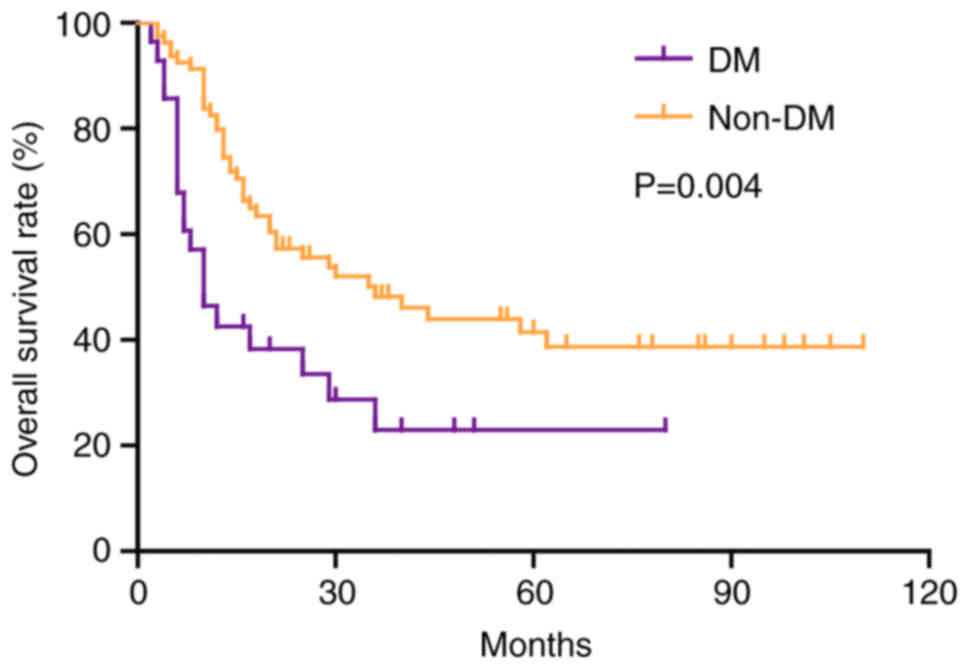
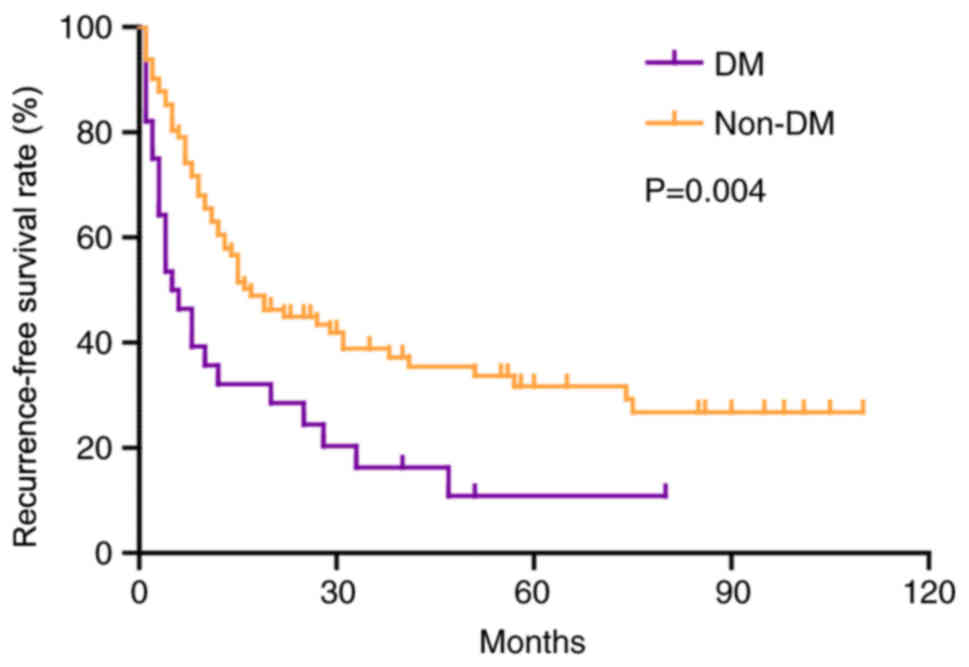
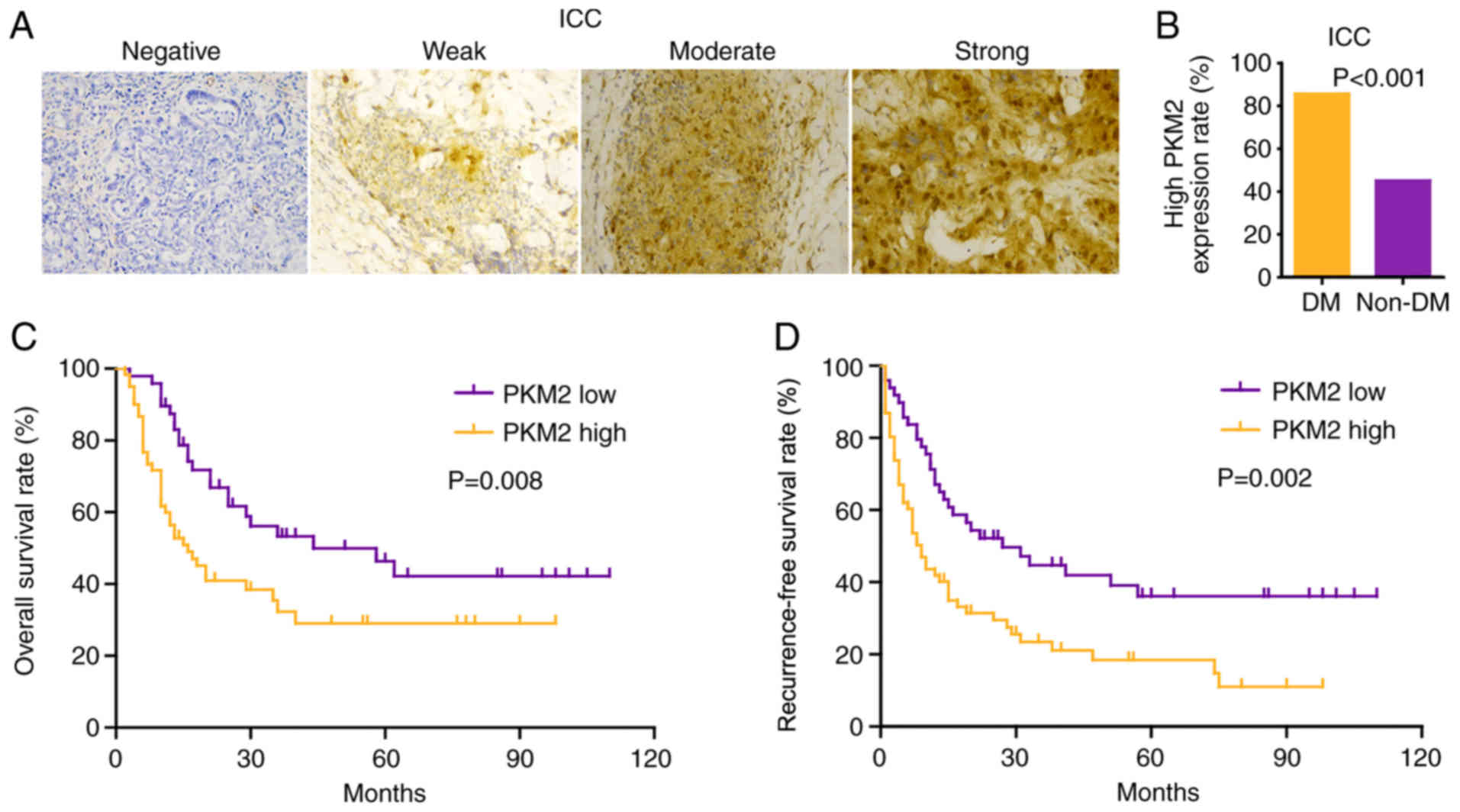
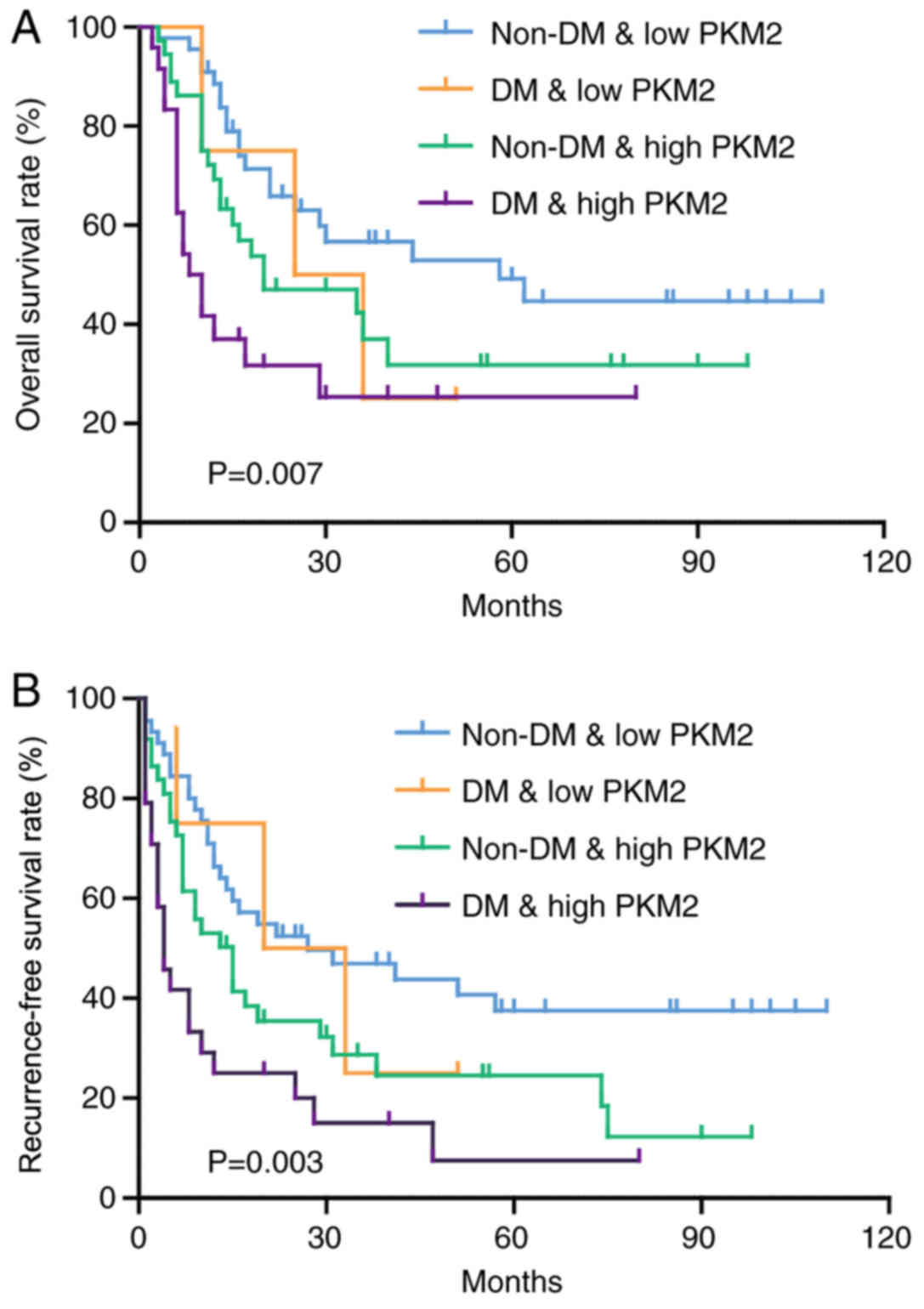
|
1
|
Shaib YH, Davila JA, McGlynn K and
El-Serag HB: Rising incidence of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in
the United States: A true increase? J Hepatol. 40:472–477. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Spolverato G, Kim Y, Alexandrescu S,
Popescu I, Marques HP, Aldrighetti L, Clark Gamblin T, Miura J,
Maithel SK, Squires MH, et al: Is hepatic resection for large or
multifocal intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma justified? Results from
a multi-institutional collaboration. Ann Surg Oncol. 22:2218–2225.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Raoof M, Dumitra S, Ituarte PHG, Melstrom
L, Warner SG, Fong Y and Singh G: Development and validation of a
prognostic score for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. JAMA Surg.
152:e1701172017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C and Shaw
J: IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates of the prevalence of
diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 94:311–321.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang WS, Shu XO, Gao J, Li HL, Cai H, Yang
G, Ji BT, Rothman N, Gao YT, Zheng W and Xiang YB: Prospective
evaluation of type 2 diabetes mellitus on the risk of primary liver
cancer in Chinese men and women. Ann Oncol. 24:1679–1685. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chaiteerakij R, Yang JD, Harmsen WS,
Slettedahl SW, Mettler TA, Fredericksen ZS, Kim WR, Gores GJ,
Roberts RO, Olson JE, et al: Risk factors for intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma: Association between metformin use and reduced
cancer risk. Hepatology. 57:648–655. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Komura T, Mizukoshi E, Kita Y, Sakurai M,
Takata Y, Arai K, Yamashita T, Ohta T, Shimizu K, Nakamoto Y, et
al: Impact of diabetes on recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma
after surgical treatment in patients with viral hepatitis. Am J
Gastroenterol. 102:1939–1946. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ting CT, Chen RC, Chen CC, Liu MH, Chu D
and Kuo NW: Diabetes worsens the surgical outcomes in cirrhotic
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Tohoku J Exp Med.
227:73–81. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang YG, Wang P, Wang B, Fu ZJ, Zhao WJ
and Yan SL: Diabetes mellitus and poorer prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
PLoS One. 9:e954852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang YY, Huang S, Zhong JH, Ke Y, Guo Z,
Liu JQ, Ma L, Li H, Ou BN and Li LQ: Impact of diabetes mellitus on
the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after
curative hepatectomy. PLoS One. 9:e1138582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Palmer WC and Patel T: Are common factors
involved in the pathogenesis of primary liver cancers? A
meta-analysis of risk factors for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
J Hepatol. 57:69–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cairns RA, Harris IS and Mak TW:
Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:85–95.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu G, Yu W, Jin G, Xu D, Chen Y, Xia T, Yu
A, Fang W, Zhang X, Li Z and Xie K: PKM2 regulates neural invasion
of and predicts poor prognosis for human hilar cholangiocarcinoma.
Mol Cancer. 14:1932015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Beyoglu D, Imbeaud S, Maurhofer O,
Bioulac-Sage P, Zucman-Rossi J, Dufour JF and Idle JR: Tissue
metabolomics of hepatocellular carcinoma: Tumor energy metabolism
and the role of transcriptomic classification. Hepatology.
58:229–238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Beyoglu D and Idle JR: The metabolomic
window into hepatobiliary disease. J Hepatol. 59:842–858. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Israelsen WJ, Dayton TL, Davidson SM,
Fiske BP, Hosios AM, Bellinger G, Li J, Yu Y, Sasaki M, Horner JW,
et al: PKM2 isoform-specific deletion reveals a differential
requirement for pyruvate kinase in tumor cells. Cell. 155:397–409.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cortes-Cros M, Hemmerlin C, Ferretti S,
Zhang J, Gounarides JS, Yin H, Muller A, Haberkorn A, Chene P,
Sellers WR and Hofmann F: M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase is
dispensable for tumor maintenance and growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 110:489–494. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li Q, Liu X, Yin Y, Zheng JT, Jiang CF,
Wang J, Shen H, Li CY, Wang M, Liu LZ and Jiang BH: Insulin
regulates glucose consumption and lactate production through
reactive oxygen species and pyruvate kinase M2. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2014:5049532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li W, Wang J, Chen QD, Qian X, Li Q, Yin
Y, Shi ZM, Wang L, Lin J, Liu LZ and Jiang BH: Insulin promotes
glucose consumption via regulation of miR-99a/mTOR/PKM2 pathway.
PLoS One. 8:e649242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
American Diabetes Association: Standards
of medical care in diabetes-2013. Diabetes Care 36 Suppl. 1 (Suppl
1):S11–S66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th. Springer;
New York, NY: 2010
|
|
23
|
Liu Y, Wu H, Mei Y, Ding X, Yang X, Li C,
Deng M and Gong J: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance
of PKM2 protein expression in cirrhotic hepatocellular carcinoma
and non-cirrhotic hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. 7:152942017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nishioka T, Kubo S, Tanaka S, Wakasa K,
Takemura S, Kinoshita M, Hamano G, Kuwae Y, Shibata T and Suehiro
S: Outcomes of hepatic resection in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
patients with diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia:
Significance of routine follow-up. Liver Cancer. 5:107–120. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee BS, Park EC, Park SW, Nam CM and Roh
J: Hepatitis B virus infection, diabetes mellitus, and their
synergism for cholangiocarcinoma development: A case-control study
in Korea. World J Gastroenterol. 21:502–510. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu Q, He XD, Yu L, Liu W and Tao LY: The
metabolic syndrome and risk factors for biliary tract cancer: A
case-control study in China. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:1963–1969.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang YJ, Wu AT, Chiou HY, Chuang MT, Meng
TC, Chien LN and Yen Y: Interactive role of diabetes mellitus and
female sex in the risk of cholangiocarcinoma: A population-based
nested case-control study. Oncotarget. 8:6642–6651. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Endo I, Gonen M, Yopp AC, Dalal KM, Zhou
Q, Klimstra D, D'Angelica M, DeMatteo RP, Fong Y, Schwartz L, et
al: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Rising frequency, improved
survival, and determinants of outcome after resection. Ann Surg.
248:84–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jing W, Jin G, Zhou X, Zhou Y, Zhang Y,
Shao C, Liu R and Hu X: Diabetes mellitus and increased risk of
cholangiocarcinoma: A meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer Prev. 21:24–31.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Welzel TM, Graubard BI, El-Serag HB, Shaib
YH, Hsing AW, Davila JA and McGlynn KA: Risk factors for
intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United
States: A population-based case-control study. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 5:1221–1228. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dayton TL, Jacks T and Vander Heiden MG:
PKM2, cancer metabolism, and the road ahead. EMBO Rep.
17:1721–1730. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou Z, Li M, Zhang L, Zhao H, Şahin Ö,
Chen J, Zhao JJ, Songyang Z and Yu D: Oncogenic kinase-induced PKM2
tyrosine 105 phosphorylation converts nononcogenic PKM2 to a tumor
promoter and induces cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Res.
78:2248–2261. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang W, Xia Y, Hawke D, Li X, Liang J,
Xing D, Aldape K, Hunter T, Alfred Yung WK and Lu Z: PKM2
phosphorylates histone H3 and promotes gene transcription and
tumorigenesis. Cell. 150:685–696. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li T, Han J, Jia L, Hu X, Chen L and Wang
Y: PKM2 Coordinates glycolysis with mitochondrial fusion and
oxidative phosphorylation. Protein Cell. 10:583–594. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Casadei Gardini A, Faloppi L, De Matteis
S, Foschi FG, Silvestris N, Tovoli F, Palmieri V, Marisi G,
Brunetti O, Vespasiani-Gentilucci U, et al: Metformin and insulin
impact on clinical outcome in patients with advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma receiving sorafenib: Validation study and biological
rationale. Eur J Cancer. 86:106–114. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|