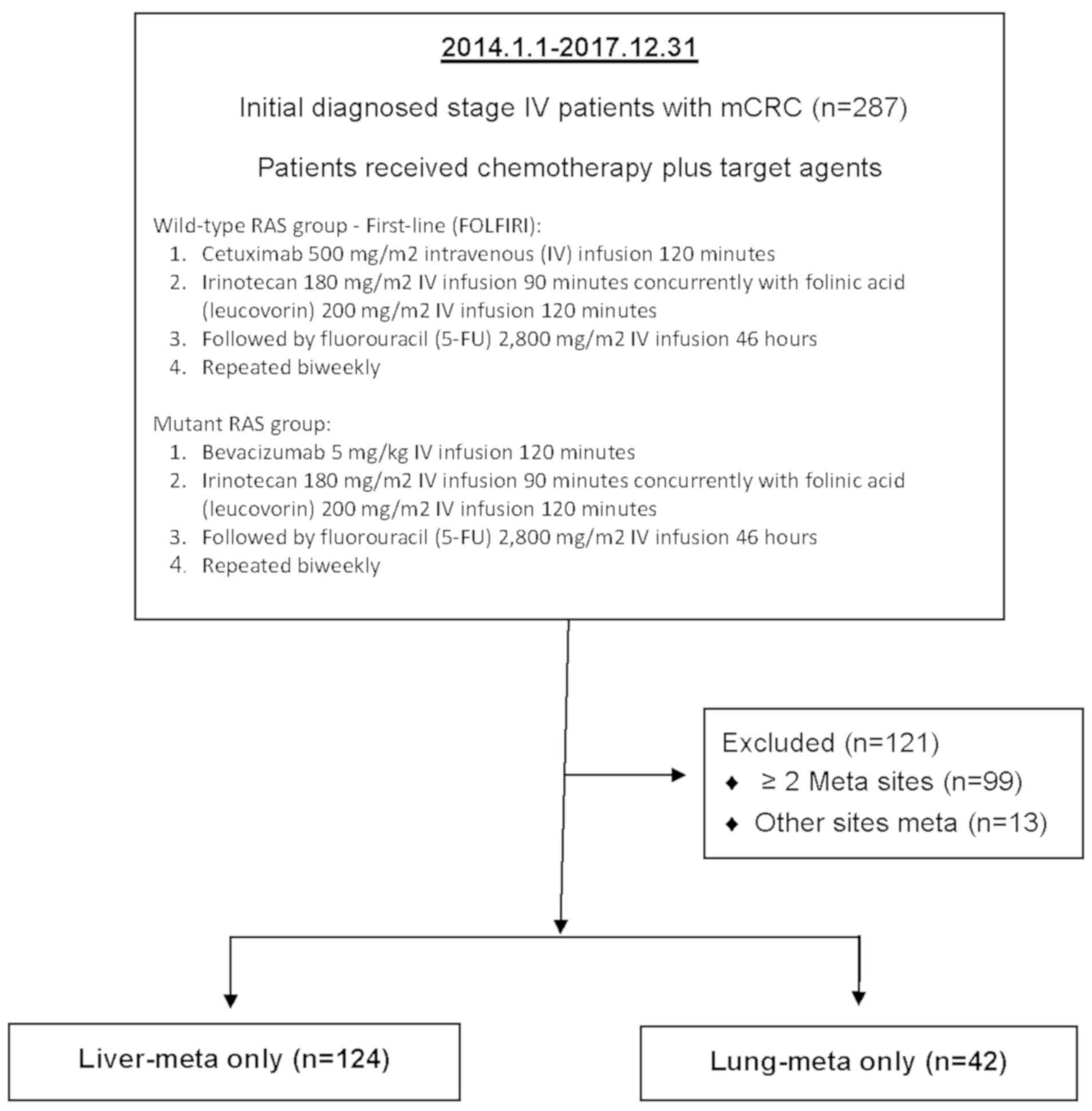
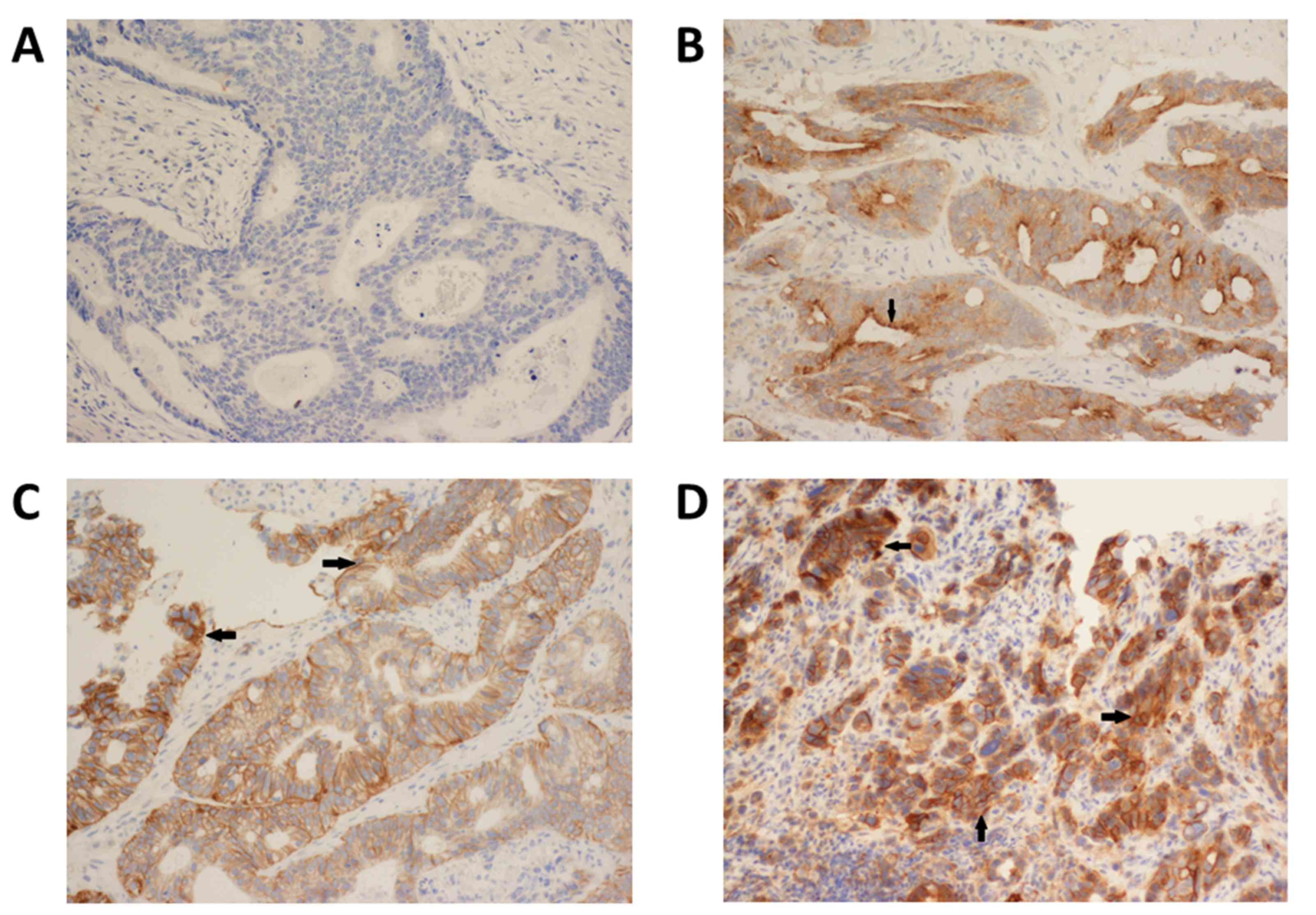
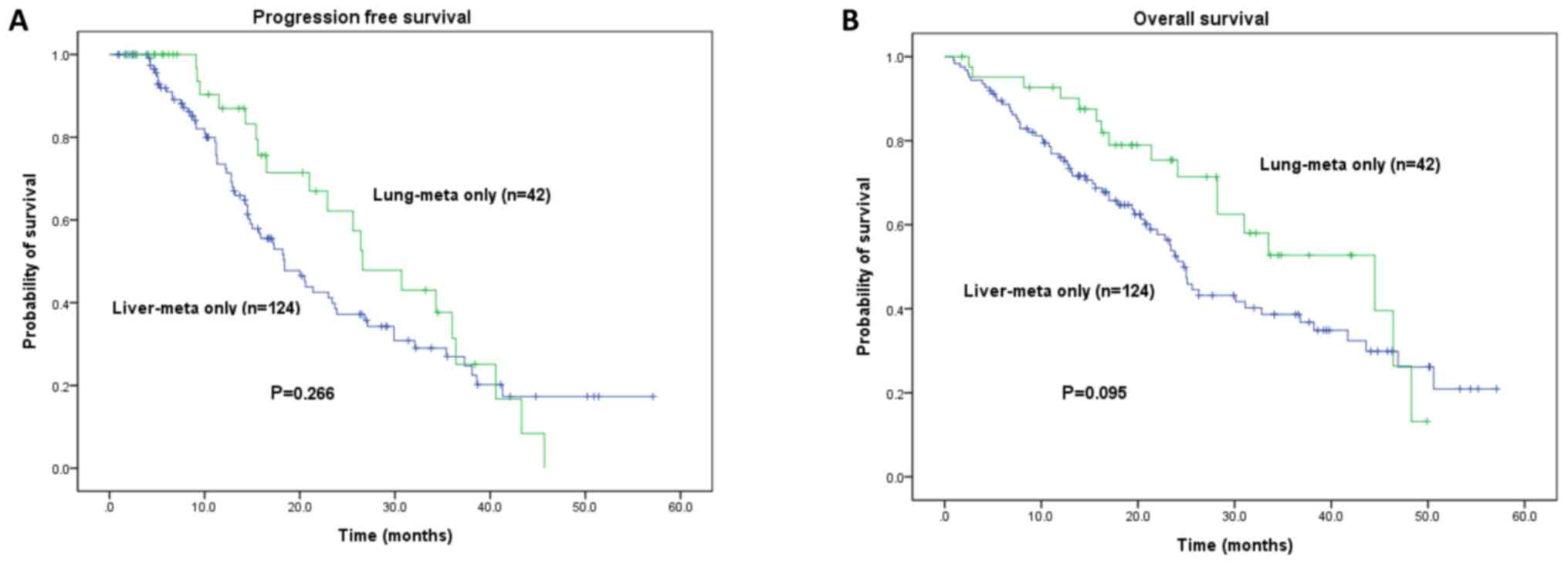
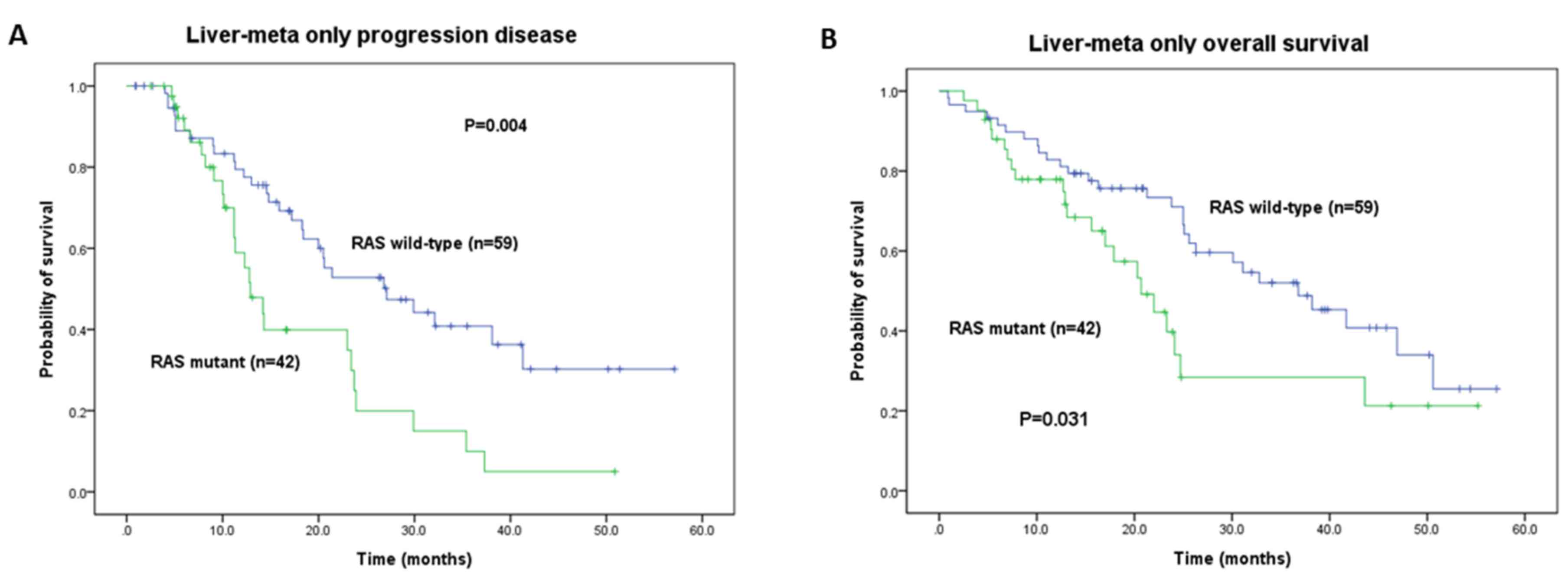
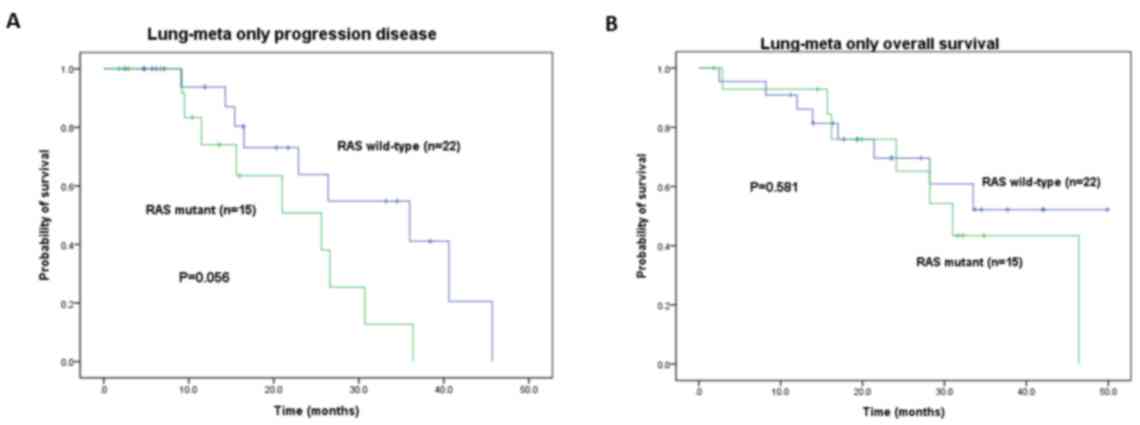
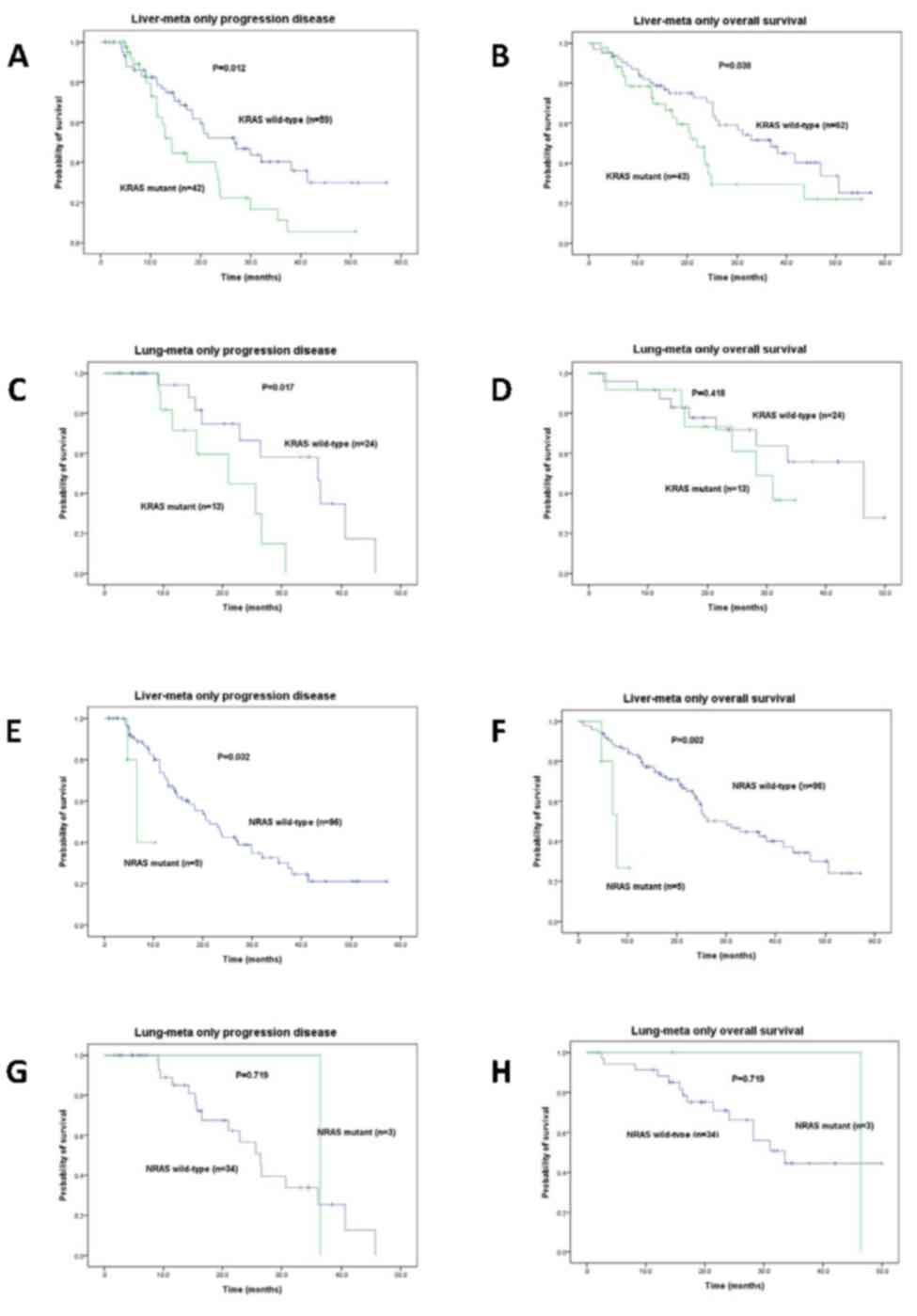
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferly J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Millikan KW, Staren ED and Doolas A:
Invasive therapy of metastatic colorectal cancer to the liver. Surg
Clin North Am. 77:27–48. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nitzkorski JR, Farma JM, Watson JC,
Siripurapu V, Zhu F, Matteotti RS and Sigurdson ER: Outcome and
natural history of patients with stage IV colorectal cancer
receiving chemotherapy without primary tumor resection. Ann Surg
Oncol. 19:379–383. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Prasanna T, Karapetis CS, Roder D, Tie J,
Padbury R, Price T, Wong R, Shapiro J, Nott L, Lee M, et al: The
survival outcome of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer
based on the site of metastases and the impact of molecular markers
and site of primary cancer on metastatic pattern. Acta Oncol.
57:1438–1444. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qiu M, Hu J, Yang D, Cosgrove DP and Xu R:
Pattern of distant metastases in colorectal cancer: A SEER based
study. Oncotarget. 6:38658–38666. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zizzo M, Galeone C, Braglia L, Ugoletti L,
Siciliani A, Nachira D, Margaritora S, Pedrazzoli C, Paci M, Lococo
F, et al: Long-Term outcomes after surgical resection for
synchronous or metachronous hepatic and pulmonary colorectal cancer
metastases. Digestion. 101:144–155. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Augestad KM, Merok MA and Ignatovic D:
Tailored treatment of colorectal cancer: Surgical, molecular, and
genetic considerations. Clin Med Insights Oncol.
11:11795549176907662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Raskov H, Pommergaard HC, Burcharth J and
Rosenberg J: Colorectal carcinogenesis-update and perspectives.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:18151–18164. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van Cutsem E,
Siena S, Freeman DJ, Juan T, Sikorski R, Suggs S, Radinsky R, et
al: Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients
with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:1626–1634.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schirripa M, Cremolini C, Loupakis F,
Morvillo M, Bergamo F, Zoratto F, Salvatore L, Antoniotti C,
Marmorino F, Sensi E, et al: Role of NRAS mutations as prognostic
and predictive markers in metastatic colorectal cancer. Int J
Cancer. 136:83–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roth AD, Tejpar S, Delorenzi M, Yan P,
Fiocca R, Klingbiel D, Dietrich D, Biesmans B, Bodoky G, Barone C,
et al: Prognostic role of KRAS and BRAF in stage II and III
resected colon cancer: Results of the translational study on the
PETACC-3, EORTC 40993, SAKK 60-00 trial. J Clin Oncol. 28:466–474.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hutchins G, Southward K, Handley K, Magill
L, Beaumont C, Stahlschmidt J, Richman S, Chambers P, Seymour M,
Kerr D, et al: Value of mismatch repair, KRAS, and BRAF mutations
in predicting recurrence and benefits from chemotherapy in
colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 29:1261–1270. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Ma J, Zhang S, Deng G, Wu X, He
J, Pei H, Shen H and Zeng S: A prognostic analysis of 895 cases of
stage III colon cancer in different colon subsites. Int J
Colorectal Dis. 30:1173–1183. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fakih M and Wong R: Efficacy of the
monoclonal antibody EGFR inhibitors for the treatment of metastatic
colorectal cancer. Curr Oncol. 17 (Suppl 1):S3–S17. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Venook AP: Epidermal growth factor
receptor-targeted treatment for advanced colorectal carcinoma.
Cancer. 103:2435–2446. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bibeau F, Boissiere-Michot F, Sabourin JC,
Gourgou-Bourgade S, Radal M, Penault-Llorca F, Rochaix P, Arnould
L, Bralet MP, Azria D and Ychou M: Assessment of epidermal growth
factor receptor (EGFR) expression in primary colorectal carcinomas
and their related metastases on tissue sections and tissue
microarray. Virchows Arch. 449:281–287. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liang Z, Zhang J, Zeng X, Gao J, Wu S and
Liu T: Relationship between EGFR expression, copy number and
mutation in lung adenocarcinomas. BMC Cancer. 10:3762010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sambrook J and Russell DW: The condensed
protocols from molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring
Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor. (NY). p. v.
8002006.
|
|
20
|
Yen LC, Uen YH, Wu DC, Lu CY, Yu FJ, Wu
IC, Lin SR and Wang JY: Activating KRAS mutations and
overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor as independent
predictors in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with
cetuximab. Ann Surg. 251:254–260. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang JY, Hsieh JS, Chen FM, Yeh CS,
Alexandersen K, Huang TJ, Chen DC and Lin SR: High frequency of
activated K-ras codon 15 mutant in colorectal carcinomas from
Taiwanese patients. Int J Cancer. 107:387–393. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang CW, Chen YT, Tsai HL, Yeh YS, Su WC,
Ma CJ, Tsai TN and Wang JY: EGFR expression in patients with stage
III colorectal cancer after adjuvant chemotherapy and on cancer
cell function. Oncotarget. 8:114663–114676. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang CW, Tsai HL, Chen YT, Huang CM, Ma
CJ, Lu CY, Kuo CH, Wu DC, Chai CY and Wang JY: The prognostic
values of EGFR expression and KRAS mutation in patients with
synchronous or metachronous metastatic colorectal cancer. BMC
Cancer. 13:5992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Scartozzi M, Bearzi I, Berardi R,
Mandolesi A, Fabris G and Cascinu S: Epidermal growth factor
receptor (EGFR) status in primary colorectal tumors does not
correlate with EGFR expression in related metastatic sites:
Implications for treatment with EGFR-targeted monoclonal
antibodies. J Clin Oncol. 1:4772–4778. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network, .
Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal
cancer. Nature. 487:330–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu Y, Sethi NS, Hinoue T, Schneider BG,
Cherniack AD, Sanchez-Vega F, Seoane JA, Farshidfar F, Bowlby R,
Islam M, et al: Comparative molecular analysis of gastrointestinal
adenocarcinomas. Cancer Cell. 33:721–735.e8. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wee P and Wang Z: Epidermal growth factor
receptor cell proliferation signaling pathways. Cancers (Basel).
9:522017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tan C and Du X: KRAS mutation testing in
metastatic colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 18:5171–5180.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lo Nigro C, Ricci V, Vivenza D, Granetto
C, Fabozzi T, Miraglio E and Merlano MC: Prognostic and predictive
biomarkers in metastatic colorectal cancer anti-EGFR therapy. World
J Gastroenterol. 22:6944–6954. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
De Stefano A and Carlomagno C: Beyond
KRAS: Predictive factors of the efficacy of anti-EGFR monoclonal
antibodies in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. World
J Gastroenterol. 20:9732–9743. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
He XK, Wu W, Ding YE, Li Y, Sun LM and Si
J: Different anatomical subsites of colon cancer and mortality: A
population-based study. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018:71536852018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Engstrand J, Nilsson H, Stromberg C, Jonas
E and Freedman J: Colorectal cancer liver metastases-a
population-based study on incidence, management and survival. BMC
Cancer. 18:782018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim HS, Heo JS, Lee J, Lee JY, Lee MY, Lim
SH, Lee WY, Kim SH, Park YA, Cho YB, et al: The impact of KRAS
mutations on prognosis in surgically resected colorectal cancer
patients with liver and lung metastases: A retrospective analysis.
BMC Cancer. 16:1202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yong ZZ, Ching GTH and Ching MTC:
Metastatic profile of colorectal cancer: Interplay between primary
tumor location and KRAS Status. J Surg Res. 246:325–334. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shankaran V, Obel J and Benson AB III:
Predicting response to EGFR inhibitors in metastatic colorectal
cancer: Current practice and future directions. Oncologist.
15:157–167. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
van Helden EJ, Menke-van der Houven van
Oordt CW, Heymans MW, Ket JCF, van den Oord R and Verheul HMW:
Optimal use of anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies for patients with
advanced colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
36:395–406. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kato S, Okamura R, Mareboina M, Lee S,
Goodman A, Patel SP, Fanta PT, Schwab RB, Vu P, Raymond VM, et al:
Revisiting Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Amplification as
a Target for Anti-EGFR therapy: Analysis of cell-free circulating
tumor DNA in patients with advanced malignancies. JCO Precis Oncol.
3:102019.
|
|
38
|
Yang ZY, Shen WX, Hu XF, Zheng DY, Wu XY,
Huang YF, Chen JZ, Mao C and Tang JL: EGFR gene copy number as a
predictive biomarker for the treatment of metastatic colorectal
cancer with anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies: A meta-analysis. J
Hematol Oncol. 5:522012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Brudvik KW, Kopetz SE, Li L, Conrad C,
Aloia TA and Vauthey JN: Meta-analysis of KRAS mutations and
survival after resection of colorectal liver metastases. Br J Surg.
102:1175–1183. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shindoh J, Nishioka Y, Yoshioka R,
Sugawara T, Sakamoto Y, Hasegawa K, Hashimoto M and Kokudo N: KRAS
mutation status predicts Site-Specific recurrence and survival
after resection of colorectal liver metastases irrespective of
location of the primary lesion. Ann Surg Oncol. 23:1890–1896. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yaeger R, Cowell E, Chou JF, Gewirtz AN,
Borsu L, Vakiani E, Solit DB, Rosen N, Capanu M, Ladanyi M and
Kemeny N: RAS mutations affect pattern of metastatic spread and
increase propensity for brain metastasis in colorectal cancer.
Cancer. 121:1195–1203. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nagakubo Y, Hirotsu Y, Amemiya K, Oyama T,
Mochizuki H and Omata M: Accurate detection of KRAS, NRAS and BRAF
mutations in metastatic colorectal cancers by bridged nucleic
acid-clamp real-time PCR. BMC Med Genomics. 12:1622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gilson P, Franczak C, Dubouis L, Husson M,
Rouyer M, Demange J, Perceau M, Leroux A, Merlin JL, Harlé A, et
al: Evaluation of KRAS, NRAS and BRAF hotspot mutations detection
for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer using direct DNA
pipetting in a fully-automated platform and next-generation
sequencing for laboratory workflow optimisation. PLoS One.
14:e02192042019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|