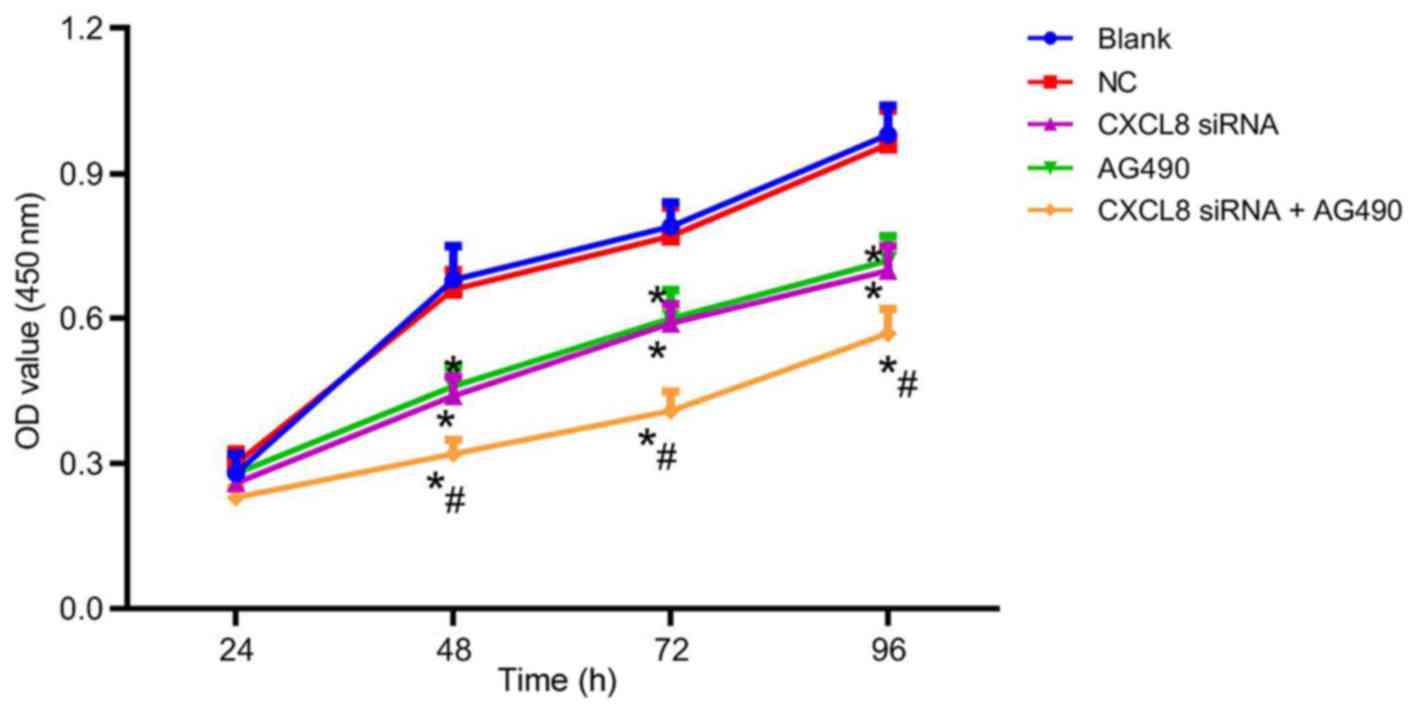
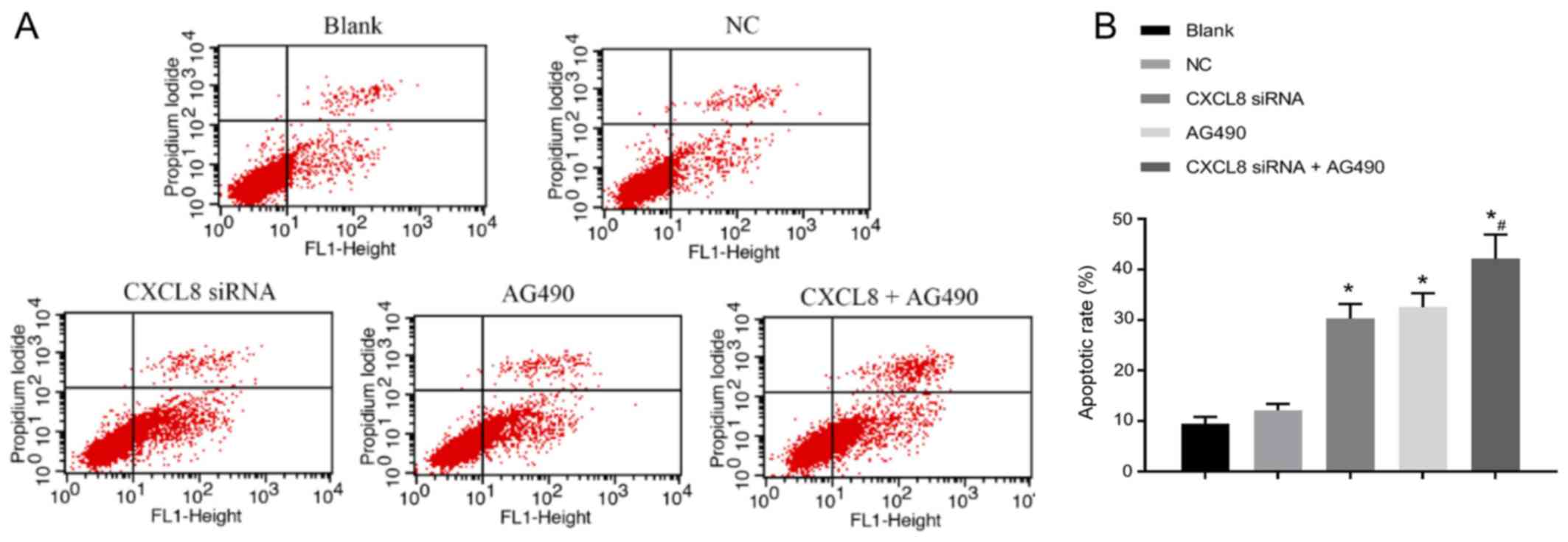
|
1
|
Aggarwal R, Dhawan S and Chopra P: Primary
gastric melanoma: A diagnostic challenge. J Gastrointest Cancer. 45
(Suppl 1):33–35. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Varamo C, Occelli M, Vivenza D, Merlano M
and Lo Nigro C: MicroRNAs role as potential biomarkers and key
regulators in melanoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 56:3–10. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu-Smith F and Ziogas A: An age-dependent
interaction between sex and geographical UV index in melanoma risk.
J Am Acad Dermatol. Dec 2–2017.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
4
|
Nissen LHC, Pierik M, Derikx LAAP, de Jong
E, Kievit W, van den Heuvel TRA, van Rosendael AR, Plasmeijer EI,
Dewint P, Verhoeven RHA, et al: Risk factors and clinical outcomes
in patients with IBD with melanoma. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
23:2018–2026. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hübner J, Waldmann A, Eisemann N, Noftz M,
Geller AC, Weinstock MA, Volkmer B, Greinert R, Breitbart EW and
Katalinic A: Association between risk factors and detection of
cutaneous melanoma in the setting of a population-based skin cancer
screening. Eur J Cancer Prev. 27:563–569. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fratangelo F, Camerlingo R, Carriero MV,
Pirozzi G, Palmieri G, Gentilcore G, Ragone C, Minopoli M, Ascierto
PA and Motti ML: Effect of ABT-888 on the apoptosis, motility and
invasiveness of BRAFi-resistant melanoma cells. Int J Oncol.
53:1149–1159. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ramgolam K, Lauriol J, Lalou C, Lauden L,
Michel L, de la Grange P, Khatib AM, Aoudjit F, Charron D, Alcaide-
Loridan C, et al: Melanoma spheroids grown under neural crest cell
conditions are highly plastic migratory/invasive tumor cells
endowed with immunomodulator function. PLoS One. 6:e187842011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tchernev G: One step melanoma surgery for
patient with thick primary melanomas: ‘To break the rules, you must
first master them!’. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 6:367–371. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Marinova L, Yordanov K and Sapundgiev N:
Primary mucosal sinonasal melanoma - case report and review of the
literature. The role of complex treatment-surgery and adjuvant
radiotherapy. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 16:40–43. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tesic N, Kamensek U, Sersa G, Kranjc S,
Stimac M, Lampreht U, Preat V, Vandermeulen G, Butinar M, Turk B,
et al: Endoglin (CD105) silencing mediated by shRNA under the
control of endothelin-1 promoter for targeted gene therapy of
melanoma. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 4:e2392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Menezes ME, Talukdar S, Wechman SL, Das
SK, Emdad L, Sarkar D and Fisher PB: Prospects of gene therapy to
treat melanoma. Adv Cancer Res. 138:213–237. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mohammed-Saeid W, Chitanda J, Al-Dulaymi
M, Verrall R and Badea I: Design and evaluation of RGD-modified
gemini surfactant-based lipoplexes for targeted gene therapy in
melanoma model. Pharm Res. 34:1886–1896. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Piccinin S, Doglioni C, Maestro R,
Vukosavljevic T, Gasparotto D, D'Orazi C and Boiocchi M: p16/CDKN2
and CDK4 gene mutations in sporadic melanoma development and
progression. Int J Cancer. 74:26–30. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Singer M, Wang C, Cong L, Marjanovic ND,
Kowalczyk MS, Zhang H, Nyman J, Sakuishi K, Kurtulus S, Gennert D,
et al: A distinct gene module for dysfunction uncoupled from
activation in tumor-infiltrating T cells. Cell. 166:1500–1511.e9.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, Han N, Zhou S, Zhou R, Yuan X, Xu
H, Zhang C, Yin T and Wu K: The DACH/EYA/SIX gene network and its
role in tumor initiation and progression. Int J Cancer.
138:1067–1075. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Volodko N, Gordon M, Salla M, Ghazaleh HA
and Baksh S: RASSF tumor suppressor gene family: Biological
functions and regulation. FEBS Lett. 588:2671–2684. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Patel M, Boo H, Kandasamy S, Patel D and
Iorio A: The advantages of dermoscopy in the diagnosis of acral
melanoma from other podiatric lesions: A literature review. J Am
Podiatr Med Assoc. 106:32016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Benton G, Kleinman HK, George J and
Arnaoutova I: Multiple uses of basement membrane-like matrix
(BME/Matrigel) in vitro and in vivo with cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 128:1751–1757. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang Y, Sun X, Nan N, Cao KX, Ma C, Yang
GW, Yu MW, Yang L, Li JP, Wang XM, et al: Elemene inhibits the
migration and invasion of 4T1 murine breast cancer cells via
heparanase. Mol Med Rep. 16:794–800. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Greenburg G and Hay ED: Cytoskeleton and
thyroglobulin expression change during transformation of thyroid
epithelium to mesenchyme-like cells. Development. 102:605–622.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Han ZH, Wang F, Wang FL, Liu Q and Zhou J:
Regulation of transforming growth factor β-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lens epithelial cells by c-Src
kinase under high glucose conditions. Exp Ther Med. 16:1520–1528.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ning X, Zhang H, Wang C and Song X:
Exosomes released by gastric cancer cells induce transition of
pericytes into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Med Sci Monit.
24:2350–2359. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dettman RW and Simon HG: Rebooting the
collagen gel: artificial hydrogels for the study of epithelial
mesenchymal transformation. Dev Dyn. 247:332–339. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang P, Dai H and Peng L: AGEs induce
epithelial to mesenchymal transformation of human peritoneal
mesothelial cells via upregulation of STAT3. Glycoconj J.
36:155–163. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou L, Yang K, Randall Wickett R and
Zhang Y: Dermal fibroblasts induce cell cycle arrest and block
epithelial-mesenchymal transition to inhibit the early stage
melanoma development. Cancer Med. 5:1566–1579. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li CY, Wang Q, Shen S, Wei XL and Li GX:
Oridonin inhibits migration, invasion, adhesion and TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of melanoma cells by inhibiting
the activity of PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Oncol Lett.
15:1362–1372. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tai KF and Wang CH: Using adenovirus armed
short hairpin RNA targeting transforming growth factor β1 inhibits
melanoma growth and metastasis in an ex vivo animal model. Ann
Plast Surg. 71 (Suppl 1):S75–S81. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sinnberg T, Levesque MP, Krochmann J,
Cheng PF, Ikenberg K, Meraz-Torres F, Niessner H, Garbe C and Busch
C: Wnt-signaling enhances neural crest migration of melanoma cells
and induces an invasive phenotype. Mol Cancer. 17:592018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tu Z, Xie S, Xiong M, Liu Y, Yang X, Tembo
KM, Huang J, Hu W, Huang X, Pan S, et al: CXCR4 is involved in
CD133-induced EMT in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol.
50:505–514. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Crosson WP, Berlinberg E and Nazarian R:
Identification of targetable EMT markers in cancer stem-like cells
derived from therapeutic resistant melanoma. Cancer Res. 77:Abst
3882. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ding Y, Li X, Hong D, Jiang L, He Y and
Fang H: Silence of MACC1 decreases cell migration and invasion in
human malignant melanoma through inhibiting the EMT. Biosci Trends.
10:258–264. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wels C, Joshi S, Koefinger P, Bergler H
and Schaider H: Transcriptional activation of ZEB1 by Slug leads to
cooperative regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition-like phenotype in melanoma. J Invest Dermatol.
131:1877–1885. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang JS, Guh JY, Chen HC, Hung WC, Lai YH
and Chuang LY: Role of receptor for advanced glycation end-product
(RAGE) and the JAK/STAT-signaling pathway in AGE-induced collagen
production in NRK-49F cells. J Cell Biochem. 81:102–113. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang R, Huang S, Fu X, Huang G, Yan X, Yue
Z, Chen S, Li Y and Xu A: The conserved ancient role of chordate
PIAS as a multilevel repressor of the NF-κB pathway. Sci Rep.
7:170632017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Erdman VV, Nasibullin TR, Tuktarova IA,
Somova RS and Mustafina OE: Association analysis of polymorphic
gene variants in the JAK/STAT signaling pathway with aging and
longevity. Russian Journal of Genetics. Russ J Genet. 55:728–737.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mullen M and Gonzalez-Perez RR:
Leptin-induced JAK/STAT signaling and cancer growth. Vaccines
(Basel). 4:262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mi C, Ma J, Wang KS, Wang Z, Li MY, Li JB,
Li X, Piao LX, Xu GH and Jin X: Amorfrutin A inhibits TNF-α induced
JAK/STAT signaling, cell survival and proliferation of human cancer
cells. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 39:338–347. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yeh CM, Chang LY, Lin SH, Chou JL, Hsieh
HY, Zeng LH, Chuang SY, Wang HW, Dittner C, Lin CY, et al:
Epigenetic silencing of the NR4A3 tumor suppressor, by aberrant
JAK/STAT signaling, predicts prognosis in gastric cancer. Sci Rep.
6:316902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Abramovich C, Yakobson B, Chebath J and
Revel M: A protein-arginine methyltransferase binds to the
intracytoplasmic domain of the IFNAR1 chain in the type I
interferon receptor. EMBO J. 16:260–266. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Khanna P, Chua PJ, Wong BSE, Yin C, Thike
AA, Wan WK, Tan PH and Baeg GH: GRAM domain-containing protein 1B
(GRAMD1B), a novel component of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway,
functions in gastric carcinogenesis. Oncotarget. 8:115370–115383.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Slattery ML, Lundgreen A, Kadlubar SA,
Bondurant KL and Wolff RK: JAK/STAT/SOCS-signaling pathway and
colon and rectal cancer. Mol Carcinog. 52:155–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ma JF, Sanchez BJ, Hall DT, Tremblay AK,
Di Marco S and Gallouzi IE: STAT3 promotes IFNγ/TNFα-induced muscle
wasting in an NF-κB-dependent and IL-6-independent manner. EMBO Mol
Med. 9:622–637. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nosaka T, Kawashima T, Misawa K, Ikuta K,
Mui AL and Kitamura T: STAT5 as a molecular regulator of
proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis in hematopoietic
cells. EMBO J. 18:4754–4765. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gurbuz V, Konac E, Varol N, Yilmaz A,
Gurocak S, Menevse S and Sozen S: Effects of AG490 and S3I-201 on
regulation of the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway in relation to
angiogenesis in TRAIL-resistant prostate cancer cells in
vitro. Oncol Lett. 7:755–763. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hwang TL, Changchien TT, Wang CC and Wu
CM: Claudin-4 expression in gastric cancer cells enhances the
invasion and is associated with the increased level of matrix
metalloproteinase-2 and −9 expression. Oncol Lett. 8:1367–1371.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Porther N and Barbieri MA: The role of
endocytic Rab GTPases in regulation of growth factor signaling and
the migration and invasion of tumor cells. Small GTPases.
6:135–144. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dong B, Liang Z, Chen Z, Li B, Zheng L,
Yang J, Zhou H and Qu L: Cryptotanshinone suppresses key
onco-proliferative and drug-resistant pathways of chronic myeloid
leukemia by targeting STAT5 and STAT3 phosphorylation. Sci China
Life Sci. 61:999–1009. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen W, He W, Cai H, Hu B, Zheng C, Ke X,
Xie L, Zheng Z, Wu X and Wang H: A-to-I RNA editing of BLCAP lost
the inhibition to STAT3 activation in cervical cancer. Oncotarget.
8:39417–39429. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wallbillich JJ, Josyula S, Saini U,
Zingarelli RA, Dorayappan KD, Riley MK, Wanner RA, Cohn DE and
Selvendiran K: High glucose-mediated STAT3 activation in
endometrial cancer is inhibited by metformin: Therapeutic
implications for endometrial cancer. PLoS One. 12:e01703182017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bao X, Ren T, Huang Y, Sun K, Wang S, Liu
K, Zheng B and Guo W: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR
increases miR-454-3p by targeting Stat3 and Atg12 to inhibit
chondrosarcoma growth. Cell Death Dis. 8:e26052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Pan Y, Wang S, Su B, Zhou F, Zhang R, Xu
T, Zhang R, Leventaki V, Drakos E, Liu W, et al: Stat3 contributes
to cancer progression by regulating Jab1/Csn5 expression. Oncogene.
36:1069–1079. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jullien N, Roche C, Brue T,
Figarella-Branger D, Graillon T, Barlier A and Herman JP:
Dose-dependent dual role of PIT-1 (POU1F1) in somatolactotroph cell
proliferation and apoptosis. PLoS One. 10:e01200102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Horton BL, Williams JB, Cabanov A,
Spranger S and Gajewski TF: Intratumoral CD8+ T-cell
apoptosis is a major component of T-cell dysfunction and impedes
antitumor immunity. Cancer Immunol Res. 6:14–24. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jiang Y, Sheng H, Meng L, Yue H, Li B,
Zhang A, Dong Y and Liu Y: RBM5 inhibits tumorigenesis of gliomas
through inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and induction of
apoptosis. World J Surg Oncol. 15:92017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Feng X, Zhao L, Shen H, Liu X, Yang Y, Lv
S and Niu Y: Expression of EMT markers and mode of surgery are
prognostic in phyllodes tumors of the breast. Oncotarget.
8:33365–33374. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sun B, Zhang D, Zhao N and Zhao X:
Epithelial-to-endothelial transition and cancer stem cells: Two
cornerstones of vasculogenic mimicry in malignant tumors.
Oncotarget. 8:30502–30510. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bo H, Zhang S, Gao L, Chen Y, Zhang J,
Chang X and Zhu M: Upregulation of Wnt5a promotes
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of pancreatic
cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 13:4962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wang Q, Qu C, Xie F, Chen L, Liu L, Liang
X, Wu X, Wang P and Meng Z: Curcumin suppresses
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of pancreatic
cancer cells by inhibiting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Am J
Cancer Res. 7:125–133. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Liu Q, Li A, Tian Y, Wu JD, Liu Y, Li T,
Chen Y, Han X and Wu K: The CXCL8-CXCR1/2 pathways in cancer.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 31:61–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kai Y, Chen QW, Sun YF, Lin JA and Xu JH:
Loss of BMI-1 dampens migration and EMT of colorectal cancer in
inflammatory microenvironment through TLR4/MD-2/MyD88-mediated
NF-κB signaling. J Cell Biochem. 119:1922–1930. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yang W, Wang JG, Xu J, Zhou D, Ren K, Hou
C, Chen L and Liu X: HCRP1 inhibits TGF-β induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int
J Oncol. 50:1233–1240. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Xiong S and Xiao GW: Reverting doxorubicin
resistance in colon cancer by targeting a key signaling protein,
steroid receptor coactivator. Exp Ther Med. 15:3751–3758.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|