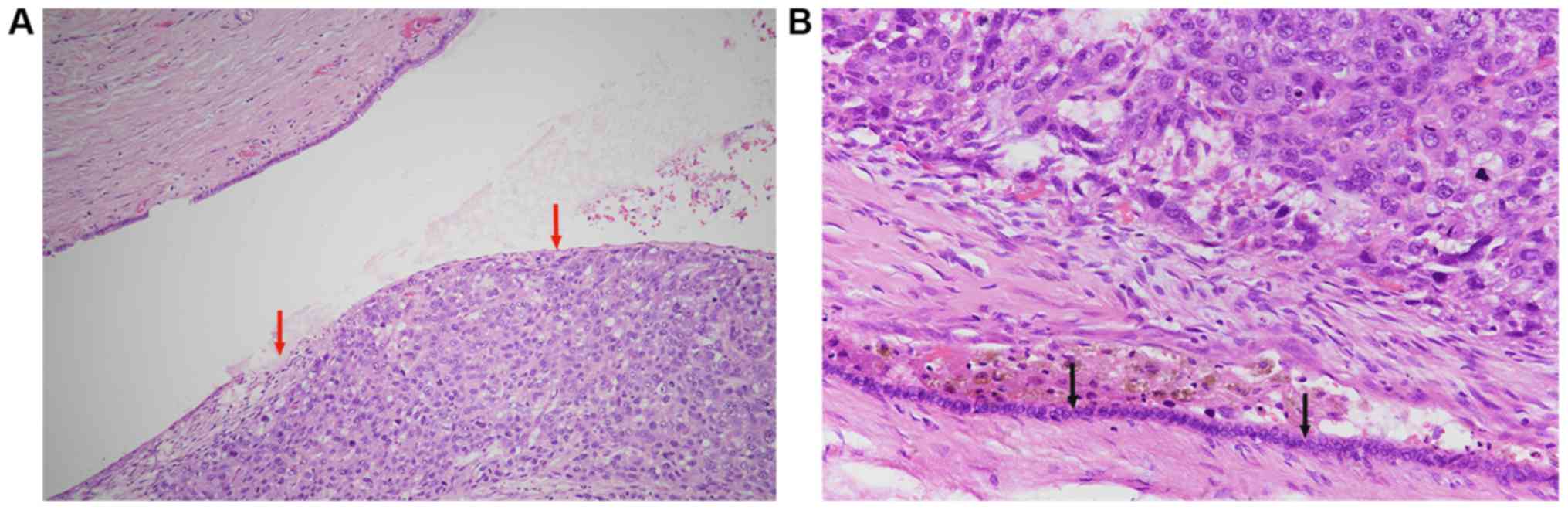
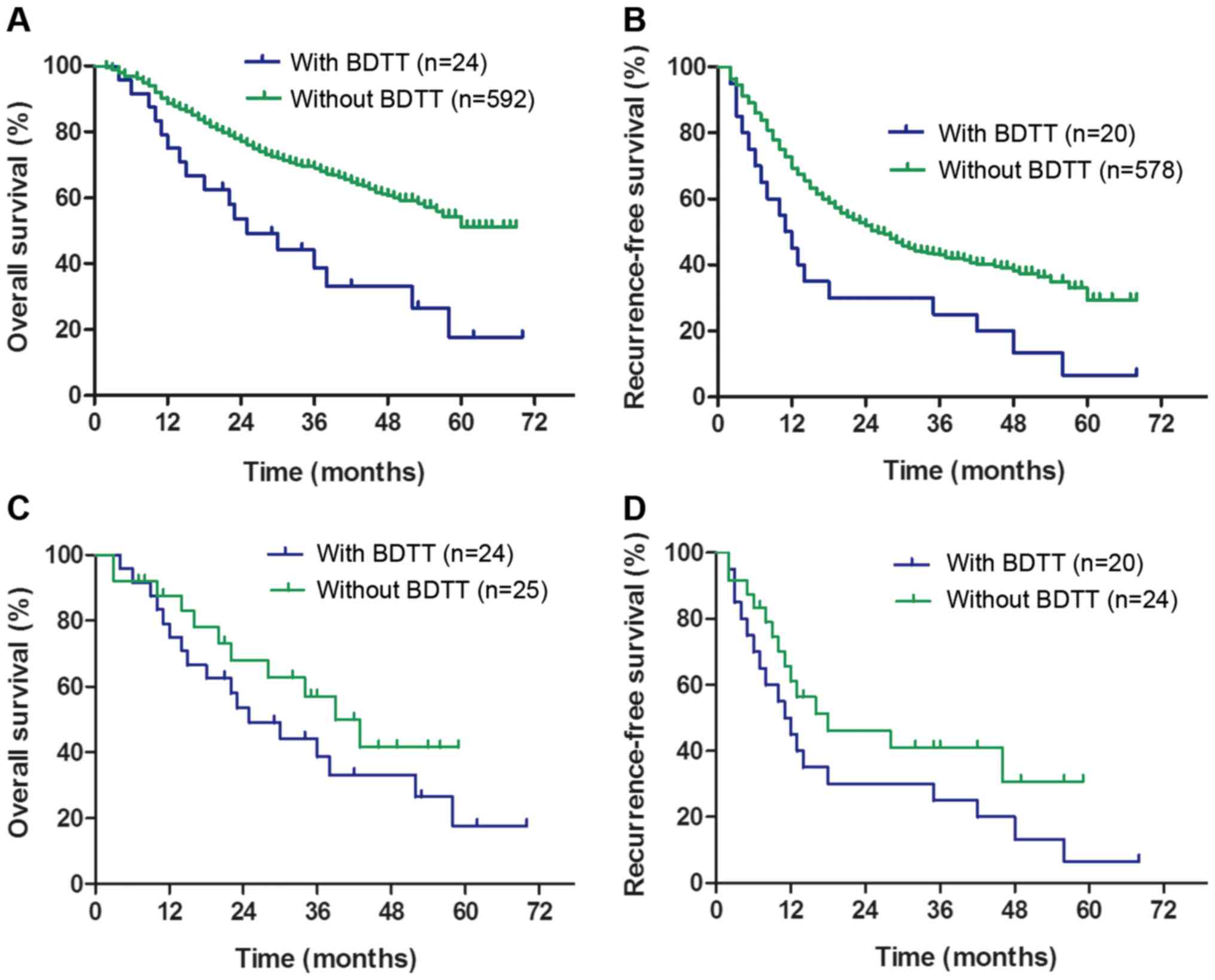
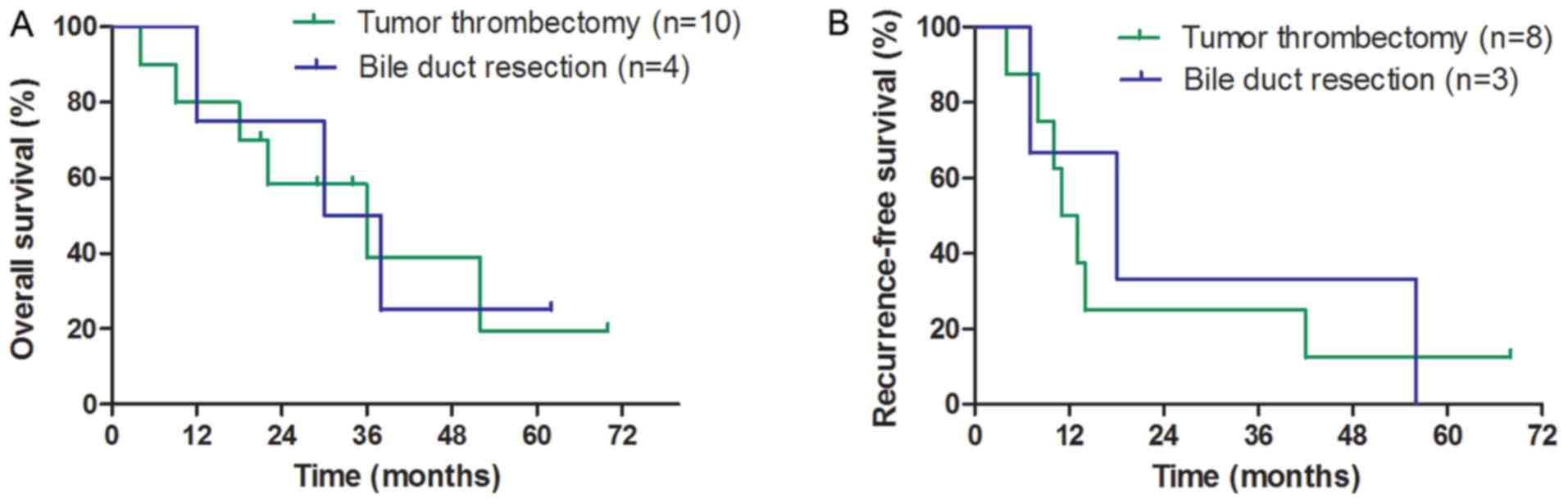
|
1
|
Shehta A, Han HS, Yoon YS, Cho JY and Choi
Y: Laparoscopic liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma in
cirrhotic patients: 10-year single-center experience. Surg Endosc.
30:638–648. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oba A, Takahashi S, Kato Y, Gotohda N,
Kinoshita T, Shibasaki H, Ikeda M and Konishi M: Usefulness of
resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with macroscopic bile duct
tumor thrombus. Anticancer Res. 34:4367–4372. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ueda M, Takeuchi T, Takayasu T, Takahashi
K, Okamoto S, Tanaka A, Morimoto T, Mori K and Yamaoka Y:
Classification and surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
(HCC) with bile duct thrombi. Hepatogastroenterology. 41:349–354.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kudo M, Izumi N, Ichida T, Ku Y, Kokudo N,
Sakamoto M, Takayama T, Nakashima O, Matsui O and Matsuyama Y:
Report of the 19th follow-up survey of primary liver cancer in
Japan. Hepatol Res. 46:372–390. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nakashima T, Okuda K, Kojiro M, Jimi A,
Yamaguchi R, Sakamoto K and Ikari T: Pathology of hepatocellular
carcinoma in Japan. 232 consecutive cases autopsied in ten years.
Cancer. 51:863–877. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meng KW, Dong M, Zhang WG and Huang QX:
Clinical characteristics and surgical prognosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma with bile duct invasion. Gastroenterol Res Pract.
2014:6049712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zeng H, Xu LB, Wen JM, Zhang R, Zhu MS,
Shi XD and Liu C: Hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct tumor
thrombus: A clinicopathological analysis of factors predictive of
recurrence and outcome after surgery. Medicine (Baltimore).
94:e3642015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shao W, Sui C, Liu Z, Yang J and Zhou Y:
Surgical outcome of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with biliary
tumor thrombi. World J Surg Oncol. 9:22011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ikenaga N, Chijiiwa K, Otani K, Ohuchida
J, Uchiyama S and Kondo K: Clinicopathologic characteristics of
hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct invasion. J Gastrointest
Surg. 13:492–497. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yamamoto S, Hasegawa K, Inoue Y, Shindoh
J, Aoki T, Sakamoto Y, Sugawara Y, Makuuchi M and Kokudo N: Bile
duct preserving surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct
tumor thrombus. Ann Surg. 261:e123–e125. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xiangji L, Weifeng T, Bin Y, Chen L,
Xiaoqing J, Baihe Z, Feng S and Mengchao W: Surgery of
hepatocellular carcinoma complicated with cancer thrombi in bile
duct: Efficacy for criteria for different therapy modalities.
Langenbecks Arch Surg. 394:1033–1039. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lau W, Leung K, Leung TW, Liew CT, Chan
MS, Yu SC and Li AK: A logical approach to hepatocellular carcinoma
presenting with jaundice. Ann Surg. 225:281–285. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bae SH, Park HC, Yoon WS, Yoon SM, Jung
IH, Lee IJ, Kim JW, Seong J, Kim TH, Nam TK, et al: Treatment
outcome after fractionated conformal radiotherapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with child-pugh classification
B in Korea (KROG 16-05). Cancer Res Treat. 51:1589–1599. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Abdel-Rahman O: Assessment of the
discriminating value of the 8th AJCC stage grouping for
hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB (Oxford). 20:41–48. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Edmondson HA and Steiner PE: Primary
carcinoma of the liver: A study of 100 cases among 48,900
necropsies. Cancer. 7:462–503. 1954. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shiomi M, Kamiya J, Nagino M, Uesaka K,
Sano T, Hayakawa N, Kanai M, Yamamoto H and Nimura Y:
Hepatocellular carcinoma with biliary tumor thrombi: Aggressive
operative approach after appropriate preoperative management.
Surgery. 129:692–698. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee NW, Wong KP, Siu KF and Wong J:
Cholangiography in hepatocellular carcinoma with obstructive
jaundice. Clin Radiol. 35:119–123. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mok KT, Chang HT, Liu SI, Jou NW, Tsai CC
and Wang BW: Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with
biliary tumor thrombi. Int Surg. 81:284–288. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Satoh S, Ikai I, Honda G, Okabe H,
Takeyama O, Yamamoto Y, Yamamoto N, Iimuro Y, Shimahara Y and
Yamaoka Y: Clinicopathologic evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma
with bile duct thrombi. Surgery. 128:779–783. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yeh CN, Jan YY, Lee WC and Chen MF:
Hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with obstructive
jaundice due to biliary tumor thrombi. World J Surg. 28:471–475.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang X, Qiu Z, Ran R, Cui L, Luo X, Wu M,
Tan WF and Jiang X: Prognostic importance of bile duct invasion in
surgical resection with curative intent for hepatocellular
carcinoma using PSM analysis. Oncol Lett. 16:3593–3602.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim JM, Kwon CH, Joh JW, Sinn DH, Park JB,
Lee JH, Kim SJ, Paik SW, Park CK and Yoo BC: Incidental microscopic
bile duct tumor thrombi in hepatocellular carcinoma after curative
hepatectomy: A matched study. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e4502015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rammohan A, Sathyanesan J, Rajendran K,
Pitchaimuthu A, Perumal SK, Balaraman K, Ramasamy R, Palaniappan R
and Govindan M: Bile duct thrombi in hepatocellular carcinoma: Is
aggressive surgery worthwhile? HPB (Oxford). 17:508–513. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wong TC, Cheung TT, Chok KS, Chan AC, Dai
WC, Chan SC, Poon RT, Fan ST and Lo CM: Outcomes of hepatectomy for
hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct tumour thrombus. HPB
(Oxford). 17:401–408. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moon DB, Hwang S, Wang HJ, Yun SS, Kim KS,
Lee YJ, Kim KH, Park YK, Xu W, Kim BW, et al: Surgical outcomes of
hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct tumor thrombus: A Korean
multicenter study. World J Surg. 37:443–451. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yasunori M and Masatoshi K: Hepatocellular
carcinoma with obstructive jaundice: Endoscopic and percutaneous
biliary drainage. Dig Dis. 30:592–597. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Orimo T, Kamiyama T, Yokoo H, Wakayama K,
Shimada S, Tsuruga Y, Kamachi H and Taketomi A: Hepatectomy for
hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct tumor thrombus, including
cases with obstructive Jaundice. Ann Surg Oncol. 23:2627–2634.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Noda T, Nagano H, Tomimaru Y, Murakami M,
Wada H, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Eguchi H, Takeda Y, Tanemura M,
et al: Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with biliary tumor
thrombi after liver surgery. Surgery. 149:371–377. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rubin DB: Estimating causal effects from
large data sets using propensity scores. Ann Intern Med.
127:757–263. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Austin PC: An introduction to propensity
score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in
observational studies. Multivariate Behav Res. 46:399–424. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cho HJ, Kim SS, Kang SY, Yang MJ, Noh CK,
Hwang JC, Lim SG, Shin SJ, Lee KM, Yoo BM, et al: A proposal for
modification of the barcelona clinic liver cancer staging system
considering the prognostic implication of performance status. Gut
Liver. 13:557–568. 2019. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vauthey JN, Klimstra D, Franceschi D, Tao
Y, Fortner J, Blumgart L and Brennan M: Factors affecting long-term
outcome after hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J
Surg. 169:28–35. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamamoto J, Kosuge T, Takayama T, Shimada
K, Yamasaki S, Ozaki H, Yamaguchi N and Makuuchi M: Recurrence of
hepatocellular carcinoma after surgery. Br J Surg. 83:1219–1222.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Esaki M, Shimada K, Sano T, Sakamoto Y,
Kosuge T and Ojima H: Surgical results for hepatocellular carcinoma
with bile duct invasion: A clinicopathologic comparison between
macroscopic and microscopic tumor thrombus. J Surg Oncol.
90:226–232. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han J, Li ZL, Xing H, Wu H, Zhu P, Lau WY,
Zhou YH, Gu WM, Wang H, Chen TH, et al: The impact of resection
margin and microvascular invasion on long-term prognosis after
curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: A
multi-institutional study. HPB (Oxford). 21:962–971. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shibata T, Yamamoto N, Ikai I, Shimahara
Y, Yamaoka Y, Itoh K and Konishi J: Choledochojejunostomy: Possible
risk factor for septic complications after percutaneous hepatic
tumor ablation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 174:985–986. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim DS, Kim BW, Hatano E, Hwang S,
Hasegawa K, Kudo A, Ariizumi S, Kaibori M, Fukumoto T, Baba H, et
al: Surgical outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct
tumor thrombus: A Korea-Japan multicenter study. Ann Surg.
271:913–921. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kojiro M, Kawabata K, Kawano Y, Shirai F,
Takemoto N and Nakashima T: Hepatocellular carcinoma presenting as
intrabile duct tumor growth: A clinicopathologic study of 24 cases.
Cancer. 49:2144–2147. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|