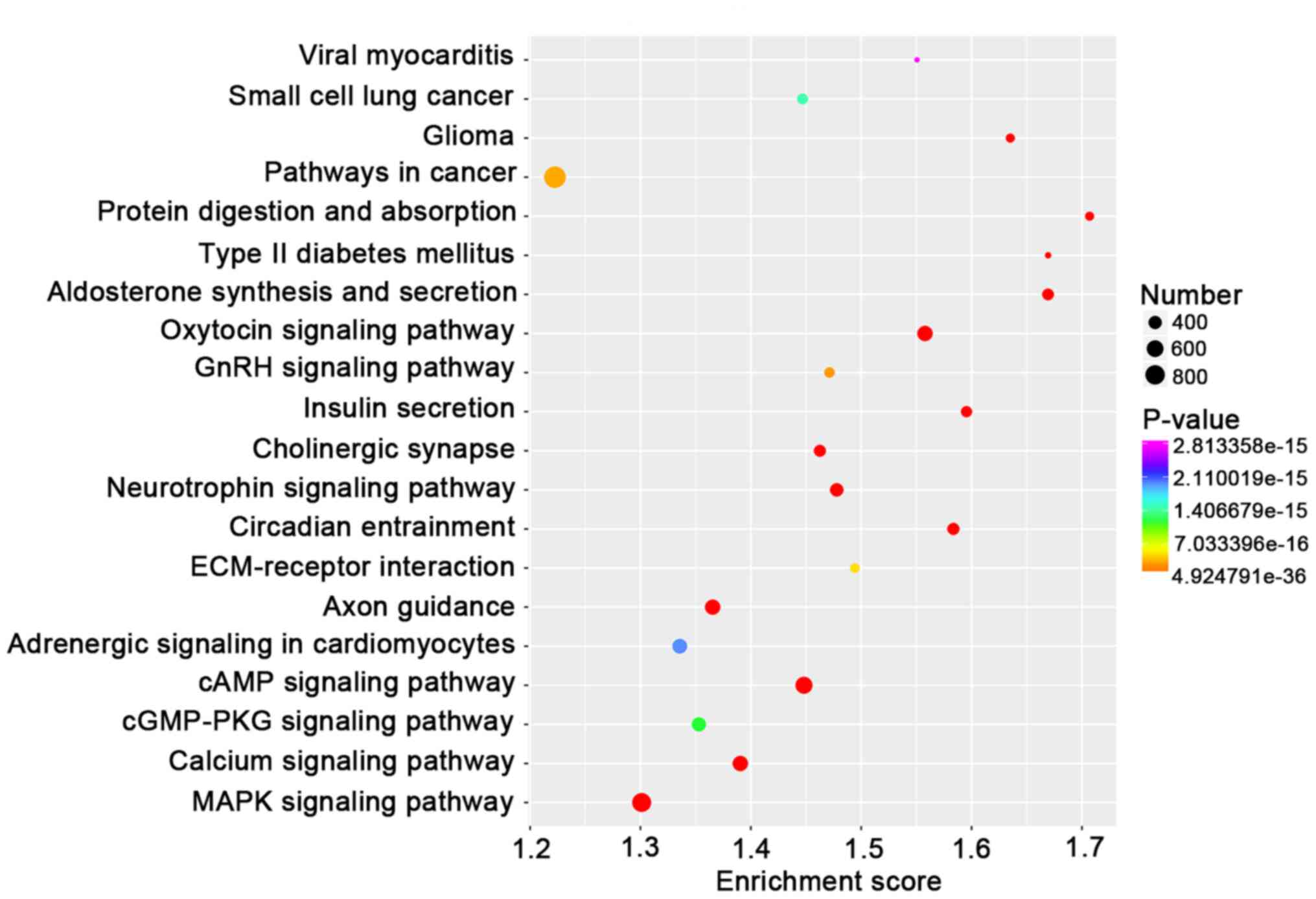
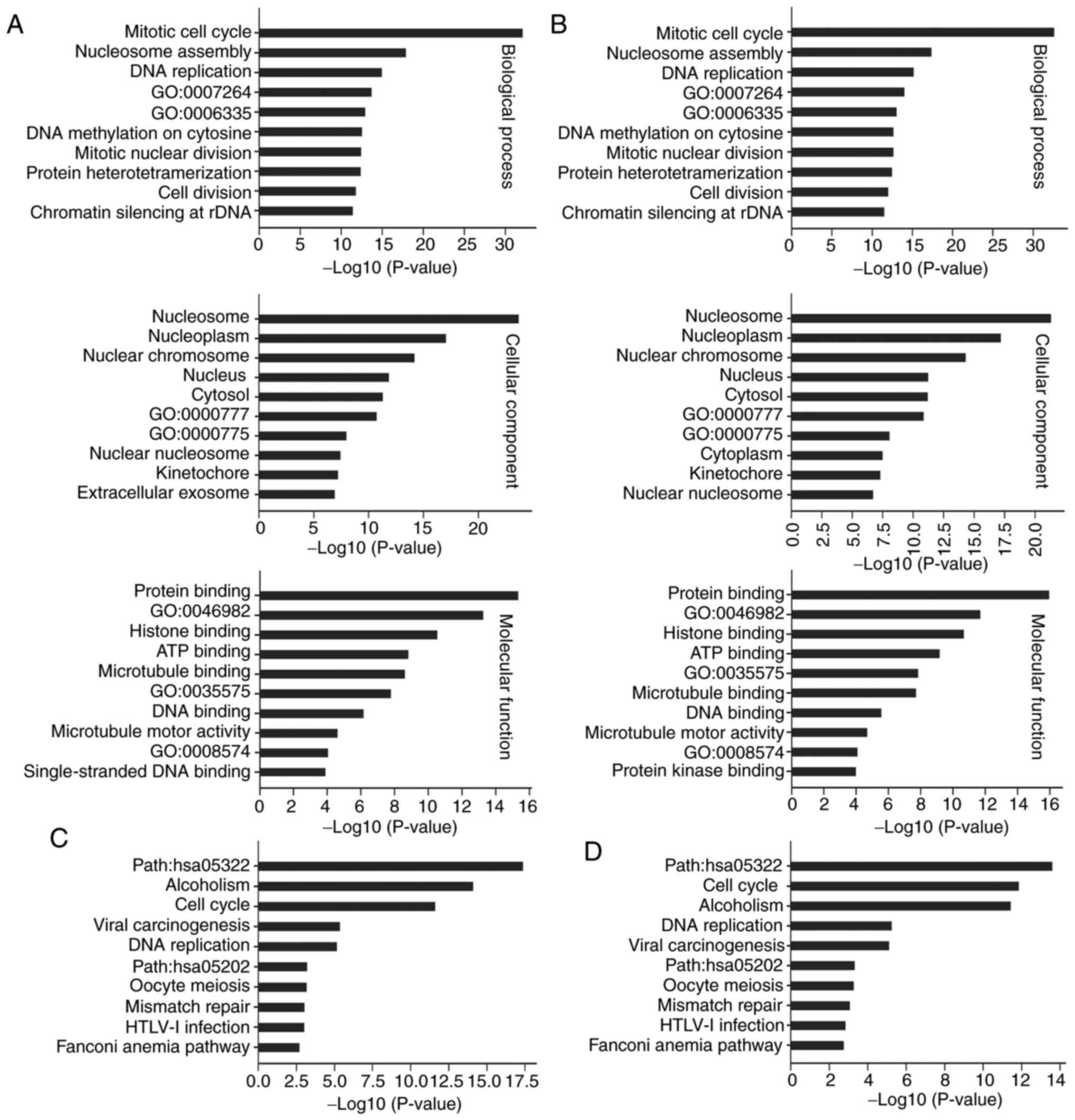
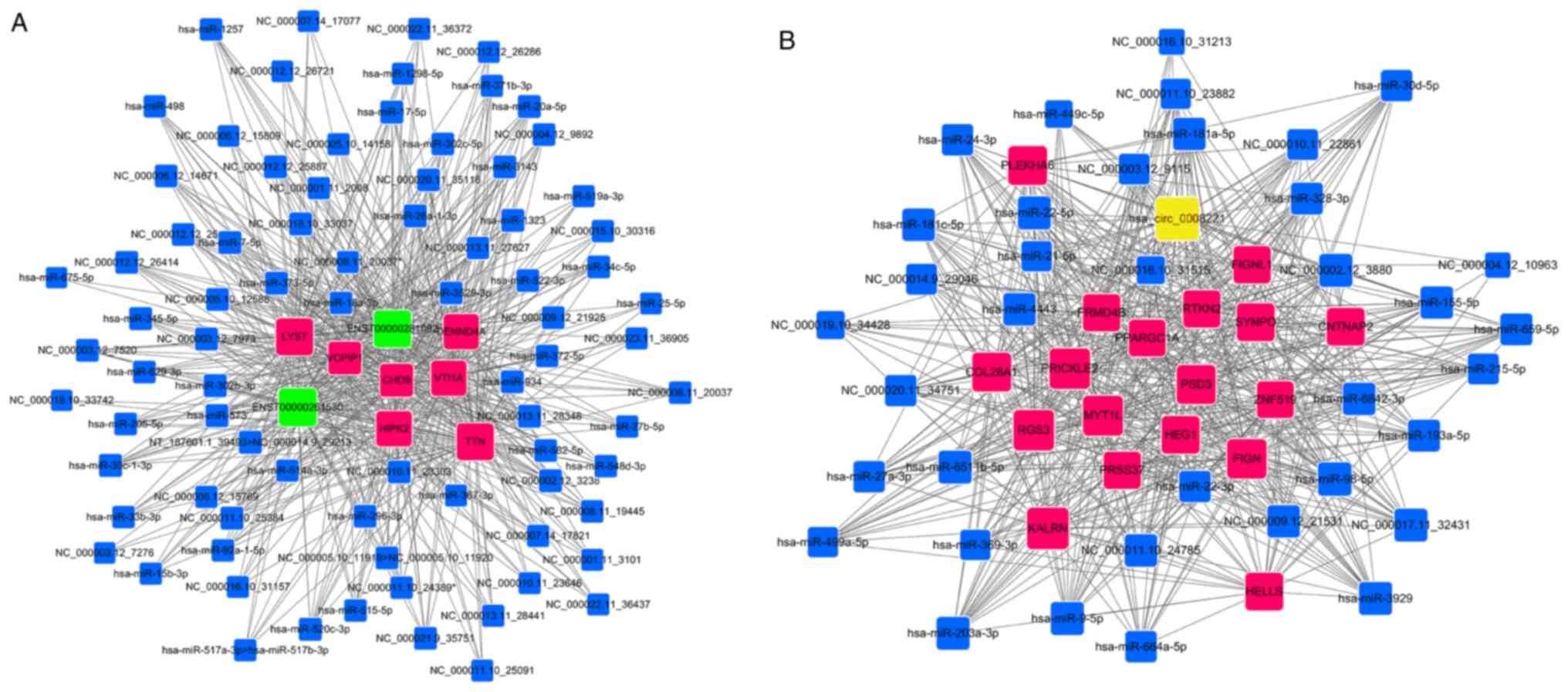
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ilson DH: Advances in the treatment of
gastric cancer. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 33:473–476. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Giustini NP, Jeong AR, Buturla J and
Bazhenova L: Advances in treatment of locally advanced or
metastatic Non-Small cell lung cancer: Targeted Therapy. Clin Chest
Med. 41:223–235. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Song YH, He L, Wang YL, Wu Q and Huang WZ:
Molecularly targeted therapy and immunotherapy for hormone
Receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative
advanced breast cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 44:3–13.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kinoshita Y, Ishimura N and Ishihara S:
Advantages and disadvantages of Long-term proton pump inhibitor
use. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 24:182–196. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ikemura K, Hiramatsu S and Okuda M: Drug
repositioning of proton pump inhibitors for enhanced efficacy and
safety of cancer chemotherapy. Front Pharmacol. 8:9112017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Watanabe SM, Ehrlich LS, Strickland M, Li
X, Soloveva V, Goff AJ, Stauft CB, Bhaduri-McIntosh S, Tjandra N
and Carter C: Selective targeting of virus replication by proton
pump inhibitors. Sci Rep. 10:40032020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fako VE, Wu X, Pflug B, Liu JY and Zhang
JT: Repositioning proton pump inhibitors as anticancer drugs by
targeting the thioesterase domain of human fatty acid synthase. J
Med Chem. 58:778–784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu ZN, Tian B and Guo XL: Repositioning of
proton pump inhibitors in cancer therapy. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 80:925–937. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lindner K, Borchardt C, Schöpp M, Bürgers
A, Stock C, Hussey DJ, Haier J and Hummel R: Proton pump inhibitors
(PPIs) impact on tumour cell survival, metastatic potential and
chemotherapy resistance, and affect expression of
resistance-relevant miRNAs in esophageal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 33:732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He J, Shi XY, Li ZM, Pan XH, Li ZL, Chen
Y, Yan SJ and Xiao L: Proton pump inhibitors can reverse the YAP
mediated paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer. BMC
Mol Cell Biol. 20:492019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ransohoff JD, Wei Y and Khavari PA: The
functions and unique features of long intergenic Non-coding RNA.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 19:143–157. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Y, Ge YZ, Xu L and Jia R: Circular RNA
ITCH: A novel tumor suppressor in multiple cancers. Life Sci.
254:1171762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hausser J and Zavolan M: Identification
and consequences of miRNA-target Interactions-beyond repression of
gene expression. Nat Rev Genet. 15:599–612. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang M, Zhong Z, Lv M, Shu J, Tian Q and
Chen J: Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed profiles
of lncRNAs and circRNAs with associated co-expression and ceRNA
networks in bladder carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:47186–47200. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu J, Zhang X, Gao W, Hu H, Wang X and
Hao D: lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in lumbar
intervertebral disc degeneration. Mol Med Report. 20:3160–3174.
2019.
|
|
17
|
Li J, Wang X, Lu W, Xiao Y, Yu Y, Wang X,
Xu C and Shen B: Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed
Non-coding RNAs and mRNAs in gastric cancer cells under hypoxic
conditions. Am J Transl Res. 10:1022–1035. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Iessi E, Logozzi M, Mizzoni D, Di Raimo R,
Supuran CT and Fais S: Rethinking the combination of proton
exchanger inhibitors in cancer therapy. Metabolites. 8:22018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang B, Ling T, Zhaxi P, Cao Y, Qian L,
Zhao D, Kang W, Zhang W, Wang L, Xu G and Zou X: Proton pump
inhibitor pantoprazole inhibits gastric cancer metastasis via
suppression of telomerase reverse transcriptase gene expression.
Cancer Lett. 452:23–30. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Marino ML, Fais S, Djavaheri-Mergny M,
Villa A, Meschini S, Lozupone F, Venturi G, Della Mina P, Pattingre
S, Rivoltini L, et al: Proton pump inhibition induces autophagy as
a survival mechanism following oxidative stress in human melanoma
cells. Cell Death Dis. 1:e872010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cao Y, Chen M, Tang D, Yan H, Ding X, Zhou
F, Zhang M, Xu GF, Zhang W, Zhang S, et al: The proton pump
inhibitor pantoprazole disrupts protein degradation systems and
sensitizes cancer cells to death under various stresses. Cell Death
Dis. 9:6042018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hou Y, Hu Q, Huang J and Xiong H:
Omeprazole inhibits cell proliferation and induces G0/G1 cell cycle
arrest through Up-regulating miR-203a-3p expression in barrett's
esophagus cells. Front Pharmacol. 8:9682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guan XW, Zhao F, Wang JY, Wang HY, Ge SH,
Wang X, Zhang L, Liu R, Ba Y, Li HL, et al: Tumor microenvironment
interruption: A novel Anti-cancer mechanism of Proton-pump
inhibitor in gastric cancer by suppressing the release of
microRNA-carrying exosomes. Am J Cancer Res. 7:1913–1925.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Geeviman K, Babu D and Prakash Babu P:
Pantoprazole induces mitochondrial apoptosis and attenuates NF-κB
signaling in glioma cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 38:1491–1504. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Y, Han T, Li J, Cai H, Xu J, Chen L
and Zhan X: Comprehensive analysis of the regulatory network of
differentially expressed mRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs in gastric
cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 122:1096862020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu D, Qiu T, Zhang Q, Kang H, Yuan S, Zhu
L and Zhu R: Systematic toxicity mechanism analysis of proton pump
inhibitors: An in silico study. Chem Res Toxicol. 28:419–430. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mescher M and Haarmann-Stemmann T:
Modulation of CYP1A1 metabolism: From adverse health effects to
chemoprevention and therapeutic options. Pharmacol Ther. 187:71–87.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yin XF, Chen J, Mao W, Wang YH and Chen
MH: A selective aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulator
3,3′-Diindolylmethane inhibits gastric cancer cell growth. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 31:462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen CC, Chu CB, Liu KJ, Huang CY, Chang
JY, Pan WY, Chen HH, Cheng YH, Lee KD, Chen MF, et al: Gene
expression profiling for analysis acquired oxaliplatin resistant
factors in human gastric carcinoma TSGH-S3 cells: The role of IL-6
signaling and Nrf2/AKR1C axis identification. Biochem Pharmacol.
86:872–887. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Z, Xing X, Shan F, Li S, Li Z, Xiao A,
Xing Z, Xue K, Li Z, Hu Y, et al: ABCC2-24C>T polymorphism is
associated with the response to platinum/5-Fu-based neoadjuvant
chemotherapy and better clinical outcomes in advanced gastric
cancer patients. Oncotarget. 7:55449–55457. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Paresi CJ, Liu Q and Li YM: Benzimidazole
covalent probes and the gastric H(+)/K(+)-ATPase as a model system
for protein labeling in a Copper-free setting. Mol Biosyst.
12:1772–1780. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang R, Song S, Harada K, Ghazanfari
Amlashi F, Badgwell B, Pizzi MP, Xu Y, Zhao W, Dong X, Jin J, et
al: Multiplex profiling of peritoneal metastases from gastric
adenocarcinoma identified novel targets and molecular subtypes that
predict treatment response. Gut. 69:18–31. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gao Y, Qi W, Sun L, Lv J, Qiu W and Liu S:
FOXO3 Inhibits human gastric adenocarcinoma (AGS) cell growth by
promoting autophagy in an acidic microenvironment. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 49:335–348. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu J, Qian Y, Peng L, Ma L, Qiu T, Liu Y,
Li X and Chen X: Long noncoding RNA EGFR-AS1 promotes cell
proliferation by increasing EGFR mRNA stability in gastric cancer.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:322–334. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim HS, Lim JM, Kim JY, Kim Y, Park S and
Sohn J: Panaxydol, a component of Panax ginseng, induces apoptosis
in cancer cells through EGFR activation and ER stress and inhibits
tumor growth in mouse models. Int J Cancer. 138:1432–1441. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qi W, Weber CR, Wasland K, Roy H, Wali R,
Joshi S and Savkovic SD: Tumor suppressor FOXO3 mediates signals
from the EGF receptor to regulate proliferation of colonic cells.
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 300:G264–G272. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nakatani K, Yamaoka T, Ohba M, Fujita KI,
Arata S, Kusumoto S, Taki-Takemoto I, Kamei D, Iwai S, Tsurutani J
and Ohmori T: KRAS and amplifications mediate resistance to
rociletinib and osimertinib in acquired afatinib-resistant NSCLC
harboring exon 19 deletion/T790M in EGFR. Mol Cancer Ther.
18:112–126. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang H, Zhang X, Li X, Meng WB, Bai ZT,
Rui SZ, Wang ZF, Zhou WC and Jin XD: Effect of CCNB1 silencing on
cell cycle, senescence, and apoptosis through the p53 signaling
pathway in pancreatic cancer. J Cell Physiol. 234:619–631. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wei GH and Wang X: lncRNA MEG3 inhibit
proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer via p53 signaling
pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:3850–3856. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kleinsimon S, Longmuss E, Rolff J, Jäger
S, Eggert A, Delebinski C and Seifert G: GADD45A and CDKN1A are
involved in apoptosis and cell cycle modulatory effects of viscumTT
with further inactivation of the STAT3 pathway. Sci Rep.
8:57502018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shang X, Liu G, Zhang Y, Tang P, Zhang H,
Jiang H and Yu Z: Downregulation of BIRC5 inhibits the migration
and invasion of esophageal cancer cells by interacting with the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 16:3373–3379.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Guo L, Zhang S, Zhang B, Chen W, Li X,
Zhang W, Zhou C, Zhang J, Ren N and Ye Q: Silencing GTSE-1
expression inhibits proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 32:263–274. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cui J, Sun W, Hao X, Wei M, Su X, Zhang Y,
Su L and Liu X: EHMT2 inhibitor BIX-01294 induces apoptosis through
PMAIP1-USP9X-MCL1 axis in human bladder cancer cells. Cancer Cell
Int. 15:42015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Le Large TYS, El Hassouni B, Funel N, Kok
B, Piersma SR, Pham TV, Olive KP, Kazemier G, van Laarhoven HWM,
Jimenez CR, et al: Proteomic analysis of gemcitabine-resistant
pancreatic cancer cells reveals that microtubule-associated protein
2 upregulation associates with taxane treatment. Ther Adv Med
Oncol. 11:17588359198412332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Blaquiere JA, Wong KKL, Kinsey SD, Wu J
and Verheyen EM: Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase promotes
tumorigenesis and metastatic cell behavior. Dis Model Mech.
11:dmm0311462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen Y, Löhr M and Jesnowski R: Inhibition
of ankyrin-B expression reduces growth and invasion of human
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreatology. 10:586–596. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cao W, Wei W, Zhan Z, Xie D, Xie Y and
Xiao Q: Role of miR-647 in human gastric cancer suppression. Oncol
Rep. 37:1401–1411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mullin JM, Gabello M, Murray LJ, Farrell
CP, Bellows J, Wolov KR, Kearney KR, Rudolph D and Thornton JJ:
Proton pump inhibitors: Actions and reactions. Drug Discov Today.
14:647–660. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
De Milito A, Canese R, Marino ML, Fais S,
Venturi G, Rodolfo M, Borghi M, Villa A, Della Mina P, Lozupone F,
et al: pH-dependent antitumor activity of proton pump inhibitors
against human melanoma is mediated by inhibition of tumor acidity.
Int J Cancer. 127:207–219. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|