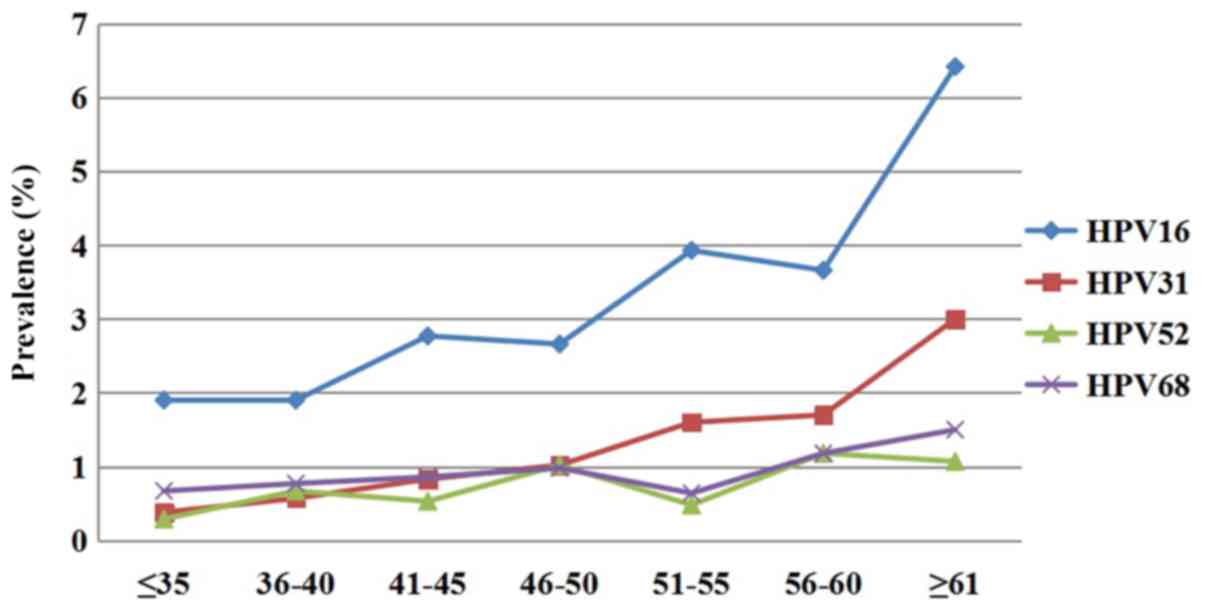
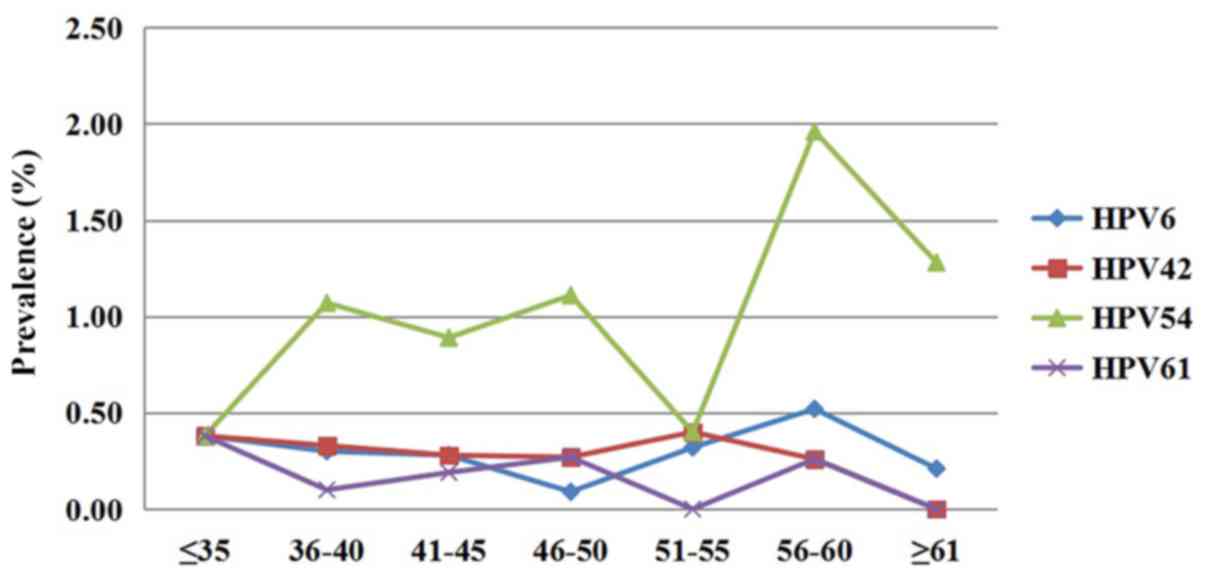
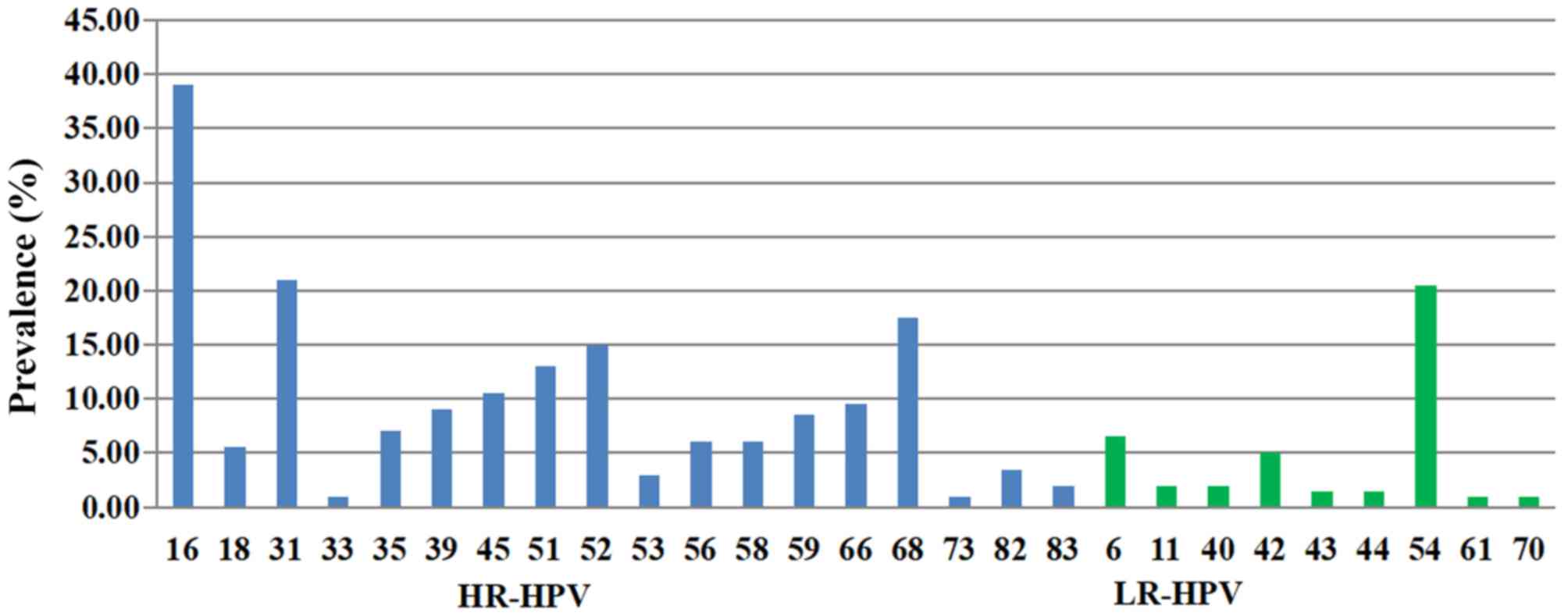
|
1
|
Kim K, Zang R, Choi SC, Ryu SY and Kim JW:
Current status of gynecological cancer in China. J Gynecol Onco.
20:72–76. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Arbyn M, Weiderpass E, Bruni L, de Sanjosé
S, Saraiya M, Ferlay J and Bray F: Estimates of incidence and
mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: A worldwide analysis. Lancet
Glob Health. 8:E191–E203. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Walboomers JM, Jacobs MV, Manos MM, Bosch
FX, Kummer JA, Shah KV, Snijders PJ, Peto J, Meijer CJ and Muñoz N:
Human papillomavirus is a necessary cause of invasive cervical
cancer worldwide. J Pathol. 189:12–19. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Forman D, Martel CD, Lacey CJ,
Soerjomataram I, Lortet-Tieulent J, Bruni L, Vignat J, Ferlay J,
Bray F, Plummer M and Franceschi S: Global burden of human
papillomavirus and related diseases. Vaccine. 30 (Suppl 5):F12–F23.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jayaraj R, Kumarasamy C, Royam MM,
Sabarimurugan S and Baxi S: Prognostic implications of pathologic
lymph nodes in HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers: Clinical
validity and strategies for routine clinical practice. Oral Oncol.
92:99–100. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao FH, Lin MJ, Chen F, Hu SY, Zhang R,
Belinson JL, Sellors JW, Franceschi S, Qiao YL and Castle PE;
Cervical Cancer Screening Group in China, : Performance of
high-risk human papillomavirus DNA testing as a primary screen for
cervical cancer: A pooled analysis of individual patient data from
17 population-based studies from China. Lancet Oncol. 11:1160–1171.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wei L, Xie X, Liu J, Zhao Y, Chen W, Zhao
C, Wang S, Liao X, Shou Q, Qiu Y, Qiao Y and Saah AJ: Efficacy of
quadrivalent human papillomavirus vaccine against persistent
infection and genital disease in Chinese women: A randomized,
placebo-controlled trial with 78-month follow-up. Vaccine.
37:3617–3624. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Giuliano AR, Joura EA, Garland SM, Huh WK,
Iversen OE, Kjaer SK, Ferenczy A, Kurman RJ, Ronnett BM, Stoler MH,
et al: Nine-valent HPV vaccine efficacy against related diseases
and definitive therapy: Comparison with historic placebo
population. Gynecol Oncol. 154:110–117. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang L, Tian X, Peng D, Zhang L, Xie F,
Bi C, Wang R, Wang J and Qi D: HPV prevalence and genotype
distribution among women in Shandong Province, China: Analysis of
94,489 HPV genotyping results from Shandong's largest independent
pathology laboratory. PLoS One. 14:e02103112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang XC, Sun LQ, Ma L, Li HX, Wang XL,
Wang X, Yun T, Meng NL and Lv D: Prevalence and genotype
distribution of human papillomavirus among women from Henan, China.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:7333–7336. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bi Q, Zhang L, Zhao Z, Mu X, Zhang M and
Wang P: Human papillomavirus prevalence and genotypes distribution
among female outpatients in Qingdao, East China. J Med Virol.
87:2114–2121. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Z, Liu F, Cheng S, Shi L, Yan Z, Yang
J, Shi L, Yao Y and Ma Y: Prevalence of HPV infection among 28,457
Chinese women in Yunnan Province, southwest China. Sci Rep.
6:210392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Tang DD, Wang K, Wang J, Zhang Z,
Chen Y, Zhang X and Ma C: HPV genotype prevalence and distribution
during 2009–2018 in Xinjiang, China: Baseline surveys prior to mass
HPV vaccination. Bmc Womens Health. 19:902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rong-Min W, Jing-Jing P and Zhi-Xue Y: The
Interpretation of 2012 ASCCP Management of Abnormal Cervical Cancer
Screening Tests and Cancer Precursors(II). Journal of International
Obstetrics and Gynecology. 42:2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li J, Huang R, Schmidt JE and Qiao YL:
Epidemiological features of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection
among women living in Mainland China. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:4015–4023. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Q, Xie LX, Qing ZR, Li LJ, Luo ZY,
Lin M, Zhang SM, Chen WZ, Lin BZ, Lin QL, et al: Epidemiologic
characterization of human papillomavirus infection in rural
chaozhou, eastern guangdong province of China. PLoS One.
7:e321492012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun B, He J, Chen X, He M, He Z, Wang Y,
Shang Q, Yu L and Wei L: Prevalence and genotype distribution of
human papillomavirus infection in Harbin, Northeast China. Arch
Virol. 159:1027–1032. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao BW, Yu JL, He H, Li ST and Zhao YL:
Meta-analysis on the Relationship between HPV Infection and
Esophageal Cancer in Chinese Population. J Capital Medical
University. 97:148–150. 2010.
|
|
19
|
Clifford GM, Gallus S, Herrero R, Muñoz N,
Snijders PJ, Vaccarella S, Anh PT, Ferreccio C, Hieu NT, Matos E,
et al: Worldwide distribution of human papillomavirus types in
cytologically normal women in the International Agency for Research
on Cancer HPV prevalence surveys: A pooled analysis. Lancet.
366:991–998. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Uusküla A, Kals M, Kosenkranius L, McNutt
LA and DeHovitz JJ: Population-based type-specific prevalence of
high-risk human papillomavirus infection in Estonia. BMC Infect
Dis. 10:632010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu EQ, Liu B, Cui JF, Chen W, Wang JB, Lu
L, Niyazi M, Zhao C, Ren SD, Li CQ, et al: Prevalence of
type-specific human papillomavirus and pap results in Chinese
women: A multi-center, population-based cross-sectional study.
Cancer Causes Control. 24:795–803. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jing L, Zhong X, Zhong Z, Huang W, Liu Y,
Yang G, Zhang X, Zou J, Jing C and Wei X: Prevalence of human
papillomavirus infection in Guangdong Province, China: A
population-based survey of 78,355 women. Sex Transm Dis.
41:732–738. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang R, Guo XL, Wisman GB, Schuuring E,
Wang WF, Zeng ZY, Zhu H and Wu SW: Nationwide prevalence of human
papillomavirus infection and viral genotype distribution in 37
cities in China. BMC Infect Dis. 15:2572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang CH, Garvilles RG and Chen CY:
Characterization of human papillomavirus infection in north Taiwan.
J Med Virol. 82:1416–1423. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Torres-Poveda K, Ruiz-Fraga I,
Madrid-Marina V, Chavez M and Richardson V: High risk HPV infection
prevalence and associated cofactors: A population-based study in
female ISSSTE beneficiaries attending the HPV screening and early
detection of cervical cancer program. Bmc Cancer. 19:12052019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Althoff KN, Paul P, Burke AE, Viscidi R,
Sangaramoorthy M and Gravitt PE: Correlates of cervicovaginal human
papillomavirus detection in perimenopausal women. J Womens Health
(Larchmt). 18:1341–1346. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kang LN, Castle PE, Zhao FH, Jeronimo J,
Chen F, Bansil P, Li J, Chen W, Zhang X and Qiao YL: A prospective
study of age trends of high-risk human papillomavirus infection in
rural China. Bmc Infect Dis. 14:962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen R and Wong E: The feasibility of
universal HPV vaccination program in Shenzhen of China: A health
policy analysis. Bmc Public Health. 19:7812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
de Sanjosé S, Diaz M, Castellsagué X,
Clifford G, Bruni L, Muñoz N and Bosch FX: Worldwide prevalence and
genotype distribution of cervical human papillomavirus DNA in women
with normal cytology: A meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis.
7:453–459. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun LL, Jin Q, Li H, Zhou XR, Song ZQ,
Cheng XM, Tao T, Liang B, Xu L, Wang YR, et al: Population-based
study on the prevalence of and risk factors for human
papillomavirus infection in Qujing of Yunnan province, Southwest
China. Virol J. 9:1532012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Argyri E, Papaspyridakos S, Tsimplaki E,
Michala L, Myriokefalitaki E, Papassideri I, Daskalopoulou D,
Tsiaoussi I, Magiakos G and Panotopoulou E: A cross sectional study
of HPV type prevalence according to age and cytology. Bmc Infect
Dis. 13:532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiang Y, Brassard P, Severini A, Mao Y, Li
YA, Laroche J, Chatwood S, Corriveau A, Kandola K, Hanley B, et al:
The prevalence of human papillomavirus and its impact on
cervical;dysplasia in Northern Canada. Infect Agent Cancer.
8:252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bouvard V, Baan R, Straif K, Grosse Y,
Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Freeman C,
Galichet L, et al: A review of human carcinogens-Part B: Biological
agents. Lancet Oncol. 10:321–322. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yoshikawa H: Progress and challenges on
HPV vaccination. Uirusu. 59:243–248. 2009.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huh WK, Joura EA, Giuliano AR, Iversen OE,
de Andrade RP, Ault KA, Bartholomew D, Cestero RM, Fedrizzi EN,
Hirschberg AL, et al: Final efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety
analyses of a nine-valent human papillomavirus vaccine in women
aged 16–26 years: A randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet.
390:2143–2159. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fife KH, Cramer HM, Schroeder JM and Brown
DR: Detection of multiple human papillomavirus types in the lower
genital tract correlates with cervical dysplasia. J Med Virol.
64:550–559. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Trottier H, Mahmud S, Prado JC, Sobrinho
JS, Costa MC, Rohan TE, Villa LL and Franco EL: Type-specific
duration of human papillomavirus infection: Implications for human
papillomavirus screening and vaccination. J Infect Dis.
197:1436–1447. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Perrons C, Jelley R, Kleter B, Quint W and
Brink N: Detection of persistent high risk human papillomavirus
infections with hybrid capture II and SPF10/LiPA. J Clin Virol.
32:278–285. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao R, Zhang WY, Wu MH, Zhang SW, Pan J,
Zhu L, Zhang YP, Li H, Gu YS and Liu XZ: Human papillomavirus
infection in Beijing, People's Republic of China: A
population-based study. Br J Cancer. 101:1635–1640. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lai CH, Chao A, Chang CJ, Huang CC, Wang
LC, Hsueh S, Lin CT, Wu TI, Jao MS and Chou HH: Age factor and
implication of human papillomavirus type-specific prevalence in
women with normal cervical cytology. Epidemiol Infect. 140:466–473.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|