|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Johnson NW, Jayasekara P and Amarasinghe
AA: Squamous cell carcinoma and precursor lesions of the oral
cavity: Epidemiology and aetiology. Periodontol. 57:19–37. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Taniguchi Y and Okura M: Prognostic
significance of perioperative blood transfusion in oral cavity
squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 25:931–936. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Koyama S, Tabuchi T, Okawa S, Morishima T,
Ishimoto S, Ishibashi M and Miyashiro I: Oral cavity cancer
incidence rates in Osaka, Japan between 2000 and 2014. Oral Oncol.
105:1046532020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu C, Li M, Meng H, Liu Y, Niu W, Zhou Y,
Zhao R, Duan Y, Zeng Z, Li X, et al: Analysis of status and
countermeasures of cancer incidence and mortality in China. Sci
China Life Sci. 62:640–647. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ and Brakenhoff
RH: The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:9–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu J, Liu Y, Gong Z, Zhang S, Guo C, Li X,
Tang Y, Yang L, He Y, Wei F, et al: Overexpression long non-coding
RNA LINC00673 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes
invasion and metastasis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 8:16621–16632. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu J, Liu Y, Guo C, Zhang S, Gong Z, Tang
Y, Yang L, He Y, Lian Y, Li X, et al: Upregulated long non-coding
RNA LINC00152 expression is associated with progression and poor
prognosis of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer. 8:523–530.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
De Angelis R, Sant M, Coleman MP,
Francisci S, Baili P, Pierannunzio D, Trama A, Visser O, Brenner H,
Ardanaz E, et al: Cancer survival in Europe 1999–2007 by country
and age: Results of EUROCARE-5-a population-based study. Lancet
Oncol. 15:23–34. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shield KD, Ferlay J, Jemal A,
Sankaranarayanan R, Chaturvedi AK, Bray F and Soerjomataram I: The
global incidence of lip, oral cavity, and pharyngeal cancers by
subsite in 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:51–64. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen PH, Mahmood Q, Mariottini GL, Chiang
TA and Lee KW: Adverse health effects of betel quid and the risk of
oral and pharyngeal cancers. Biomed Res Int. 2017:39040982017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chuerduangphui J, Ekalaksananan T,
Chaiyarit P, Patarapadungkit N, Chotiyano A, Kongyingyoes B,
Promthet S and Pientong C: Effects of arecoline on proliferation of
oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by dysregulating c-Myc and
miR-22, directly targeting oncostatin M. PLoS One. 13:e01920092018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li YC, Cheng AJ, Lee LY, Huang YC and
Chang JT: Multifaceted mechanisms of areca nuts in oral
carcinogenesis: The molecular pathology from precancerous condition
to malignant transformation. J Cancer. 10:4054–4062. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shih YH, Wang TH, Shieh TM and Tseng YH:
Oral submucous fibrosis: A review on etiopathogenesis, diagnosis,
and therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 20:29402019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Arakeri G, Rai KK, Hunasgi S, Merkx MAW,
Gao S and Brennan PA: Oral submucous fibrosis: An update on current
theories of pathogenesis. J Oral Pathol Med. 46:406–412. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang YY, Tail YH, Wang WC, Chen CY, Kao
YH, Chen YK and Chen CH: Malignant transformation in 5071 southern
Taiwanese patients with potentially malignant oral mucosal
disorders. BMC Oral Health. 14:992014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Merchant A, Husain SS, Hosain M, Fikree
FF, Pitiphat W, Siddiqui AR, Hayder SJ, Haider SM, Ikram M, Chuang
SK and Saeed SA: Paan without tobacco: An independent risk factor
for oral cancer. Int J Cancer. 86:128–131. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Srinivasan M and Jewell SD: Evaluation of
TGF-alpha and EGFR expression in oral leukoplakia and oral
submucous fibrosis by quantitative immunohistochemistry. Oncology.
61:284–292. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ray JG, Ranganathan K and Chattopadhyay A:
Malignant transformation of oral submucous fibrosis: Overview of
histopathological aspects. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
Radiol. 122:200–209. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Arora S and Squier C: Areca nut trade,
globalisation and its health impact: Perspectives from India and
South-east Asia. Perspect Public Health. 139:44–48. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nigam NK, Aravinda K, Dhillon M, Gupta S,
Reddy S and Srinivas Raju M: Prevalence of oral submucous fibrosis
among habitual gutkha and areca nut chewers in Moradabad district.
J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 4:8–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pindborg JJ, Mehta FS, Gupta PC and
Daftary DK: Prevalence of oral submucous fibrosis among 50,915
Indian villagers. Br J Cancer. 22:646–654. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hazarey VK, Erlewad DM, Mundhe KA and
Ughade SN: Oral submucous fibrosis: Study of 1,000 cases from
central India. J Oral Pathol Med. 36:12–17. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Warnakulasuriya S: Global epidemiology of
oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 45:309–316. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang SS, Li WH, Gao YJ, Liu ZW, Liu L,
Tang JQ and Ling TY: Betel-quid and oral submucous fibrosis: A
cross-sectional study in Hunan province, China. J Oral Pathol Med.
41:748–754. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu B, Shen M, Xiong J, Yuan Y, Wu X, Gao
X, Xu J, Guo F and Jian X: Synergistic effects of betel quid
chewing, tobacco use (in the form of cigarette smoking), and
alcohol consumption on the risk of malignant transformation of oral
submucous fibrosis (OSF): A case-control study in Hunan province,
China. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 120:337–345.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hu Y, Zhong R, Li H and Zou Y: Effects of
betel quid, smoking and alcohol on oral cancer risk: A case-control
study in hunan province, China. Subst Use Misuse. 55:1501–1508.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Levine AJ: p53: 800 million years of
evolution and 40 years of discovery. Nat Rev Cancer. 20:471–480.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baluapuri A, Wolf E and Eilers M: Target
gene-independent functions of MYC oncoproteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 21:255–267. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang L, Meng X, Zhu XW, Yang DC, Chen R,
Jiang Y and Xu T: Long non-coding RNAs in Oral squamous cell
carcinoma: Biologic function, mechanisms and clinical implications.
Mol Cancer. 18:1022019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang L, Tang Y, He Y, Wang Y, Lian Y,
Xiong F, Shi L, Zhang S, Gong Z, Zhou Y, et al: High expression of
LINC01420 indicates an unfavorable prognosis and modulates cell
migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Cancer.
8:97–103. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fan C, Tang Y, Wang J, Xiong F, Guo C,
Wang Y, Zhang S, Gong Z, Wei F, Yang L, et al: Role of long
non-coding RNAs in glucose metabolism in cancer. Mol Cancer.
16:1302017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
He Y, Jing Y, Wei F, Tang Y, Yang L, Luo
J, Yang P, Ni Q, Pang J, Liao Q, et al: Long non-coding RNA PVT1
predicts poor prognosis and induces radioresistance by regulating
DNA repair and cell apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell
Death Dis. 9:2352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Y, Mo Y, Yang X, Zhou R, Wu Z, He Y,
Yang X, Zhong Y, Du Y, Zhou H, et al: Long non-coding RNA AFAP1-AS1
is a novel biomarker in various cancers: A systematic review and
meta-analysis based on the literature and GEO datasets. Oncotarget.
8:102346–102360. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tang Y, He Y, Zhang P, Wang J, Fan C, Yang
L, Xiong F, Zhang S, Gong Z, Nie S, et al: LncRNAs regulate the
cytoskeleton and related Rho/ROCK signaling in cancer metastasis.
Mol Cancer. 17:772018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lian Y, Xiong F, Yang L, Bo H, Gong Z,
Wang Y, Wei F, Tang Y, Li X, Liao Q, et al: Long noncoding RNA
AFAP1-AS1 acts as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-423-5p to
facilitate nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis through regulating
the Rho/Rac pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:2532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fan C, Tang Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Xiong F,
Zhang S, Li X, Xiang B, Wu X, Guo C, et al: Long non-coding RNA
LOC284454 promotes migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma via modulating the Rho/Rac signaling pathway.
Carcinogenesis. 40:380–391. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bo H, Fan L, Gong Z, Liu Z, Shi L, Guo C,
Li X, Liao Q, Zhang W, Zhou M, et al: Upregulation and
hypomethylation of lncRNA AFAP1-AS1 predicts a poor prognosis and
promotes the migration and invasion of cervical cancer. Oncol Rep.
41:2431–2439. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wei F, Jing YZ, He Y, Tang YY, Yang LT, Wu
YF, Tang L, Shi L, Gong ZJ, Guo C, et al: Cloning and
characterization of the putative AFAP1-AS1 promoter region. J
Cancer. 10:1145–1153. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vuity D, McMahon J, Takhiuddin S, Slinger
C, McLellan D, Wales C, MacIver C, Thomson E, McCaul J, Hislop S,
et al: Is the 8th edition of the union for international cancer
control staging of oral cancer good enough? Br J Oral Maxillofac
Surg. 56:272–277. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
van Schothorst EM, Pagmantidis V, de Boer
VC, Hesketh J and Keijer J: Assessment of reducing RNA input for
Agilent oligo microarrays. Anal Biochem. 363:315–317. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jolliffe IT and Cadima J: Principal
component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos Trans
A Math Phys Eng Sci. 374:201502022016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
DiLeo MV, Strahan GD, den Bakker M and
Hoekenga OA: Weighted correlation network analysis (WGCNA) applied
to the tomato fruit metabolome. PLoS One. 6:e266832011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rentoft M, Coates PJ, Laurell G and
Nylander K: Transcriptional profiling of formalin fixed paraffin
embedded tissue: Pitfalls and recommendations for identifying
biologically relevant changes. PLoS One. 7:e352762012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Subramanian A, Kuehn H, Gould J, Tamayo P
and Mesirov JP: GSEA-P: A desktop application for Gene set
enrichment analysis. Bioinformatics. 23:3251–3253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
He W, Fu L, Yan Q, Zhou Q, Yuan K, Chen L
and Han Y: Gene set enrichment analysis and meta-analysis
identified 12 key genes regulating and controlling the prognosis of
lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett. 17:5608–5618. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jin X, Li J, Li W, Wang X, Du C, Geng Z,
Geng Y, Kang L, Zhang X, Wang M and Tian S: Weighted gene
Co-expression network analysis reveals specific modules and
biomarkers in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 728:1349502020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang B and Horvath S: A general framework
for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat Appl Genet
Mol Biol. 4:Article172005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Krämer A, Green J, Pollard J Jr and
Tugendreich S: Causal analysis approaches in ingenuity pathway
analysis. Bioinformatics. 30:523–530. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lv H, Liu L, Zhang Y, Song T, Lu J and
Chen X: Ingenuity pathways analysis of urine metabonomics
phenotypes toxicity of gentamicin in multiple organs. Mol Biosyst.
6:2056–2067. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ooi AT, Gower AC, Zhang KX, Vick JL, Hong
L, Nagao B, Wallace WD, Elashoff DA, Walser TC, Dubinett SM, et al:
Molecular profiling of premalignant lesions in lung squamous cell
carcinomas identifies mechanisms involved in stepwise
carcinogenesis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila 7). 487–495. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Kharbanda OP, Ivaturi A, Priya H, Dorji G
and Gupta S: Digital possibilities in the prevention and early
detection of oral cancer in the WHO South-East Asia Region. WHO
South East Asia J Public Health. 8:95–100. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Marchese FP, Raimondi I and Huarte M: The
multidimensional mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function. Genome
Biol. 18:2062017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lin C and Yang L: Long Noncoding RNA in
cancer: Wiring signaling circuitry. Trends Cell Biol. 28:287–301.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wang D, Zeng Z, Zhang S, Xiong F, He B, Wu
Y, Li W, Tang L, Wei F, Xiang B, et al: Epstein-Barr virus-encoded
miR-BART6-3p inhibits cancer cell proliferation through the
LOC553103-STMN1 axis. FASEB J. 34:8012–8027. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ban Y, Tan P, Cai J, Li J, Hu M, Zhou Y,
Mei Y, Tan Y, Li X, Zeng Z, et al: LNCAROD is stabilized by m6A
methylation and promotes cancer progression via forming a ternary
complex with HSPA1A and YBX1 in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Mol Oncol. 14:1282–1296. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wu P, Mo Y, Peng M, Tang T, Zhong Y, Deng
X, Xiong F, Guo C, Wu X, Li Y, et al: Emerging role of
tumor-related functional peptides encoded by lncRNA and circRNA.
Mol Cancer. 19:222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang W, Zhou R, Wu Y, Liu Y, Su W, Xiong W
and Zeng Z: PVT1 promotes cancer progression via MicroRNAs. Front
Oncol. 9:6092019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Jin K, Wang S, Zhang Y, Xia M, Mo Y, Li X,
Li G, Zeng Z, Xiong W and He Y: Long non-coding RNA PVT1 interacts
with MYC and its downstream molecules to synergistically promote
tumorigenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:4275–4289. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Fan CM, Wang JP, Tang YY, Zhao J, He SY,
Xiong F, Guo C, Xiang B, Zhou M, Li XL, et al: circMAN1A2 could
serve as a novel serum biomarker for malignant tumors. Cancer Sci.
110:2180–2188. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang D, Tang L, Wu Y, Fan C, Zhang S,
Xiang B, Zhou M, Li X, Li Y, Li G, et al: Abnormal X chromosome
inactivation and tumor development. Cell Mol Life Sci.
77:2949–2958. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Tang T, Yang L, Cao Y, Wang M, Zhang S,
Gong Z, Xiong F, He Y, Zhou Y, Liao Q, et al: LncRNA AATBC
regulates Pinin to promote metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Mol Oncol. 14:2251–2270. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Li N, Jian X, Hu Y, Xu C, Yao Z and Zhong
X: Discovery of novel biomarkers in oral submucous fibrosis by
microarray analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
17:2249–2259. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Qiu YL, Liu YH, Ban JD, Wang WJ, Han M,
Kong P and Li BH: Pathway analysis of a genomewide association
study on a long noncoding RNA expression profile in oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 41:895–907. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Potapova TA, Zhu J and Li R: Aneuploidy
and chromosomal instability: A vicious cycle driving cellular
evolution and cancer genome chaos. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
32:377–389. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Janjetovic S, Sticht C, Knoepfle K, Joos
S, Hofele C, Lichter P and Freier K: Comparative expressed sequence
hybridization detects recurrent patterns of altered sequence
expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 24:369–374.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Sakai N, Kajiyama Y, Iwanuma Y, Tomita N,
Amano T, Isayama F, Ouchi K and Tsurumaru M: Study of abnormal
chromosome regions in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by
comparative genomic hybridization: Relationship of lymph node
metastasis and distant metastasis to selected abnormal regions. Dis
Esophagus. 23:415–421. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Freier K, Knoepfle K, Flechtenmacher C,
Pungs S, Devens F, Toedt G, Hofele C, Joos S, Lichter P and
Radlwimmer B: Recurrent copy number gain of transcription factor
SOX2 and corresponding high protein expression in oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 49:9–16. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Cao Y, Liu Y, Yang X, Liu X, Han N, Zhang
K and Lin D: Estimation of the survival of patients with lung
squamous cell carcinoma using genomic copy number aberrations. Clin
Lung Cancer. 17:68–74.e5. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yoshikawa Y, Emi M, Hashimoto-Tamaoki T,
Ohmuraya M, Sato A, Tsujimura T, Hasegawa S, Nakano T, Nasu M,
Pastorino S, et al: High-density array-CGH with targeted NGS unmask
multiple noncontiguous minute deletions on chromosome 3p21 in
mesothelioma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:13432–13437. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Dimova I, Orsetti B, Negre V, Rouge C,
Ursule L, Lasorsa L, Dimitrov R, Doganov N, Toncheva D and Theillet
C: Genomic markers for ovarian cancer at chromosomes 1, 8 and 17
revealed by array CGH analysis. Tumori. 95:357–366. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Uchida K, Oga A, Okafuji M, Mihara M,
Kawauchi S, Furuya T, Chochi Y, Ueyama Y and Sasaki K: Molecular
cytogenetic analysis of oral squamous cell carcinomas by
comparative genomic hybridization, spectral karyotyping, and
fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cancer Genet Cytogenet.
167:109–116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Tang J, Kong D, Cui Q, Wang K, Zhang D,
Gong Y and Wu G: Prognostic genes of breast cancer identified by
gene co-expression network analysis. Front Oncol. 8:3742018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Antonczyk A, Krist B, Sajek M, Michalska
A, Piaszyk-Borychowska A, Plens-Galaska M, Wesoly J and Bluyssen
HAR: Direct inhibition of IRF-dependent transcriptional regulatory
mechanisms associated with disease. Front Immunol. 10:11762019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
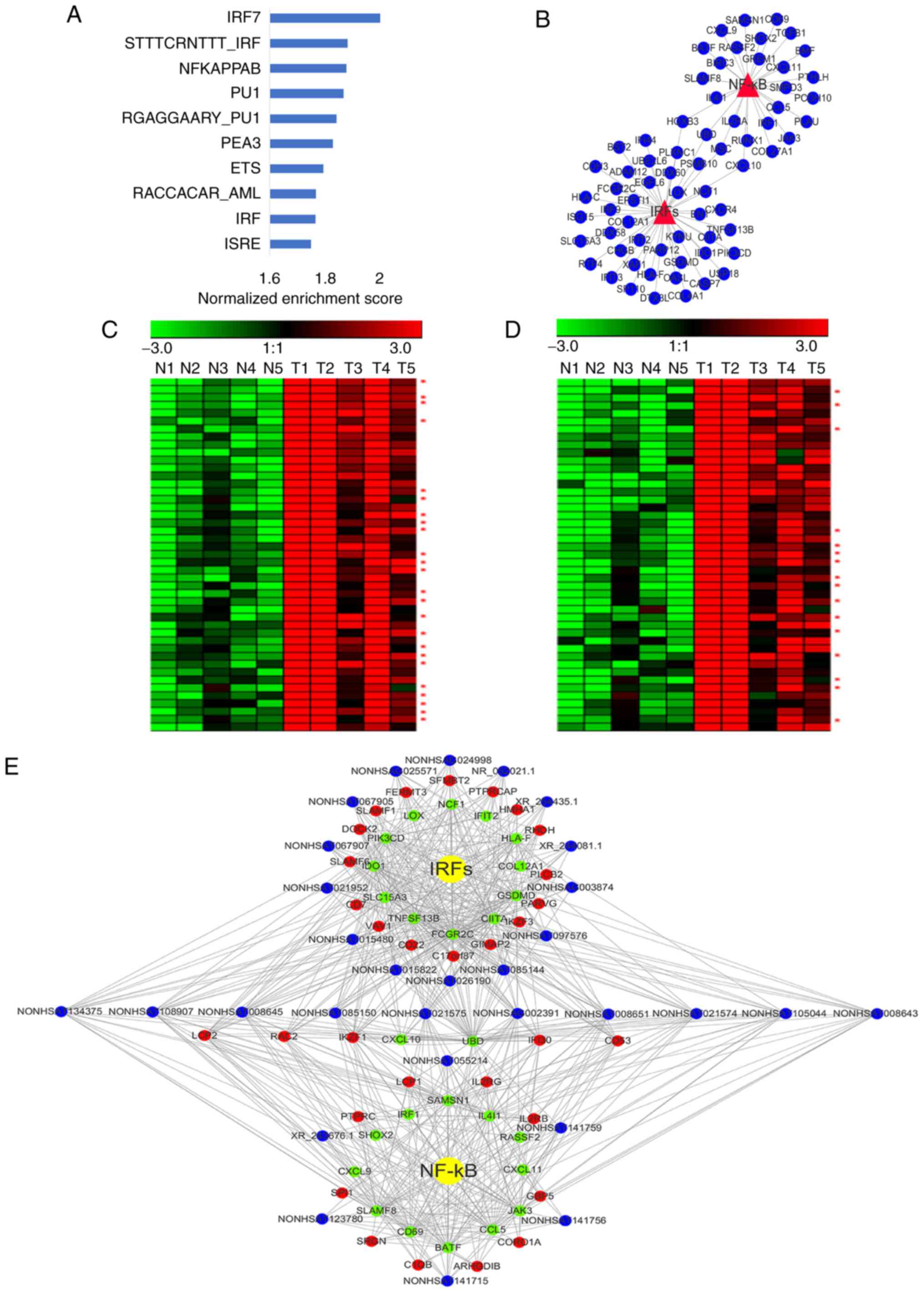
Taniguchi K and Karin M: NF-κB,
inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat Rev Immunol.
18:309–324. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Monisha J, Roy NK, Bordoloi D, Kumar A,
Golla R, Kotoky J, Padmavathi G and Kunnumakkara AB: Nuclear Factor
Kappa B: A potential target to persecute head and neck cancer. Curr
Drug Targets. 18:232–253. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Alsamman K and El-Masry OS: Interferon
regulatory factor 1 inactivation in human cancer. Bioscience Rep.
38:BSR201716722018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Manzella L, Tirro E, Pennisi MS, Massimino
M, Stella S, Romano C, Vitale SR and Vigneri P: Roles of interferon
regulatory factors in chronic myeloid leukemia. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 16:594–605. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Chuang JY, Yang WH, Chen HT, Huang CY, Tan
TW, Lin YT, Hsu CJ, Fong YC and Tang CH: CCL5/CCR5 axis promotes
the motility of human oral cancer cells. J Cell Physiol.
220:418–426. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Pick J, Arra A, Lingel H, Hegel JK, Huber
M, Nishanth G, Jorch G, Fischer KD, Schlüter D, Tedford K and
Brunner-Weinzierl MC: CTLA-4 (CD152) enhances the Tc17
differentiation program. Eur J Immunol. 44:2139–2152. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Jiang GM, Wang HS, Du J, Ma WF, Wang H,
Qiu Y, Zhang QG, Xu W, Liu HF and Liang JP: Bortezomib relieves
immune tolerance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via STAT1 suppression
and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase downregulation. Cancer Immunol Res.
5:42–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Haque MF, Harris M, Meghji S and Speight
PM: An immunohistochemical study of oral submucous fibrosis. J Oral
Pathol Med. 26:75–82. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Demaria S, Pikarsky E, Karin M, Coussens
LM, Chen YC, El-Omar EM, Trinchieri G, Dubinett SM, Mao JT, Szabo
E, et al: Cancer and inflammation: Promise for biologic therapy. J
Immunother. 33:335–351. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Huang W, Zhou X, Liao Q, Tang Y, Zuo L,
Wang H, Chen X, Chen X, Li J, Zhu S, et al: Clinicopathological and
prognostic significance of PD-1/PD-L1 axis expression in patients
with tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 235:6942–6953.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Kujan O, van Schaijik B and Farah CS:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma
and oral potentially malignant disorders: A systematic review.
Cancers (Basel). 12:19372020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Wherry EJ and Kurachi M: Molecular and
cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat Rev Immunol.
15:486–499. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ren D, Hua Y, Yu B, Ye X, He Z, Li C, Wang
J, Mo Y, Wei X, Chen Y, et al: Predictive biomarkers and mechanisms
underlying resistance to PD1/PD-L1 blockade cancer immunotherapy.
Mol Cancer. 19:192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhao J, Guo C, Xiong F, Yu J, Ge J, Wang
H, Liao Q, Zhou Y, Gong Q, Xiang B, et al: Single cell RNA-seq
reveals the landscape of tumor and infiltrating immune cells in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 477:131–143. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Peng M, Mo Y, Wang Y, Wu P, Zhang Y, Xiong
F, Guo C, Wu X, Li Y, Li X, et al: Neoantigen vaccine: An emerging
tumor immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. 18:1282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Xiong F, Deng S, Huang HB, Li XY, Zhang
WL, Liao QJ, Ma J, Li XL, Xiong W, Li GY, et al: Effects and
mechanisms of innate immune molecules on inhibiting nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Chin Med J (Engl). 132:749–752. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Duan S, Guo W, Xu Z, He Y, Liang C, Mo Y,
Wang Y, Xiong F, Guo C, Li Y, et al: Natural killer group 2D
receptor and its ligands in cancer immune escape. Mol Cancer.
18:292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Jiang X, Wang J, Deng X, Xiong F, Ge J,
Xiang B, Wu X, Ma J, Zhou M, Li X, et al: Role of the tumor
microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape. Mol
Cancer. 18:102019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Wang YA, Li XL, Mo YZ, Fan CM, Tang L,
Xiong F, Guo C, Xiang B, Zhou M, Ma J, et al: Effects of tumor
metabolic microenvironment on regulatory T cells. Mol Cancer.
17:1682018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Tang Y, He Y, Shi L, Yang L, Wang J, Lian
Y, Fan C, Zhang P, Guo C, Zhang S, et al: Co-expression of
AFAP1-AS1 and PD-1 predicts poor prognosis in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:39001–39011. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zhou B, Yuan Y, Zhang S, Guo C, Li X, Li
G, Xiong W and Zeng Z: Intestinal flora and disease mutually shape
the regional immune system in the intestinal tract. Front Immunol.
11:5752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Zhang L, Sun S, Wang Y, Mo Y, Xiong F,
Zhang S, Zeng Z, Xiong W, Li G, Chen H and Guo C: Gossypol induces
apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells through the JUN-JNK pathway. Am
J Cancer Res. 10:870–883. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Mo Y, Wang Y, Zhang L, Yang L, Zhou M, Li
X, Li Y, Li G, Zeng Z, Xiong W, et al: The role of Wnt signaling
pathway in tumor metabolic reprogramming. J Cancer. 10:3789–3797.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|