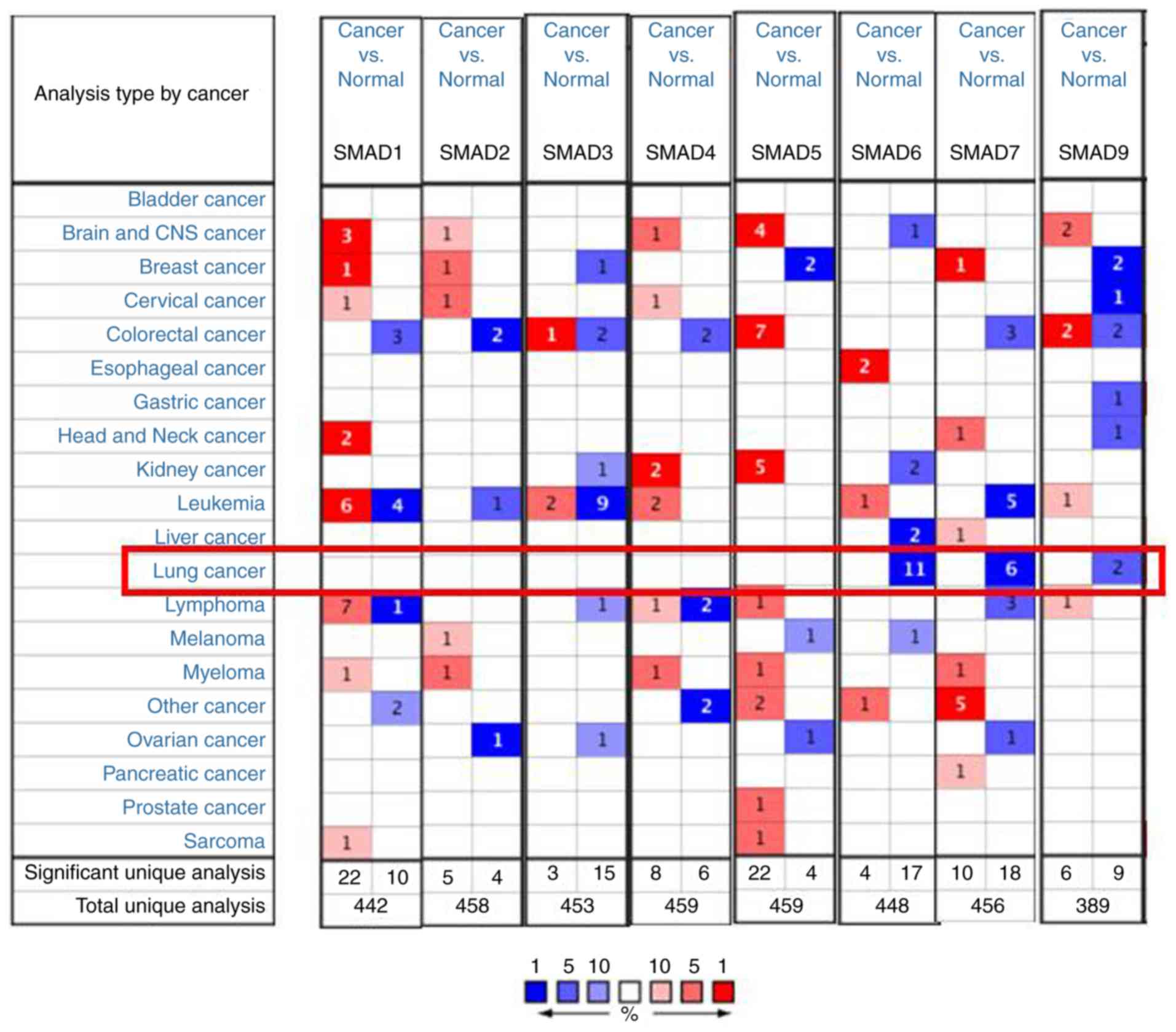
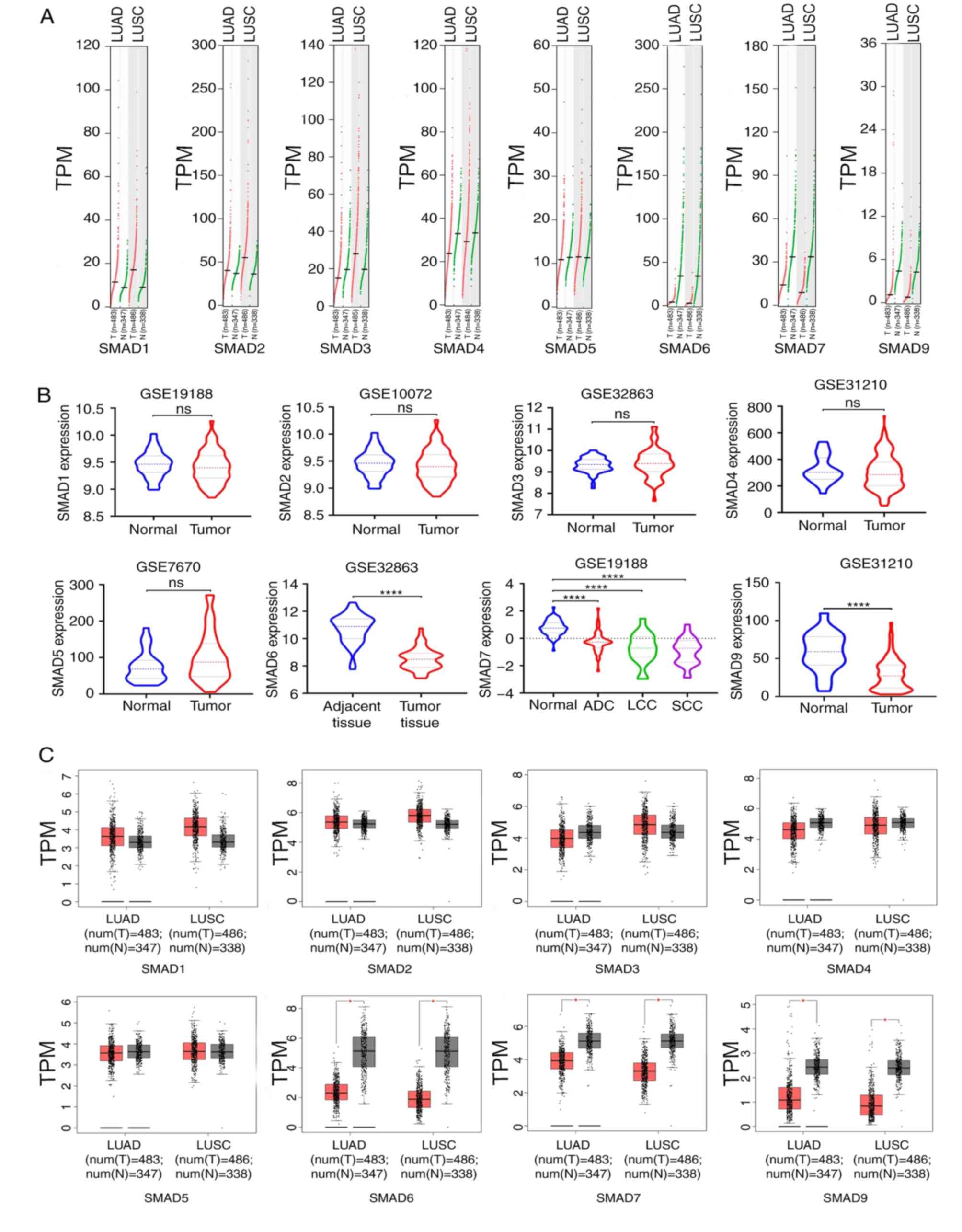
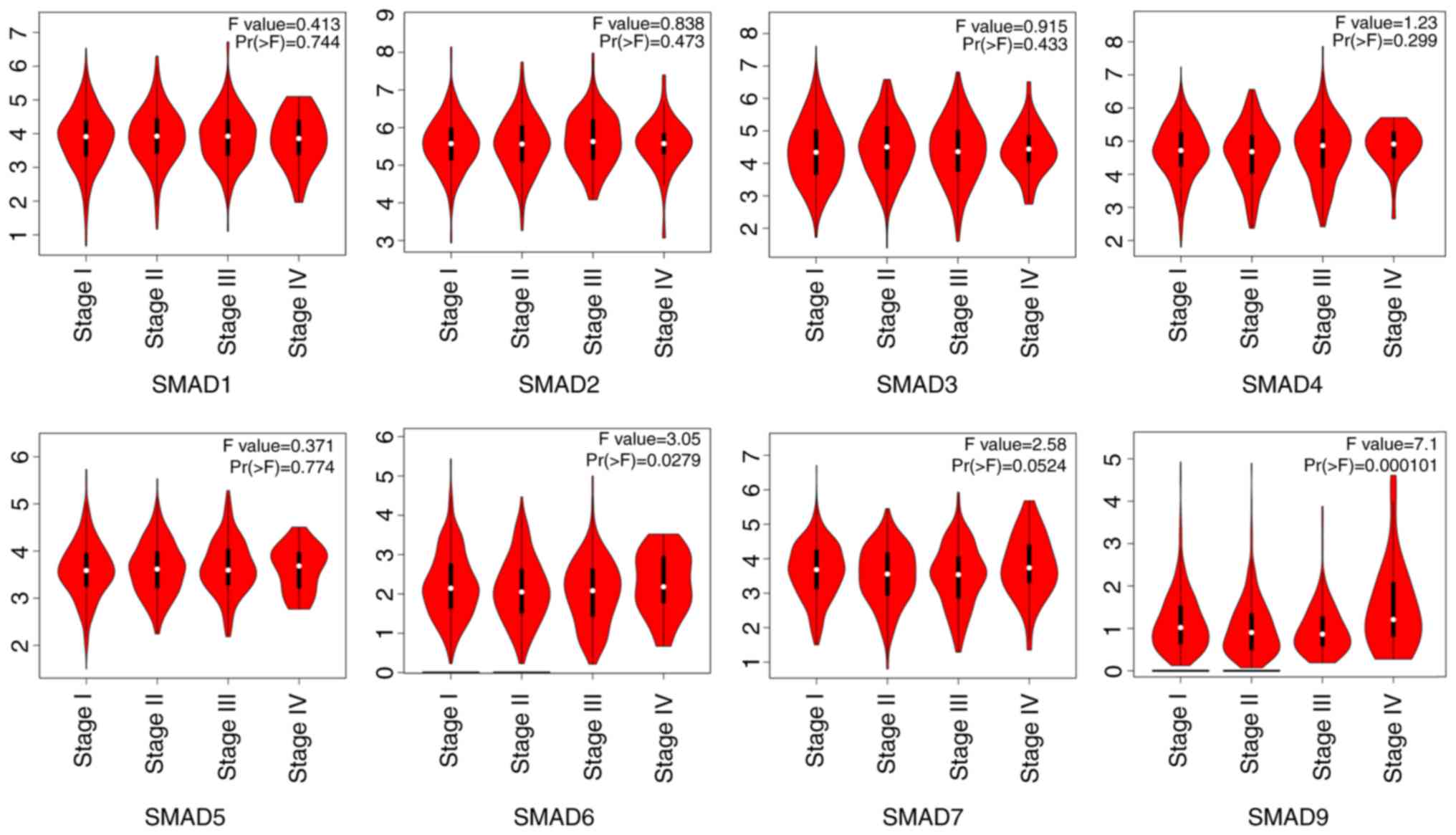
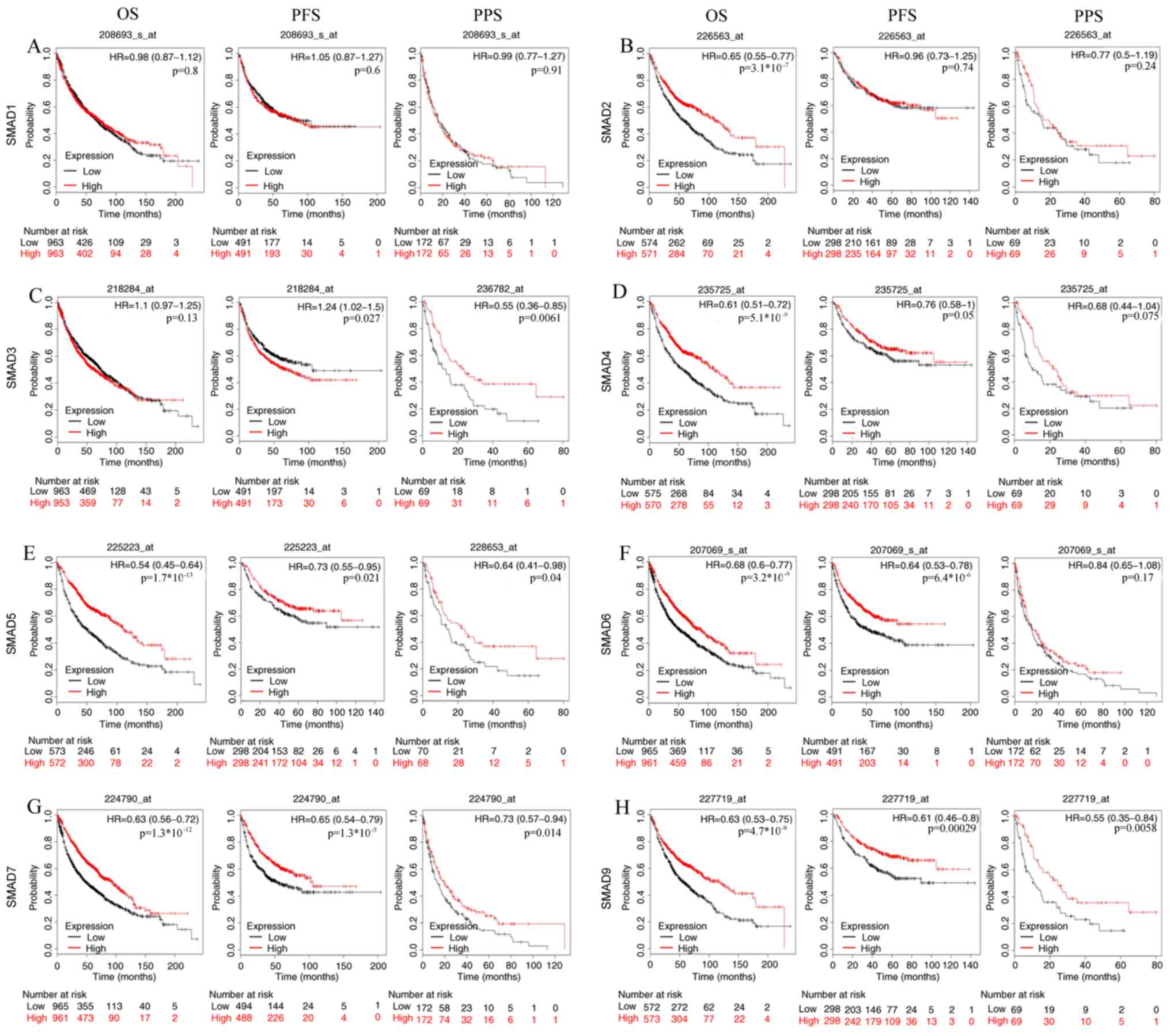
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weller DP, Peake MD and Field JK:
Presentation of lung cancer in primary care. NPJ Prim Care Respir
Med. 29:212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao Y, Wang W, Liang H, Yang CJ, D'Amico
T, Ng CSH, Liu CC, Petersen RH, Rocco G, Brunelli A, et al: The
optimal treatment for stage IIIA-N2 non-small cell lung cancer: A
network meta-analysis. Ann Thorac Surg. 107:1866–1875. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Budi EH, Duan D and Derynck R:
Transforming growth factor-β receptors and smads: Regulatory
complexity and functional versatility. Trends Cell Biol.
27:658–672. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Luo K: signaling cross talk between
TGF-β/Smad and other signaling pathways. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 9:a0221372017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yu Y and Feng XH: TGF-β signaling in cell
fate control and cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 61:56–63. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kamato D, Do BH, Osman N, Ross BP, Mohamed
R, Xu S and Little PJ: Smad linker region phosphorylation is a
signalling pathway in its own right and not only a modulator of
canonical TGF-β signalling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:243–251. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Silvestri L, Nai A, Dulja A and Pagani A:
Hepcidin and the BMP-SMAD pathway: An unexpected liaison. Vitam
Horm. 110:71–99. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dai J, Xu M, Zhang X, Niu Q, Hu Y, Li Y
and Li S: Bi-directional regulation of TGF-β/Smad pathway by
arsenic: A systemic review and meta-analysis of in vivo and in
vitro studies. Life Sci. 220:92–105. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eckhardt BL, Cao Y, Redfern AD, Chi LH,
Burrows AD, Roslan S, Sloan EK, Parker BS, Loi S, Ueno NT, et al:
Activation of canonical BMP4-SMAD7 signaling suppresses breast
cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 80:1304–1315. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lang C, Dai Y, Wu Z, Yang Q, He S, Zhang
X, Guo W, Lai Y, Du H, Wang H, et al: SMAD3/SP1 complex-mediated
constitutive active loop between lncRNA PCAT7 and TGF-β signaling
promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis. Mol Oncol. 14:808–828.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Zeng Y, Liu T, Du W, Zhu J, Liu Z
and Huang JA: The canonical TGF-β/Smad signalling pathway is
involved in PD-L1-induced primary resistance to EGFR-TKIs in
EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Respir Res. 20:1642019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tuncer E, Calcada RR, Zingg D, Varum S,
Cheng P, Freiberger SN, Deng CX, Kleiter I, Levesque MP, Dummer R
and Sommer L: SMAD signaling promotes melanoma metastasis
independently of phenotype switching. J Clin Invest. 129:2702–2716.
2019. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jung M, Lee JH, Lee C, Park JH, Park YR
and Moon KC: Prognostic implication of pAMPK immunohistochemical
staining by subcellular location and its association with SMAD
protein expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancers
(Basel). 11:16022019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Leng Z, Li Y, Zhou G, Lv X, Ai W, Li J and
Hou L: Krüppel-like factor 4 regulates stemness and mesenchymal
properties of colorectal cancer stem cells through the
TGF-β1/Smad/snail pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 24:1866–1877. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bai Y, Li LD, Li J, Chen RF, Yu HL, Sun
HF, Wang JY and Lu X: A FXYD5/TGF-β/SMAD positive feedback loop
drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and promotes tumor
growth and metastasis in ovarian cancer. Int J Oncol. 56:301–314.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen J, Deng Y, Ao L, Song Y, Xu Y, Wang
CC, Choy KW, Tony Chung KH, Du Q, Sui Y, et al: The high-risk HPV
oncogene E7 upregulates miR-182 expression through the TGF-β/Smad
pathway in cervical cancer. Cancer Lett. 460:75–85. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu CW, Li CH, Peng YJ, Cheng YW, Chen HW,
Liao PL, Kang JJ and Yeng MH: Snail regulates Nanog status during
the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Smad1/Akt/GSK3β
signaling pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget.
5:3880–3894. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang D, Ma M, Zhou W, Yang B and Xiao C:
Inhibition of miR-32 activity promoted EMT induced by PM2.5
exposure through the modulation of the Smad1-mediated signaling
pathways in lung cancer cells. Chemosphere. 184:289–298. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tang YN, Ding WQ, Guo XJ, Yuan XW, Wang DM
and Song JG: Epigenetic regulation of Smad2 and Smad3 by profilin-2
promotes lung cancer growth and metastasis. Nat Commun. 6:82302015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Q, Xiao M, Gu S, Xu Y, Liu T, Li H,
Yu Y, Qin L, Zhu Y, Chen F, et al: ALK phosphorylates SMAD4 on
tyrosine to disable TGF-β tumour suppressor functions. Nat Cell
Biol. 21:179–189. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rao G, Pierobon M, Kim IK, Hsu WH, Deng J,
Moon YW, Petricoin EF, Zhang YW, Wang Y and Giaccone G: Inhibition
of AKT1 signaling promotes invasion and metastasis of non-small
cell lung cancer cells with K-RAS or EGFR mutations. Sci Rep.
7:70662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu J, Lei R, Zhuang X, Li X, Li G, Lev S,
Segura MF, Zhang X and Hu G: MicroRNA-182 targets SMAD7 to
potentiate TGFβ-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
metastasis of cancer cells. Nat Commun. 7:138842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu W, Ouyang S, Zhou Z, Wang M, Wang T,
Qi Y, Zhao C, Chen K and Dai L: Identification of genes associated
with cancer progression and prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma:
Analyses based on microarray from oncomine and the cancer genome
atlas databases. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 7:e005282019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Beer DG, Kardia SL, Huang CC, Giordano TJ,
Levin AM, Misek DE, Lin L, Chen G, Gharib TG, Thomas DG, et al:
Gene-expression profiles predict survival of patients with lung
adenocarcinoma. Nat Med. 8:816–824. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Garber ME, Troyanskaya OG, Schluens K,
Petersen S, Thaesler Z, Pacyna-Gengelbach M, van de Rijn M, Rosen
GD, Perou CM, Whyte RI, et al: Diversity of gene expression in
adenocarcinoma of the lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:13784–13789.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yamagata N, Shyr Y, Yanagisawa K, Edgerton
M, Dang TP, Gonzalez A, Nadaf S, Larsen P, Roberts JR, Nesbitt JC,
et al: A training-testing approach to the molecular classification
of resected non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
9:4695–4704. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pei YF, Xu XN, Wang ZF, Wang FW, Wu WD,
Geng JF and Liu XQ: Methyl-CpG binding domain protein 2 inhibits
the malignant characteristic of lung adenocarcinoma through the
epigenetic modulation of 10 to 11 translocation 1 and miR-200s. Am
J Pathol. 189:1065–1076. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Loraine AE, Blakley IC, Jagadeesan S,
Harper J, Miller G and Firon N: Analysis and visualization of
RNA-Seq expression data using RStudio, bioconductor, and integrated
genome browser. Methods Mol Biol. 1284:481–501. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Benso A, Di Carlo S, Politano G, Savino A
and Hafeezurrehman H: Building gene expression profile classifiers
with a simple and efficient rejection option in R. BMC
Bioinformatics. 12 (Suppl 13):S32011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leek JT, Johnson WE, Parker HS, Jaffe AE
and Storey JD: The sva package for removing batch effects and other
unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics.
28:882–883. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45 (W1).
W98–W102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Israel Y, Rachmiel A, Gourevich K and
Nagler R: Kaplan-Meier analysis of salivary gland tumors: Prognosis
and long-term survival. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 145:2123–2130.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim J: Drawing guideline for JKMS
manuscript (01) Kaplan-Meier curve and survival analysis. J Korean
Med Sci. 34:e352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun CC, Zhou Q, Hu W, Li SJ, Zhang F, Chen
ZL, Li G, Bi ZY, Bi YY, Gong FY, et al: Transcriptional E2F1/2/5/8
as potential targets and transcriptional E2F3/6/7 as new biomarkers
for the prognosis of human lung carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY).
10:973–987. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Unberath P, Knell C, Prokosch HU and
Christoph J: Developing new analysis functions for a translational
research platform: Extending the cBioPortal for cancer genomics.
Stud Health Technol Inform. 258:46–50. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tarca AL, Romero R, Erez O, Gudicha DW,
Than NG, Benshalom-Tirosh N, Pacora P, Hsu CD, Chaiworapongsa T,
Hassan SS and Gomez-Lopez N: Maternal whole blood mRNA signatures
identify women at risk of early preeclampsia: A longitudinal study.
J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 1–12. 2020.(Online ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li B and Dewey CN: RSEM: Accurate
transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a
reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics. 12:3232011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Selamat SA, Chung BS, Girard L, Zhang W,
Zhang Y, Campan M, Siegmund KD, Koss MN, Hagen JA, Lam WL, et al:
Genome-scale analysis of DNA methylation in lung adenocarcinoma and
integration with mRNA expression. Genome Res. 22:1197–1211. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bhattacharjee A, Richards WG, Staunton J,
Li C, Monti S, Vasa P, Ladd C, Beheshti J, Bueno R, Gillette M, et
al: Classification of human lung carcinomas by mRNA expression
profiling reveals distinct adenocarcinoma subclasses. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:13790–13795. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Okayama H, Kohno T, Ishii Y, Shimada Y,
Shiraishi K, Iwakawa R, Furuta K, Tsuta K, Shibata T, Yamamoto S,
et al: Identification of genes upregulated in ALK-positive and
EGFR/KRAS/ALK-negative lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res.
72:100–111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rami-Porta R, Asamura H, Travis WD and
Rusch VW: Lung cancer-major changes in the American joint committee
on cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin.
67:138–155. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gurrapu S, Franzolin G, Fard D, Accardo M,
Medico E, Sarotto I, Sapino A, Isella C and Tamagnone L: Reverse
signaling by semaphorin 4C elicits SMAD1/5- and ID1/3-dependent
invasive reprogramming in cancer cells. Sci Signal.
12:eaav20412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Girolami I, Veronese N, Smith L, Caruso
MG, Reddavide R, Leandro G, Demurtas J and Nottegar A: The
activation status of the TGF-β transducer Smad2 is associated with
a reduced survival in gastrointestinal cancers: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 20:38312019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Liang C, Xu J, Meng Q, Zhang B, Liu J, Hua
J, Zhang Y, Shi S and Yu X: TGFB1-induced autophagy affects the
pattern of pancreatic cancer progression in distinct ways depending
on SMAD4 status. Autophagy. 16:486–500. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jeon HS, Dracheva T, Yang SH, Meerzaman D,
Fukuoka J, Shakoori A, Shilo K, Travis WD and Jen J: SMAD6
contributes to patient survival in non-small cell lung cancer and
its knockdown reestablishes TGF-beta homeostasis in lung cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 68:9686–9692. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ma L, Jiang H, Xu X, Zhang C, Niu Y, Wang
Z, Tao Y, Li Y, Cai F, Zhang X, et al: Tanshinone IIA mediates
SMAD7-YAP interaction to inhibit liver cancer growth by
inactivating the transforming growth factor beta signaling pathway.
Aging (Albany NY). 11:9719–9737. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Karmokar PF, Asaduzzaman M, Islam MS,
Shahriar M and Shabnaz S: The influence of SMAD1 gene polymorphisms
on colorectal cancer susceptibility in Bangladeshi population: A
case-control study. FEBS Open Bio. 8:3402018.
|
|
49
|
Cheng M, Jiang Y, Yang H, Zhao D, Li L and
Liu X: FLNA promotes chemoresistance of colorectal cancer through
inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and smad2 signaling
pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 10:403–423. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tone AA, McConechy MK, Yang W, Ding J, Yip
S, Kong E, Wong KK, Gershenson DM, Mackay H, Shah S, et al:
Intratumoral heterogeneity in a minority of ovarian low-grade
serous carcinomas. BMC Cancer. 14:9822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Opyrchal M, Gil M, Salisbury JL, Goetz MP,
Suman V, Degnim A, McCubrey J, Haddad T, Iankov I, Kurokawa CB, et
al: Molecular targeting of the Aurora-A/SMAD5 oncogenic axis
restores chemosensitivity in human breast cancer cells. Oncotarget.
8:91803–91816. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ryu TY, Kim K, Kim SK, Oh JH, Min JK, Jung
CR, Son MY, Kim DS and Cho HS: SETDB1 regulates SMAD7 expression
for breast cancer metastasis. BMB Rep. 52:139–144. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gao YQ, Liu M and Zhang H: Expression
profiles of Smad1 protein in lung cancer tissues and normal tissues
and its effect on lung cancer incidence. J Biol Regul Homeost
Agents. 30:165–171. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chae DK, Ban E, Yoo YS, Kim EE, Baik JH
and Song EJ: MIR-27a regulates the TGF-β signaling pathway by
targeting SMAD2 and SMAD4 in lung cancer. Mol Carcinog.
56:1992–1998. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sun W, Ma Y, Chen P and Wang D:
MicroRNA-10a silencing reverses cisplatin resistance in the
A549/cisplatin human lung cancer cell line via the transforming
growth factor-β/Smad2/STAT3/STAT5 pathway. Mol Med Rep.
11:3854–3859. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang Z, Lu Y, Sheng B, Ding Y and Cheng X:
Catalpol inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in human non-small-cell lung cancer cells through the inactivation
of Smad2/3 and NF-κB signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem. Sep
11–2018.(Online ahead of print).
|
|
57
|
Wei Y, Li D, Wang D, Qiu T and Liu K:
WITHDRAWN: Evaluation of microRNA-203 in bone metastasis of
patients with non-small cell lung cancer through TGF-β/SMAD2
expression. Oncol Rep. Sep 21–2017.(Online ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Zhang JX, Zhai JF, Yang XT and Wang J:
MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in
human non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
20:3793–3801. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chen Y, Xing P, Chen Y, Zou L, Zhang Y, Li
F and Lu X: High p-Smad2 expression in stromal fibroblasts predicts
poor survival in patients with clinical stage I to IIIA non-small
cell lung cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 12:3282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Qian Z, Zhang QK, Hu Y, Zhang T, Li J, Liu
Z, Zheng H, Gao Y, Jia W, Hu A, et al: Investigating the mechanism
by which SMAD3 induces PAX6 transcription to promote the
development of non-small cell lung cancer. Respir Res. 19:2622018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ziemke M, Patil T, Nolan K, Tippimanchai D
and Malkoski SP: Reduced Smad4 expression and DNA topoisomerase
inhibitor chemosensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung
Cancer. 109:28–35. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chen H, Wang JW, Liu LX, Yan JD, Ren SH,
Li Y and Lu Z: Expression and significance of transforming growth
factor-β receptor type II and DPC4/Smad4 in non-small cell lung
cancer. Exp Ther Med. 9:227–231. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
D'Haene N, Le Mercier M, Salmon I, Mekinda
Z, Remmelink M and Berghmans T: SMAD4 mutation in small cell
transformation of epidermal growth factor receptor mutated lung
adenocarcinoma. Oncologist. 24:9–13. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Haeger SM, Thompson JJ, Kalra S, Cleaver
TG, Merrick D, Wang XJ and Malkoski SP: Smad4 loss promotes lung
cancer formation but increases sensitivity to DNA topoisomerase
inhibitors. Oncogene. 35:577–586. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zeng YY, Zhu JJ, Shen D, Qin H, Lei Z, Li
W, Liu Z and Huang JA: MicroRNA-205 targets SMAD4 in non-small cell
lung cancer and promotes lung cancer cell growth in vitro and in
vivo. Oncotarget. 8:30817–30829. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Takahashi K, Nishikawa S, Miyata R,
Noguchi M, Ishikawa H, Yutaka Y, Nakajima D, Hamaji M, Ohsumi A,
Menju T, et al: Tranilast inhibits TGF-beta-induced EMT and
invasion/metastasis via the suppression of smad4 in lung cancer
cell lines. Ann Oncol 29:. (Suppl 8):viii1–viii13. 2018.
|
|
67
|
Lee CC, Yang WH, Li CH, Cheng YW, Tsai CH
and Kang JJ: Ligand independent aryl hydrocarbon receptor inhibits
lung cancer cell invasion by degradation of Smad4. Cancer Lett.
376:211–217. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yanagisawa K, Uchida K, Nagatake M, Masuda
A, Sugiyama M, Saito T, Yamaki K, Takahashi T and Osada H:
Heterogeneities in the biological and biochemical functions of
Smad2 and Smad4 mutants naturally occurring in human lung cancers.
Oncogene. 19:2305–2311. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang Z, Wang J, Zeng X, Li D, Ding M,
Guan R, Yuan L, Zhou Q, Guo M, Xiong M, et al: Two-stage study of
lung cancer risk modification by a functional variant in the
3′-untranslated region of SMAD5 based on the bone morphogenetic
protein pathway. Mol Clin Oncol. 8:38–46. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ngeow J, Yu W, Yehia L, Niazi F, Chen J,
Tang X, Heald B, Lei J, Romigh T, Tucker-Kellogg L, et al: Exome
sequencing reveals germline SMAD9 mutation that reduces phosphatase
and tensin homolog expression and is associated with hamartomatous
polyposis and gastrointestinal ganglioneuromas. Gastroenterology.
149:886–889 e5. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhang Q, Gan H, Song W, Chai D and Wu S:
MicroRNA-145 promotes esophageal cancer cells proliferation and
metastasis by targeting SMAD5. Scand J Gastroenterol. 53:769–776.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Shi JQ, Wang B, Cao XQ, Wang YX, Cheng X,
Jia CL, Wen T, Luo BJ and Liu ZD: Circular RNA_LARP4 inhibits the
progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by regulating the
expression of SMAD7. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:1863–1869.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Jin L, Zhu C, Wang X, Li C, Cao C, Yuan J
and Li S: Urocortin attenuates TGFβ1-induced Snail1 and slug
expressions: Inhibitory role of Smad7 in Smad2/3 signaling in
breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 116:2494–2503. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|