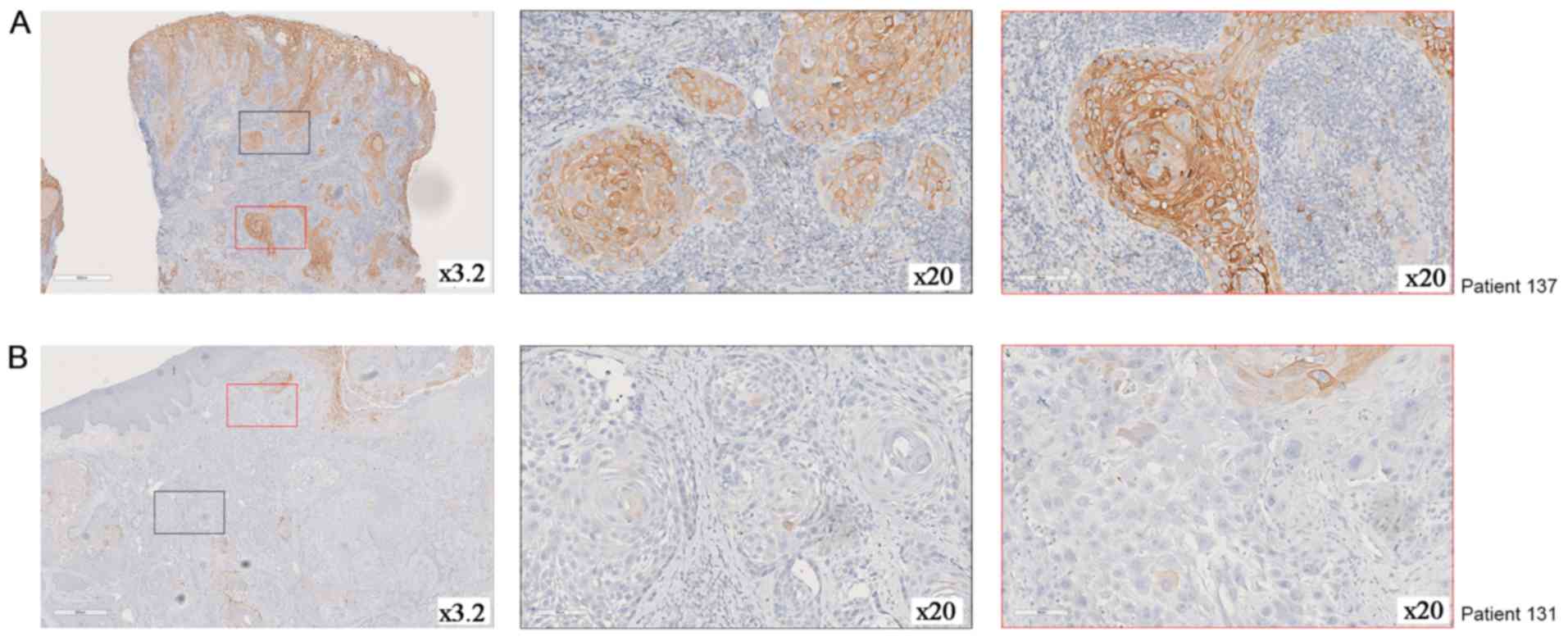
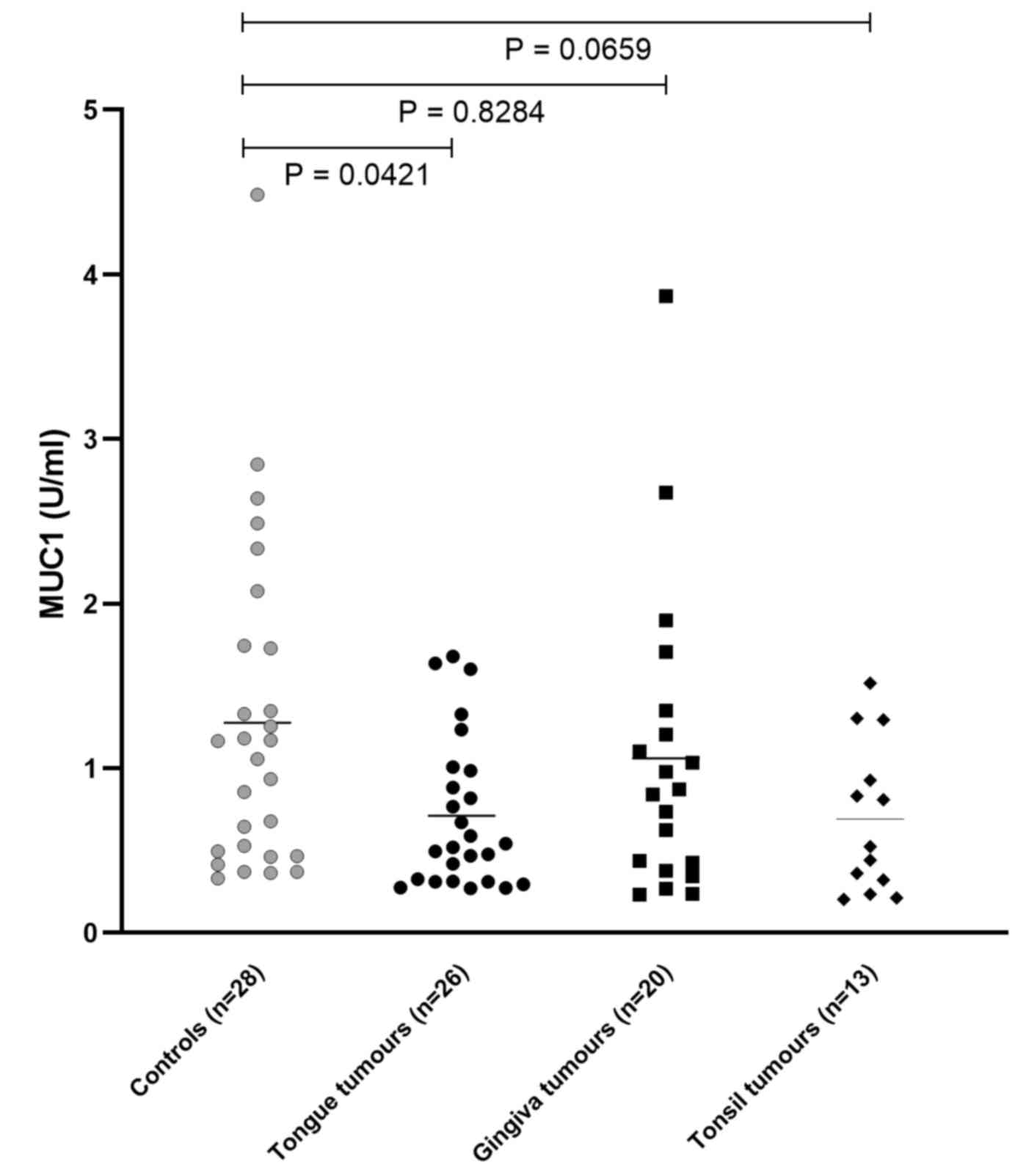
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lubin JH, Purdue M, Kelsey K, Zhang ZF,
Winn D, Wei Q, Talamini R, Szeszenia-Dabrowska N, Sturgis EM, Smith
E, et al: Total exposure and exposure rate effects for alcohol and
smoking and risk of head and neck cancer: A pooled analysis of
case-control studies. Am J Epidemiol. 170:937–947. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mork J, Lie AK, Glattre E, Hallmans G,
Jellum E, Koskela P, Møller B, Pukkala E, Schiller TJ, Youngman L,
et al: Human papillomavirus infection as a risk factor for
squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med.
344:1125–1131. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Agra IM, Carvalho AL, Pinto CA, Martins
EP, Filho JG, Soares FA and Kowalski LP: Biological markers and
prognosis in recurrent oral cancer after salvage surgery. Arch
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 134:743–749. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carvalho AL, Magrin J and Kowalski LP:
Sites of recurrence in oral and oropharyngeal cancers according to
the treatment approach. Oral Dis. 9:112–118. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sgaramella N, Gu X, Boldrup L, Coates PJ,
Fahraeus R, Califano L, Tartaro G, Colella G, Spaak LN, Strom A, et
al: Searching for new targets and treatments in the battle against
squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, with specific focus
on tumours of the tongue. Curr Top Med Chem. 18:214–218. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li G, Da M, Zhang W, Wu H, Ye J, Chen J,
Ma L, Gu N, Wu Y and Song X: Alteration of serum lipid profile and
its prognostic value in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J
Oral Pathol Med. 45:167–172. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schaaij-Visser TB, Brakenhoff RH, Leemans
CR, Heck AJ and Slijper M: Protein biomarker discovery for head and
neck cancer. J Proteomics. 73:1790–1803. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hsiung DT, Marsit CJ, Houseman EA, Eddy K,
Furniss CS, McClean MD and Kelsey KT: Global DNA methylation level
in whole blood as a biomarker in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16:108–114. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Boldrup L, Gu X, Coates PJ, Norberg-Spaak
L, Fahraeus R, Laurell G, Wilms T and Nylander K: Gene expression
changes in tumor free tongue tissue adjacent to tongue squamous
cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:19389–19402. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
van Putten JPM and Strijbis K:
Transmembrane mucins: Signaling receptors at the intersection of
inflammation and cancer. J Innate Immun. 9:281–299. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lau SK, Weiss LM and Chu PG: Differential
expression of MUC1, MUC2, and MUC5AC in carcinomas of various
sites: An immunohistochemical study. Am J Clin Pathol. 122:61–69.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ahmad R, Rajabi H, Kosugi M, Joshi MD,
Alam M, Vasir B, Kawano T, Kharbanda S and Kufe D: MUC1-C
oncoprotein promotes STAT3 activation in an autoinductive
regulatory loop. Sci Signal. 4:ra92011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Carson DD: The cytoplasmic tail of MUC1: A
very busy place. Sci Signal. 1:pe352008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thathiah A and Carson DD: MT1-MMP mediates
MUC1 shedding independent of TACE/ADAM17. Biochem J. 382:363–373.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li X, Dai D, Chen B, Tang H, Xie X and Wei
W: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of cancer
antigen 15-3 and carcinoembryonic antigen in breast cancer: A
meta-analysis including 12,993 patients. Dis Markers.
2018:98630922018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Angadi PV, Savitha JK, Rao SS and
Sivaranjini Y: Oral field cancerization: Current evidence and
future perspectives. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 16:171–180. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lochhead P, Chan AT, Nishihara R, Fuchs
CS, Beck AH, Giovannucci E and Ogino S: Etiologic field effect:
Reappraisal of the field effect concept in cancer predisposition
and progression. Mod Pathol. 28:14–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: TNM classification of malignant tumours. 7th. Wiley-Blackwell;
Chichester, West Sussex: 2009
|
|
21
|
Detre S, Saclani Jotti G and Dowsett M: A
‘quickscore’ method for immunohistochemical semiquantitation:
Validation for oestrogen receptor in breast carcinomas. J Clin
Pathol. 48:876–878. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kumar MH, Sanjai K, Kumarswamy J,
Keshavaiah R, Papaiah L and Divya S: Expression of MUC1 mucin in
potentially malignant disorders, oral squamous cell carcinoma and
normal oral mucosa: An immunohistochemical study. J Oral Maxillofac
Pathol. 20:214–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nitta T, Sugihara K, Tsuyama S and Murata
F: Immunohistochemical study of MUC1 mucin in premalignant oral
lesions and oral squamous cell carcinoma: Association with disease
progression, mode of invasion, and lymph node metastasis. Cancer.
88:245–254. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
de Sousa Abreu R, Penalva LO, Marcotte EM
and Vogel C: Global signatures of protein and mRNA expression
levels. Mol Biosyst. 5:1512–1526. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Maier T, Guell M and Serrano L:
Correlation of mRNA and protein in complex biological samples. FEBS
Lett. 583:3966–3973. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Safi F, Kohler I, Rottinger E and Beger H:
The value of the tumor marker CA 15-3 in diagnosing and monitoring
breast cancer. A comparative study with carcinoembryonic antigen.
Cancer. 68:574–582. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Steinberg W: The clinical utility of the
CA 19-9 tumor-associated antigen. Am J Gastroenterol. 85:350–355.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Duffy MJ, Duggan C, Keane R, Hill ASK,
McDermott E, Crown J and O'Higgins N: High preoperative CA 15-3
concentrations predict adverse outcome in node-negative and
node-positive breast cancer: Study of 600 patients with
histologically confirmed breast cancer. Clin Chem. 50:559–563.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Duffy MJ, Evoy D and McDermott EW: CA
15-3: Uses and limitation as a biomarker for breast cancer. Clin
Chim Acta. 411:1869–1874. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Boldrup L, Coates PJ, Laurell G and
Nylander K: Differences in p63 expression in SCCHN tumours of
different sub-sites within the oral cavity. Oral Oncol. 47:861–865.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Boldrup L, Coates PJ, Wahlgren M, Laurell
G and Nylander K: Subsite-based alterations in miR-21, miR-125b,
and miR-203 in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and
correlation to important target proteins. J Carcinog. 11:182012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ledgerwood LG, Kumar D, Eterovic AK, Wick
J, Chen K, Zhao H, Tazi L, Manna P, Kerley S, Joshi R, et al: The
degree of intratumor mutational heterogeneity varies by primary
tumor sub-site. Oncotarget. 7:27185–27198. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
De Vita A, Miserocchi G, Recine F,
Mercatali L, Pieri F, Medri L, Bongiovanni A, Cavaliere D, Liverani
C, Spadazzi C, et al: Activity of eribulin in a primary culture of
well-differentiated/dedifferentiated adipocytic sarcoma. Molecules.
21:16622016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Oppel F, Shao S, Schurmann M, Goon P,
Albers AE and Sudhoff H: An effective primary head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma in vitro model. Cells. 8:5552019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yuan Z, Wong S, Borrelli A and Chung MA:
Down-regulation of MUC1 in cancer cells inhibits cell migration by
promoting E-cadherin/catenin complex formation. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 362:740–746. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tanimoto T, Tanaka S, Haruma K, Yoshihara
M, Sumii K, Kajiyama G, Shimamoto F and Kohno N: MUC1 expression in
intramucosal colorectal neoplasms. Possible involvement in
histogenesis and progression. Oncology. 56:223–231. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|