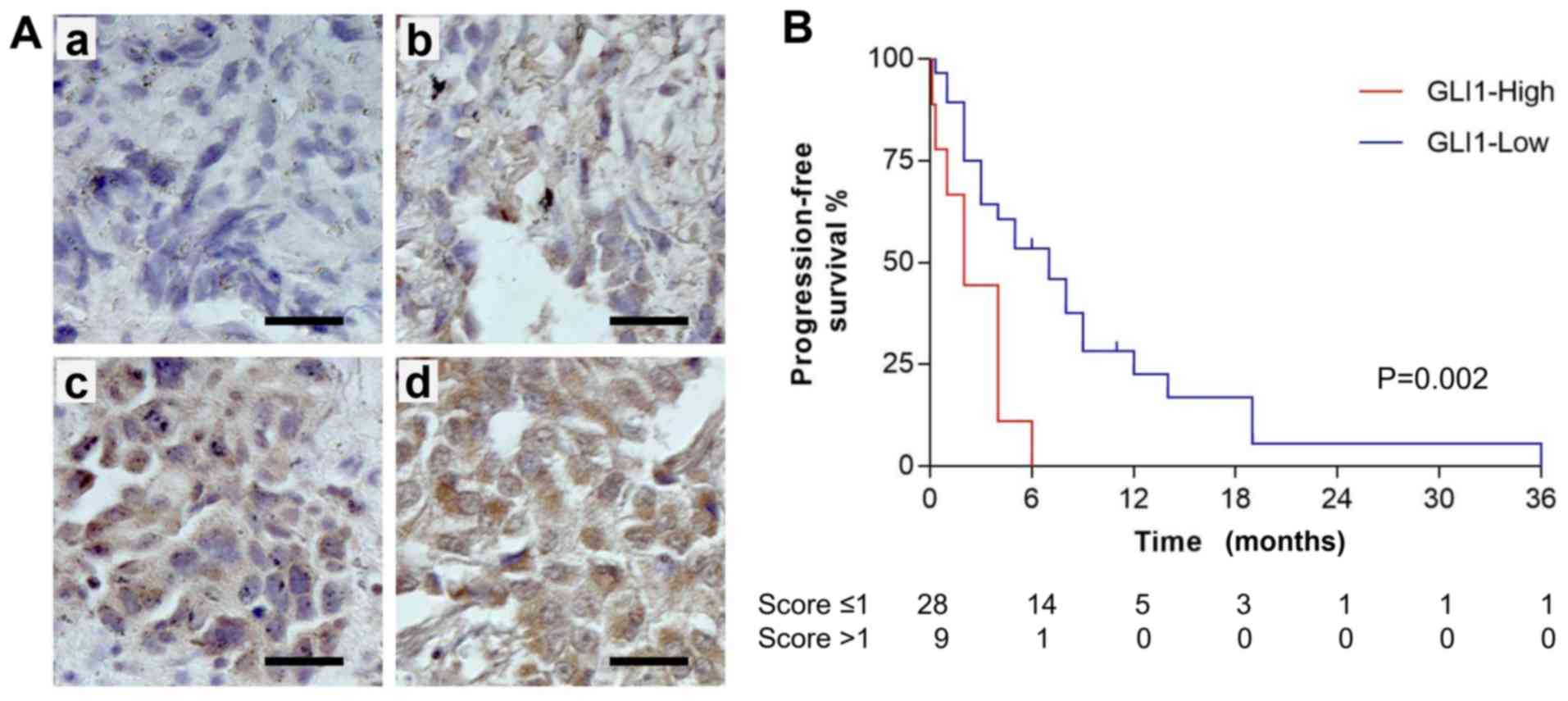
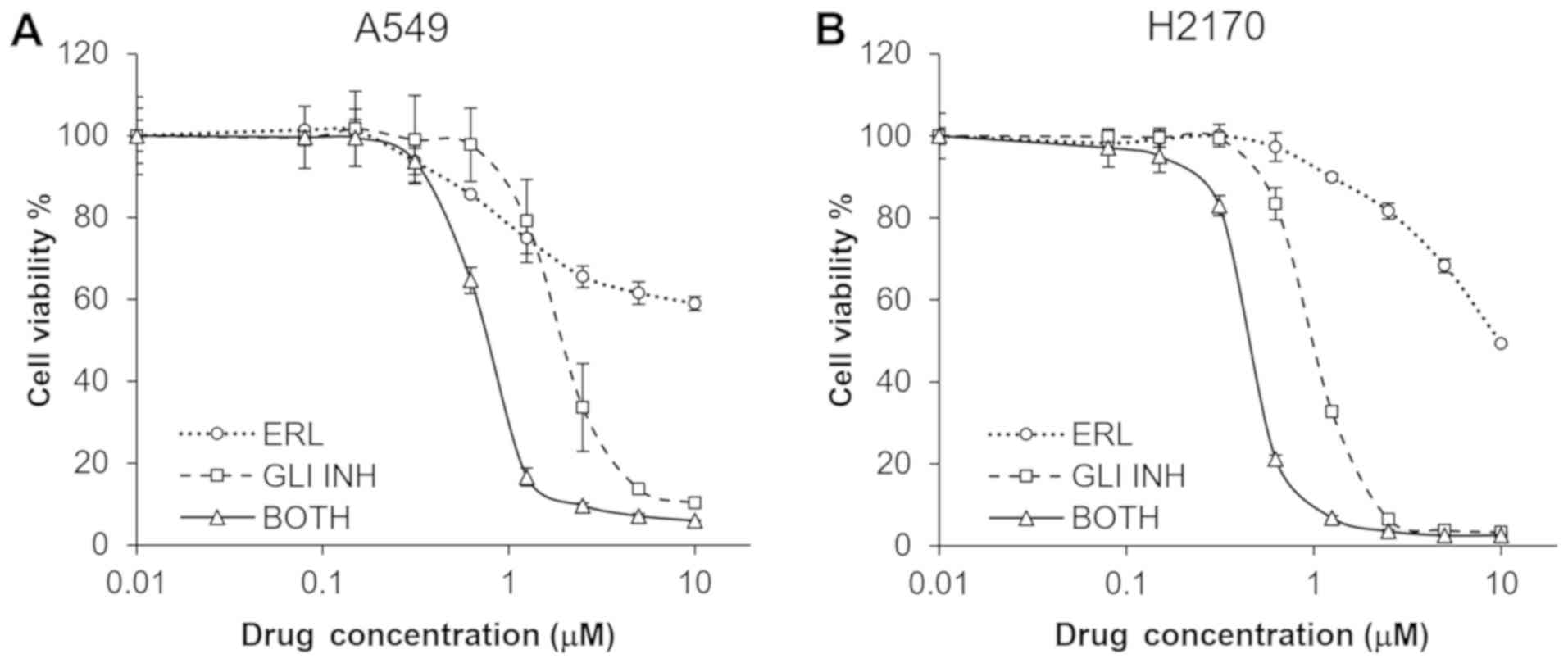
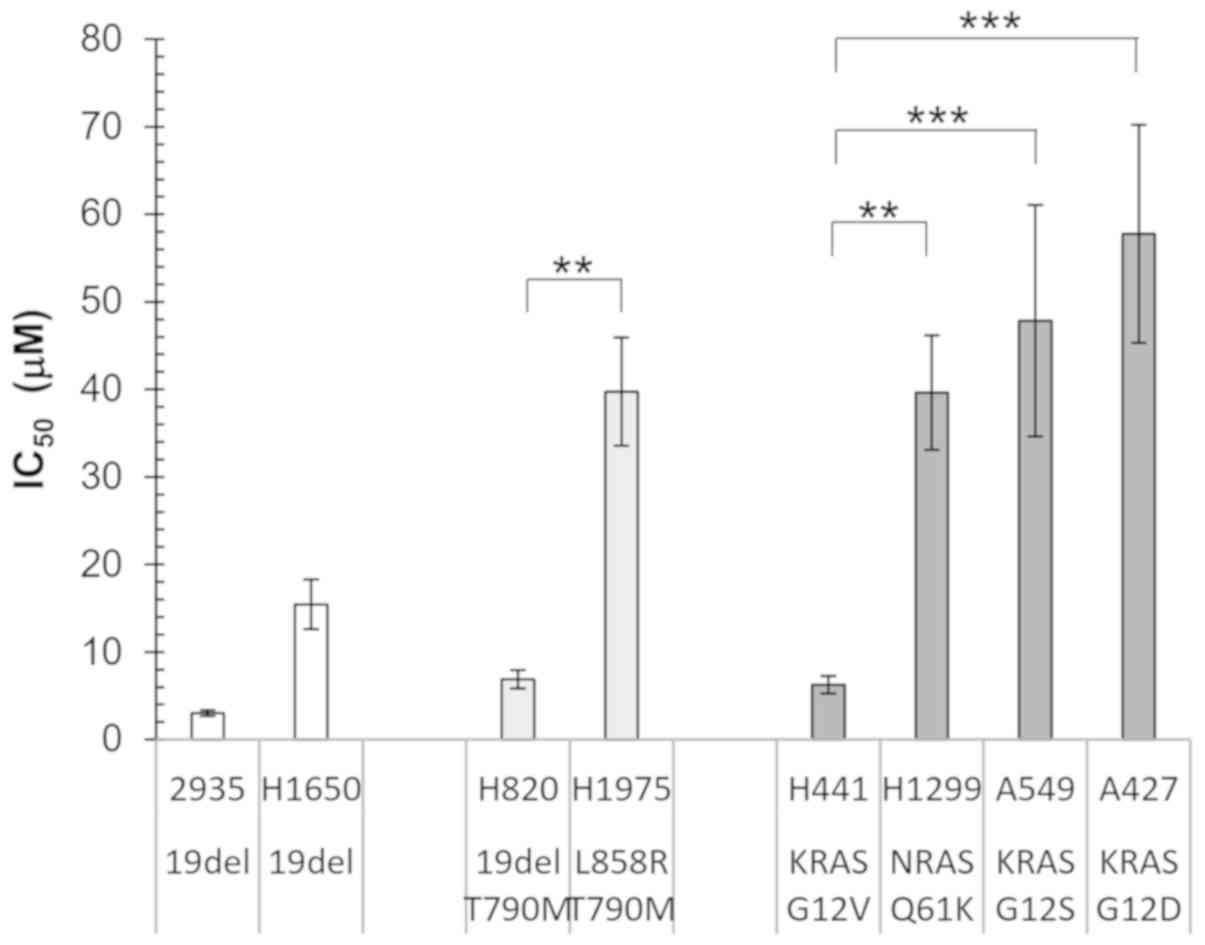
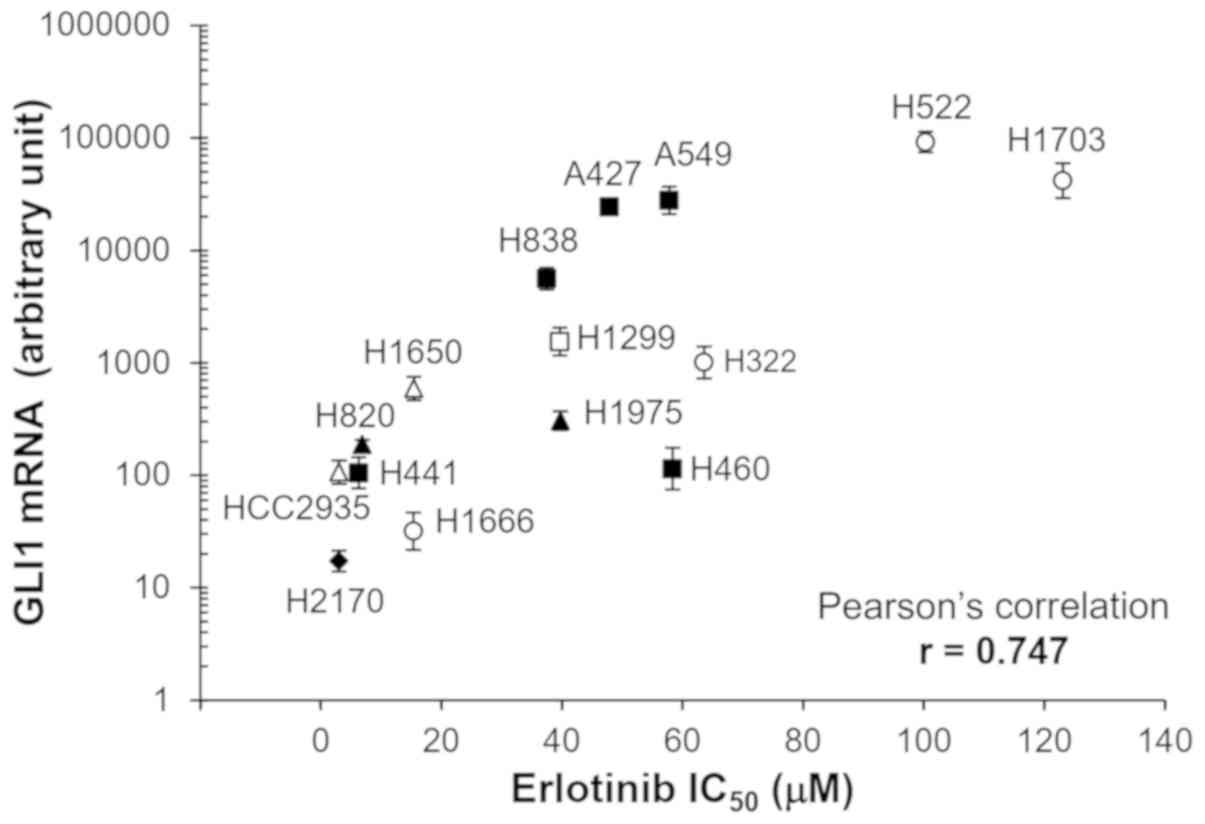
|
1
|
Boloker G, Wang C and Zhang J: Updated
statistics of lung and bronchus cancer in United States (2018). J
Thorac Dis. 10:1158–1161. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Duma N, Santana-Davila R and Molina JR:
Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and
treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 94:1623–1640. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cronin KA, Lake AJ, Scott S, Sherman RL,
Noone AM, Howlader N, Henley SJ, Anderson RN, Firth AU, Ma J, et
al: Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, part I:
National cancer statistics. Cancer. 124:2785–2800. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Feng RM, Zong YN, Cao SM and Xu RH:
Current cancer situation in China: Good or bad news from the 2018
global cancer statistics? Cancer Commun (Lond). 39:222019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
da Cunha Santos G, Shepherd FA and Tsao
MS: EGFR mutations and lung cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:49–69. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S,
Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et
al: EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical
response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 304:1497–1500. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Selvaggi G, Novello S, Torri V, Leonardo
E, De Giuli P, Borasio P, Mossetti C, Ardissone F, Lausi P and
Scagliotti GV: Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression
correlates with a poor prognosis in completely resected
non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 15:28–32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J and Haber
DA: Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:169–181. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pao W, Miller VA, Politi KA, Riely GJ,
Somwar R, Zakowski MF, Kris MG and Varmus H: Acquired resistance of
lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib is associated with a
second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain. PLoS Med. 2:e732005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Jänne
PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, Johnson BE, Eck MJ, Tenen DG and Halmos
B: EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to
gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 352:786–792. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gazdar AF: Activating and resistance
mutations of EGFR in non-small-cell lung cancer: Role in clinical
response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncogene. 28 (Suppl
1):S24–S31. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pao W, Wang TY, Riely GJ, Miller VA, Pan
Q, Ladanyi M, Zakowski MF, Heelan RT, Kris MG and Varmus HE: KRAS
mutations and primary resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to
gefitinib or erlotinib. PLoS Med. 2:e172005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Takezawa K, Pirazzoli V, Arcila ME, Nebhan
CA, Song X, de Stanchina E, Ohashi K, Janjigian YY, Spitzler PJ,
Melnick MA, et al: HER2 amplification: A potential mechanism of
acquired resistance to EGFR inhibition in EGFR-mutant lung cancers
that lack the second-site EGFRT790M mutation. Cancer Discov.
2:922–933. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T,
Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, Lindeman N, Gale CM, Zhao X, Christensen
J, et al: MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung
cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 316:1039–1043. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Massarelli E, Varella-Garcia M, Tang X,
Xavier AC, Ozburn NC, Liu DD, Bekele BN, Herbst RS and Wistuba II:
KRAS mutation is an important predictor of resistance to therapy
with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2890–2896. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dragnev KH, Ma T, Cyrus J, Galimberti F,
Memoli V, Busch AM, Tsongalis GJ, Seltzer M, Johnstone D, Erkmen
CP, et al: Bexarotene plus erlotinib suppress lung carcinogenesis
independent of KRAS mutations in two clinical trials and transgenic
models. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 4:818–828. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Linardou H, Dahabreh IJ, Kanaloupiti D,
Siannis F, Bafaloukos D, Kosmidis P, Papadimitriou CA and Murray S:
Assessment of somatic k-RAS mutations as a mechanism associated
with resistance to EGFR-targeted agents: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of studies in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and
metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 9:962–972. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu SG and Shih JY: Management of acquired
resistance to EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell
lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 17:382018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Merchant AA and Matsui W: Targeting
hedgehog-a cancer stem cell pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 16:3130–3140.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Velcheti V and Govindan R: Hedgehog
signaling pathway and lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2:7–10. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Amakye D, Jagani Z and Dorsch M:
Unraveling the therapeutic potential of the hedgehog pathway in
cancer. Nat Med. 19:1410–1422. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuan Z, Goetz JA, Singh S, Ogden SK, Petty
WJ, Black CC, Memoli VA, Dmitrovsky E and Robbins DJ: Frequent
requirement of hedgehog signaling in non-small cell lung carcinoma.
Oncogene. 26:1046–1055. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Giroux-Leprieur E, Costantini A, Ding VW
and He B: Hedgehog signaling in lung cancer: From oncogenesis to
cancer treatment resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 19:28352018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Niyaz M, Khan MS and Mudassar S: Hedgehog
signaling: An achilles' heel in cancer. Transl Oncol. 12:1334–1344.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sabol M, Trnski D, Musani V, Ozretić P and
Levanat S: Role of GLI transcription factors in pathogenesis and
their potential as new therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci.
19:25622018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ruiz i Altaba A: Gli proteins encode
context-dependent positive and negative functions: Implications for
development and disease. Development. 126:3205–3216.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hui CC and Angers S: Gli proteins in
development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:513–537. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Niewiadomski P, Niedziółka SM, Markiewicz
Ł, Uśpieński T, Baran B and Chojnowska K: Gli proteins: Regulation
in development and cancer. Cells. 8:1472019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sasaki H, Nishizaki Y, Hui C, Nakafuku M
and Kondoh H: Regulation of Gli2 and Gli3 activities by an
amino-terminal repression domain: Implication of Gli2 and Gli3 as
primary mediators of Shh signaling. Development. 126:3915–3924.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang L, Xie G, Fan Q and Xie J: Activation
of the hedgehog-signaling pathway in human cancer and the clinical
implications. Oncogene. 29:469–481. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sekulic A, Migden MR, Oro AE, Dirix L,
Lewis KD, Hainsworth JD, Solomon JA, Yoo S, Arron ST, Friedlander
PA, et al: Efficacy and safety of vismodegib in advanced basal-cell
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 366:2171–2179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Basset-Séguin N, Hauschild A, Kunstfeld R,
Grob J, Dréno B, Mortier L, Ascierto PA, Licitra L, Dutriaux C,
Thomas L, et al: Vismodegib in patients with advanced basal cell
carcinoma: Primary analysis of STEVIE, an international, open-label
trial. Eur J Cancer. 86:334–348. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lear JT, Migden MR, Lewis KD, Chang ALS,
Guminski A, Gutzmer R, Dirix L, Combemale P, Stratigos A, Plummer
R, et al: Long-term efficacy and safety of sonidegib in patients
with locally advanced and metastatic basal cell carcinoma: 30-month
analysis of the randomized phase 2 BOLT study. J Eur Acad Dermatol
Venereol. 32:372–381. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rodon J, Tawbi HA, Thomas AL, Stoller RG,
Turtschi CP, Baselga J, Sarantopoulos J, Mahalingam D, Shou Y,
Moles MA, et al: A phase I, multicenter, open-label,
first-in-human, dose-escalation study of the oral smoothened
inhibitor Sonidegib (LDE225) in patients with advanced solid
tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 20:1900–1909. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kieran MW, Chisholm J, Casanova M, Brandes
AA, Aerts I, Bouffet E, Bailey S, Leary S, MacDonald TJ, Mechinaud
F, et al: Phase I study of oral sonidegib (LDE225) in pediatric
brain and solid tumors and a phase II study in children and adults
with relapsed medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 19:1542–1552. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Minami H, Ando Y, Ma BB, Hsiang Lee J,
Momota H, Fujiwara Y, Li L, Fukino K, Ito K, Tajima T, et al: Phase
I, multicenter, open-label, dose-escalation study of sonidegib in
Asian patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Sci.
107:1477–1483. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ko AH, LoConte N, Tempero MA, Walker EJ,
Kate Kelley R, Lewis S, Chang WC, Kantoff E, Vannier MW, Catenacci
DV, et al: A Phase I study of FOLFIRINOX plus IPI-926, a hedgehog
pathway inhibitor, for advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Pancreas. 45:370–375. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jimeno A, Weiss GJ, Miller WH Jr,
Gettinger S, Eigl BJ, Chang AL, Dunbar J, Devens S, Faia K, Skliris
G, et al: Phase I study of the hedgehog pathway inhibitor IPI-926
in adult patients with solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 19:2766–2774.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lauth M and Toftgård R: Non-canonical
activation of GLI transcription factors: Implications for targeted
anti-cancer therapy. Cell Cycle. 6:2458–2463. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mimeault M and Batra SK: Frequent
deregulations in the hedgehog signaling network and cross-talks
with the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway involved in
cancer progression and targeted therapies. Pharmacol Rev.
62:497–524. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ou SI and Shirai K: Anaplastic lymphoma
kinase (ALK) signaling in lung cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol.
893:179–187. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Garrido-Castro AC and Felip E: HER2 driven
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Potential therapeutic
approaches. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2:122–127. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Benvenuto M, Masuelli L, De Smaele E,
Fantini M, Mattera R, Cucchi D, Bonanno E, Di Stefano E, Frajese
GV, Orlandi A, et al: In vitro and in vivo inhibition of breast
cancer cell growth by targeting the Hedgehog/GLI pathway with SMO
(GDC-0449) or GLI (GANT-61) inhibitors. Oncotarget. 7:9250–9270.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Srivastava RK, Kaylani SZ, Edrees N, Li C,
Talwelkar SS, Xu J, Palle K, Pressey JG and Athar M: GLI inhibitor
GANT-61 diminishes embryonal and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma growth
by inhibiting Shh/AKT-mTOR axis. Oncotarget. 5:12151–12165. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ishikawa M, Sonobe M, Imamura N, Sowa T,
Shikuma K and Date H: Expression of the GLI family genes is
associated with tumor progression in advanced lung adenocarcinoma.
World J Surg Oncol. 12:2532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tate JG, Bamford S, Jubb HC, Sondka Z,
Beare DM, Bindal N, Boutselakis H, Cole CG, Creatore C, Dawson E,
et al: COSMIC: The catalogue of somatic mutations in cancer.
Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D941–D947. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Forbes SA, Tang G, Bindal N, Bamford S,
Dawson E, Cole C, Kok CY, Jia M, Ewing R, Menzies A, et al: COSMIC
(the Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer): A resource to
investigate acquired mutations in human cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
38:D652–D657. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ramos AH, Dutt A, Mermel C, Perner S, Cho
J, Lafargue CJ, Johnson LA, Stiedl AC, Tanaka KE, Bass AJ, et al:
Amplification of chromosomal segment 4q12 in non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:2042–2050. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mo ML, Chen Z, Zhou HM, Li H, Hirata T,
Jablons DM and He B: Detection of E2A-PBX1 fusion transcripts in
human non-small-cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 32:292013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bean J, Brennan C, Shih JY, Riely G, Viale
A, Wang L, Chitale D, Motoi N, Szoke J, Broderick S, et al: MET
amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant
lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:20932–20937. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Minakata K, Takahashi F, Nara T, Hashimoto
M, Tajima K, Murakami A, Nurwidya F, Yae S, Koizumi F, Moriyama H,
et al: Hypoxia induces gefitinib resistance in non-small-cell lung
cancer with both mutant and wild-type epidermal growth factor
receptors. Cancer Sci. 103:1946–1954. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cortes JR, Ambesi-Impiombato A, Couronné
L, Quinn SA, Kim CS, da Silva Almeida AC, West Z, Belver L, Martin
MS, Scourzic L, et al: RHOA G17V induces T follicular helper cell
specification and promotes lymphomagenesis. Cancer Cell.
33:259–273.e7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Pratilas CA, Hanrahan AJ, Halilovic E,
Persaud Y, Soh J, Chitale D, Shigematsu H, Yamamoto H, Sawai A,
Janakiraman M, et al: Genetic predictors of MEK dependence in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 68:9375–9383. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Landrum MJ, Lee JM, Riley GR, Jang W,
Rubinstein WS, Church DM and Maglott DR: ClinVar: Public archive of
relationships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic
Acids Res. 42:D980–D985. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bosco-Clément G, Zhang F, Chen Z, Zhou HM,
Li H, Mikami I, Hirata T, Yagui-Beltran A, Lui N, Do HT, et al:
Targeting Gli transcription activation by small molecule suppresses
tumor growth. Oncogene. 33:2087–2097. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Gialmanidis IP, Bravou V, Amanetopoulou
SG, Varakis J, Kourea H and Papadaki H: Overexpression of hedgehog
pathway molecules and FOXM1 in non-small cell lung carcinomas. Lung
Cancer. 66:64–74. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bora-Singhal N, Perumal D, Nguyen J and
Chellappan S: Gli1-mediated regulation of Sox2 facilitates
self-renewal of stem-like cells and confers resistance to EGFR
inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Neoplasia. 17:538–551.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Armas-López L, Piña-Sánchez P, Arrieta O,
de Alba EG, Ortiz-Quintero B, Santillán-Doherty P, Christiani DC,
Zúñiga J and Ávila-Moreno F: Epigenomic study identifies a novel
mesenchyme homeobox2-GLI1 transcription axis involved in cancer
drug resistance, overall survival and therapy prognosis in lung
cancer patients. Oncotarget. 8:67056–67081. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Dimou A, Bamias A, Gogas H and Syrigos K:
Inhibition of the hedgehog pathway in lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
133:56–61. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nguyen KS, Kobayashi S and Costa DB:
Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine
kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the
epidermal growth factor receptor pathway. Clin Lung Cancer.
10:281–289. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D,
Digumarthy S, Turke AB, Fidias P, Bergethon K, Shaw AT, Gettinger
S, Cosper AK, et al: Genotypic and histological evolution of lung
cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med.
3:75ra262011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cooke DT, Nguyen DV, Yang Y, Chen SL, Yu C
and Calhoun RF: Survival comparison of adenosquamous, squamous
cell, and adenocarcinoma of the lung after lobectomy. Ann Thorac
Surg. 90:943–948. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kawase A, Yoshida J, Ishii G, Nakao M,
Aokage K, Hishida T, Nishimura M and Nagai K: Differences between
squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the lung: Are
adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma prognostically equal?
Jpn J Clin Oncol. 42:189–195. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bai XY, Zhang XC, Yang SQ, An SJ, Chen ZH,
Su J, Xie Z, Gou LY and Wu YL: Blockade of hedgehog signaling
synergistically increases sensitivity to epidermal growth factor
receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer
cell lines. PLoS One. 11:e01493702016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Jin S, He J, Li J, Guo R, Shu Y and Liu P:
MiR-873 inhibition enhances gefitinib resistance in non-small cell
lung cancer cells by targeting glioma-associated oncogene homolog
1. Thorac Cancer. 9:1262–1270. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|