|
1
|
Finnegan EF and Pasquinelli AE: MicroRNA
biogenesis: Regulating the regulators. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol.
48:51–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Acunzo M, Romano G, Wernicke D and Croce
CM: MicroRNA and cancer-a brief overview. Adv Biol Regul. 57:1–9.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee YS and Dutta A: MicroRNAs in cancer.
Annu Rev Pathol. 4:199–227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kappel A and Keller A: miRNA assays in the
clinical laboratory: Workflow, detection technologies and
automation aspects. Clin Chem Lab Med. 55:636–647. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
The Lancet, . GLOBOCAN 2018: Counting the
toll of cancer. Lancet. 392:9852018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M
and Croce CM: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at
fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R,
Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and
miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:15524–15529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT,
Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, Powers S, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe
SW, Hannon GJ and Hammond SM: A microRNA polycistron as a potential
human oncogene. Nature. 435:828–833. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shell S, Park SM, Radjabi AR, Schickel R,
Kistner EO, Jewell DA, Feig C, Lengyel E and Peter ME: Let-7
expression defines two differentiation stages of cancer. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:11400–11405. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pineau P, Volinia S, McJunkin K, Marchio
A, Battiston C, Terris B, Mazzaferro V, Lowe SW, Croce CM and
Dejean A: miR-221 overexpression contributes to liver
tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:264–269. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Felli N, Fontana L, Pelosi E, Botta R,
Bonci D, Facchiano F, Liuzzi F, Lulli V, Morsilli O, Santoro S, et
al: MicroRNAs 221 and 222 inhibit normal erythropoiesis and
erythroleukemic cell growth via kit receptor down-modulation. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:18081–18086. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang Z, Li Y, Huang K, Wagar N and Shim
H: Regulation of miR-19 to breast cancer chemoresistance through
targeting PTEN. Pharm Res. 28:3091–3100. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi GH, Ye DW, Yao XD, Zhang SL, Dai B,
Zhang HL, Shen YJ, Zhu Y, Zhu YP, Xiao WJ and Ma CG: Involvement of
microRNA-21 in mediating chemo-resistance to docetaxel in
androgen-independent prostate cancer PC3 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
31:867–873. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Acunzo M, Visone R, Romano G, Veronese A,
Lovat F, Palmieri D, Bottoni A, Garofalo M, Gasparini P, Condorelli
G, et al: miR-130a targets MET and induces TRAIL-sensitivity in
NSCLC by downregulating miR-221 and 222. Oncogene. 31:634–642.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bao L, Hazari S, Mehra S, Kaushal D, Moroz
K and Dash S: Increased expression of P-glycoprotein and
doxorubicin chemoresistance of metastatic breast cancer is
regulated by miR-298. Am J Pathol. 180:2490–2503. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rottiers V and Näär AM: MicroRNAs in
metabolism and metabolic disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
13:239–250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fernández-Hernando C, Suárez Y, Rayner KJ
and Moore KJ: MicroRNAs in lipid metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol.
22:86–92. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brown MS and Goldstein JL: The SREBP
pathway: Regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a
membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell. 89:331–340. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bengoechea-Alonso MT and Ericsson J: SREBP
in signal transduction: Cholesterol metabolism and beyond. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 19:215–222. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Boren J and Brindle KM: Apoptosis-induced
mitochondrial dysfunction causes cytoplasmic lipid droplet
formation. Cell Death Differ. 19:1561–1570. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gharipour M and Sadeghi M: Pivotal role of
microRNA-33 in metabolic syndrome: A systematic review. ARYA
Atheroscler. 9:372–376. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nishida N and Goel A: Genetic and
epigenetic signatures in human hepatocellular carcinoma: A
systematic review. Curr Genomics. 12:130–137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Karkampouna S, van der Helm D, Gray PC,
Chen L, Klima I, Grosjean J, Burgmans MC, Farina-Sarasqueta A,
Snaar-Jagalska EB, Stroka DM, et al: CRIPTO promotes an aggressive
tumour phenotype and resistance to treatment in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Pathol. 245:297–310. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu W, Liu H, Liu ZG, Wang HS, Zhang F,
Wang H, Zhang J, Chen JJ, Huang HJ, Tan Y, et al: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors upregulate Snail via Smad2/3 phosphorylation
and stabilization of Snail to promote metastasis of hepatoma cells.
Cancer Lett. 420:1–13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gingold JA, Zhu D, Lee DF, Kaseb A and
Chen J: Genomic profiling and metabolic homeostasis in primary
liver cancers. Trends Mol Med. 24:395–411. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
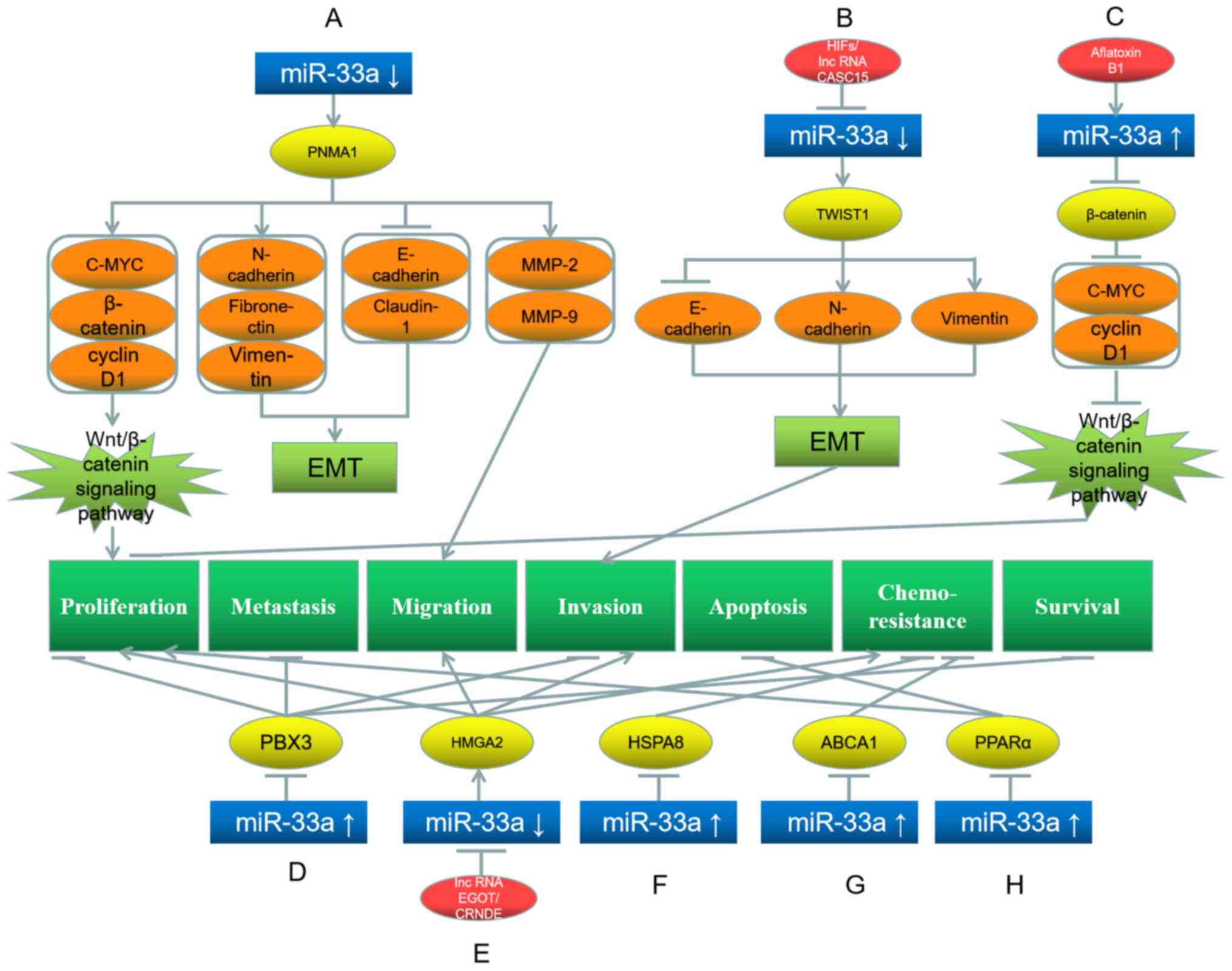
Liu P, Chen B, Gu Y and Liu Q: PNMA1,
regulated by miR-33a-5p, promotes proliferation and EMT in
hepatocellular carcinoma by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Biomed Pharmacother. 108:492–499. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guo XF, Wang AY and Liu J:
HIFs-MiR-33a-Twsit1 axis can regulate invasiveness of
hepatocellular cancer cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
20:3011–3016. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Chen G, Yan Y and Fan Q: CASC15
promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition and facilitates
malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by increasing TWIST1
gene expression via miR-33a-5p sponging. Eur J Pharmacol.
860:1725892019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fang Y, Feng Y, Wu T, Srinivas S, Yang W,
Fan J, Yang C and Wang S: Aflatoxin B1 negatively regulates
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway through activating miR-33a. PLoS
One. 8:e730042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Han SY, Han HB, Tian XY, Sun H, Xue D,
Zhao C, Jiang ST, He XR, Zheng WX, Wang J, et al: MicroRNA-33a-3p
suppresses cell migration and invasion by directly targeting PBX3
in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:42461–42473. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu S, Ai H, Zhang K, Yun H and Xie F: Long
non-coding RNA EGOT promotes the malignant phenotypes of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells and increases the expression of
HMGA2 via down-regulating miR-33a-5p. Onco Targets Ther.
12:11623–11635. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han S, Han B, Li Z and Sun D:
Downregulation of long noncoding RNA CRNDE suppresses drug
resistance of liver cancer cells by increasing microRNA-33a
expression and decreasing HMGA2 expression. Cell Cycle.
18:2524–2537. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Meng W, Tai Y, Zhao H, Fu B, Zhang T, Liu
W, Li H, Yang Y, Zhang Q, Feng Y and Chen G: Downregulation of
miR-33a-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma: A possible mechanism for
chemotherapy resistance. Med Sci Monit. 23:1295–1304. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hou H, Kang Y, Li Y, Zeng Y, Ding G and
Shang J: miR-33a expression sensitizes Lgr5+ HCC-CSCs to
doxorubicin via ABCA1. Neoplasma. 64:81–91. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chang W, Zhang L, Xian Y and Yu Z:
MicroRNA-33a promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by
targeting PPARα in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Ther Med.
13:2507–2514. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pasechnikov V, Chukov S, Fedorov E,
Kikuste I and Leja M: Gastric cancer: Prevention, screening and
early diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol. 20:13842–13862. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hartgrink HH, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC
and van de Velde CJ: Gastric cancer. Lancet. 374:477–490. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
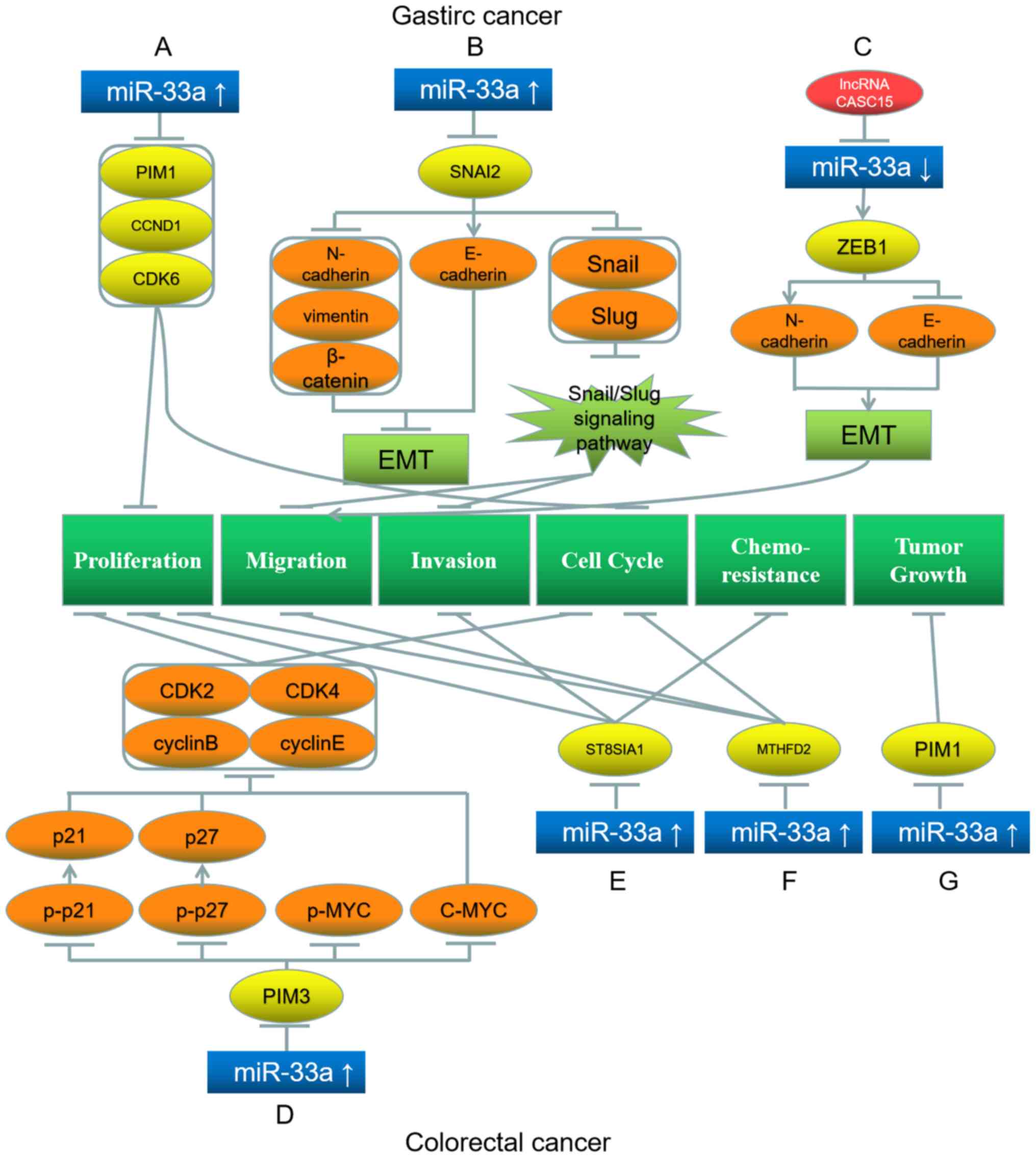
Wang Y, Zhou X, Shan B, Han J, Wang F, Fan
X, Lv Y, Chang L and Liu W: Downregulation of microRNA-33a promotes
cyclin- dependent kinase 6, cyclin D1 and PIM1 expression and
gastric cancer cell proliferation. Mol Med Rep. 12:6491–6500. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen DD, Cheng JT, Chandoo A, Sun XW,
Zhang L, Lu MD, Sun WJ and Huang YP: microRNA-33a prevents
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and metastasis of
gastric cancer cells through the Snail/Slug pathway. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 317:G147–G160. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wu Q, Xiang S, Ma J, Hui P, Wang T, Meng
W, Shi M and Wang Y: Long non-coding RNA CASC15 regulates gastric
cancer cell proliferation, migration and epithelial mesenchymal
transition by targeting CDKN1A and ZEB1. Mol Oncol. 12:799–813.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Herbey II, Ivankova NV, Katkoori VR and
Mamaeva OA: Colorectal cancer and hypercholesterolemia: Review of
current research. Exp Oncol. 27:166–178. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gray RT, Loughrey MB, Bankhead P, Cardwell
CR, McQuaid S, O'Neill RF, Arthur K, Bingham V, McGready C, Gavin
AT, et al: Statin use, candidate mevalonate pathway biomarkers, and
colon cancer survival in a population-based cohort study. Br J
Cancer. 116:1652–1659. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Murai T: Cholesterol lowering: Role in
cancer prevention and treatment. Biol Chem. 396:1–11. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jacobs RJ, Voorneveld PW, Kodach LL and
Hardwick JC: Cholesterol metabolism and colorectal cancers. Curr
Opin Pharmacol. 12:690–695. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang Y, Liu C and Hu L: Cholesterol
regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer by
modulating miR-33a-PIM3 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
511:685–692. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shan Y, Liu Y, Zhao L, Liu B, Li Y and Jia
L: MicroRNA-33a and let-7e inhibit human colorectal cancer
progression by targeting ST8SIA1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
90:48–58. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yan Y, Zhang D, Lei T, Zhao C, Han J, Cui
J and Wang Y: MicroRNA-33a-5p suppresses colorectal cancer cell
growth by inhibiting MTHFD2. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
46:928–936. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ibrahim AF, Weirauch U, Thomas M,
Grünweller A, Hartmann RK and Aigner A: MicroRNA replacement
therapy for miR-145 and miR-33a is efficacious in a model of colon
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 71:5214–5224. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sener SF, Fremgen A, Menck HR and
Winchester DP: Pancreatic cancer: A report of treatment and
survival trends for 100,313 patients diagnosed from 1985–1995,
using the national cancer database. J Am Coll Surg. 189:1–7. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Moffat GT, Epstein AS and O'Reilly EM:
Pancreatic cancer-A disease in need: Optimizing and integrating
supportive care. Cancer. 125:3927–3935. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liang C, Yu XJ, Guo XZ, Sun MH, Wang Z,
Song Y, Ni QX, Li HY, Mukaida N and Li YY: MicroRNA-33a-mediated
downregulation of Pim-3 kinase expression renders human pancreatic
cancer cells sensitivity to gemcitabine. Oncotarget. 6:14440–14455.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liang C, Wang Z, Li YY, Yu BH, Zhang F and
Li HY: miR-33a suppresses the nuclear translocation of β-catenin to
enhance gemcitabine sensitivity in human pancreatic cancer cells.
Tumour Biol. 36:9395–9403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sharma A, Sharma KL, Gupta A, Yadav A and
Kumar A: Gallbladder cancer epidemiology, pathogenesis and
molecular genetics: Recent update. World J Gastroenterol.
23:3978–3998. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhang M, Gong W, Zuo B, Chu B, Tang Z,
Zhang Y, Yang Y, Zhou D, Weng M, Qin Y, et al: The microRNA miR-33a
suppresses IL-6-induced tumor progression by binding Twist in
gallbladder cancer. Oncotarget. 7:78640–78652. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Arnold M, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J and
Forman D: Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological
subtype in 2012. Gut. 64:381–387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Abnet CC, Arnold M and Wei WQ:
Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 154:360–373. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang C, Wang L, Yang J, Fu Y, Li H, Xie L
and Cui Y: MicroRNA-33a-5p suppresses esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma progression via regulation of lncRNA DANCR and ZEB1. Eur
J Pharmacol. 861:1725902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang L, Yu X, Zhang Z, Pang L, Xu J, Jiang
J, Liang W, Chai Y, Hou J and Li F: Linc-ROR promotes esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma progression through the derepression of
SOX9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:1822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer: #pidemiology, risk
factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Du M, Zhang Y, Mao Y, Mou J, Zhao J, Xue
Q, Wang D, Huang J, Gao S and Gao Y: MiR-33a suppresses
proliferation of NSCLC cells via targeting METTL3 mRNA. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 482:582–589. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kang M, Li Y, Zhao Y, He S and Shi J:
miR-33a inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by targeting CAND1
in lung cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 20:457–466. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Amaar YG and Reeves ME: RASSF1C regulates
miR-33a and EMT marker gene expression in lung cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 10:123–132. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yang L, Yang J, Li J, Shen X, Le Y, Zhou
C, Wang S, Zhang S, Xu D and Gong Z: MircoRNA-33a inhibits
epithelial-to- mesenchymal transition and metastasis and could be a
prognostic marker in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep.
5:136772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kang J, Kim W, Lee S, Kwon D, Chun J, Son
B, Kim E, Lee JM, Youn H and Youn B: TFAP2C promotes lung
tumorigenesis and aggressiveness through miR-183- and
miR-33a-mediated cell cycle regulation. Oncogene. 36:1585–1596.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wang Y, Zhao W and Zhang S: STAT3-induced
upregulation of circCCDC66 facilitates the progression of non-small
cell lung cancer by targeting miR-33a-5p/KPNA4 axis. Biomed
Pharmacother. 126:1100192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Li YJ, Sun YX, Hao RM, Wu P, Zhang LJ, Ma
X, Ma Y, Wang PY, Xie N, Xie SY and Chen W: miR-33a-5p enhances the
sensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma cells to celastrol by regulating
mTOR signaling. Int J Oncol. 52:1328–1338. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kuo PL, Liao SH, Hung JY, Huang MS and Hsu
YL: MicroRNA-33a functions as a bone metastasis suppressor in lung
cancer by targeting parathyroid hormone related protein. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1830:3756–3766. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Pan J, Fang S, Tian H, Zhou C, Zhao X,
Tian H, He J, Shen W, Meng X, Jin X and Gong Z: lncRNA
JPX/miR-33a-5p/Twist1 axis regulates tumorigenesis and metastasis
of lung cancer by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol Cancer.
19:92020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Rice SJ, Lai SC, Wood LW, Helsley KR,
Runkle EA, Winslow MM and Mu D: MicroRNA-33a mediates the
regulation of high mobility group AT-hook 2 gene (HMGA2) by thyroid
transcription factor 1 (TTF-1/NKX2-1). J Biol Chem.
288:16348–16360. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhu C, Zhao Y, Zhang Z, Ni Y, Li X and
Yong H: MicroRNA-33a inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation and
invasion by regulating the expression of β-catenin. Mol Med Rep.
11:3647–3651. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Boldrini L, Giordano M, Niccoli C, Melfi
F, Lucchi M, Mussi A and Fontanini G: Role of microRNA-33a in
regulating the expression of PD-1 in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer
Cell Int. 17:1052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Li M, Zhao X, Liu Y, An J, Xiao H and Wang
C: Aberrant expression of CDK8 regulates the malignant phenotype
and associated with poor prognosis in human laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 274:2205–2213. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Marioni G, Marchese-Ragona R, Cartei G,
Marchese F and Staffieri A: Current opinion in diagnosis and
treatment of laryngeal carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 32:504–515.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Karatas OF: Antiproliferative potential of
miR-33a in laryngeal cancer Hep-2 cells via targeting PIM1. Head
Neck. 40:2455–2461. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Karatas OF, Oner M, Abay A and Diyapoglu
A: MicroRNAs in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma: From
pathogenesis to therapeutic implications. Oral Oncol. 67:124–130.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zuo Z, Ma L, Gong Z, Xue L and Wang Q:
Long non-coding RNA CASC15 promotes tongue squamous carcinoma
progression through targeting miR-33a-5p. Environ Sci Pollut Res
Int. 25:22205–22212. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Trotter SC, Sroa N, Winkelmann RR, Olencki
T and Bechtel M: A global review of melanoma follow-up guidelines.
J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 6:18–26. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhou J, Xu D, Xie H, Tang J, Liu R, Li J,
Wang S, Chen X, Su J, Zhou X, et al: miR-33a functions as a tumor
suppressor in melanoma by targeting HIF-1α. Cancer Biol Ther.
16:846–855. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Dimitriou F, Krattinger R, Ramelyte E,
Barysch MJ, Micaletto S, Dummer R and Goldinger SM: The world of
melanoma: Epidemiologic, genetic, and anatomic differences of
melanoma across the globe. Curr Oncol Rep. 20:872018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Cao K, Li J, Chen J, Qian L, Wang A, Chen
X, Xiong W, Tang J, Tang S, Chen Y, et al: microRNA-33a-5p
increases radiosensitivity by inhibiting glycolysis in melanoma.
Oncotarget. 8:83660–83672. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Tian F, Wei H, Tian H, Qiu Y and Xu J:
miR-33a is downregulated in melanoma cells and modulates cell
proliferation by targeting PCTAIRE1. Oncol Lett. 11:2741–2746.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Lv L, Jia JQ and Chen J: The lncRNA CCAT1
upregulates proliferation and invasion in melanoma cells via
suppressing miR-33a. Oncol Res. 26:201–208. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Fu Y, Bi Y, Wang F, Chen X and Liu H:
Declination of long noncoding RNA paternally expressed gene 10
inhibits A375 cells proliferation, migration, and invasion via
mediating microRNA-33a. J Cell Biochem. 120:19868–19877. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Oltean MA, Matuz R, Sitar-Taut A, Mihailov
A, Rednic N, Tantau A, Toganel R, Minciuna IA, Orasan O, Muresan F
and Cozma A: Renal cell carcinoma with extensive tumor thrombus
into the inferior vena cava and right atrium in a 70-year-old man.
Am J Mens Health. 13:15579883198464042019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Capitanio U, Bensalah K, Bex A, Boorjian
SA, Bray F, Coleman J, Gore JL, Sun M, Wood C and Russo P:
Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 75:74–84. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Jiang K, Sun F, Zhu J, Luo G, Ban Y and
Zhang P: miR-33a inhibits cell growth in renal cancer by
downregulation of MDM4 expression. Mol Genet Genomic Med.
7:e8332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Kim J, Gosnell JE and Roman SA: Geographic
influences in the global rise of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 16:17–29. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Takeshita H, Shiozaki A, Bai XH, Iitaka D,
Kim H, Yang BB, Keshavjee S and Liu M: XB130, a new adaptor
protein, regulates expression of tumor suppressive microRNAs in
cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e590572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Awad AJ, Burns TC, Zhang Y and Abounader
R: Targeting MET for glioma therapy. Neurosurg Focus. 37:E102014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Chang M, Qiao L, Li B, Wang J, Zhang G,
Shi W, Liu Z, Gu N, Di Z, Wang X and Tian Y: Suppression of SIRT6
by miR-33a facilitates tumor growth of glioma through apoptosis and
oxidative stress resistance. Oncol Rep. 38:1251–1258. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Wang H, Sun T, Hu J, Zhang R, Rao Y, Wang
S, Chen R, McLendon RE, Friedman AH, Keir ST, et al: miR-33a
promotes glioma-initiating cell self-renewal via PKA and NOTCH
pathways. J Clin Invest. 124:4489–4502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data
from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program.
Cancer. 115:1531–1543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Jiang N, Wang X, Xie X, Liao Y, Liu N, Liu
J, Miao N, Shen J and Peng T: lncRNA DANCR promotes tumor
progression and cancer stemness features in osteosarcoma by
upregulating AXL via miR-33a-5p inhibition. Cancer Lett. 405:46–55.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Huang Y, Zhang J, Shao H, Liu J, Jin M,
Chen J and Zhao H: miR-33a mediates the anti-tumor effect of
lovastatin in osteosarcoma by targeting CYR61. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 51:938–948. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zhang J, Wang D, Xiong J, Chen L and Huang
J: MicroRNA-33a-5p suppresses growth of osteosarcoma cells and is
downregulated in human osteosarcoma. Oncol Lett. 10:2135–2141.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Zhou Y, Huang Z, Wu S, Zang X, Liu M and
Shi J: miR-33a is up-regulated in chemoresistant osteosarcoma and
promotes osteosarcoma cell resistance to cisplatin by
down-regulating TWIST. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Gaudreau PO, Stagg J, Soulières D and Saad
F: The present and future of biomarkers in prostate cancer:
Proteomics, genomics, and immunology advancements. Biomark Cancer.
8 (Suppl 2):S15–S33. 2016.
|
|
104
|
Nelson WG, DeWeese TL and DeMarzo AM: The
diet, prostate inflammation, and the development of prostate
cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 21:3–16. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Marshall JR: Diet and prostate cancer
prevention. World J Urol. 30:157–165. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Karatas OF, Wang J, Shao L, Ozen M, Zhang
Y, Creighton CJ and Ittmann M: miR-33a is a tumor suppressor
microRNA that is decreased in prostate cancer. Oncotarget.
8:60243–60256. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Li Q, Lu S, Li X, Hou G, Yan L, Zhang W
and Qiao B: Biological function and mechanism of miR-33a in
prostate cancer survival and metastasis: Via downregulating
Engrailed-2. Clin Transl Oncol. 19:562–570. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Dai Y, Wu Z, Lang C, Zhang X, He S, Yang
Q, Guo W, Lai Y, Du H, Peng X and Ren D: Copy number gain of ZEB1
mediates a double-negative feedback loop with miR-33a-5p that
regulates EMT and bone metastasis of prostate cancer dependent on
TGF-β signaling. Theranostics. 9:6063–6079. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Hong W and Dong E: The past, present and
future of breast cancer research in China. Cancer Lett. 351:1–5.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Shield KD, Soerjomataram I and Rehm J:
Alcohol use and breast cancer: A critical review. Alcohol Clin Exp
Res. 40:1166–1181. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Liang J and Shang Y: Estrogen and cancer.
Annu Rev Physiol. 75:225–240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Zhang C, Zhang Y, Ding W, Lin Y, Huang Z
and Luo Q: MiR-33a suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation and
metastasis by targeting ADAM9 and ROS1. Protein Cell. 6:881–889.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Wolfe AR, Bambhroliya A, Reddy JP, Debeb
BG, Huo L, Larson R, Li L, Ueno NT and Woodward WA: MiR-33a
decreases high-density lipoprotein-induced radiation sensitivity in
breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 95:791–799. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Zeng W, Zuo G, Cao X and Li W: MiR-33a
functions as a tumor suppressor in triple-negative breast cancer by
targeting EZH2. Cancer Cell Int. 20:852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Guan X, Gu S, Yuan M, Zheng X and Wu J:
MicroRNA-33a-5p overexpression sensitizes triple-negative breast
cancer to doxorubicin by inhibiting eIF5A2 and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Lett. 18:5986–5994.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Jang JS, Jeon HS, Sun Z, Aubry MC, Tang H,
Park CH, Rakhshan F, Schultz DA, Kolbert CP, Lupu R, et al:
Increased miR-708 expression in NSCLC and its association with poor
survival in lung adenocarcinoma from never smokers. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:3658–3667. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Wu X, Liu T, Fang O, Dong W, Zhang F,
Leach L, Hu X and Luo Z: MicroRNA-708-5p acts as a therapeutic
agent against metastatic lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:2417–2432.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V, Barker N,
Clevers H, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: Activation of
beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in
beta-catenin or APC. Science. 275:1787–1790. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Zheng S, Zhang X, Wang X and Li J: MIR31HG
promotes cell proliferation and invasion by activating the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncol Lett. 17:221–229. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Zheng M, Jiang YP, Chen W, Li KD, Liu X,
Gao SY, Feng H, Wang SS, Jiang J, Ma XR, et al: Snail and Slug
collaborate on EMT and tumor metastasis through miR-101-mediated
EZH2 axis in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget.
6:6797–6810. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Buehler D, Hardin H, Shan W,
Montemayor-Garcia C, Rush PS, Asioli S, Chen H and Lloyd RV:
Expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulators SNAI2
and TWIST1 in thyroid carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 26:54–61. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Cao YW, Wan GX, Sun JP, Cui XB, Hu JM,
Liang WH, Zheng YQ, Li WQ and Li F: Implications of the
Notch1-Snail/Slug-epithelial to mesenchymal transition axis for
lymph node metastasis in infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Kaohsiung J
Med Sci. 31:70–76. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Carreras-Torres R, Johansson M, Gaborieau
V, Haycock PC, Wade KH, Relton CL, Martin RM, Davey Smith G and
Brennan P: The role of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic
factors in pancreatic cancer: A mendelian randomization study. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 109:djx0122017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Ercin M, Sancar-Bas S, Bolkent S and
Gezginci-Oktayoglu S: Tub and β-catenin play a key role in insulin
and leptin resistance-induced pancreatic beta-cell differentiation.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1865:1934–1944. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Wijesekara N, Zhang LH, Kang MH, Abraham
T, Bhattacharjee A, Warnock GL, Verchere CB and Hayden MR: miR-33a
modulates ABCA1 expression, cholesterol accumulation, and insulin
secretion in pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 61:653–658. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Lekmine F, Uddin S, Sassano A, Parmar S,
Brachmann SM, Majchrzak B, Sonenberg N, Hay N, Fish EN and
Platanias LC: Activation of the p70 S6 kinase and phosphorylation
of the 4E-BP1 repressor of mRNA translation by type I interferons.
J Biol Chem. 278:27772–27780. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Xia P and Xu XY: PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling
pathway in cancer stem cells: From basic research to clinical
application. Am J Cancer Res. 5:1602–1609. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Yu JS and Cui W: Proliferation, survival
and metabolism: The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in
pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development.
143:3050–3060. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Yip PY: Phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase-AKT-mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K-Akt-mTOR)
signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer
Res. 4:165–176. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Fournier PG, Juárez P, Jiang G, Clines GA,
Niewolna M, Kim HS, Walton HW, Peng XH, Liu Y, Mohammad KS, et al:
The TGF-β signaling regulator PMEPA1 suppresses prostate cancer
metastases to bone. Cancer Cell. 27:809–821. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Feng J, Yan PF, Zhao HY, Zhang FC, Zhao WH
and Feng M: SIRT6 suppresses glioma cell growth via induction of
apoptosis, inhibition of oxidative stress and suppression of
JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway activation. Oncol Rep. 35:1395–1402.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Liu SC, Huang CM, Bamodu OA, Lin CS, Liu
BL, Tzeng YM, Tsai JT, Lee WH and Chen TM: Ovatodiolide suppresses
nasopharyngeal cancer by targeting stem cell-like population,
inducing apoptosis, inhibiting EMT and dysregulating JAK/STAT
signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 56:269–278. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Liu K, Tian T, Zheng Y, Zhou L, Dai C,
Wang M, Lin S, Deng Y, Hao Q, Zhai Z and Dai Z: Scutellarin
inhibits proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells via down-regulation of JAK2/STAT3 pathway. J Cell Mol Med.
23:3040–3044. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Tang J, Xu J, Zhi Z, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhou
Y and Chen R: MiR-876-3p targets KIF20A to block JAK2/STAT3 pathway
in glioma. Am J Transl Res. 11:4957–4966. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Tanabe K, Kozawa O and Iida H: cAMP/PKA
enhances interleukin-1β-induced interleukin-6 synthesis through
STAT3 in glial cells. Cell Signal. 28:19–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Liu M, Inoue K, Leng T, Guo S and Xiong
ZG: TRPM7 channels regulate glioma stem cell through STAT3 and
Notch signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 26:2773–2781. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Xie RT, Cong XL, Zhong XM, Luo P, Yang HQ,
Lu GX, Luo P, Chang ZY, Sun R, Wu TM, et al: MicroRNA-33a
downregulation is associated with tumorigenesis and poor prognosis
in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
15:4571–4577. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Hou LK, Ma YS, Han Y, Lu GX, Luo P, Chang
ZY, Xie RT, Yang HQ, Chai L, Cai MX, et al: Association of
microRNA-33a molecular signature with non-small cell lung cancer
diagnosis and prognosis after chemotherapy. PLoS One.
12:e01704312017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Pan J, Zhou C, Zhao X, He J, Tian H, Shen
W, Han Y, Chen J, Fang S, Meng X, et al: A two-miRNA signature
(miR-33a-5p and miR-128-3p) in whole blood as potential biomarker
for early diagnosis of lung cancer. Sci Rep. 8:166992018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Kandimalla R, Gao F, Matsuyama T, Ishikawa
T, Uetake H, Takahashi N, Yamada Y, Becerra C, Kopetz S, Wang X and
Goel A: Genome-wide discovery and identification of a novel miRNA
signature for recurrence prediction in stage II and III colorectal
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 24:3867–3877. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Ma Y, Zhou G, Li M, Hu D, Zhang L, Liu P
and Lin K: Long noncoding RNA DANCR mediates cisplatin resistance
in glioma cells via activating AXL/PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling
pathway. Neurochem Int. 118:233–241. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|