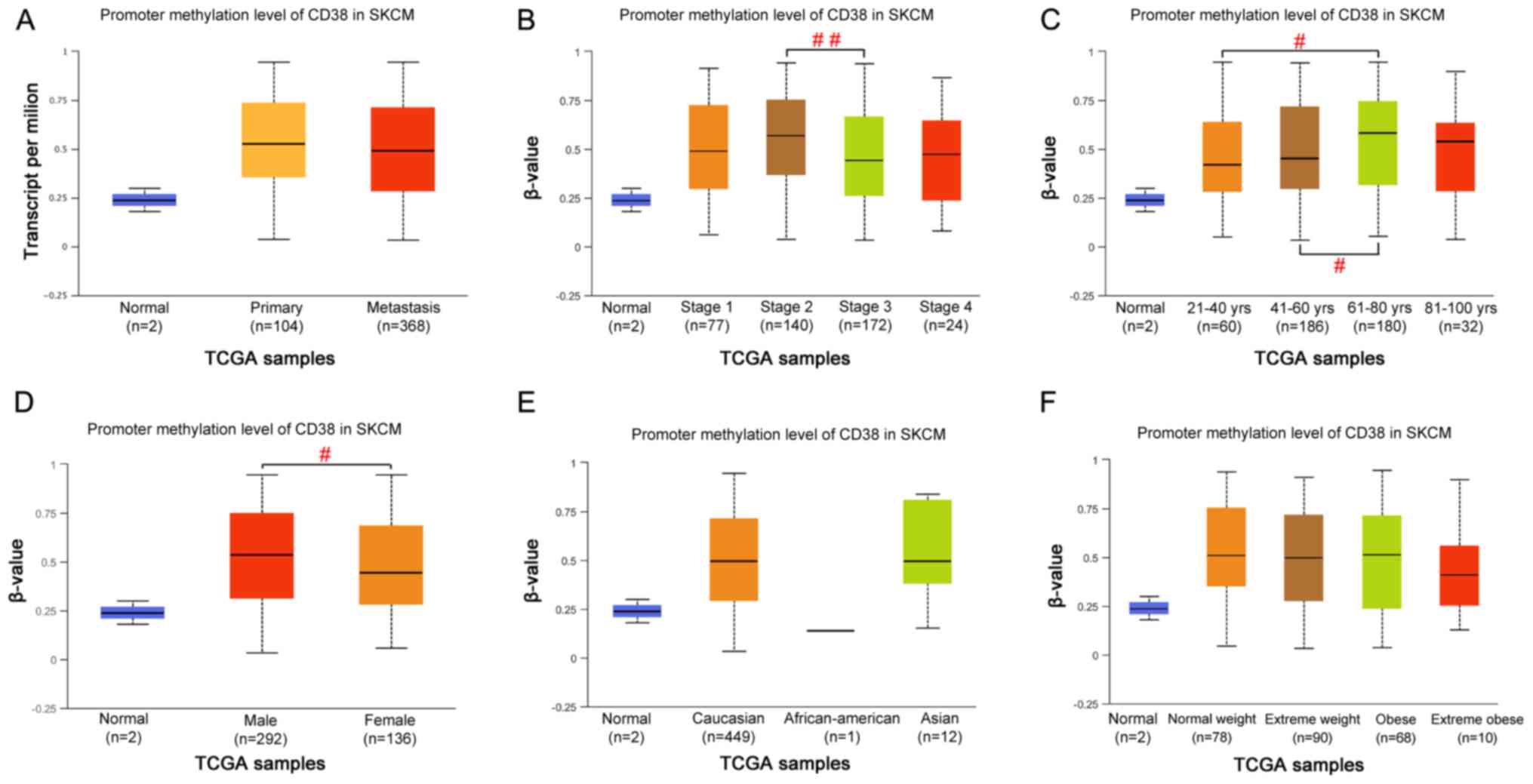
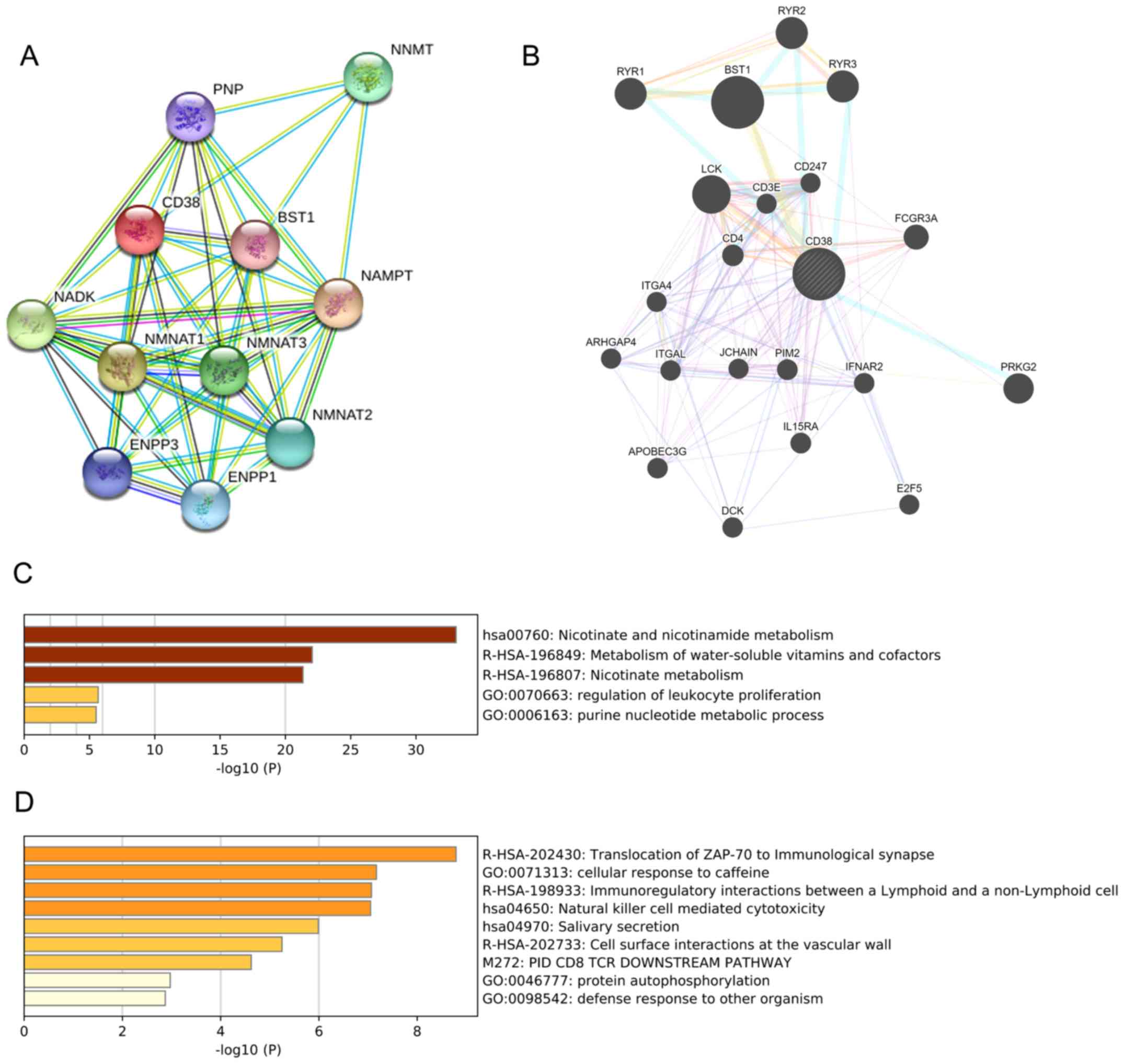
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khunger A, Buchwald ZS, Lowe M, Khan MK,
Delman KA and Tarhini AA: Neoadjuvant therapy of locally/regionally
advanced melanoma. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 11:17588359198669592019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Krayem M, Sabbah M, Najem A, Wouters A,
Lardon F, Simon S, Sales F, Journe F, Awada A, Ghanem GE and Van
Gestel D: The benefit of reactivating p53 under MAPK inhibition on
the efficacy of radiotherapy in melanoma. Cancers (Basel).
11:10932019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dummer R, Siano M, Hunger RE, Lindenblatt
N, Braun R, Michielin O, Mihic-Probst D, von Moos R, Najafi Y,
Guckenberger M and Arnold A: The updated Swiss guidelines 2016 for
the treatment and follow-up of cutaneous melanoma. Swiss Med Wkly.
146:w142792016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee EH, Lim SJ and Lee MK: Chitosan-coated
liposomes to stabilize and enhance transdermal delivery of
indocyanine green for photodynamic therapy of melanoma. Carbohydr
Polym. 224:1151432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shi L, Liu P, Wu J, Ma L, Zheng H, Antosh
MP, Zhang H, Wang B, Chen W and Wang X: The effectiveness and
safety of X-PDT for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma.
Nanomedicine (Lond). 14:2027–2043. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network, . Genomic
classification of cutaneous melanoma. Cell. 161:1681–1696. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Q, Pan F, Li S, Huang R, Wang X, Wang
S, Liao X, Li D and Zhang L: The prognostic value of the proteasome
activator subunit gene family in skin cutaneous melanoma. J Cancer.
10:2205–2219. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Q, Wang X, Liang Q, Wang S, Xiwen L,
Pan F, Chen H and Li D: Distinct prognostic value of mRNA
expression of guanylate-binding protein genes in skin cutaneous
melanoma. Oncol Lett. 15:7914–7922. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiong J, Bing Z and Guo S: Observed
survival interval: A supplement to TCGA pan-cancer clinical data
resource. Cancers (Basel). 11:2802019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang X, Song J, Wu Z, Fan B and Mode X:
Dual roles of CD38 in autophagy. Yangtze Medicine. 01:8–19. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
O'Steen S, Comstock ML, Orozco JJ, Hamlin
DK, Wilbur DSS, Jones JC, Kenoyer A, Nartea ME, Lin Y, Miller BW,
et al: The α-Emitter astatine-211 targeted to CD38 can eradicate
multiple myeloma in a disseminated disease model. Blood.
134:1247–1256. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ben Baruch B, Blacher E, Mantsur E,
Schwartz H, Vaknine H, Erez N and Stein R: Stromal CD38 regulates
outgrowth of primary melanoma and generation of spontaneous
metastasis. Oncotarget. 9:31797–31811. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Morandi F, Marimpietri D, Horenstein AL,
Corrias MV and Malavasi F: Microvesicles expressing adenosinergic
ectoenzymes and their potential role in modulating bone marrow
infiltration by neuroblastoma cells. Oncoimmunology.
8:e15741982019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schutze K, Petry K, Hambach J, Schuster N,
Fumey W, Schriewer L, Rockendorf J, Menzel S, Albrecht B, Haag F,
et al: CD38-Specific biparatopic heavy chain antibodies display
potent complement-dependent cytotoxicity against multiple myeloma
cells. Front Immunol. 9:25532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu T, Qiao C, Lv M and Tang L: Novel
anti-CD38 humanized mAb SG003 possessed enhanced cytotoxicity in
lymphoma than Daratumumab via antibody-dependent cell-mediated
cytotoxicity. BMC Biotechnol. 19:282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Peng X, Zhang X, Xu H, Lu C, Liu
L, Song J and Zhang Y: The emerging roles of CIB1 in cancer. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 43:1413–1424. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Morandi F, Morandi B, Horenstein AL,
Chillemi A, Quarona V, Zaccarello G, Carrega P, Ferlazzo G, Mingari
MC, Moretta L, et al: A non-canonical adenosinergic pathway led by
CD38 in human melanoma cells induces suppression of T cell
proliferation. Oncotarget. 6:25602–25618. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene
expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45(W1):
W98–W102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43((Database Issue)): D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Franz M, Rodriguez H, Lopes C, Zuberi K,
Montojo J, Bader GD and Morris Q: GeneMANIA update 2018. Nucleic
Acids Res. 46(W1): W60–W64. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M,
Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C and Chanda SK: Metascape
provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of
systems-level datasets. Nat Commun. 10:15232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Selitsky SR, Mose LE, Smith CC, Chai S,
Hoadley KA, Dittmer DP, Moschos SJ, Parker JS and Vincent BG:
Prognostic value of B cells in cutaneous melanoma. Genome Med.
11:362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guan J, Gupta R and Filipp FV: Cancer
systems biology of TCGA SKCM: Efficient detection of genomic
drivers in melanoma. Sci Rep. 5:78572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Harcharik S, Bernardo S, Moskalenko M, Pan
M, Sivendran M, Bell H, Hall LD, Castillo-Martin M, Fox K,
Cordon-Cardo C, et al: Defining the role of CD2 in disease
progression and overall survival among patients with completely
resected stage-II to -III cutaneous melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol.
70:1036–1044. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hyams DM, Cook RW and Buzaid AC:
Identification of risk in cutaneous melanoma patients: Prognostic
and predictive markers. J Surg Oncol. 119:175–186. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
van de Donk NWCJ, Richardson PG and
Malavasi F: CD38 antibodies in multiple myeloma: Back to the
future. Blood. 131:13–29. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu Q, Graeff R, Kriksunov IA, Lam CM, Lee
HC and Hao Q: Conformational closure of the catalytic site of human
CD38 induced by calcium. Biochemistry. 47:13966–13973. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brazill JM, Li C, Zhu Y and Zhai RG:
NMNAT: It's an NAD+ synthase. It's a chaperone. It's a
neuroprotector. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 44:156–162. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shen YT, Wang JW, Wang M, Zhi Y, Li JY,
Yuan YS, Wang XX, Zhang H and Zhang KZ: BST1 rs4698412 allelic
variant increases the risk of gait or balance deficits in patients
with Parkinson's disease. CNS Neurosci Ther. 25:422–429. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ceroni F, Sagar A, Simpson NH, Gawthrope
AJ, Newbury DF, Pinto D, Francis SM, Tessman DC, Cook EH, Monaco
AP, et al: A deletion involving CD38 and BST1 results in a fusion
transcript in a patient with autism and asthma. Autism Res.
7:254–263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vendrell E, Ribas M, Valls J, Sole X, Grau
M, Moreno V, Capella G and Peinado MA: Genomic and transcriptomic
prognostic factors in R0 Dukes B and C colorectal cancer patients.
Int J Oncol. 30:1099–1107. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xie W, Stopsack KH, Drouin SJ, Fu H,
Pomerantz MM, Mucci LA, Lee GM and Kantoff PW: Association of
genetic variation of the six gene prognostic model for
castration-resistant prostate cancer with survival. Prostate.
79:73–80. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li Y, Xu Y, Peng X, Huang J, Yang M and
Wang X: A novel photosensitizer Znln2S4
mediated photodynamic therapy Induced-HepG2 cell apoptosis. Radiat
Res. 192:422–430. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang X, He X, Hu S, Sun A and Lu C:
Involvement of Bim in Photofrin-mediated photodynamically induced
apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:1527–1536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Roepcke S, Plock N, Yuan J, Fedyk ER, Lahu
G, Zhao L and Smithson G: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of
the cytolytic anti-CD38 human monoclonal antibody TAK-079 in
monkey-model assisted preparation for the first in human trial.
Pharmacol Res Perspect. 6:e004022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Manna A, Aulakh S, Jani P, Ahmed S, Akhtar
S, Coignet M, Heckman M, Meghji Z, Bhatia K, Sharma A, et al:
Targeting CD38 enhances the antileukemic activity of ibrutinib in
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 25:3974–3985. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|