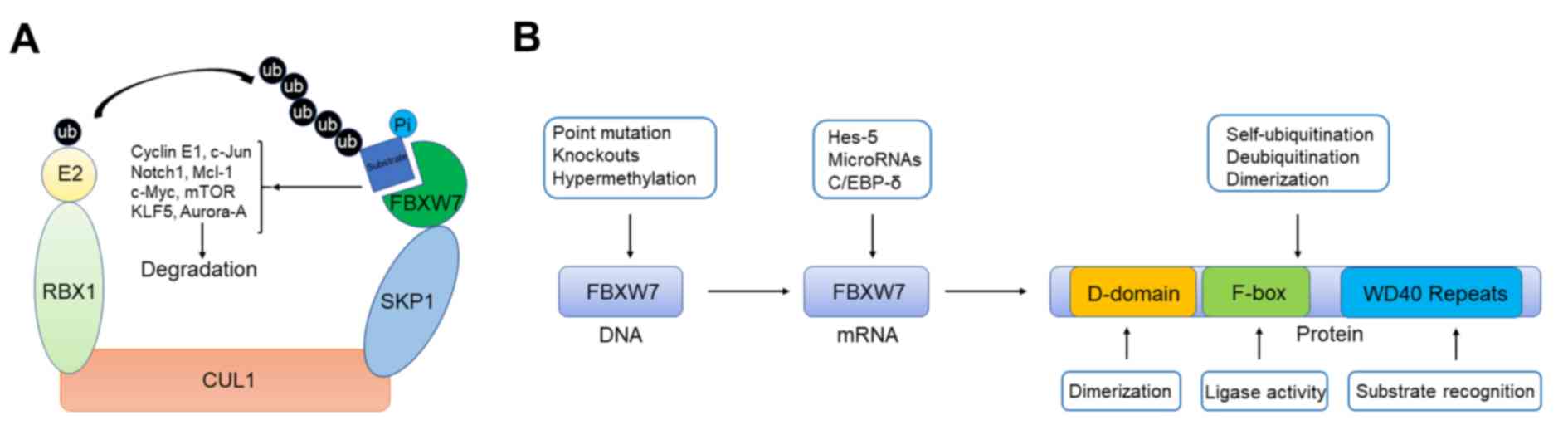
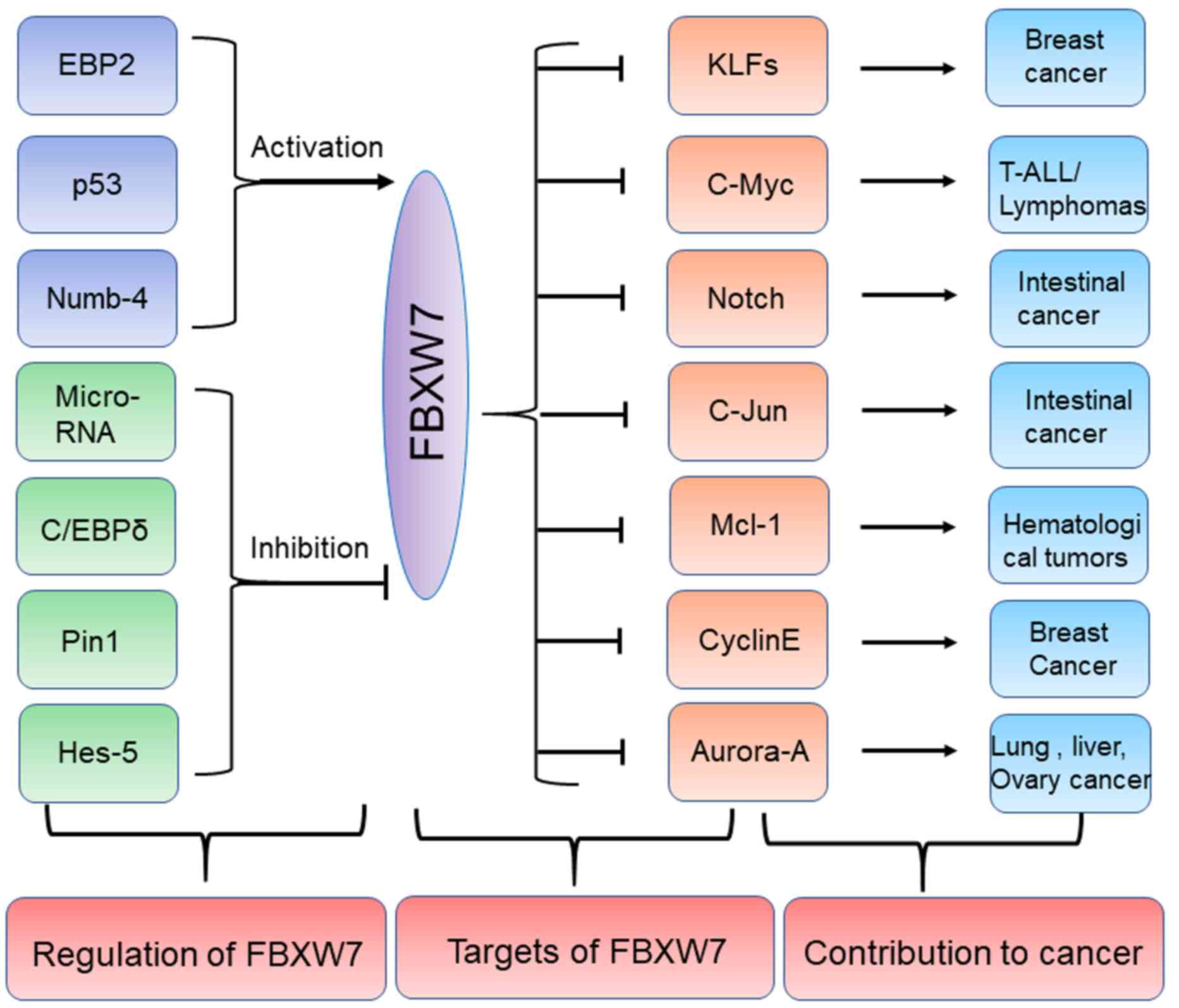
|
1
|
Hershko A and Ciechanover A: The ubiquitin
system. Annu Rev Biochem. 67:425–479. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schulman BA and Harper JW: Ubiquitin-like
protein activation by E1 enzymes: The apex for downstream
signalling pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:319–331. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wenzel DM, Stoll KE and Klevit RE: E2s:
Structurally economical and functionally replete. Biochem J.
433:31–42. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Deng L, Meng T, Chen L, Wei W and Wang P:
The role of ubiquitination in tumorigenesis and targeted drug
discovery. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zheng N and Shabek N: Ubiquitin ligases:
Structure, function, and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 86:129–157.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Deshaies RJ and Joazeiro CA: RING domain
E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu Rev Biochem. 78:399–434. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zimmerman ES, Schulman BA and Zheng N:
Structural assembly of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complexes. Curr
Opin Struct Biol. 20:714–721. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Diaz VM and de Herreros AG: F-box
proteins: Keeping the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in
check. Semin Cancer Biol. 36:71–79. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zheng N, Zhou Q, Wang Z and Wei W: Recent
advances in SCF ubiquitin ligase complex: Clinical implications.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1866:12–22. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bai C, Sen P, Hofmann K, Ma L, Goebl M,
Harper JW and Elledge SJ: SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to
the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the
F-box. Cell. 86:263–274. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pei XH, Bai F, Li Z, Smith MD, Whitewolf
G, Jin R and Xiong Y: Cytoplasmic CUL9/PARC ubiquitin ligase is a
tumor suppressor and promotes p53-dependent apoptosis. Cancer Res.
71:2969–2977. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nguyen HC, Wang W and Xiong Y: Cullin-RING
E3 ubiquitin ligases: Bridges to destruction. Subcell Biochem.
83:323–347. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Harper JW and Tan MK: Understanding
cullin-RING E3 biology through proteomics-based substrate
identification. Mol Cell Proteomics. 11:1541–1550. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nakagawa T, Nakayama K and Nakayama KI:
Knockout mouse models provide insight into the biological functions
of CRL1 components. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1217:147–171. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gupta-Rossi N, Le Bail O, Gonen H, Brou C,
Logeat F, Six E, Ciechanover A and Israel A: Functional interaction
between SEL-10, an F-box protein, and the nuclear form of activated
Notch1 receptor. J Biol Chem. 276:34371–34378. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jin J, Cardozo T, Lovering RC, Elledge SJ,
Pagano M and Harper JW: Systematic analysis and nomenclature of
mammalian F-box proteins. Genes Dev. 18:2573–2580. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matsumoto A, Onoyama I and Nakayama KI:
Expression of mouse Fbxw7 isoforms is regulated in a cell cycle- or
p53-dependent manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 350:114–119.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Welcker M, Orian A, Grim JE, Eisenman RN
and Clurman BE: A nucleolar isoform of the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase
regulates c-Myc and cell size. Curr Biol. 14:1852–1857. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Grim JE, Gustafson MP, Hirata RK, Hagar
AC, Swanger J, Welcker M, Hwang HC, Ericsson J, Russell DW and
Clurman BE: Isoform- and cell cycle-dependent substrate degradation
by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase. J Cell Biol. 181:913–920. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Welcker M, Larimore EA, Frappier L and
Clurman BE: Nucleolar targeting of the fbw7 ubiquitin ligase by a
pseudosubstrate and glycogen synthase kinase 3. Mol Cell Biol.
31:1214–1224. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yumimoto K and Nakayama KI: Recent insight
into the role of FBXW7 as a tumor suppressor. Semin Cancer Biol.
Feb 27–2020.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Inuzuka H, Shaik S, Onoyama I, Gao D,
Tseng A, Maser RS, Zhai B, Wan L, Gutierrez A, Lau AW, et al:
SCF(FBW7) regulates cellular apoptosis by targeting MCL1 for
ubiquitylation and destruction. Nature. 471:104–109. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wei W, Jin J, Schlisio S, Harper JW and
Kaelin WG Jr: The v-Jun point mutation allows c-Jun to escape
GSK3-dependent recognition and destruction by the Fbw7 ubiquitin
ligase. Cancer Cell. 8:25–33. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Welcker M, Singer J, Loeb KR, Grim J,
Bloecher A, Gurien-West M, Clurman BE and Roberts JM: Multisite
phosphorylation by Cdk2 and GSK3 controls cyclin E degradation. Mol
Cell. 12:381–392. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moberg KH, Bell DW, Wahrer DC, Haber DA
and Hariharan IK: Archipelago regulates Cyclin E levels in
Drosophila and is mutated in human cancer cell lines.
Nature. 413:311–316. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yada M, Hatakeyama S, Kamura T, Nishiyama
M, Tsunematsu R, Imaki H, Ishida N, Okumura F, Nakayama K and
Nakayama KI: Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of c-Myc is
mediated by the F-box protein Fbw7. EMBO J. 23:2116–2125. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mao JH, Kim IJ, Wu D, Climent J, Kang HC,
DelRosario R and Balmain A: FBXW7 targets mTOR for degradation and
cooperates with PTEN in tumor suppression. Science. 321:1499–1502.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rajagopalan H and Lengauer C: hCDC4 and
genetic instability in cancer. Cell Cycle. 3:693–694. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rajagopalan H, Jallepalli PV, Rago C,
Velculescu VE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B and Lengauer C:
Inactivation of hCDC4 can cause chromosomal instability. Nature.
428:77–81. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maser RS, Choudhury B, Campbell PJ, Feng
B, Wong KK, Protopopov A, O'Neil J, Gutierrez A, Ivanova E, Perna
I, et al: Chromosomally unstable mouse tumours have genomic
alterations similar to diverse human cancers. Nature. 447:966–971.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wertz IE, Kusam S, Lam C, Okamoto T,
Sandoval W, Anderson DJ, Helgason E, Ernst JA, Eby M, Liu J, et al:
Sensitivity to antitubulin chemotherapeutics is regulated by MCL1
and FBW7. Nature. 471:110–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tetzlaff MT, Yu W, Li M, Zhang P, Finegold
M, Mahon K, Harper JW, Schwartz RJ and Elledge SJ: Defective
cardiovascular development and elevated cyclin E and Notch proteins
in mice lacking the Fbw7 F-box protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:3338–3345. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Z, Inuzuka H, Fukushima H, Wan L, Gao
D, Shaik S, Sarkar FH and Wei W: Emerging roles of the FBW7 tumour
suppressor in stem cell differentiation. EMBO Rep. 13:36–43. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Balamurugan K, Sharan S, Klarmann KD,
Zhang Y, Coppola V, Summers GH, Roger T, Morrison DK, Keller JR and
Sterneck E: FBXW7α attenuates inflammatory signalling by
downregulating C/EBP δ and its target gene Tlr4. Nat Commun.
4:16622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kourtis N, Moubarak RS, Aranda-Orgilles B,
Lui K, Aydin IT, Trimarchi T, Darvishian F, Salvaggio C, Zhong J,
Bhatt K, et al: FBXW7 modulates cellular stress response and
metastatic potential through HSF1 post-translational modification.
Nat Cell Biol. 17:322–332. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yumimoto K, Akiyoshi S, Ueo H, Sagara Y,
Onoyama I, Ueo H, Ohno S, Mori M, Mimori K and Nakayama KI: F-box
protein FBXW7 inhibits cancer metastasis in a non-cell-autonomous
manner. J Clin Invest. 125:621–635. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rocher-Ros V, Marco S, Mao JH, Gines S,
Metzger D, Chambon P, Balmain A and Saura CA: Presenilin modulates
EGFR signaling and cell transformation by regulating the ubiquitin
ligase Fbw7. Oncogene. 29:2950–2961. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Grinkevich VV, Nikulenkov F, Shi Y, Enge
M, Bao W, Maljukova A, Gluch A, Kel A, Sangfelt O and Selivanova G:
Ablation of key oncogenic pathways by RITA-reactivated p53 is
required for efficient apoptosis. Cancer Cell. 31:724–726. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mansour MR, Sanda T, Lawton LN, Li X,
Kreslavsky T, Novina CD, Brand M, Gutierrez A, Kelliher MA,
Jamieson CH, et al: The TAL1 complex targets the FBXW7 tumor
suppressor by activating miR-223 in human T cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. J Exp Med. 210:1545–1557. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kumar V, Palermo R, Talora C, Campese AF,
Checquolo S, Bellavia D, Tottone L, Testa G, Miele E, Indraccolo S,
et al: Notch and NF-kB signaling pathways regulate miR-223/FBXW7
axis in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia.
28:2324–2335. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lerner M, Lundgren J, Akhoondi S, Jahn A,
Ng HF, Akbari Moqadam F, Oude Vrielink JA, Agami R, Den Boer ML,
Grander D and Sangfelt O: MiRNA-27a controls FBW7/hCDC4-dependent
cyclin E degradation and cell cycle progression. Cell Cycle.
10:2172–2183. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang Q, Li DC, Li ZF, Liu CX, Xiao YM,
Zhang B, Li XD, Zhao J, Chen LP, Xing XM, et al: Upregulation of
miR-27a contributes to the malignant transformation of human
bronchial epithelial cells induced by SV40 small T antigen.
Oncogene. 30:3875–3886. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Spruck C: MiR-27a regulation of SCF(Fbw7)
in cell division control and cancer. Cell Cycle. 10:3232–3233.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Olive V, Sabio E, Bennett MJ, De Jong CS,
Biton A, McGann JC, Greaney SK, Sodir NM, Zhou AY, Balakrishnan A,
et al: A component of the mir-17-92 polycistronic oncomir promotes
oncogene-dependent apoptosis. Elife. 2:e008222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhou C, Shen L, Mao L, Wang B, Li Y and Yu
H: MiR-92a is upregulated in cervical cancer and promotes cell
proliferation and invasion by targeting FBXW7. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 458:63–69. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang P, Cao L, Fan P, Mei Y and Wu M:
LncRNA-MIF, a c-Myc-activated long non-coding RNA, suppresses
glycolysis by promoting Fbxw7-mediated c-Myc degradation. EMBO Rep.
17:1204–1220. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu X, Ma J, Xu F and Li L: TINCR
suppresses proliferation and invasion through regulating
miR-544a/FBXW7 axis in lung cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 99:9–17.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang Y, Liu Z, Yao B, Li Q, Wang L, Wang
C, Dou C, Xu M, Liu Q and Tu K: Long non-coding RNA CASC2
suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells through CASC2/miR-367/FBXW7 axis. Mol Cancer.
16:1232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li L, Sarver AL, Khatri R, Hajeri PB,
Kamenev I, French AJ, Thibodeau SN, Steer CJ and Subramanian S:
Sequential expression of miR-182 and miR-503 cooperatively targets
FBXW7, contributing to the malignant transformation of colon
adenoma to adenocarcinoma. J Pathol. 234:488–501. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tang B, Lei B, Qi G, Liang X, Tang F, Yuan
S, Wang Z, Yu S and He S: MicroRNA-155-3p promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma formation by suppressing FBXW7 expression. J Exp Clin
Canc Res. 35:932016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Xia W, Zhou J, Luo H, Liu Y, Peng C, Zheng
W and Ma W: MicroRNA-32 promotes cell proliferation, migration and
suppresses apoptosis in breast cancer cells by targeting FBXW7.
Cancer Cell Int. 17:142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xu W, Taranets L and Popov N: Regulating
Fbw7 on the road to cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 36:62–70. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mo JS, Ann EJ, Yoon JH, Jung J, Choi YH,
Kim HY, Ahn JS, Kim SM, Kim MY, Hong JA, et al: Serum- and
glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1) controls Notch1 signaling
by downregulation of protein stability through Fbw7 ubiquitin
ligase. J Cell Sci. 124:(Pt 1). 100–112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Schulein C, Eilers M and Popov N:
PI3K-dependent phosphorylation of Fbw7 modulates substrate
degradation and activity. FEBS Lett. 585:2151–2157. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cao J, Ge MH and Ling ZQ: Fbxw7 tumor
suppressor: A vital regulator contributes to human tumorigenesis.
Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e24962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Akhoondi S, Lindstrom L, Widschwendter M,
Corcoran M, Bergh J, Spruck C, Grander D and Sangfelt O:
Inactivation of FBXW7/hCDC4-β expression by promoter
hypermethylation is associated with favorable prognosis in primary
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 12(R105)2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kitade S, Onoyama I, Kobayashi H, Yagi H,
Yoshida S, Kato M, Tsunematsu R, Asanoma K, Sonoda K, Wake N, et
al: FBXW7 is involved in the acquisition of the malignant phenotype
in epithelial ovarian tumors. Cancer Sci. 107:1399–1405. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Min SH, Lau AW, Lee TH, Inuzuka H, Wei S,
Huang P, Shaik S, Lee DY, Finn G, Balastik M, et al: Negative
regulation of the stability and tumor suppressor function of Fbw7
by the Pin1 prolyl isomerase. Mol Cell. 46:771–783. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ji S, Qin Y, Shi S, Liu X, Hu H, Zhou H,
Gao J, Zhang B, Xu W, Liu J, et al: ERK kinase phosphorylates and
destabilizes the tumor suppressor FBW7 in pancreatic cancer. Cell
Res. 25:561–573. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cizmecioglu O, Krause A, Bahtz R, Ehret L,
Malek N and Hoffmann I: Plk2 regulates centriole duplication
through phosphorylation-mediated degradation of Fbxw7 (human Cdc4).
J Cell Sci. 125:(Pt 4). 981–992. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chen J, Shin JH, Zhao R, Phan L, Wang H,
Xue Y, Post SM, Ho Choi H, Chen JS, Wang E, et al: CSN6 drives
carcinogenesis by positively regulating Myc stability. Nat Commun.
5:53842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Diefenbacher ME, Popov N, Blake SM,
Schulein-Volk C, Nye E, Spencer-Dene B, Jaenicke LA, Eilers M and
Behrens A: The deubiquitinase USP28 controls intestinal homeostasis
and promotes colorectal cancer. J Clin Invest. 124:3407–3418. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Schulein-Volk C, Wolf E, Zhu J, Xu W,
Taranets L, Hellmann A, Janicke LA, Diefenbacher ME, Behrens A,
Eilers M and Popov N: Dual regulation of Fbw7 function and
oncogenic transformation by Usp28. Cell Rep. 9:1099–1109. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Welcker M, Larimore EA, Swanger J,
Bengoechea-Alonso MT, Grim JE, Ericsson J, Zheng N and Clurman BE:
Fbw7 dimerization determines the specificity and robustness of
substrate degradation. Genes Dev. 27:2531–2536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Davis RJ, Welcker M and Clurman BE: Tumor
suppression by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase: Mechanisms and
opportunities. Cancer Cell. 26:455–464. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Tang X, Orlicky S, Lin Z, Willems A,
Neculai D, Ceccarelli D, Mercurio F, Shilton BH, Sicheri F and
Tyers M: Suprafacial orientation of the SCFCdc4 dimer accommodates
multiple geometries for substrate ubiquitination. Cell.
129:1165–1176. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bonetti P, Davoli T, Sironi C, Amati B,
Pelicci PG and Colombo E: Nucleophosmin and its AML-associated
mutant regulate c-Myc turnover through Fbw7 gamma. J Cell Biol.
182:19–26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Durgan J and Parker PJ: Regulation of the
tumour suppressor Fbw7α by PKC-dependent phosphorylation and
cancer-associated mutations. Biochem J. 432:77–87. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Akhoondi S, Sun D, von der Lehr N,
Apostolidou S, Klotz K, Maljukova A, Cepeda D, Fiegl H, Dafou D,
Marth C, et al: FBXW7/hCDC4 is a general tumor suppressor in human
cancer. Cancer Res. 67:9006–9012. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
King B, Trimarchi T, Reavie L, Xu L,
Mullenders J, Ntziachristos P, Aranda-Orgilles B, Perez-Garcia A,
Shi J, Vakoc C, et al: The ubiquitin ligase FBXW7 modulates
leukemia-initiating cell activity by regulating MYC stability.
Cell. 153:1552–1566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Davis H, Lewis A, Behrens A and Tomlinson
I: Investigation of the atypical FBXW7 mutation spectrum in human
tumours by conditional expression of a heterozygous propellor tip
missense allele in the mouse intestines. Gut. 63:792–799. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ju Y, Yu A, Sun X, Wu D and Zhang H:
Glucosamine, a naturally occurring amino monosaccharide, inhibits
A549 and H446 cell proliferation by blocking G1/S transition. Mol
Med Rep. 8:794–798. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Dong JT and Chen C: Essential role of KLF5
transcription factor in cell proliferation and differentiation and
its implications for human diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci.
66:2691–2706. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Klotz K, Cepeda D, Tan Y, Sun D, Sangfelt
O and Spruck C: SCF(Fbxw7/hCdc4) targets cyclin E2 for
ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. Exp Cell Res. 315:1832–1839. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Byrd KN, Huey B, Roydasgupta R, Fridlyand
J, Snijders AM and Albertson DG: FBXW7 and DNA copy number
instability. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 109:47–54. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Liu X, Zhang Y, Wu S, Xu M, Shen Y, Yu M,
Fan J, Wei S, Xu C, Huang L, et al: Palmatine induces G2/M phase
arrest and mitochondrial-associated pathway apoptosis in colon
cancer cells by targeting AURKA. Biochem Pharmacol. 175:1139332020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhang H, Bao J, Zhao S, Huo Z and Li B:
MicroRNA-490-3p suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell
proliferation and migration by targeting the aurora kinase A gene
(AURKA). Arch Med Sci. 16:395–406. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Finkin S, Aylon Y, Anzi S, Oren M and
Shaulian E: Fbw7 regulates the activity of endoreduplication
mediators and the p53 pathway to prevent drug-induced polyploidy.
Oncogene. 27:4411–4421. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
McIntyre B, Asahara T and Alev C: Overview
of basic mechanisms of notch signaling in development and disease.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 1227:9–27. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Nowell CS and Radtke F: Notch as a tumour
suppressor. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:145–159. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Bray SJ: Notch signalling in context. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:722–735. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Pancewicz J, Taylor JM, Datta A, Baydoun
HH, Waldmann TA, Hermine O and Nicot C: Notch signaling contributes
to proliferation and tumor formation of human T-cell leukemia virus
type 1-associated adult T-cell leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:16619–16624. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wu G, Lyapina S, Das I, Li J, Gurney M,
Pauley A, Chui I, Deshaies RJ and Kitajewski J: SEL-10 is an
inhibitor of notch signaling that targets notch for
ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation. Mol Cell Biol.
21:7403–7415. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Tsunematsu R, Nakayama K, Oike Y,
Nishiyama M, Ishida N, Hatakeyama S, Bessho Y, Kageyama R, Suda T
and Nakayama KI: Mouse Fbw7/Sel-10/Cdc4 is required for notch
degradation during vascular development. J Biol Chem.
279:9417–9423. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Matsumoto A, Onoyama I, Sunabori T,
Kageyama R, Okano H and Nakayama KI: Fbxw7-dependent degradation of
Notch is required for control of ‘stemness’ and neuronal-glial
differentiation in neural stem cells. J Biol Chem. 286:13754–13764.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Yang-Yen HF: Mcl-1: A highly regulated
cell death and survival controller. J Biomed Sci. 13:201–204. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Welcker M, Orian A, Jin J, Grim JE, Harper
JW, Eisenman RN and Clurman BE: The Fbw7 tumor suppressor regulates
glycogen synthase kinase 3 phosphorylation-dependent c-Myc protein
degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:9085–9090. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Kanei-Ishii C, Nomura T, Takagi T,
Watanabe N, Nakayama KI and Ishii S: Fbxw7 acts as an E3 ubiquitin
ligase that targets c-Myb for nemo-like kinase (NLK)-induced
degradation. J Biol Chem. 283:30540–30548. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Popov N, Wanzel M, Madiredjo M, Zhang D,
Beijersbergen R, Bernards R, Moll R, Elledge SJ and Eilers M: The
ubiquitin-specific protease USP28 is required for MYC stability.
Nat Cell Biol. 9:765–774. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Li M, Ouyang L, Zheng Z, Xiang D, Ti A, Li
L, Dan Y, Yu C and Li W: E3 ubiquitin ligase FBW7α inhibits
cholangiocarcinoma cell proliferation by downregulating c-Myc and
cyclin E. Oncol Rep. 37:1627–1636. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Qin J, Zhou Z, Chen W, Wang C, Zhang H, Ge
G, Shao M, You D, Fan Z, Xia H, et al: BAP1 promotes breast cancer
cell proliferation and metastasis by deubiquitinating KLF5. Nat
Commun. 6:84712015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Liu N, Li H, Li S, Shen M, Xiao N, Chen Y,
Wang Y, Wang W, Wang R, Wang Q, et al: The Fbw7/human CDC4 tumor
suppressor targets proproliferative factor KLF5 for ubiquitination
and degradation through multiple phosphodegron motifs. J Biol Chem.
285:18858–18867. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhao D, Zheng HQ, Zhou Z and Chen C: The
Fbw7 tumor suppressor targets KLF5 for ubiquitin-mediated
degradation and suppresses breast cell proliferation. Cancer Res.
70:4728–4738. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Rottmann S, Wang Y, Nasoff M, Deveraux QL
and Quon KC: A TRAIL receptor-dependent synthetic lethal
relationship between MYC activation and GSK3beta/FBW7 loss of
function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15195–15200. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Goga A, Yang D, Tward AD, Morgan DO and
Bishop JM: Inhibition of CDK1 as a potential therapy for tumors
over-expressing MYC. Nat Med. 13:820–827. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Liu L, Ulbrich J, Muller J, Wustefeld T,
Aeberhard L, Kress TR, Muthalagu N, Rycak L, Rudalska R, Moll R, et
al: Deregulated MYC expression induces dependence upon AMPK-related
kinase 5. Nature. 483:608–612. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Chauhan D, Tian Z, Nicholson B, Kumar KG,
Zhou B, Carrasco R, McDermott JL, Leach CA, Fulcinniti M, Kodrasov
MP, et al: A small molecule inhibitor of ubiquitin-specific
protease-7 induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells and
overcomes bortezomib resistance. Cancer Cell. 22:345–358. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Grim JE, Knoblaugh SE, Guthrie KA, Hagar
A, Swanger J, Hespelt J, Delrow JJ, Small T, Grady WM, Nakayama KI
and Clurman BE: Fbw7 and p53 cooperatively suppress advanced and
chromosomally unstable intestinal cancer. Mol Cell Biol.
32:2160–2167. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Selivanova G and Wiman KG: Reactivation of
mutant p53: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential.
Oncogene. 26:2243–2254. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Csizmok V, Montecchio M, Lin H, Tyers M,
Sunnerhagen M and Forman-Kay JD: Multivalent interactions with Fbw7
and Pin1 facilitate recognition of c-Jun by the SCFFbw7
Ubiquitin Ligase. Structure. 26:28–39.e2. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|