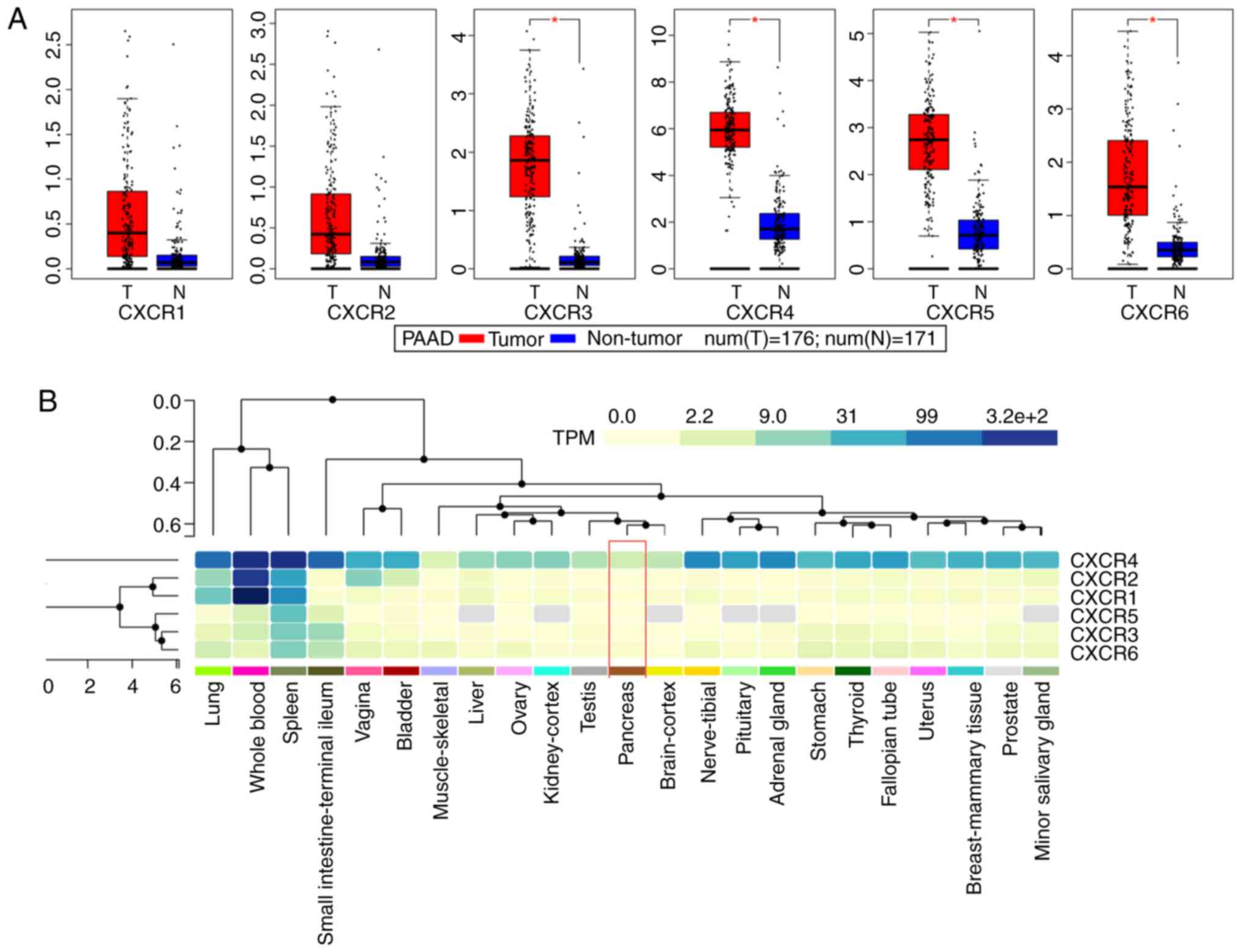
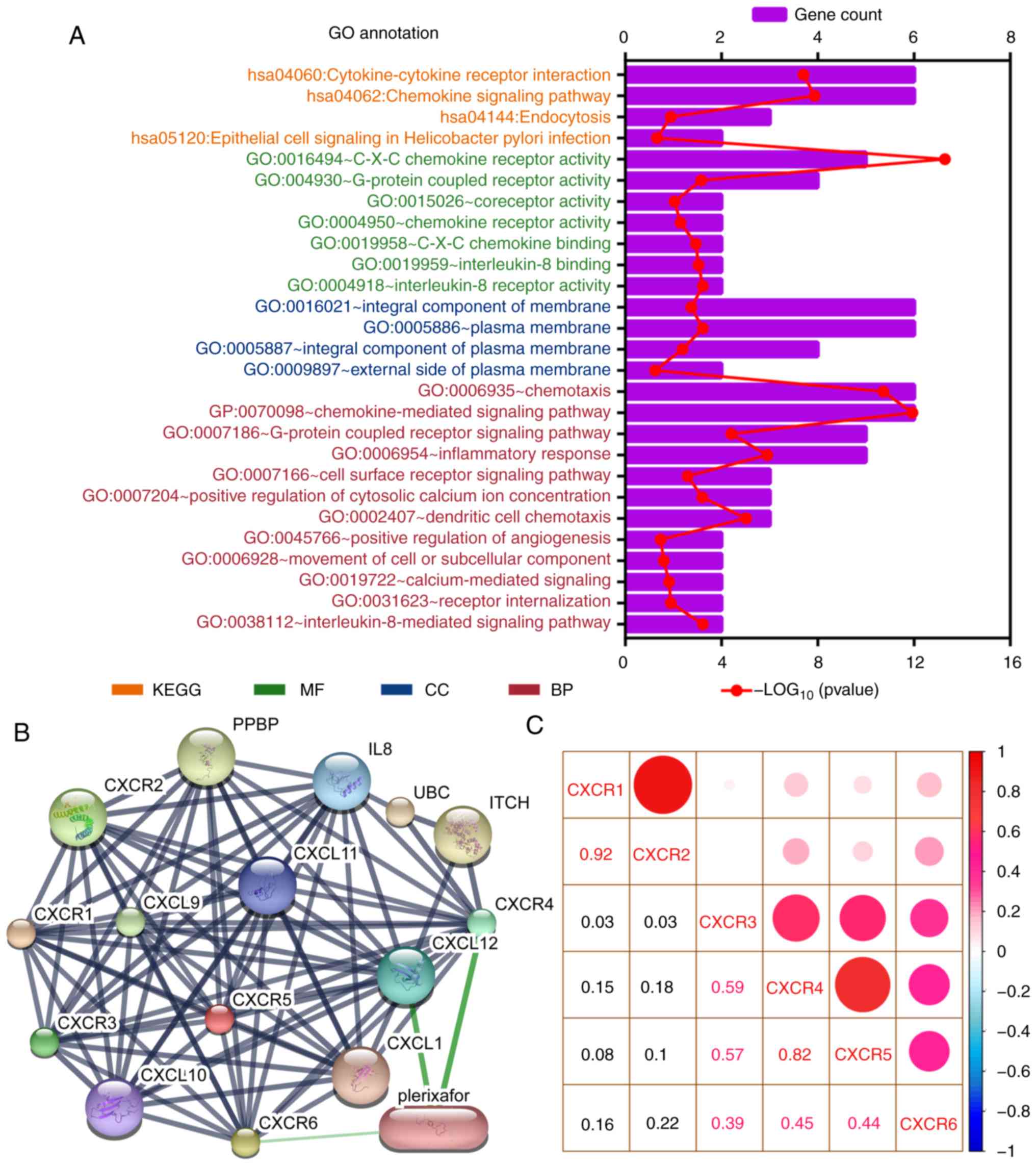
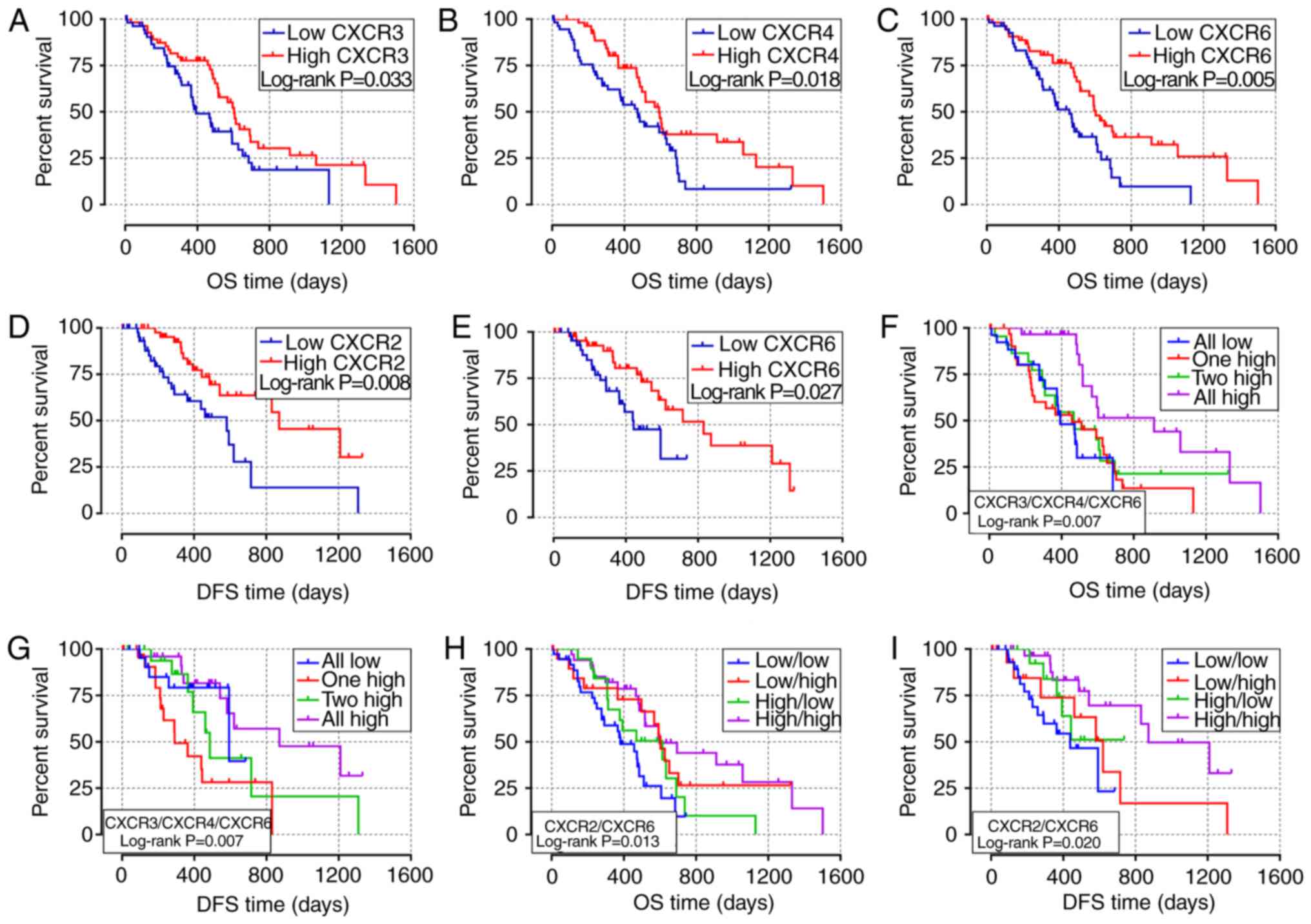
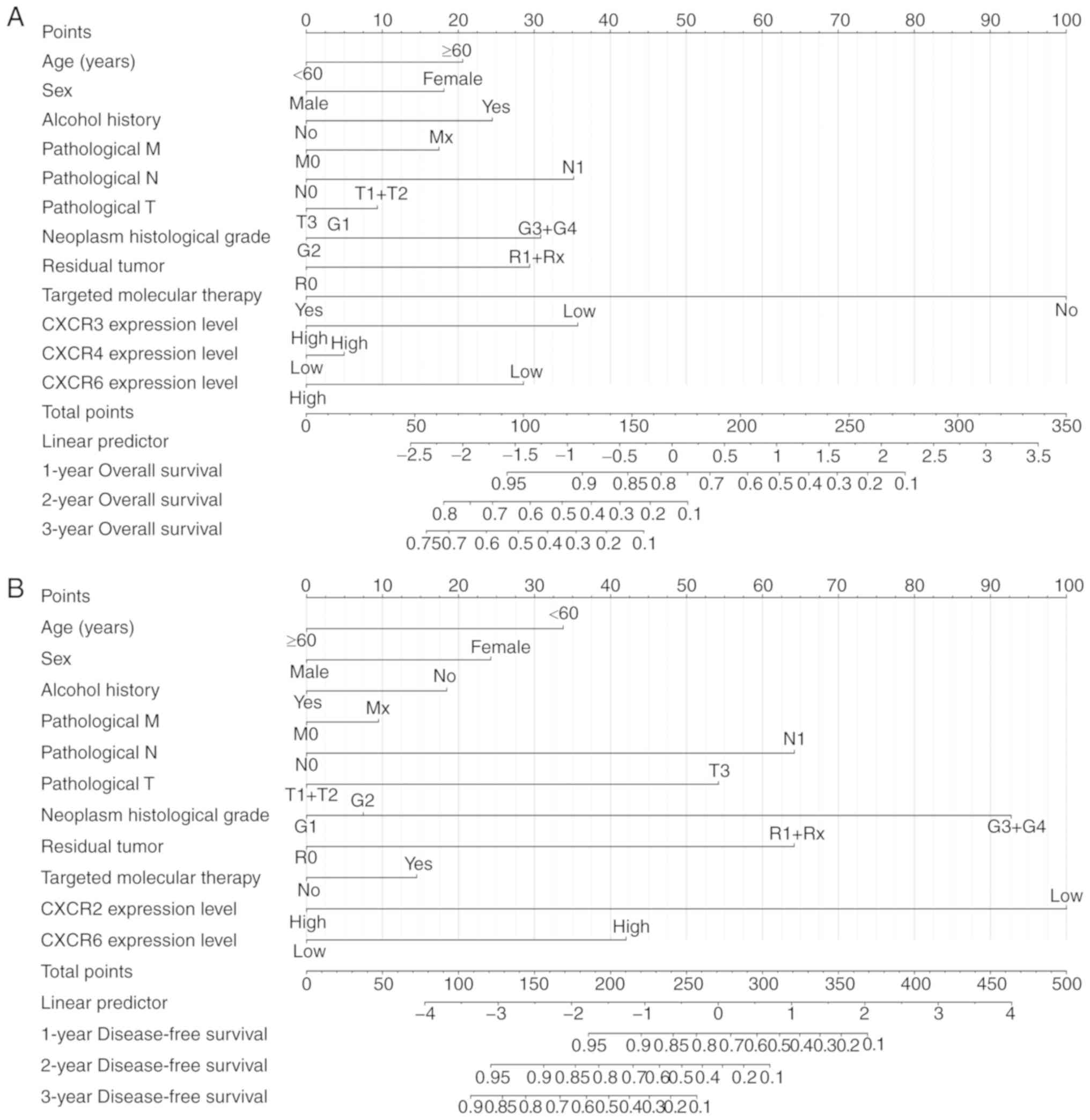
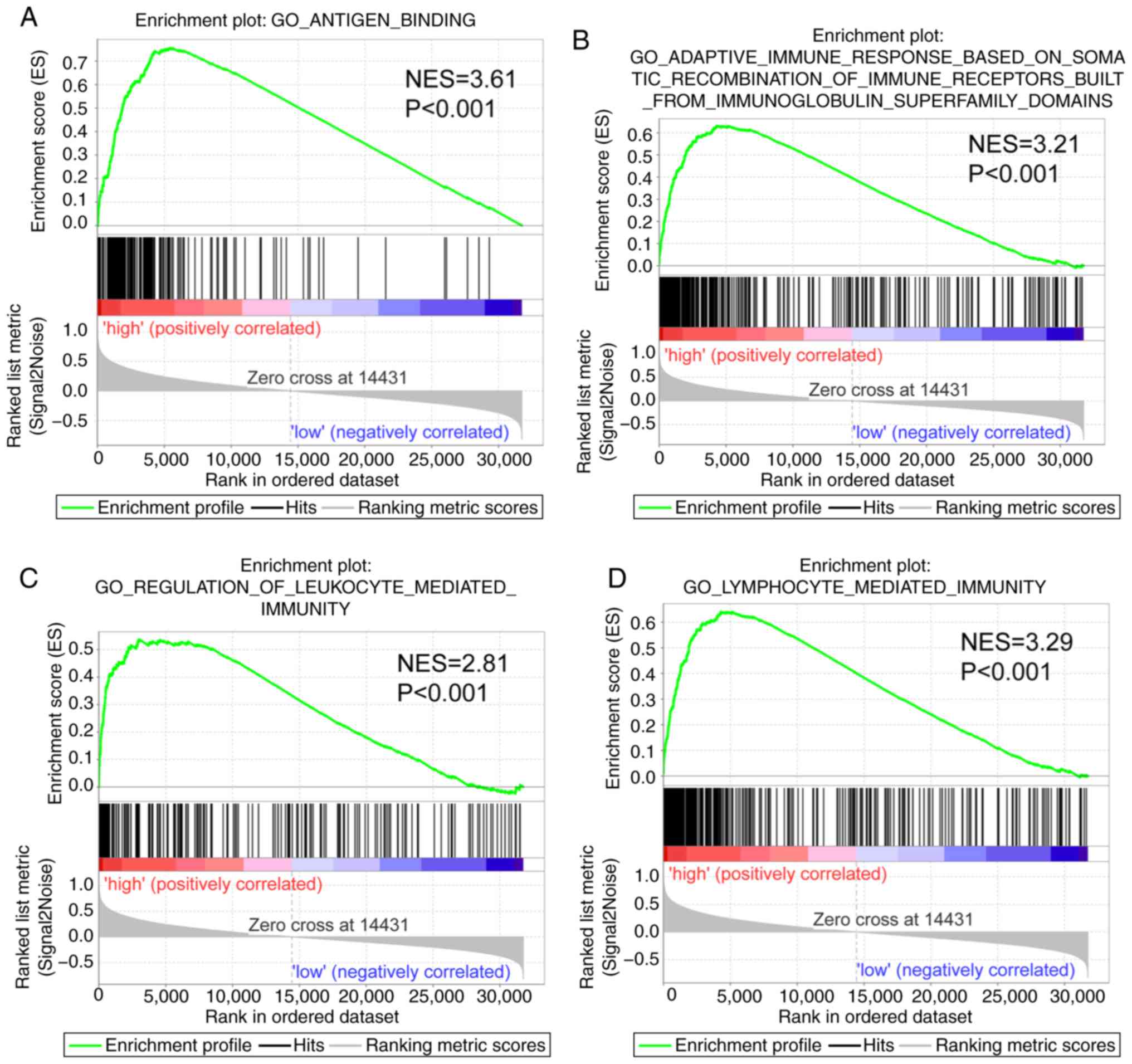
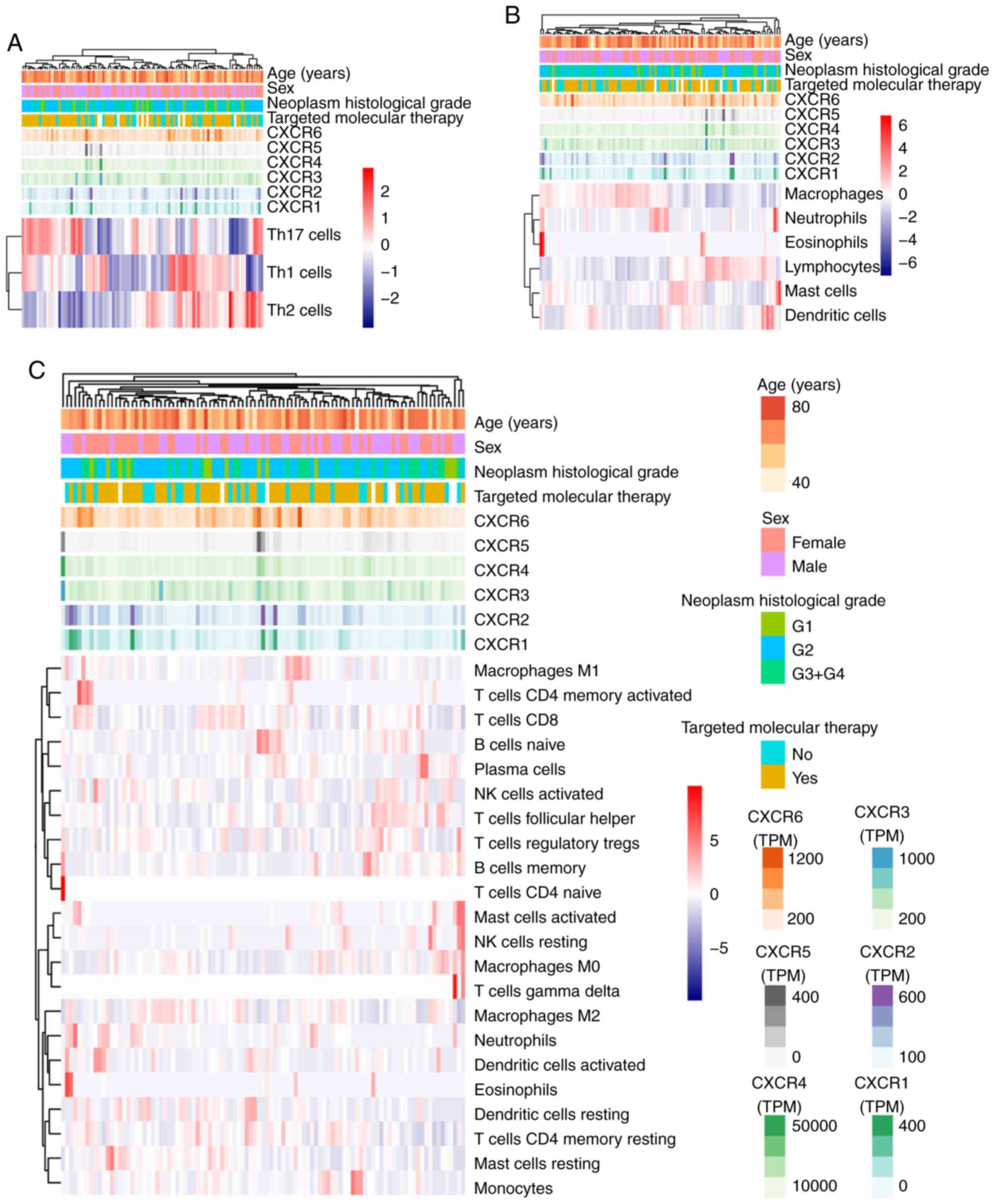
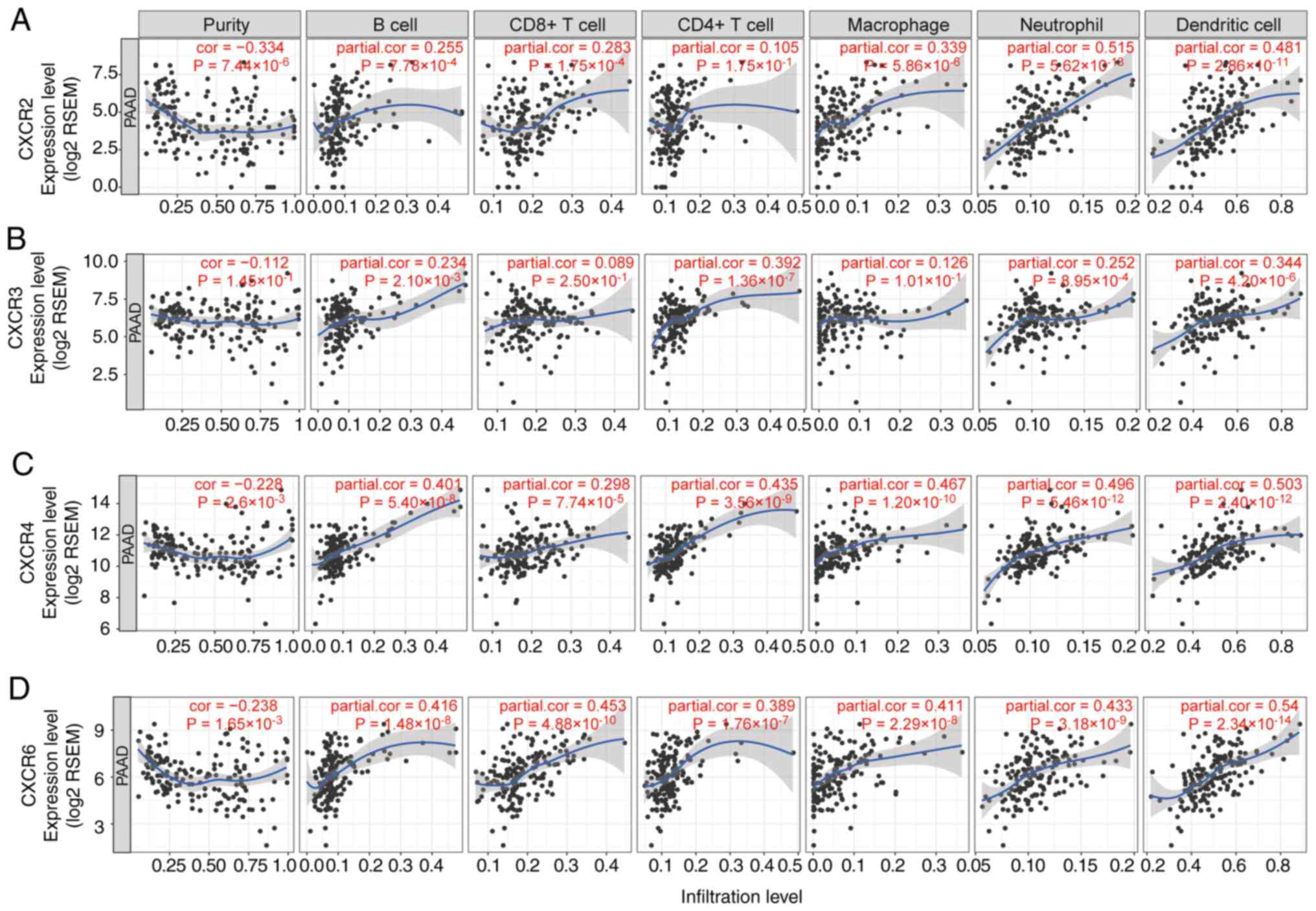
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tanaka S: Molecular pathogenesis and
targeted therapy of pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 23 (Suppl
2):S197–S205. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hidalgo M, Cascinu S, Kleeff J, Labianca
R, Löhr JM, Neoptolemos J, Real FX, Van Laethem JL and Heinemann V:
Addressing the challenges of pancreatic cancer: Future directions
for improving outcomes. Pancreatology. 15:8–18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
D'Agostino G, Cecchinato V and Uguccioni
M: Chemokine heterocomplexes and cancer: A novel chapter to be
written in tumor immunity. Front Immunol. 9:21852018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Weiss SA, Han SW, Lui K, Tchack J, Shapiro
R, Berman R, Zhong J, Krogsgaard M, Osman I and Darvishian F:
Immunologic heterogeneity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte
composition in primary melanoma. Hum Pathol. 57:116–125. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tumeh PC, Harview CL, Yearley JH, Shintaku
IP, Taylor EJ, Robert L, Chmielowski B, Spasic M, Henry G, Ciobanu
V, et al: PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive
immune resistance. Nature. 515:568–571. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fridman WH, Pages F, Sautes-Fridman C and
Galon J: The immune contexture in human tumours: Impact on clinical
outcome. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:298–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Becht E, Giraldo NA, Dieu-Nosjean MC,
Sautès-Fridman C and Fridman WH: Cancer immune contexture and
immunotherapy. Curr Opin Immunol. 39:7–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tahkola K, Mecklin JP, Wirta EV, Ahtiainen
M, Helminen O, Böhm J and Kellokumpu I: High immune cell score
predicts improved survival in pancreatic cancer. Virchows Arch.
472:653–665. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lianyuan T, Dianrong X, Chunhui Y, Zhaolai
M and Bin J: The predictive value and role of stromal
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
(PDAC). Cancer Biol Ther. 19:296–305. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Poschke I, Faryna M, Bergmann F, Flossdorf
M, Lauenstein C, Hermes J, Hinz U, Hank T, Ehrenberg R, Volkmar M,
et al: Identification of a tumor-reactive T-cell repertoire in the
immune infiltrate of patients with resectable pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Oncoimmunology. 5:e12408592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Martins-Green M, Petreaca M and Wang L:
Chemokines and their receptors are key players in the orchestra
that regulates wound healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle).
2:327–347. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Palomino DCT and Marti LC: Chemokines and
immunity. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 13:469–473. 2015.(In English,
Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Saintigny P, Massarelli E, Lin S, Ahn YH,
Chen Y, Goswami S, Erez B, O'Reilly MS, Liu D, Lee JJ, et al: CXCR2
expression in tumor cells is a poor prognostic factor and promotes
invasion and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res.
73:571–582. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Z, Liu H, Shen Z, Wang X, Zhang H,
Qin J, Xu J, Sun Y and Qin X: The prognostic value of CXC-chemokine
receptor 2 (CXCR2) in gastric cancer patients. BMC Cancer.
15:7662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu C, Zheng L, Li D, Chen G, Gu J, Chen J
and Yao Q: CXCR4 overexpression is correlated with poor prognosis
in colorectal cancer. Life Sci. 208:333–340. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao Q, Zhao YJ, Wang XY, Qiu SJ, Shi YH,
Sun J, Yi Y, Shi JY, Shi GM, Ding ZB, et al: CXCR6 upregulation
contributes to a proinflammatory tumor microenvironment that drives
metastasis and poor patient outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 72:3546–3556. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu C and Zhang Y: Characterization of the
prognostic values of CXCR family in gastric cancer. Cytokine.
123:1547852019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Szklarczyk D, Santos A, Von Mering C,
Jensen LJ, Bork P and Kuhn M: STITCH 5: Augmenting protein-chemical
interaction networks with tissue and affinity data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 44:D380–D384. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liao X, Huang K, Huang R, Liu X, Han C, Yu
L, Yu T, Yang C, Wang X and Peng T: Genome-scale analysis to
identify prognostic markers in patients with early-stage pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Onco Targets
Ther. 10:4493–4506. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang C, Yu T, Liu Z, Ye X, Liao X, Wang X,
Han C, Zhu G, Qin W and Peng T: Cystatin F as a key family 2
cystatin subunit and prognostic biomarker for early-stage
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 42:79–90.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American joint
committee on cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Harrell FE Jr: Package ‘rms’: Regression
modeling strategies. Package Version 5.1-4. 2016.
|
|
27
|
Li T, Fan J, Wang B, Traugh N, Chen Q, Liu
JS, Li B and Liu XS: TIMER: A Web server for comprehensive analysis
of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Cancer Res. 77:e108–e110. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mermel CH, Schumacher SE, Hill B, Meyerson
ML, Beroukhim R and Getz G: GISTIC2.0 facilitates sensitive and
confident localization of the targets of focal somatic copy-number
alteration in human cancers. Genome Biol. 12:R412011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thorsson V, Gibbs DL, Brown SD, Wolf D,
Bortone DS, Ou Yang TH, Porta-Pardo E, Gao GF, Plaisier CL, Eddy
JA, et al: The immune landscape of cancer. Immunity.
48:812–830.e14. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chow MT and Luster AD: Chemokines in
cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 2:1125–1131. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zlotnik A and Yoshie O: Chemokines: A new
classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity.
12:121–127. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Coffelt SB, Wellenstein MD and de Visser
KE: Neutrophils in cancer: Neutral no more. Nat Rev Cancer.
16:431–446. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bronte V, Brandau S, Chen SH, Colombo MP,
Frey AB, Greten TF, Mandruzzato S, Murray PJ, Ochoa A,
Ostrand-Rosenberg S, et al: Recommendations for myeloid-derived
suppressor cell nomenclature and characterization standards. Nat
Commun. 7:121502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fridlender ZG and Albelda SM:
Tumor-associated neutrophils: Friend or foe? Carcinogenesis.
33:949–955. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chao T, Furth EE and Vonderheide RH:
CXCR2-dependent accumulation of tumor-associated neutrophils
regulates T-cell immunity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Immunol Res. 4:968–982. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ijichi H, Chytil A, Gorska AE, Aakre ME,
Bierie B, Tada M, Mohri D, Miyabayashi K, Asaoka Y, Maeda S, et al:
Inhibiting Cxcr2 disrupts tumor-stromal interactions and improves
survival in a mouse model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J
Clin Invest. 121:4106–4117. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Idorn M, Olsen M, Halldórsdóttir HR,
Skadborg SK, Pedersen M, Høgdall C, Høgdall E, Met Ö and Thor
Straten P: Improved migration of tumor ascites lymphocytes to
ovarian cancer microenvironment by CXCR2 transduction.
Oncoimmunology. 7:e14120292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sano M, Ijichi H, Takahashi R, Miyabayashi
K, Fujiwara H, Yamada T, Kato H, Nakatsuka T, Tanaka Y, Tateishi K,
et al: Blocking CXCLs-CXCR2 axis in tumor-stromal interactions
contributes to survival in a mouse model of pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma through reduced cell invasion/migration and a shift
of immune-inflammatory microenvironment. Oncogenesis. 8:82019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Acosta JC, O'Loghlen A, Banito A, Guijarro
MV, Augert A, Raguz S, Fumagalli M, Da Costa M, Brown C, Popov N,
et al: Chemokine signaling via the CXCR2 receptor reinforces
senescence. Cell. 133:1006–1018. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Acosta JC and Jesús G: A role for CXCR2 in
senescence, but what about in cancer? Cancer Res. 69:2167–2170.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B,
Fredriksen T, Mauger S, Bindea G, Berger A, Bruneval P, Fridman WH,
Pagès F and Galon J: Clinical impact of different classes of
infiltrating T cytotoxic and helper cells (Th1, th2, treg, th17) in
patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 71:1263–1271. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang J, Wang H, Cai J, Du S, Xin B, Wei W,
Zhang T and Shen X: Artemin regulates CXCR4 expression to induce
migration and invasion in pancreatic cancer cells through
activation of NF-κB signaling. Exp Cell Res. 365:12–23. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zlotnik A, Burkhardt AM and Homey B:
Homeostatic chemokine receptors and organ-specific metastasis. Nat
Rev Immunol. 11:597–606. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Machado ID, Spatti M, Hastreiter A, Santin
JR, Fock RA, Gil CD, Oliani SM, Perretti M and Farsky SH: Annexin
A1 is a physiological modulator of neutrophil maturation and
recirculation acting on the CXCR4/CXCL12 pathway. J Cell Physiol.
231:2418–2427. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Maréchal R, Demetter P, Nagy N, Berton A,
Decaestecker C, Polus M, Closset J, Devière J, Salmon I and Van
Laethem JL: High expression of CXCR4 may predict poor survival in
resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 100:1444–1451.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gebauer F, Tachezy M, Effenberger K, von
Loga K, Zander H, Marx A, Kaifi JT, Sauter G, Izbicki JR and
Bockhorn M: Prognostic impact of CXCR4 and CXCR7 expression in
pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 104:140–145. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ma Q, Jones D, Borghesani PR, Segal RA,
Nagasawa T, Kishimoto T, Bronson RT and Springer TA: Impaired
B-lymphopoiesis, myelopoiesis, and derailed cerebellar neuron
migration in CXCR4- and SDF-1-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:9448–9453. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tachibana K, Hirota S, Iizasa H, Yoshida
H, Kawabata K, Kataoka Y, Kitamura Y, Matsushima K, Yoshida N,
Nishikawa S, et al: The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is essential for
vascularization of the gastrointestinal tract. Nature. 393:591–594.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Schmidt M, Böhm D, Von Törne C, Steiner E,
Puhl A, Pilch H, Lehr HA, Hengstler JG, Kölbl H and Gehrmann M: The
humoral immune system has a key prognostic impact in node-negative
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 68:5405–5413. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Nedergaard BS, Ladekarl M, Nyengaard JR
and Nielsen K: A comparative study of the cellular immune response
in patients with stage IB cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Low
numbers of several immune cell subtypes are strongly associated
with relapse of disease within 5 years. Gynecol Oncol. 108:106–111.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Milne K, Köbel M, Kalloger SE, Barnes RO,
Gao D, Gilks CB, Watson PH and Nelson BH: Systematic analysis of
immune infiltrates in high-grade serous ovarian cancer reveals
CD20, FoxP3 and TIA-1 as positive prognostic factors. PLoS One.
4:e64122009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jin JJ, Dai FX, Long ZW, Cai H, Liu XW,
Zhou Y, Hong Q, Dong QZ, Wang YN and Huang H: CXCR6 predicts poor
prognosis in gastric cancer and promotes tumor metastasis through
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Rep. 37:3279–3286. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chang Y, Zhou L, Xu L, Fu Q, Yang Y, Lin Z
and Xu J: High expression of CXC chemokine receptor 6 associates
with poor prognosis in patients with clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Urol Oncol. 35:675.e17–675.e24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Neesse A, Michl P, Frese KK, Feig C, Cook
N, Jacobetz MA, Lolkema MP, Buchholz M, Olive KP, Gress TM and
Tuveson DA: Stromal biology and therapy in pancreatic cancer. Gut.
60:861–868. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hartmann N, Giese NA, Giese T, Poschke I,
Offringa R, Werner J and Ryschich E: Prevailing role of contact
guidance in intrastromal T-cell trapping in human pancreatic
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:3422–3433. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chaudary N, Pintilie M, Jelveh S, Lindsay
P, Hill RP and Milosevic M: Plerixafor improves primary tumor
response and reduces metastases in cervical cancer treated with
radio-chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 23:1242–1249. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Conley-LaComb MK, Semaan L, Singareddy R,
Li Y, Heath EI, Kim S, Cher ML and Chinni SR: Pharmacological
targeting of CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling in prostate cancer bone
metastasis. Mol Cancer. 15:682016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|