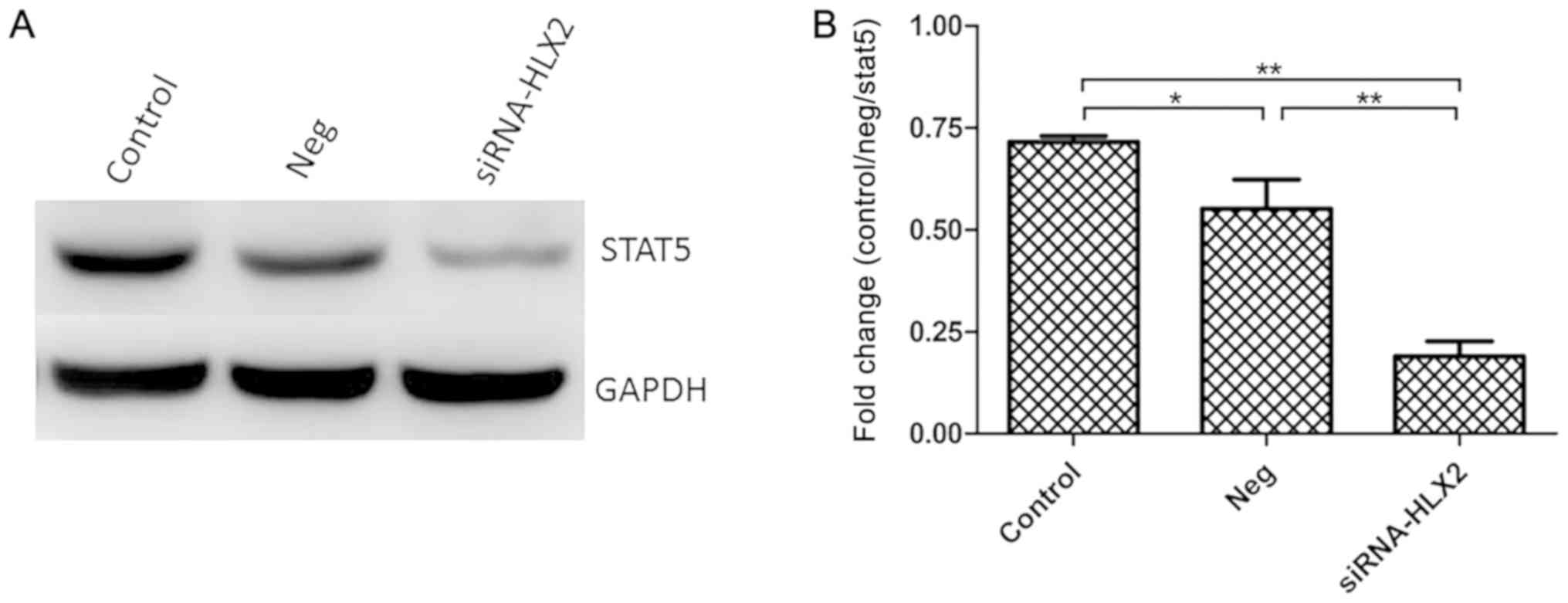
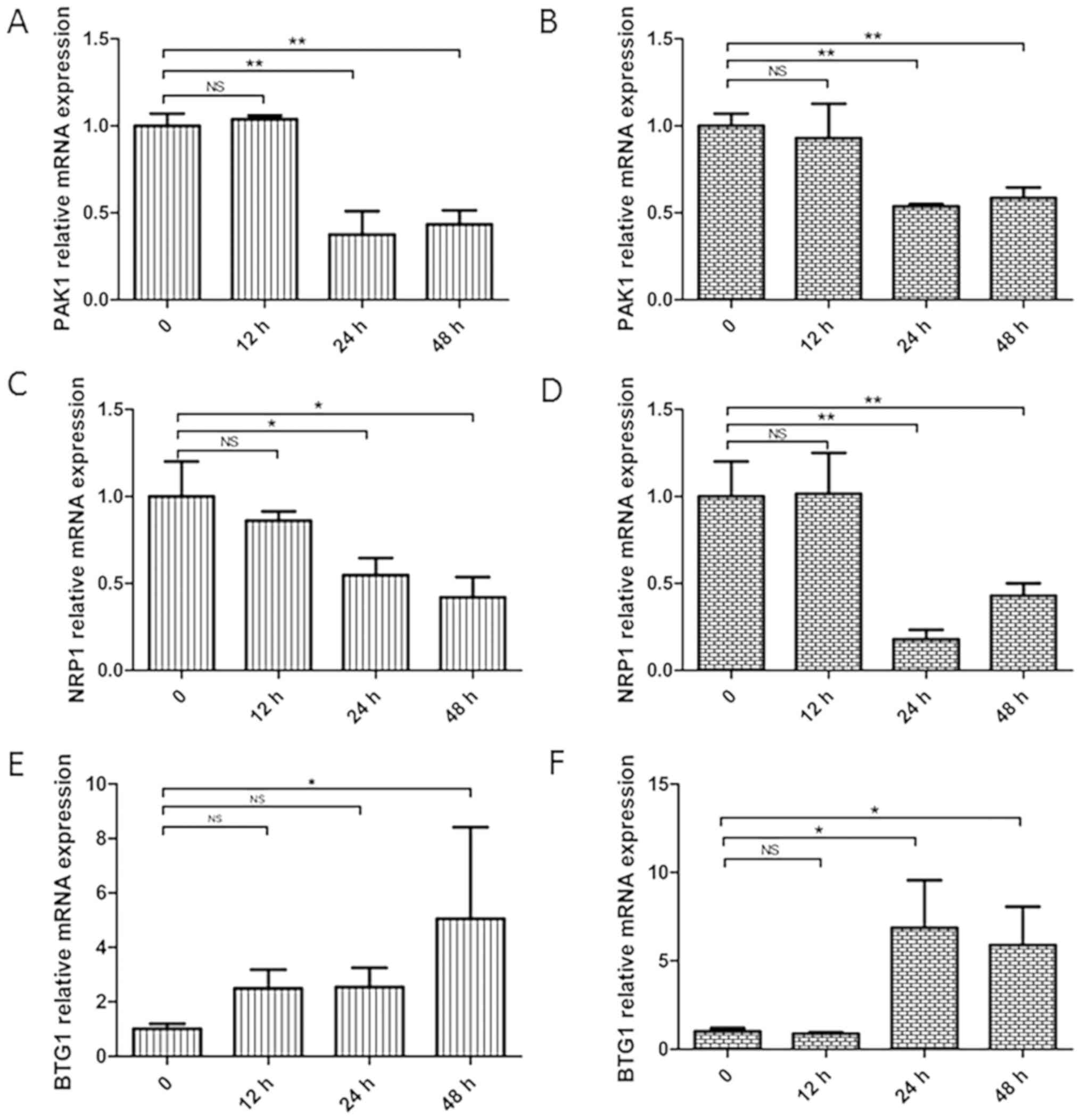
|
1
|
Seifert A, Werheid DF, Knapp SM and
Tobiasch E: Role of Hox genes in stem cell differentiation. World J
Stem Cells. 7:583–595. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Casaca VI, Illi S, Suttner K, Schleich I,
Ballenberger N, Klucker E, Turan E, Mutius EV, Kabesch M and Schaub
B: TBX21 and HLX1 polymorphisms influence cytokine secretion at
birth. PLoS One. 7:e310692012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rajaraman G, Murthi P, Pathirage N,
Brennecke SP and Kalionis B: Downstream targets of homeobox gene
HLX show altered expression in human idiopathic fetal growth
restriction. Am J Pathol. 176:278–287. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Prahst C, Kasaai B, Moraes F, Jahnsen ED,
Larrivee B, Villegas D, Pardanaud L, Pibouin-Fragner L, Zhang F,
Zaun HC, et al: The H2.0-like homeobox transcription factor
modulates yolk sac vascular remodeling in mouse embryos.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:1468–1476. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu ZY, Zhong NS, Xie Y and Hu PJ: Internal
Medicine. People's Health Press. (China). 563–674. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Leukemia & Lymphoma Group, Chinese
Society of Hematology, Chinese Medical Association, . The
Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Myelogenous
Leukemia (Relapse/Refractory) in China (2017). Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue
Za Zhi. 38:183–184. 2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Luo B, Que ZJ, Zhou ZY, Wang Q, Dong CS,
Jiang Y, Hu B, Shi H, Jin Y, Liu JW, et al: Feiji recipe inhibits
the growth of lung cancer by modulating T-cell immunity through
indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase pathway in an orthotopic implantation
model. J Integr Med. 19:283–289. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ghasemi R, Struthers H, Wilson ER and
Spencer DH: Contribution of CTCF binding to transcriptional
activity at the HOXA locus in NPM1-mutant AML cells. Leukemia. May
12–2020.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Zhang YM, Zhang YS, Tang GS,
Zhang WP, Yang JM, Wang JM and Hu XX: Prognostic significance of
minimal residual disease before post-remission therapy in younger
adult acute myeloid leukemia patients with intermediate risk and
negative of FLT3-ITD, NPM1 and biallelic CEBPA mutations. Zhonghua
Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 40:597–601. 2019.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pandolfi A and Steidl U: HLX in AML: Novel
prognostic and therapeutic target. Oncotarget. 3:1059–1060. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kawahara M, Pandolfi A, Bartholdy B,
Barreyro L, Will B, Roth M, Okoye-okafor UC, Todorova TI, Figueroa
ME, Melnick A, et al: H2.0-like homeobox (HLX) regulates early
hematopoiesis and promotes acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell.
22:194–208. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pandolfi A, Stanley RF, Yu Y, Bartholdy B,
Pendurti G, Gritsman K, Boultwood J, Chernoff J, Verma A and Steidl
U: PAK1 is a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia and
myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood. 126:1118–1127. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Van Galen JC, Kuiper RP, Van EL, Levers M,
Tijchon E, Scheijen B, Waanders E, van Reijmersdal SV, Gilissen C,
van Kessel AG, et al: BTG1 regulates glucocorticoid receptor
autoinduction in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood.
115:4810–4819. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zheng HC, Li J, Shen DF, Yang XF, Zhao S,
Wu YZ, Takano Y, Sun HZ, Su RJ, Luo JS and Gou WF: BTG1 expression
correlates with pathogenesis, aggressive behaviors and prognosis of
gastric cancer: A potential target for gene therapy. Oncotarget.
6:19685–19705. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fröhling S: Widespread over-expression of
the non-clustered homeobox gene HLX in acute myeloid leukemia.
Haematologica. 97:14532012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Testori J, Schweighofer B, Helfrich I,
Sturtzel C, Lipnik K, Gesierich S, Nasarre P, Hofer-Warbinek R,
Bilban M, Augustin HG and Hofer E: The VEGF-regulated transcription
factor HLX controls the expression of guidance cues and negatively
regulates sprouting of endothelial cells. Blood. 117:2735–2744.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamakawa T, Sato Y, Matsumura Y, Kobayashi
Y, Kawamura Y, Goshima N, Yamanaka S and Okita K: Screening of
human cDNA library reveals two differentiation-related genes, HHEX
and HLX, as promoters of early phase reprogramming toward
pluripotency. Stem Cells. 34:2661–2669. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zheng WP, Zhao Q, Zhao X, Li B, Hubank M,
Schatz DG and Flavell RA: Up-regulation of Hlx in immature Th cells
induces IFN-gamma expression. J Immunol. 172:114–122. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu Y, Gao J, Su Z, Dai X, Li Y, Liu Y,
Chen J, Tong J, Zhang Y, Wu C, et al: Downregulation of Hlx closely
related to the decreased expressions of T-bet and Runx3 in patients
with gastric cancer may be associated with a pathological event
leading to the imbalance of Th1/Th2. Clin Dev Immunol.
2012:9498212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morita M, Watanabe M, Inoue N, Inaoka C,
Akamizu T, Tatsumi KI, Hidaka Y and Iwatani Y: Functional
polymorphisms in TBX21 and HLX are associated with development and
prognosis of Graves' disease. Autoimmunity. 45:129–136. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Prada-Arismendy J, Arroyave JC and
Röthlisberger S: Molecular biomarkers in acute myeloid leukemia.
Blood Rev. 31:63–76. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li L, Jiang X, Zhang Q, Dong X, Gao Y, He
Y, Qiao H, Xie F, Xie X and Sun X: Neuropilin-1 is associated with
clinicopathology of gastric cancer and contributes to cell
proliferation and migration as multifunctional co-receptors. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 35:162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hendricks C, Dubail J, Brohée L, Delforge
Y, Colige A and Deroanne C: A novel physiological
glycosaminoglycan-deficient splice variant of neuropilin-1 is
anti-tumorigenic in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 11:e01651532016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Piechnik A, Dmoszynska A, Omiotek M, Mlak
R, Kowal M, Stilgenbauer S, Bullinger L and Giannopoulos K: The
VEGF receptor, neuropilin-1, represents a promising novel target
for chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. Int J Cancer.
133:1489–1496. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Z and Bunting KD: STAT5 activation in
B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Damned if you do, damned if
you don't. Cancer Cell Microenviron. 3:e11862016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Eswaran J, Li DQ, Shah A and Kumar R:
Molecular pathways: Targeting P21-activated kinase 1 signaling in
cancer-opportunities, challenges and limitations. Clin Cancer Res.
18:3743–3749. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chatterjee A, Ghosh J, Ramdas B, Mali RS,
Martin H, Kobayashi M, Vemula S, Canela VH, Waskow ER, Visconte V,
et al: Regulation of Stat5 by FAK and PAK1 in oncogenic FLT3- and
KIT-driven leukemogenesis. Cell Rep. 9:1333–1348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yamada O and Kawauchi K: The role of the
JAK-STAT pathway and related signal cascades in telomerase
activation during the development of hematologic malignancies.
JAKSTAT. 2:e252562013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Breitinger C, Maethner E, Garciacuellar MP
and Slany RK: The homeodomain region controls the phenotype of
HOX-induced murine leukemia. Blood. 120:4018–4027. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|