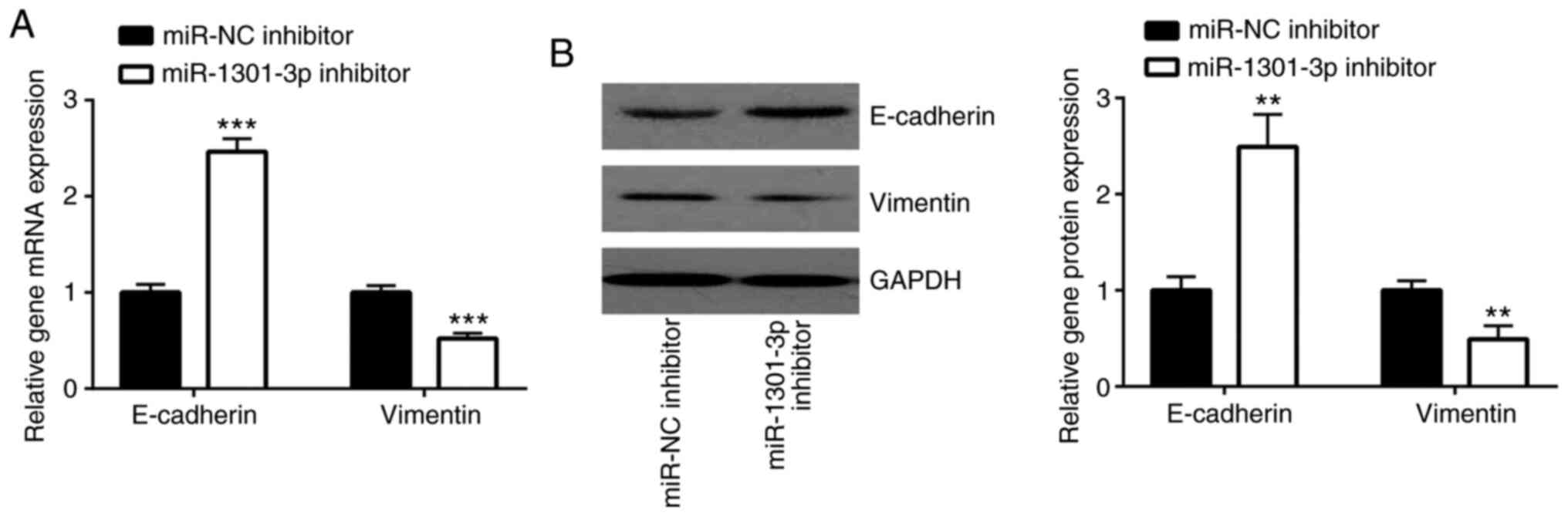
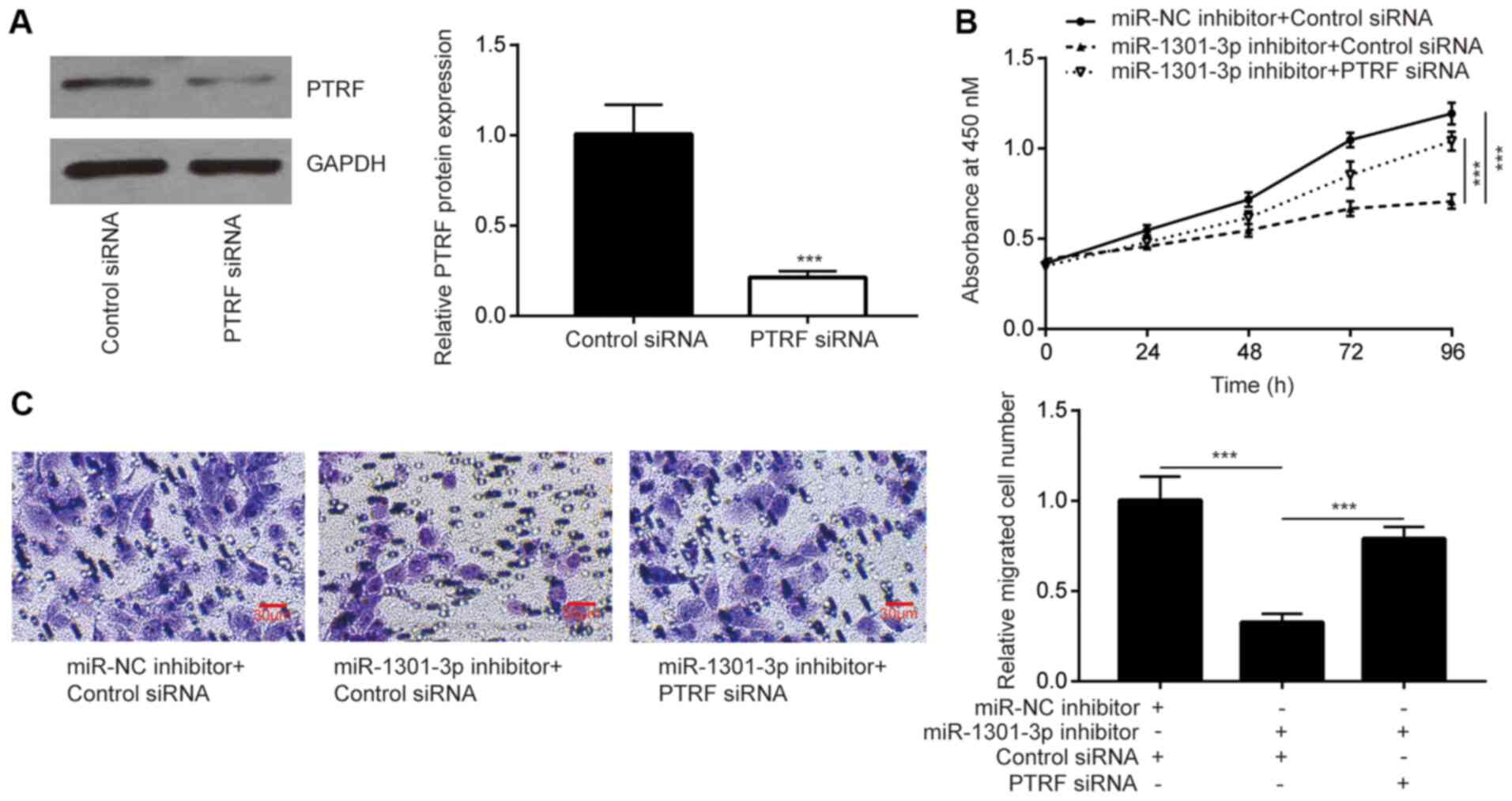
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D and Boshoff C:
The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature.
553:446–454. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen Z, Fillmore CM, Hammerman PS, Kim CF
and Wong KK: Non-small-cell lung cancers: A heterogeneous set of
diseases. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:535–546. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hirono T, Jingushi K, Nagata T, Sato M,
Minami K, Aoki M, Takeda AH, Umehara T, Egawa H, Nakatsuji Y, et
al: MicroRNA-130b functions as an oncomiRNA in non-small cell lung
cancer by targeting tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2. Sci
Rep. 9:69562019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang R, Chen XF and Shu YQ: Prediction of
non-small cell lung cancer metastasis-associated microRNAs using
bioinformatics. Am J Cancer Res. 5:32–51. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yates LA, Norbury CJ and Gilbert RJ: The
long and short of microRNA. Cell. 153:516–519. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao Y and Srivastava D: A developmental
view of microRNA function. Trends Biochem Sci. 32:189–197.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Liang Y and Lu Q: MicroRNA
epigenetic alterations: Predicting biomarkers and therapeutic
targets in human diseases. Clin Genet. 74:307–315. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Sui J, Shen X, Li C, Yao W, Hong
W, Peng H, Pu Y, Yin L and Liang G: Differential expression
profiles of microRNAs as potential biomarkers for the early
diagnosis of lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 37:3543–3553. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tamiya H, Mitani A, Saito A, Ishimori T,
Saito M, Isago H, Jo T, Yamauchi Y, Tanaka G and Nagase T: Exosomal
microRNA expression profiling in patients with lung
adenocarcinoma-associated malignant pleural effusion. Anticancer
Res. 38:6707–6714. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun G, Ding X, Bi N, Wang Z, Wu L, Zhou W,
Zhao Z, Wang J, Zhang W, Fan J, et al: Molecular predictors of
brain metastasis-related microRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS
Genet. 15:e10078882019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mavridis K, Gueugnon F, Petit-Courty A,
Courty Y, Barascu A, Guyetant S and Scorilas A: The oncomiR miR-197
is a novel prognostic indicator for non-small cell lung cancer
patients. Br J Cancer. 112:1527–1535. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu J, Wang S, Chen Y, Li X, Jiang Y, Yang
X, Li Y, Wang X, Meng Y, Zhu M, et al: Mir-19 targeting of GSK3β
mediates sulforaphane suppression of lung cancer stem cells. J Nutr
Biochem. 44:80–91. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Grosso S, Doyen J, Parks SK, Bertero T,
Paye A, Cardinaud B, Gounon P, Lacas-Gervais S, Noël A, Pouysségur
J, et al: MiR-210 promotes a hypoxic phenotype and increases
radioresistance in human lung cancer cell lines. Cell Death Dis.
4:e5442013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Baumgartner U, Berger F, Hashemi Gheinani
A, Burgener SS, Monastyrskaya K and Vassella E: miR-19b enhances
proliferation and apoptosis resistance via the EGFR signaling
pathway by targeting PP2A and BIM in non-small cell lung cancer.
Mol Cancer. 17:442018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou KR, Liu S, Cai L and Bin L: ENCORI:
The encyclopedia of RNA interactomes.
|
|
20
|
Cai Y, Ruan J, Yao X, Zhao L and Wang B:
MicroRNA-187 modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition by
targeting PTRF in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep.
37:2787–2794. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang L, Zhao Y, Xu M, Zhou F and Yan J:
Serum miR-1301-3p, miR-335-5p, miR-28-5p, and their target B7-H3
may serve as novel biomarkers for colorectal cancer. J BUON.
24:1120–1127. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dou D, Yang S, Lin Y and Zhang J: An
eight-miRNA signature expression-based risk scoring system for
prediction of survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer
Biomark. 23:79–93. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bi D, Ning H, Liu S, Que X and Ding K:
miR-1301 promotes prostate cancer proliferation through directly
targeting PPP2R2C. Biomed Pharmacother. 81:25–30. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang B, Wu H, Chai C, Lewis J, Pichiorri
F, Eisenstat DD, Pomeroy SL and Leng RP: MicroRNA-1301 suppresses
tumor cell migration and invasion by targeting the p53/UBE4B
pathway in multiple human cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 401:20–32.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu L and Pilch PF: A critical role of
cavin (polymerase I and transcript release factor) in caveolae
formation and organization. J Biol Chem. 283:4314–4322.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gamez-Pozo A, Sanchez-Navarro I, Calvo E,
Agulló-Ortuño MT, López-Vacas R, Díaz E, Camafeita E, Nistal M,
Madero R, Espinosa E, et al: PTRF/cavin-1 and MIF proteins are
identified as non-small cell lung cancer biomarkers by label-free
proteomics. PLoS One. 7:e337522012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nassar ZD, Moon H, Duong T, Neo L, Hill
MM, Francois M, Parton RG and Parat MO: PTRF/Cavin-1 decreases
prostate cancer angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Oncotarget.
4:1844–1855. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yi JS, Mun DG, Lee H, Park JS, Lee JW, Lee
JS, Kim SJ, Cho BR, Lee SW and Ko YG: PTRF/cavin-1 is essential for
multidrug resistance in cancer cells. J Proteome Res. 12:605–614.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aung CS, Hill MM, Bastiani M, Parton RG
and Parat MO: PTRF-cavin-1 expression decreases the migration of
PC3 prostate cancer cells: Role of matrix metalloprotease 9. Eur J
Cell Biol. 90:136–142. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peng J, Liu HZ, Zhong J, Deng ZF, Tie CR,
Rao Q, Xu W, You T, Li J, Cai CB, et al: MicroRNA187 is an
independent prognostic factor in lung cancer and promotes lung
cancer cell invasion via targeting of PTRF. Oncol Rep.
36:2609–2618. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yochum ZA, Cades J, Wang H, Chatterjee S,
Simons BW, O'Brien JP, Khetarpal SK, Lemtiri-Chlieh G, Myers KV,
Huang EH, et al: Targeting the EMT transcription factor TWIST1
overcomes resistance to EGFR inhibitors in EGFR-mutant
non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 38:656–670. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dai L, Chen F, Zheng Y, Zhang D, Qian B,
Ji H, Long F and Cretoiu D: miR-21 regulates growth and EMT in lung
cancer cells via PTEN/Akt/GSK3β signaling. Front Biosci (Landmark
Ed). 24:1426–1439. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Amaar YG and Reeves ME: RASSF1C regulates
miR-33a and EMT marker gene expression in lung cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 10:123–132. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|