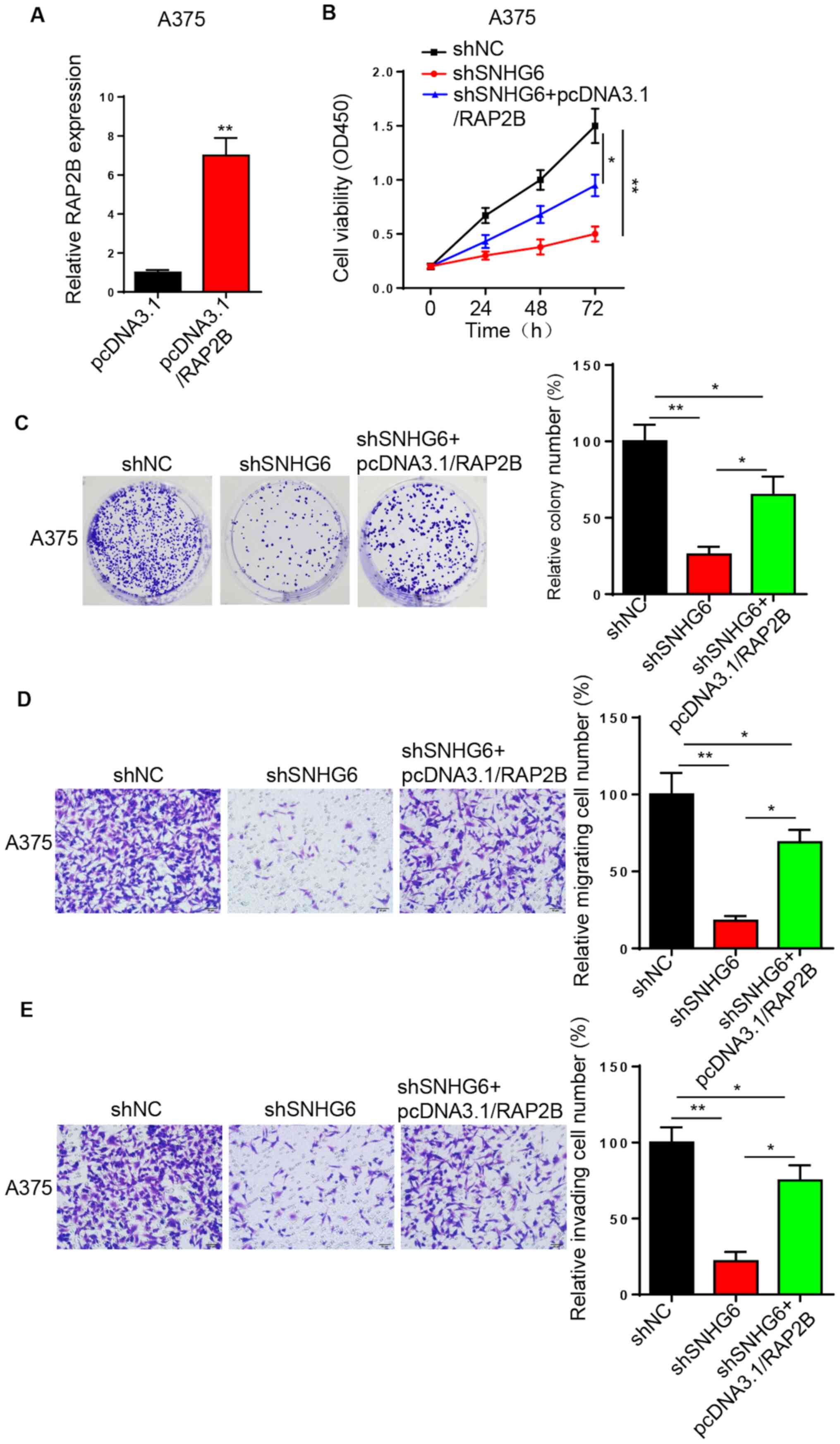
|
1
|
Kozar I, Margue C, Rothengatter S, Haan C
and Kreis S: Many ways to resistance: How melanoma cells evade
targeted therapies. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1871:313–322.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Clarke CA, McKinley M, Hurley S, Haile RW,
Glaser SL, Keegan THM and Swetter SM: Continued increase in
melanoma incidence across all socioeconomic status groups in
California, 1998–2012. J Invest Dermatol. 137:2282–2290. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Slipicevic A and Herlyn M: Narrowing the
knowledge gaps for melanoma. Ups J Med Sci. 117:237–243. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gershenwald JE, Scolyer RA, Hess KR,
Sondak VK, Long GV, Ross MI, Lazar AJ, Faries MB, Kirkwood JM,
McArthur GA, et al: Melanoma staging: Evidence-based changes in the
American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer staging
manual. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:472–492. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baharara J, Amini E, Nikdel N and
Salek-Abdollahi F: The cytotoxicity of dacarbazine potentiated by
sea cucumber saponin in resistant b16f10 melanoma cells through
apoptosis induction. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 8:112–119.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Qi P and Du X: The long non-coding RNAs, a
new cancer diagnostic and therapeutic gold mine. Mod Pathol.
26:155–165. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Luan W, Ding Y, Yuan H, Ma S, Ruan H, Wang
J, Lu F and Bu X: Long non-coding RNA LINC00520 promotes the
proliferation and metastasis of malignant melanoma by inducing the
miR-125b-5p/EIF5A2 axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:962020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wan N, Yang W, Cheng H and Wang J:
FOXD3-AS1 contributes to the progression of melanoma Via
miR-127-3p/FJX1 axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020.(Epub ahead
of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yao X, Lan Z, Lai Q, Li A, Liu S and Wang
X: lncRNA SNHG6 plays an oncogenic role in colorectal cancer and
can be used as a prognostic biomarker for solid tumors. J Cell
Physiol. 235:7620–7634. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang H, Wang L, Tang L, Luo J, Ji H, Zhang
W, Zhou J, Li Q and Miao L: Long noncoding RNA SNHG6 promotes
proliferation and angiogenesis of cholangiocarcinoma cells through
sponging miR-101-3p and activation of E2F8. J Cancer. 11:3002–3012.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li K, Ma YB, Tian YH, Xu XL, Gao Y, He YQ,
Pan WT, Zhang JW, He CJ and Wei L: Silencing lncRNA SNHG6
suppresses proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells
through miR-26a/VASP axis. Pathol Res Pract. 215:1525752019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiao F, Li Y, Wan Y and Xue M:
MircroRNA-139 sensitizes ovarian cancer cell to cisplatin-based
chemotherapy through regulation of ATP7A/B. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 81:935–947. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wei H, He WR, Chen KM, Wang XW and Yi CJ:
miR-101 affects proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer
cells by inhibition of JAK2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:5640–5647. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li L, Shao MY, Zou SC, Xiao ZF and Chen
ZC: miR-101-3p inhibits EMT to attenuate proliferation and
metastasis in glioblastoma by targeting TRIM44. J Neurooncol.
141:19–30. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marts AR, Kaine JC, Baum RR, Clayton VL,
Bennett JR, Cordonnier LJ, McCarrick R, Hasheminasab A, Crandall
LA, Ziegler CJ and Tierney DL: Paramagnetic resonance of cobalt(II)
trispyrazolylmethanes and counterion association. Inorg Chem.
56:618–626. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu Y, Sun H, Hu J and Zhang X: lncRNA
DLX6-AS1 promotes the progression of neuroblastoma by activating
STAT2 via targeting miR-506-3p. Cancer Manag Res. 12:7451–7463.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qu Y and Liu J: lncRNA MAFG-AS1
contributes to esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma progression via
regulating miR143/LASP1. Onco Targets Ther. 13:8359–8370. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ouyang Q, Cui Y, Yang S, Wei W, Zhang M,
Zeng J and Qu F: lncRNA MT1JP suppresses biological activities of
breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo by Regulating the
miRNA-214/RUNX3 axis. Onco Targets Ther. 13:5033–5046. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
An LF, Huang JW, Han X and Wang J:
Downregulation of lncRNA H19 sensitizes melanoma cells to cisplatin
by regulating the miR-18b/IGF1 axis. Anticancer Drugs. 31:473–482.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu F, Hu L, Pei Y, Zheng K, Wang W, Li S,
Qiu E, Shang G, Zhang J and Zhang X: Long non-coding RNA AFAP1-AS1
accelerates the progression of melanoma by targeting
miR-653-5p/RAI14 axis. BMC Cancer. 20:2582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu JH, Zhao WY, Fang QQ, Wang XF, Zhang
DD, Hu YY, Zheng B and Tan WQ: Long noncoding RNA LUADT1 is
upregulated in melanoma and may sponge miR-28-5p to upregulate
RAP1B. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 35:307–312. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zou JX and Ge TW: Long non-coding RNA
NEAT1 promotes tumor development and metastasis through targeting
miR-224-5p in malignant melanoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
24:1302–1308. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu S, Chen H, Zuo L, Jiang H and Yan H:
Suppression of Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 inhibits the development
of uveal melanoma via microRNA-608-mediated inhibition of HOXC4. Am
J Physiol Cell Physiol. 318:C903–C912. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dong Z, Liu H and Zhao G: Long noncoding
RNA SNHG6 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in
non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating miR-490-3p/RSF1
axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 35:351–361. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu G, Ju X, Wang Y, Li Z and Gan X:
Up-regulation of SNHG6 activates SERPINH1 expression by competitive
binding to miR-139-5p to promote hepatocellular carcinoma
progression. Cell Cycle. 18:1849–1867. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ji D, Wang Y, Li H, Sun B and Luo X: Long
non-coding RNA LINC00461/miR-149-5p/LRIG2 axis regulates
hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
512:176–181. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou FC, Zhang YH, Liu HT, Song J and Shao
J: lncRNA LINC00588 suppresses the progression of osteosarcoma by
acting as a ceRNA for miRNA-1972. Front Pharmacol. 11:2552020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu Y, Gao F, He Q, Li G and Ding G: lncRNA
UCA1 functions as a ceRNA to promote prostate cancer progression
via sponging miR143. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 19:751–758. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ma Y, Liu Y, Pu YS, Cui ML, Mao ZJ, Li ZZ,
He L, Wu M and Wang JH: lncRNA IGFL2-AS1 functions as a ceRNA in
regulating ARPP19 through competitive binding to miR-802 in gastric
cancer. Mol Carcinog. 59:311–322. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li K, Jiang Y, Xiang X, Gong Q, Zhou C,
Zhang L, Ma Q and Zhuang L: Long non-coding RNA SNHG6 promotes the
growth and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by downregulating
miR-101-3p. Thorac Cancer. 11:1180–1190. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Meng Q, Yang BY, Liu B, Yang JX and Sun Y:
Long non-coding RNA SNHG6 promotes glioma tumorigenesis by sponging
miR-101-3p. Int J Biol Markers. 33:148–155. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chang L, Yuan Y, Li C, Guo T, Qi H, Xiao
Y, Dong X, Liu Z and Liu Q: Upregulation of SNHG6 regulates ZEB1
expression by competitively binding miR-101-3p and interacting with
UPF1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 383:183–194. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Peng YG, Zhang ZQ, Chen YB and Huang JA:
Rap2b promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung
cancer cells. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 36:459–464. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang M, Zhuang Q and Cui L: miR-194
inhibits cell proliferation and invasion via repression of RAP2B in
bladder cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 80:268–275. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lv GY, Miao J and Zhang XL: Long noncoding
RNA XIST promotes osteosarcoma progression by targeting Ras-Related
protein RAP2B via miR-320b. Oncol Res. 26:837–846. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|