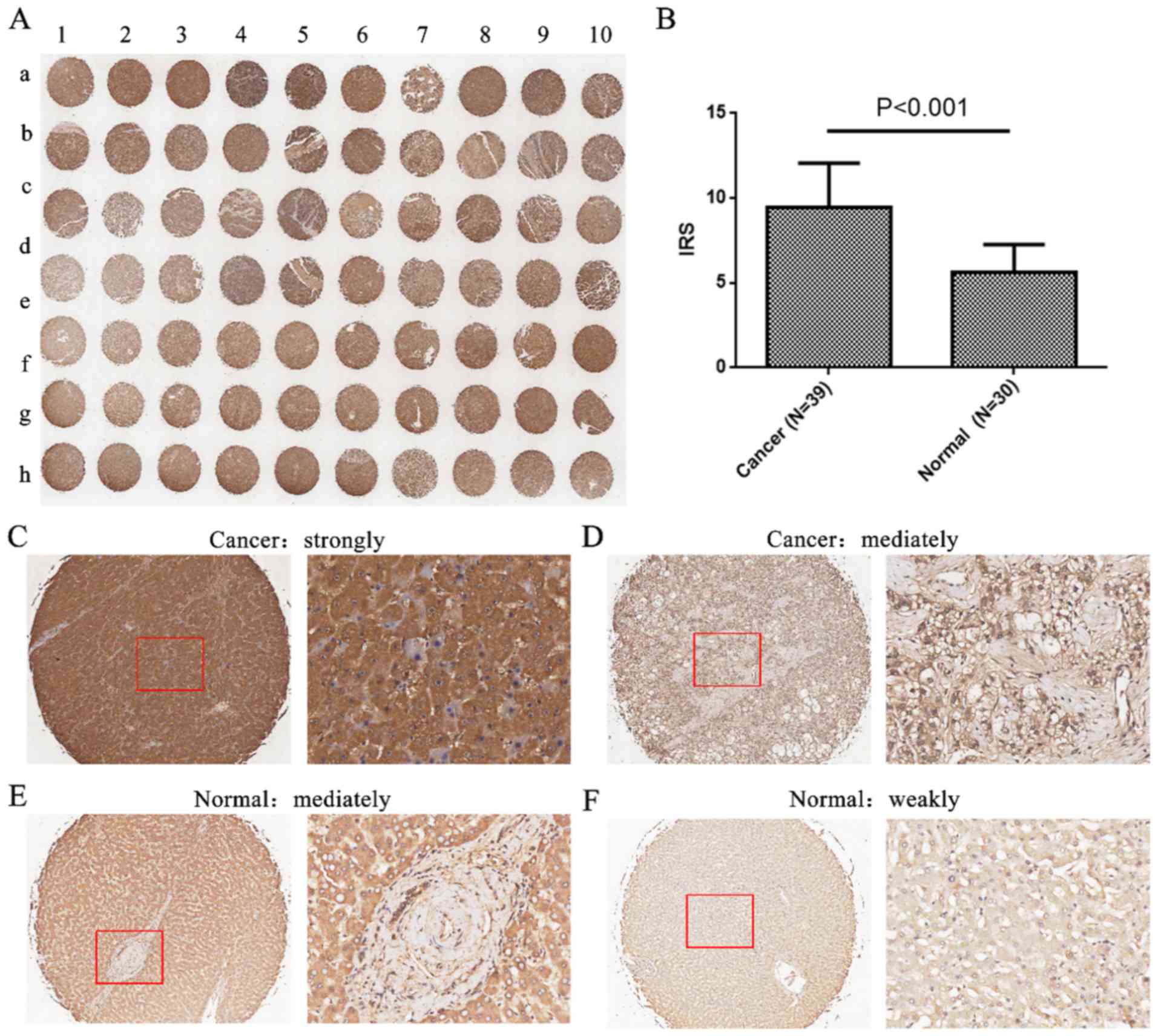
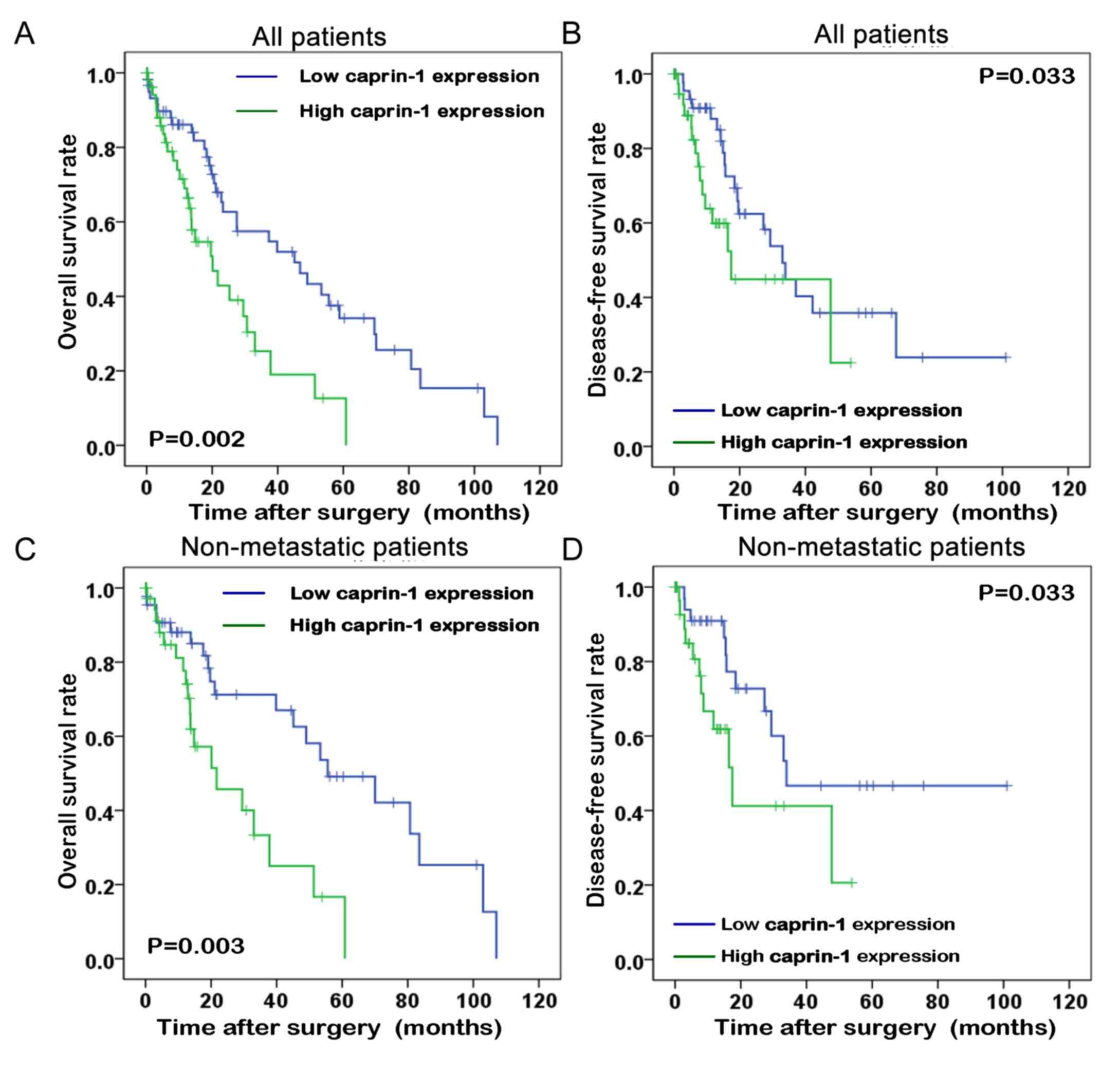
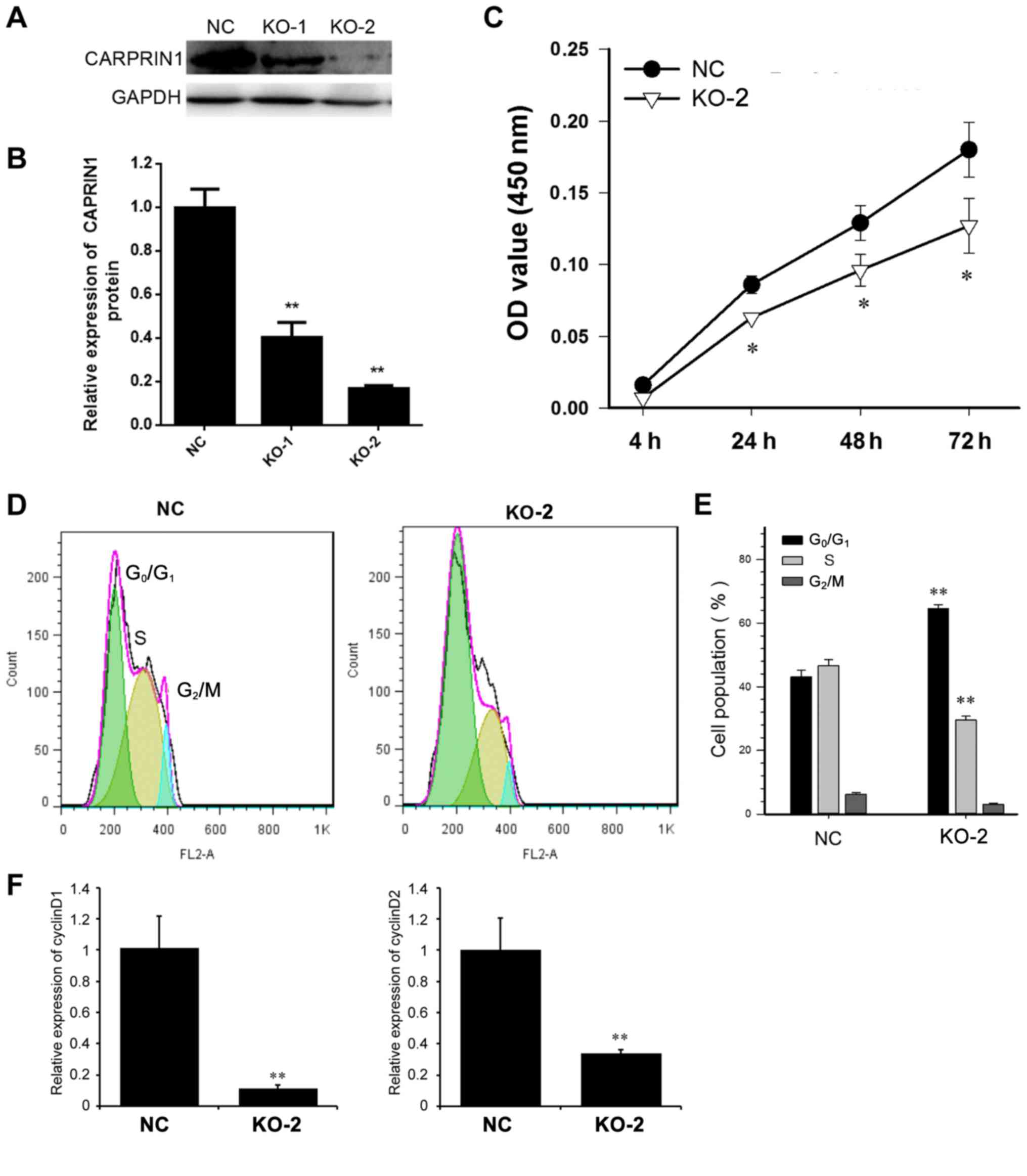
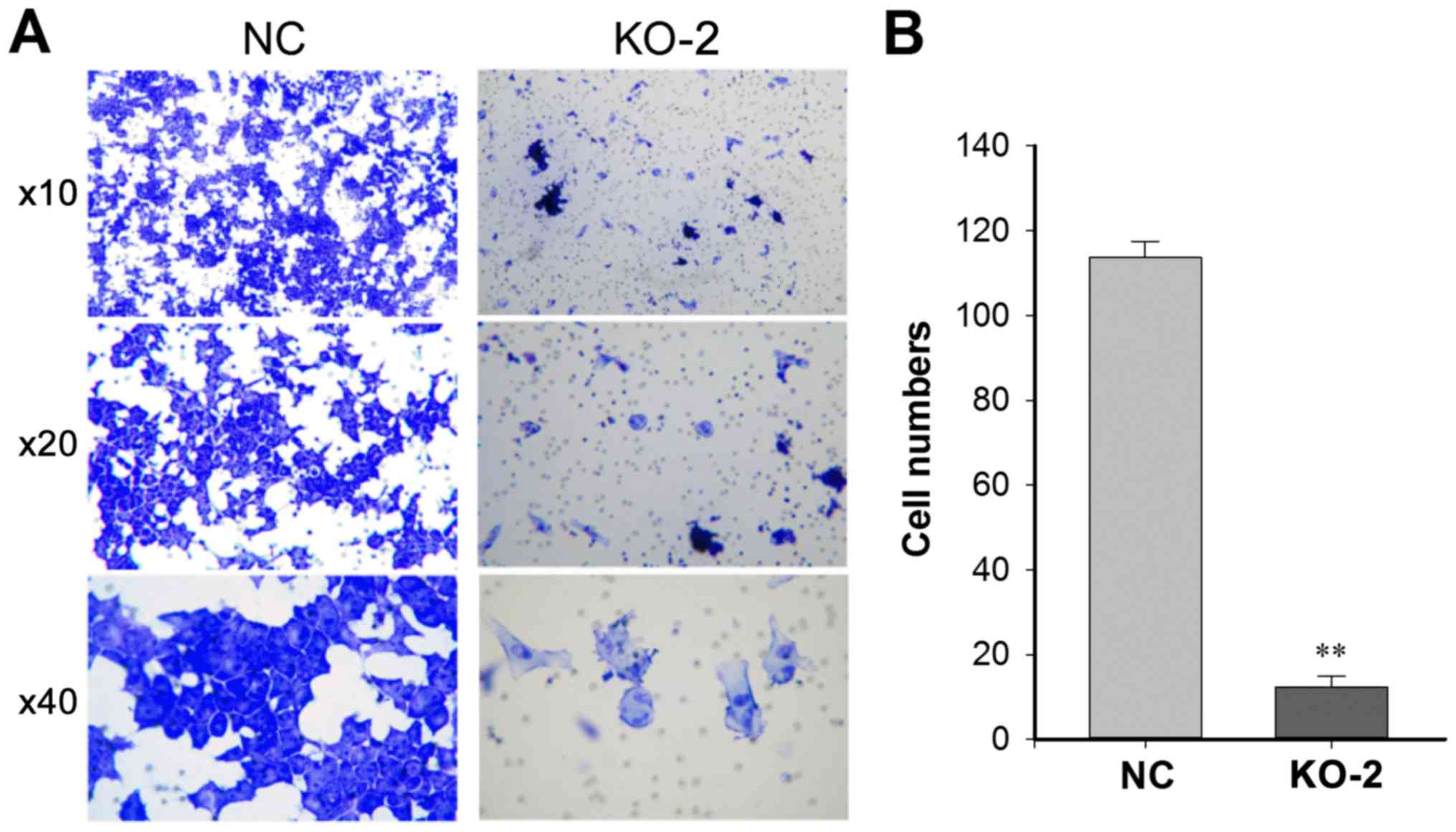
|
1
|
Global Burden of Disease Cancer
Collaboration, . Fitzmaurice C, Dicker D, Pain A, Hamavid H,
Moradi-Lakeh M, MacIntyre MF, Allen C, Hansen G, Woodbrook R, et
al: The global burden of cancer 2013. JAMA Oncol. 1:505–527. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death
Collaborators, . Global, regional, and national age-sex specific
all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death,
1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease
Study 2013. Lancet. 385:117–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Daher S, Massarwa M, Benson AA and Khoury
T: Current and future treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: An
updated comprehensive review. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 6:69–78. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Llovet JM and Bruix J: Early diagnosis and
treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Baillieres Best Pract Res
Clin Gastroenterol. 14:991–1008. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang TS, Shyu YC, Turner R, Chen HY and
Chen PJ: Diagnostic performance of alpha-fetoprotein, lens
culinaris agglutinin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein, des-gamma
carboxyprothrombin, and glypican-3 for the detection of
hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
protocol. Syst Rev. 2:372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ioannou GN, Perkins JD and Carithers RL
Jr: Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Impact of
the MELD allocation system and predictors of survival.
Gastroenterology. 134:1342–1351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li J, Gao JZ, Du JL and Wei LX: Prognostic
and clinicopathological significance of glypican-3 overexpression
in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:6336–6344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Peng C, Cheng Z, Wang X, Wu L, Li
J, Huang C, Guo Q and Cai H: The prognostic significance of
preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma receiving hepatectomy: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 55:73–80. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou Y, Sui C, Li B, Yin Z, Tan Y, Yang J
and Liu Z: Repeat hepatectomy for recurrent hepatocellular
carcinoma: A local experience and a systematic review. World J Surg
Oncol. 8:552010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ludwig JA and Weinstein JN: Biomarkers in
cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:845–856. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang J, Zhang M, Ma H, Song X, He L, Ye X
and Li X: Overexpression of glypican-3 is a predictor of poor
prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: An updated meta-analysis.
Medicine (Baltimore). 97:e111302018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Q, Wang G, Liu C and He X: Prognostic
value of CpG island methylator phenotype among hepatocellular
carcinoma patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J
Surg. 54:92–99. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zheng J, Cai J, Li H, Zeng K, He L, Fu H,
Zhang J, Chen L, Yao J, Zhang Y, et al: Neutrophil to lymphocyte
ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio as prognostic predictors for
hepatocellular carcinoma patients with various treatments: A
meta-analysis and systematic review. Cell Physiol Biochem.
44:967–981. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Grill B, Wilson GM, Zhang KX, Wang B,
Doyonnas R, Quadroni M and Schrader JW: Activation/division of
lymphocytes results in increased levels of cytoplasmic
activation/proliferation-associated protein-1: Prototype of a new
family of proteins. J Immunol. 172:2389–2400. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang B, David MD and Schrader JW: Absence
of caprin-1 results in defects in cellular proliferation. J
Immunol. 175:4274–4282. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Solomon S, Xu Y, Wang B, David MD,
Schubert P, Kennedy D and Schrader JW: Distinct structural features
of caprin-1 mediate its interaction with G3BP-1 and its induction
of phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2
alpha, entry to cytoplasmic stress granules, and selective
interaction with a subset of mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 27:2324–2342.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kedersha N, Panas MD, Achorn CA, Lyons S,
Tisdale S, Hickman T, Thomas M, Lieberman J, McInerney GM, Ivanov
P, et al: G3BP-Caprin1-USP10 complexes mediate stress granule
condensation and associate with 40S subunits. J Cell Biol.
212:845–860. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Copsey AC, Cooper S, Parker R, Lineham E,
Lapworth C, Jallad D, Sweet S and Morley SJ: The helicase, DDX3X,
interacts with poly(A)-binding protein 1 (PABP1) and caprin-1 at
the leading edge of migrating fibroblasts and is required for
efficient cell spreading. Biochem J. 474:3109–3120. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sabile AA, Arlt MJ, Muff R, Husmann K,
Hess D, Bertz J, Langsam B, Aemisegger C, Ziegler U, Born W, et al:
Caprin-1, a novel Cyr61-interacting protein, promotes osteosarcoma
tumor growth and lung metastasis in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1832:1173–1182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gong B, Hu H, Chen J, Cao S, Yu J, Xue J,
Chen F, Cai Y, He H and Zhang L: Caprin-1 is a novel microRNA-223
target for regulating the proliferation and invasion of human
breast cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 67:629–636. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Teng Y, Ren Y, Hu X, Mu J, Samykutty A,
Zhuang X, Deng Z, Kumar A, Zhang L, Merchant ML, et al:
MVP-mediated exosomal sorting of miR-193a promotes colon cancer
progression. Nat Commun. 8:144482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Edge SB: American Joint Committee on
Cancer: AJCC cancer staging manual. (7th). (New York). Springer.
2010.
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sherr CJ: D-type cyclins. Trends Biochem
Sci. 20:187–190. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Musgrove EA, Caldon CE, Barraclough J,
Stone A and Sutherland RL: Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:558–572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tan N, Dai L, Liu X, Pan G, Chen H, Huang
J and Xu Q: Upregulation of caprin1 expression is associated with
poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract.
213:1563–1567. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|