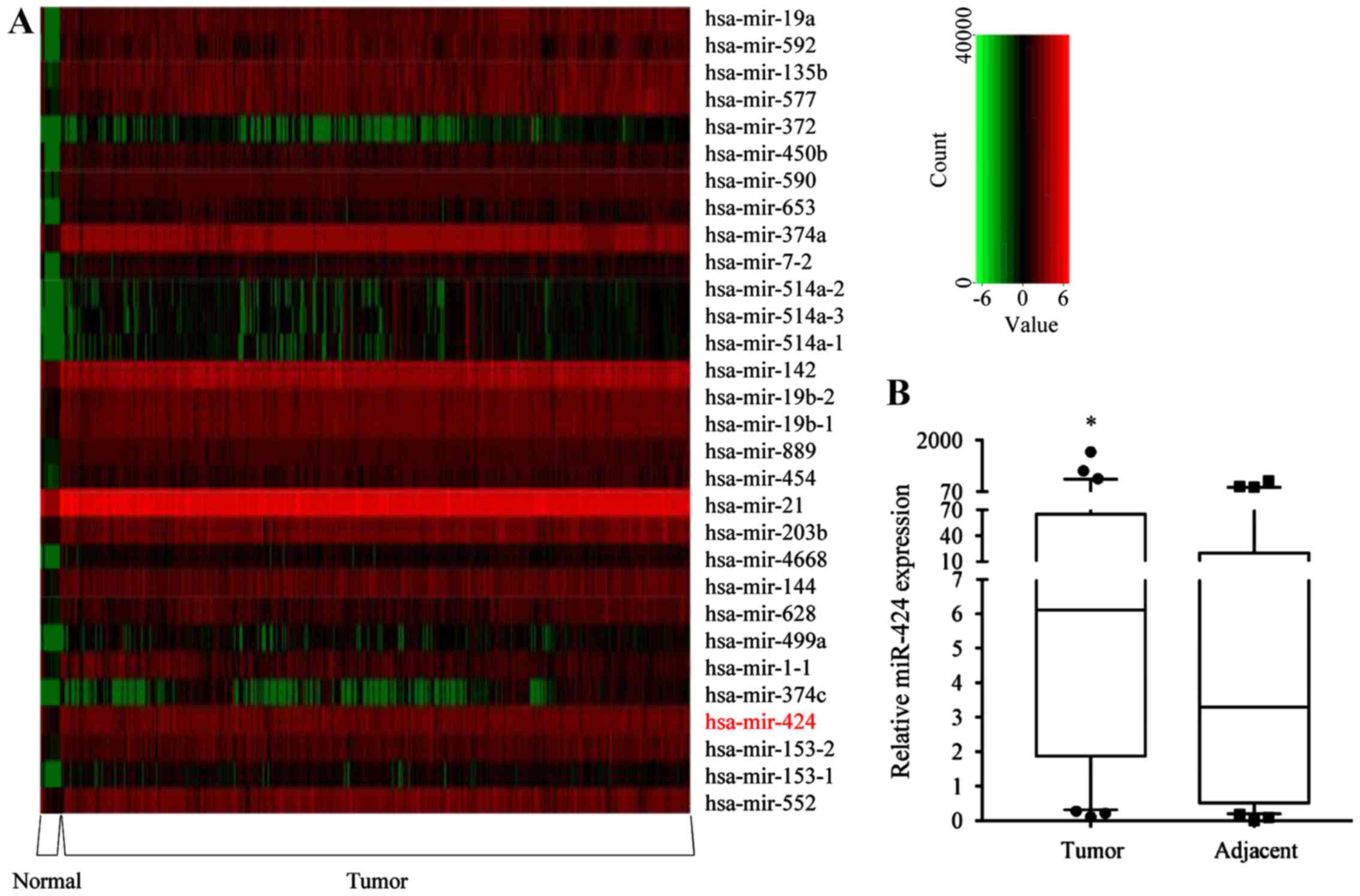
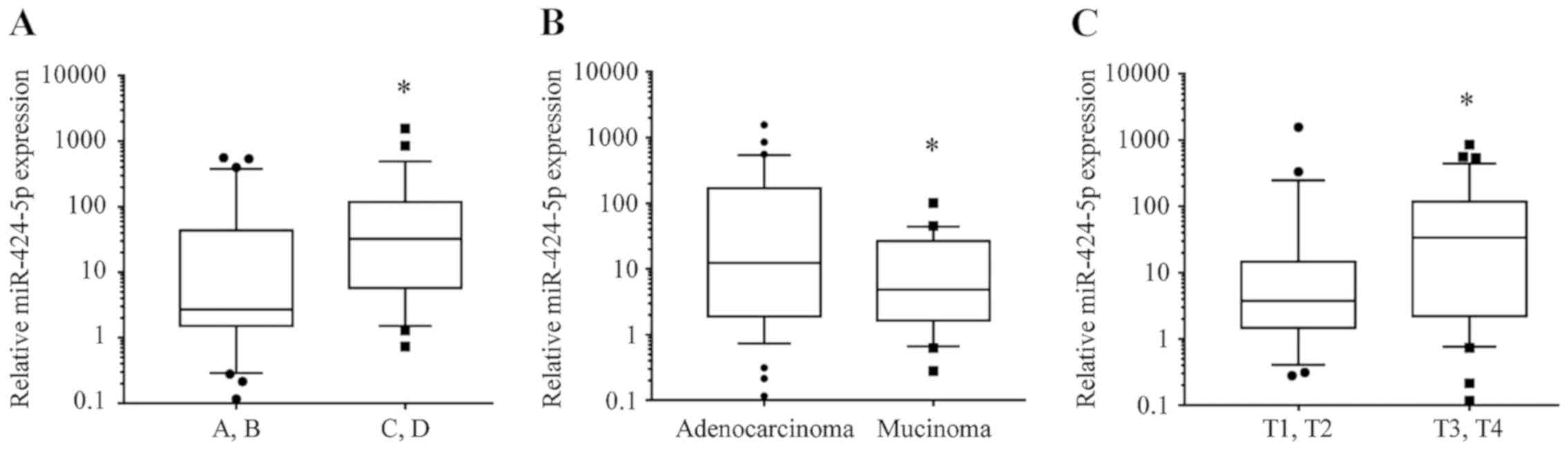
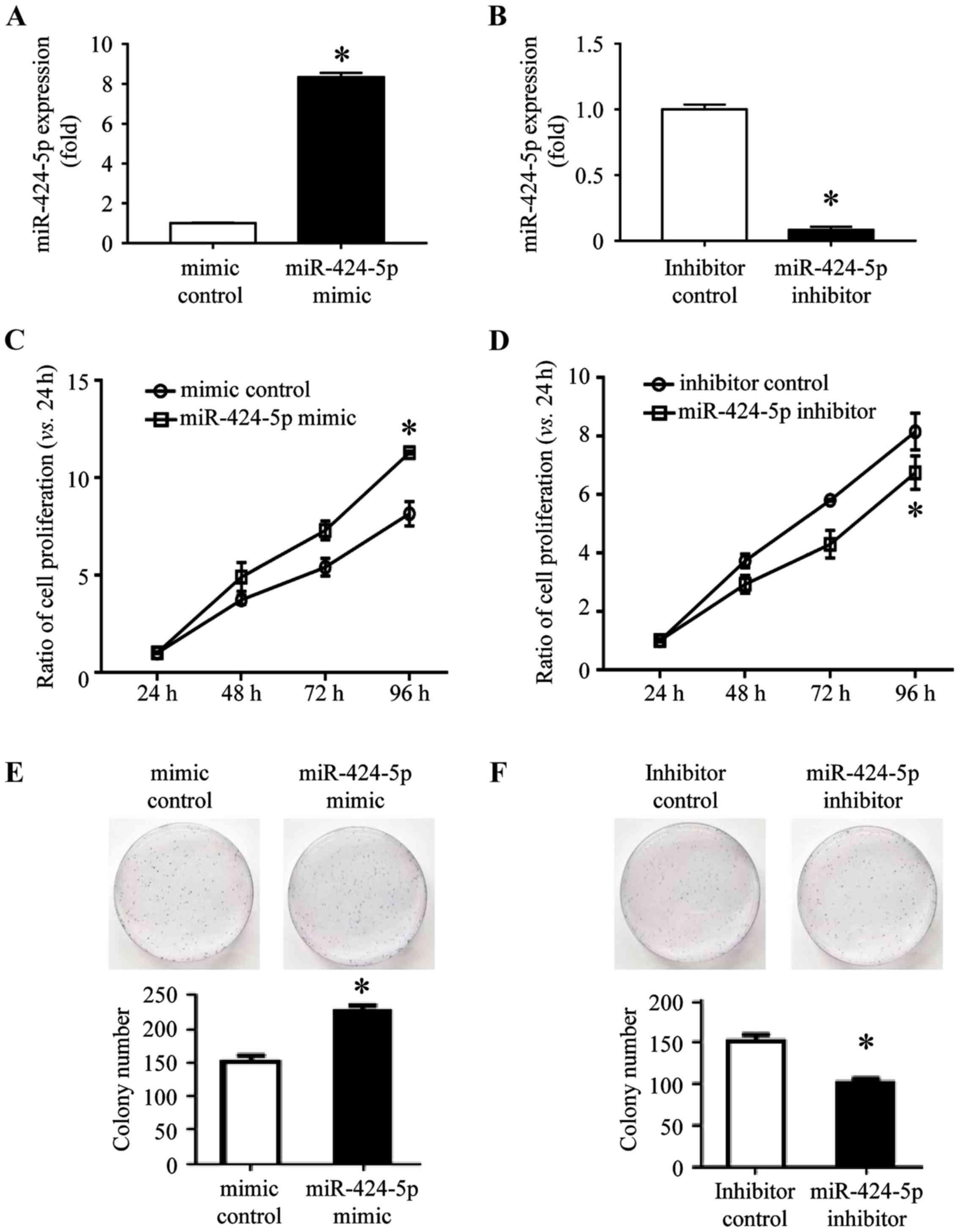
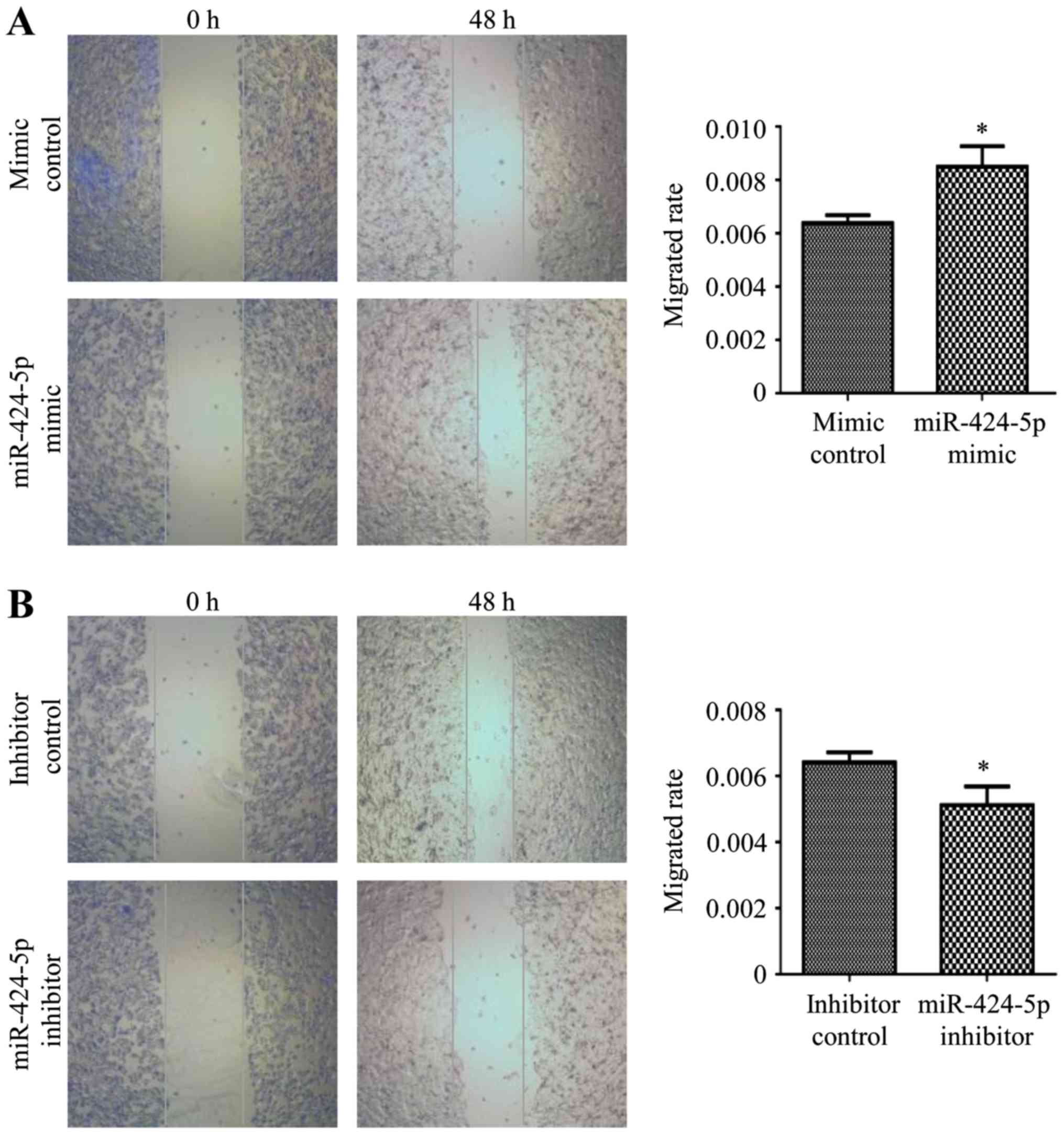
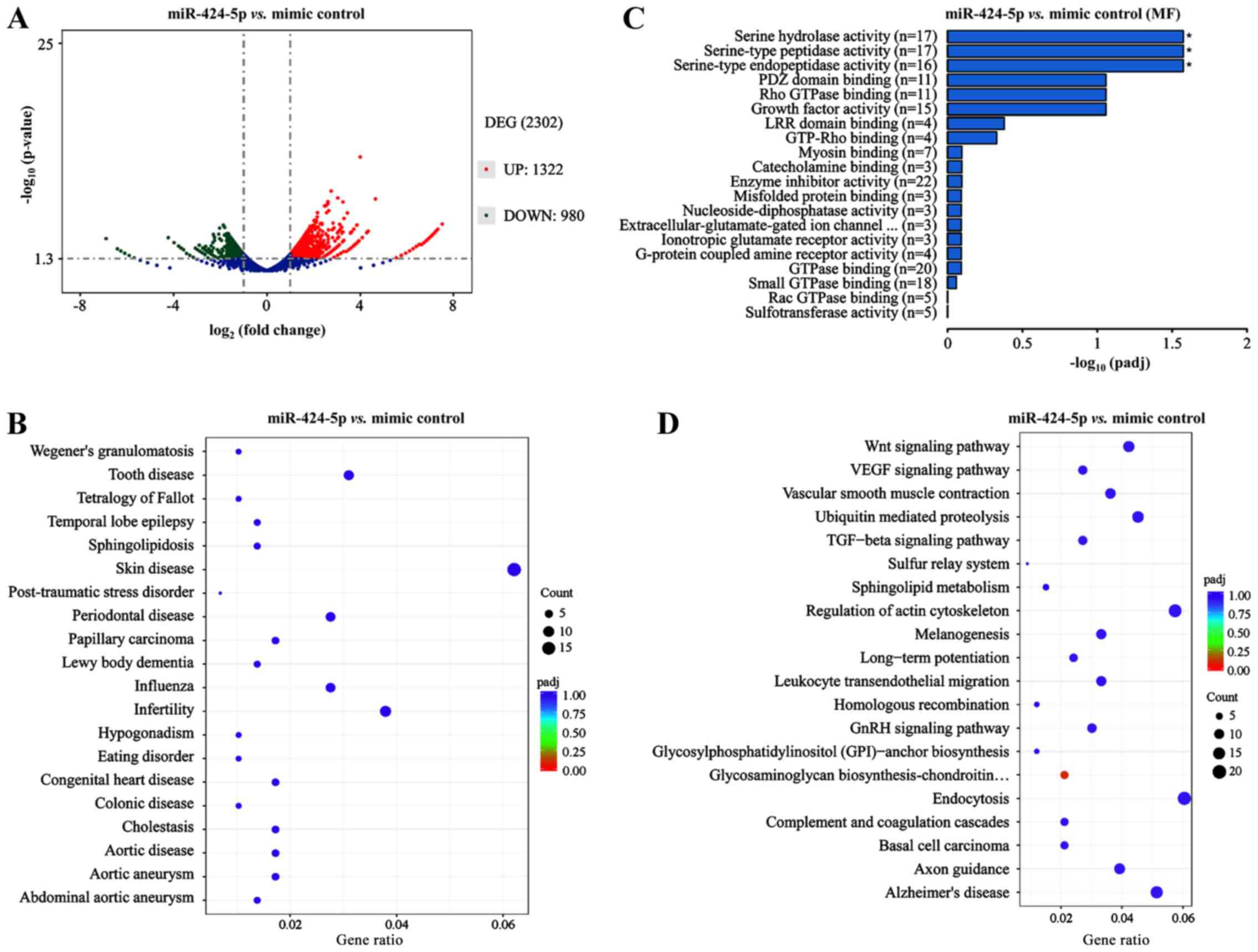
|
1
|
Cao L, Liu Y, Wang D, Huang L, Li F, Liu
J, Zhang C, Shen Z, Gao Q, Yuan W and Zhang Y: MiR-760 suppresses
human colorectal cancer growth by targeting BATF3/AP-1/cyclinD1
signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:832018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang Q and Ma Q: MicroRNA-106a inhibits
cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer
cells. Oncol Lett. 15:8941–8944. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gu S, Jin L, Zhang F, Sarnow P and Kay MA:
Biological basis for restriction of microRNA targets to the 3′
untranslated region in mammalian mRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
16:144–150. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ye JJ and Cao J: MicroRNAs in colorectal
cancer as markers and targets: Recent advances. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:4288–4299. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fayyad-Kazan H, Bitar N, Najar M, Lewalle
P, Fayyad-Kazan M, Badran R, Hamade E, Daher A, Hussein N, ElDirani
R, et al: Circulating miR-150 and miR-342 in plasma are novel
potential biomarkers for acute myeloid leukemia. J Transl Med.
11:312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang B, Yin M, Cheng C, Jiang H, Jiang K,
Shen Z, Ye Y and Wang S: Decreased expression of miR4903p in
colorectal cancer predicts poor prognosis and promotes cell
proliferation and invasion by targeting RAB14. Int J Oncol.
53:1247–1256. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kassambara A, Jourdan M, Bruyer A, Robert
N, Pantesco V, Elemento O, Klein B and Moreaux J: Global miRNA
expression analysis identifies novel key regulators of plasma cell
differentiation and malignant plasma cell. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:5639–5652. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gozuacik D, Akkoc Y, Ozturk DG and Kocak
M: Autophagy-regulating microRNAs and Cancer. Front Oncol.
7:652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu J, Gu Z, Tang Y, Hao J, Zhang C and
Yang X: Tumour-suppressive microRNA-424-5p directly targets CCNE1
as potential prognostic markers in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cell
Cycle. 17:309–318. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu K, Hu G, He X, Zhou P, Li J, He B and
Sun W: MicroRNA-424-5p suppresses the expression of SOCS6 in
pancreatic cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 19:739–748. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wei S, Li Q, Li Z, Wang L, Zhang L and Xu
Z: MiR-424-5p promotes proliferation of gastric cancer by targeting
Smad3 through TGF-β signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 7:75185–75196.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Li T, Guo P, Kang J, Wei Q, Jia
X, Zhao W, Huai W, Qiu Y, Sun L and Han L: MiR-424-5p reversed
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of anchorage-independent HCC
cells by directly targeting ICAT and suppressed HCC progression.
Sci Rep. 4:62482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang F, Wang J, Yang X, Chen D and Wang L:
MiR-424-5p participates in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
invasion and metastasis via SMAD7 pathway mediated EMT. Diagn
Pathol. 11:882016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou Y, An Q, Guo RX, Qiao YH, Li LX,
Zhang XY and Zhao XL: MiR424-5p functions as an anti-oncogene in
cervical cancer cell growth by targeting KDM5B via the Notch
signaling pathway. Life Sci. 171:9–15. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee JS: Exploring cancer genomic data from
the cancer genome atlas project. BMB Rep. 49:607–611. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Wang S, Zhou J and Qian Q:
MiR-424-5p regulates cell proliferation, migration and invasion by
targeting doublecortin-like kinase 1 in basal-like breast cancer.
Biomed Pharmacother. 102:147–152. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li D, Liu K, Li Z, Wang J and Wang X:
MiR-19a and miR-424 target TGFBR3 to promote
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration of tongue
squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Adh Migr. 12:236–246. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Q, Qiu XM, Li QH, Wang XY, Li L, Xu M,
Dong M and Xiao YB: MicroRNA-424 may function as a tumor suppressor
in endometrial carcinoma cells by targeting E2F7. Oncol Rep.
33:2354–2360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu J, Li Y, Wang F, Wang X, Cheng B, Ye F,
Xie X, Zhou C and Lu W: Suppressed miR-424 expression via
upregulation of target gene Chk1 contributes to the progression of
cervical cancer. Oncogene. 32:976–987. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang M, Zeng J, Zhao Z and Liu Z: Loss of
MiR-424-3p, not miR-424-5p, confers chemoresistance through
targeting YAP1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Carcinog.
56:821–832. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hershkovitz-Rokah O, Modai S,
Pasmanik-Chor M, Toren A, Shomron N, Raanani P, Shpilberg O and
Granot G: Restoration of miR-424 suppresses BCR-ABL activity and
sensitizes CML cells to imatinib treatment. Cancer Lett.
360:245–256. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu M, Kong X, Wang H, Huang G, Ye C and He
Z: A novel microRNAs expression signature for hepatocellular
carcinoma diagnosis and prognosis. Oncotarget. 8:8775–8784. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu CT, Lin WY, Chang YH, Lin PY, Chen WC
and Chen MF: DNMT1-dependent suppression of microRNA424 regulates
tumor progression in human bladder cancer. Oncotarget.
6:24119–24131. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang H, Zheng W, Shuai X, Chang RM, Yu L,
Fang F and Yang LY: MicroRNA-424 inhibits Akt3/E2F3 axis and tumor
growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:27736–27750.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yu L, Ding GF, He C, Sun L, Jiang Y and
Zhu L: MicroRNA-424 is down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma
and suppresses cell migration and invasion through c-Myb. PLoS One.
9:e916612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang X, Li Q, Jin H, Zou H, Xia W, Dai N,
Dai XY, Wang D, Xu CX and Qing Y: MiR-424 acts as a tumor
radiosensitizer by targeting aprataxin in cervical cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:77508–77515. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kent OA, Fox-Talbot K and Halushka MK:
RREB1 repressed miR-143/145 modulates KRAS signaling through
downregulation of multiple targets. Oncogene. 32:2576–2585. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Resende TP, Marshall Lund L, Rossow S and
Vannucci FA: Next generation sequencing coupled with in situ
hybridization: A novel diagnostic platform to investigate swine
emerging pathogens and new variants of endemic viruses. Front Vet
Sci. 6:4032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|