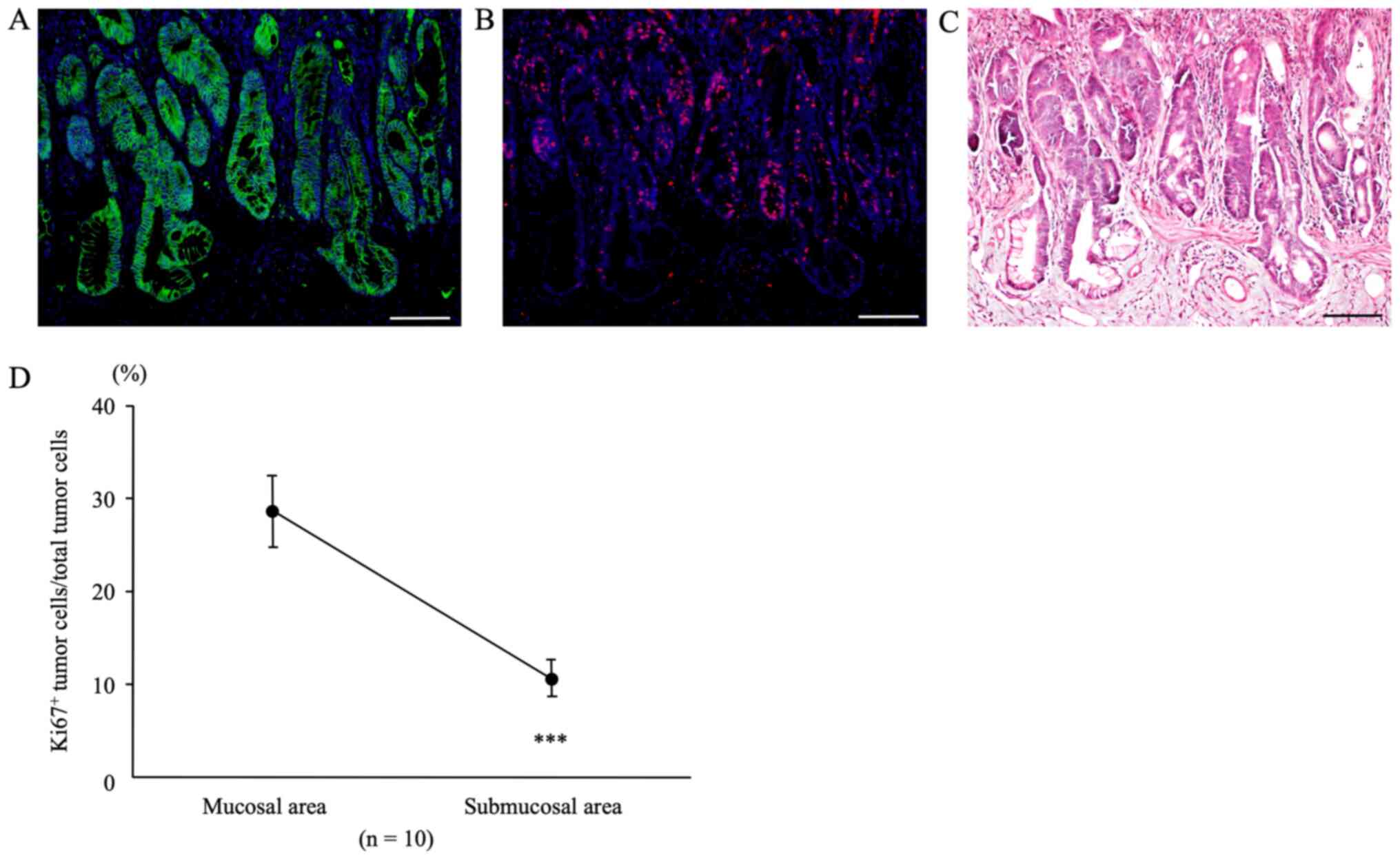
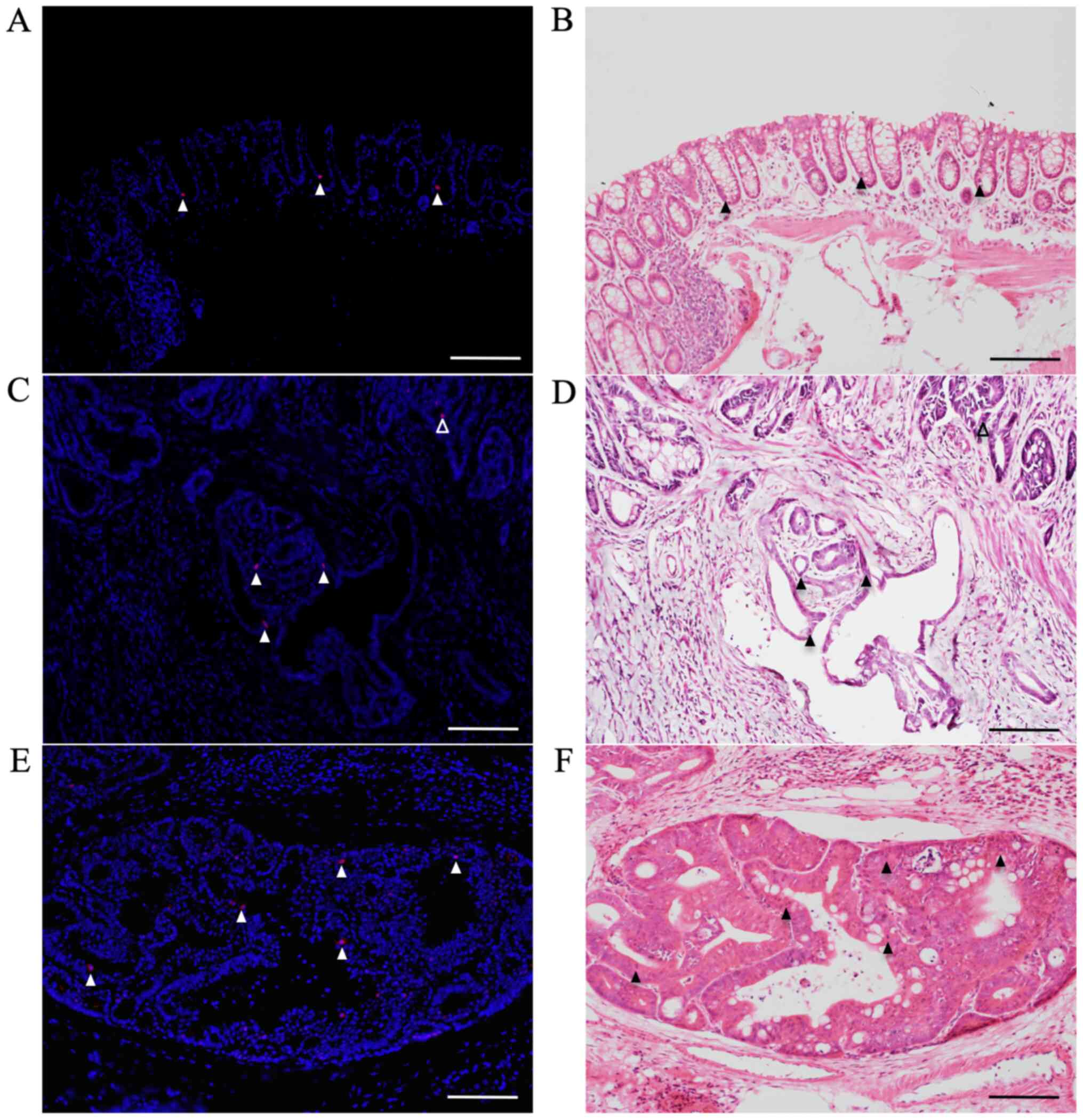
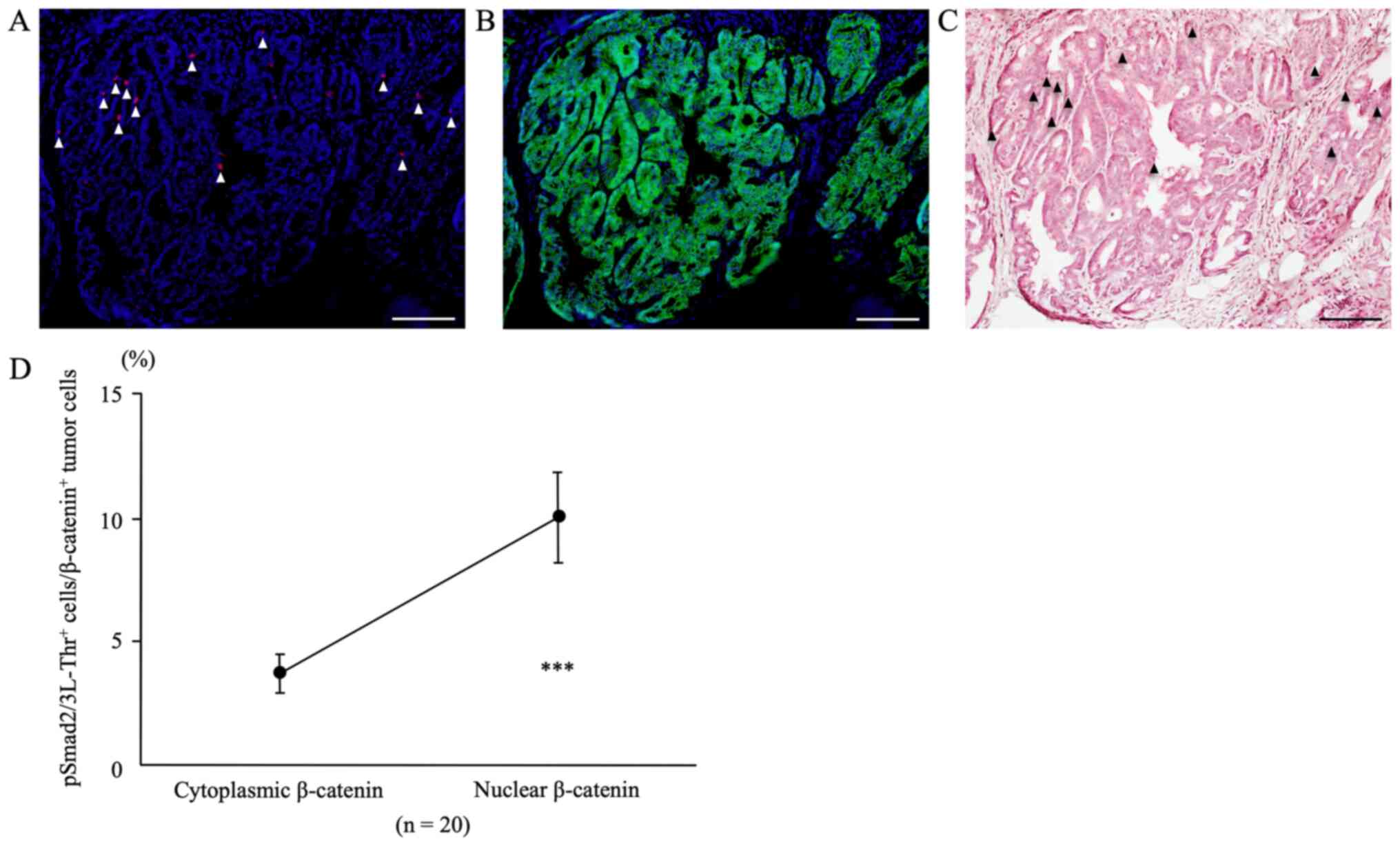
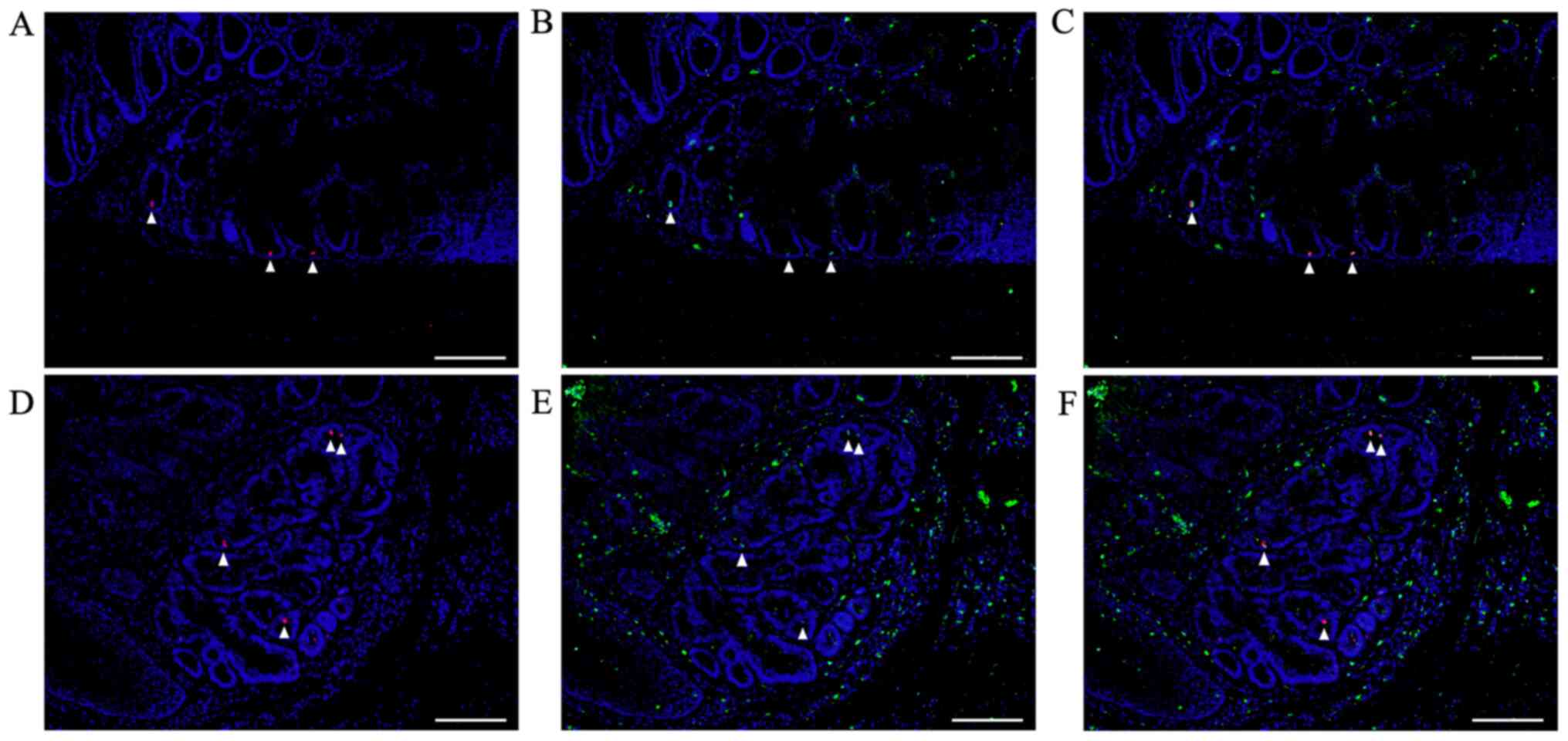
|
1
|
Eaden JA, Abrams KR and Mayberry JF: The
risk of colorectal cancer in ulcerative colitis: A meta-analysis.
Gut. 48:526–535. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ekbom A, Helmick C, Zack M and Adami HO:
Ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer. A population-based study.
N Engl J Med. 323:1228–1233. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Seril DN, Liao J, Yang GY and Yang CS:
Oxidative stress and ulcerative colitis-associated carcinogenesis:
Studies in humans and animal models. Carcinogenesis. 24:353–362.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tanaka T: Development of an
inflammation-associated colorectal cancer model and its application
for research on carcinogenesis and chemoprevention. Int J Inflamm.
2012:6587862012.
|
|
5
|
Tanaka T, Kohno H, Suzuki R, Yamada Y,
Sugie S and Mori H: A novel inflammation-related mouse colon
carcinogenesis model induced by azoxymethane and dextran sodium
sulfate. Cancer Sci. 94:965–973. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tanaka T: Colorectal carcinogenesis:
Review of human and experimental animal studies. J Carcinog.
8:52009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boivin GP, Washington K, Yang K, Ward JM,
Pretlow TP, Russell R, Besselsen DG, Godfrey VL, Doetschman T, Dove
WF, et al: Pathology of mouse models of intestinal cancer:
Consensus report and recommendations. Gastroenterology.
124:762–777. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rosenberg DW, Giardina C and Tanaka T:
Mouse models for the study of colon carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis.
30:183–196. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Clarke MF, Dick JE, Dirks PB, Eaves CJ,
Jamieson CH, Jones DL, Visvader J, Weissman IL and Wahl GM: Cancer
stem cells - perspectives on current status and future directions:
AACR Workshop on cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 66:9339–9344. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Campbell LL and Polyak K: Breast tumor
heterogeneity: Cancer stem cells or clonal evolution? Cell Cycle.
6:2332–2338. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z and Kong D:
Pancreatic cancer stem cells and EMT in drug resistance and
metastasis. Minerva Chir. 64:489–500. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brabletz T, Hlubek F, Spaderna S,
Schmalhofer O, Hiendlmeyer E, Jung A and Kirchner T: Invasion and
metastasis in colorectal cancer: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition,
mesenchymal-epithelial transition, stem cells and beta-catenin.
Cells Tissues Organs. 179:56–65. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heldin CH, Miyazono K and ten Dijke P:
TGF-beta signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD
proteins. Nature. 390:465–471. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Massagué J: TGF-beta signal transduction.
Annu Rev Biochem. 67:753–791. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wrana JL: Crossing Smads. Sci STKE.
2000:re12000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kretzschmar M, Doody J, Timokhina I and
Massagué J: A mechanism of repression of TGFbeta/Smad signaling by
oncogenic Ras. Genes Dev. 13:804–816. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Matsuura I, Denissova NG, Wang G, He D,
Long J and Liu F: Cyclin-dependent kinases regulate the
antiproliferative function of Smads. Nature. 430:226–231. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mori S, Matsuzaki K, Yoshida K, Furukawa
F, Tahashi Y, Yamagata H, Sekimoto G, Seki T, Matsui H, Nishizawa
M, et al: TGF-beta and HGF transmit the signals through
JNK-dependent Smad2/3 phosphorylation at the linker regions.
Oncogene. 23:7416–7429. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tarasewicz E and Jeruss JS:
Phospho-specific Smad3 signaling: Impact on breast oncogenesis.
Cell Cycle. 11:2443–2451. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Matsuzaki K: Smad3 phosphoisoform-mediated
signaling during sporadic human colorectal carcinogenesis. Histol
Histopathol. 21:645–662. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Matsuzaki K, Kitano C, Murata M, Sekimoto
G, Yoshida K, Uemura Y, Seki T, Taketani S, Fujisawa J and Okazaki
K: Smad2 and Smad3 phosphorylated at both linker and COOH-terminal
regions transmit malignant TGF-beta signal in later stages of human
colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 69:5321–5330. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sapkota G, Knockaert M, Alarcón C,
Montalvo E, Brivanlou AH and Massagué J: Dephosphorylation of the
linker regions of Smad1 and Smad2/3 by small C-terminal domain
phosphatases has distinct outcomes for bone morphogenetic protein
and transforming growth factor-beta pathways. J Biol Chem.
281:40412–40419. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Derynck R and Zhang YE: Smad-dependent and
Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature.
425:577–584. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kishimoto M, Fukui T, Suzuki R, Takahashi
Y, Sumimoto K, Okazaki T, Sakao M, Sakaguchi Y, Yoshida K, Uchida
K, et al: Phosphorylation of Smad2/3 at specific linker threonine
indicates slow-cycling intestinal stem-like cells before reentry to
cell cycle. Dig Dis Sci. 60:362–374. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Suzuki R, Fukui T, Kishimoto M, Miyamoto
S, Takahashi Y, Takeo M, Mitsuyama T, Sakaguchi Y, Uchida K, Nishio
A, et al: Smad2/3 linker phosphorylation is a possible marker of
cancer stem cells and correlates with carcinogenesis in a mouse
model of colitis-associated colorectal cancer. J Crohn's Colitis.
9:565–574. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Suzuki R, Kohno H, Sugie S and Tanaka T:
Sequential observations on the occurrence of preneoplastic and
neoplastic lesions in mouse colon treated with azoxymethane and
dextran sodium sulfate. Cancer Sci. 95:721–727. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ward JM: Morphogenesis of chemically
induced neoplasms of the colon and small intestine in rats. Lab
Invest. 30:505–513. 1974.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Murata M, Matsuzaki K, Yoshida K, Sekimoto
G, Tahashi Y, Mori S, Uemura Y, Sakaida N, Fujisawa J, Seki T, et
al: Hepatitis B virus X protein shifts human hepatic transforming
growth factor (TGF)-beta signaling from tumor suppression to
oncogenesis in early chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 49:1203–1217.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sekimoto G, Matsuzaki K, Yoshida K, Mori
S, Murata M, Seki T, Matsui H, Fujisawa J and Okazaki K: Reversible
Smad-dependent signaling between tumor suppression and oncogenesis.
Cancer Res. 67:5090–5096. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Furukawa F, Matsuzaki K, Mori S, Tahashi
Y, Yoshida K, Sugano Y, Yamagata H, Matsushita M, Seki T, Inagaki
Y, et al: p38 MAPK mediates fibrogenic signal through Smad3
phosphorylation in rat myofibroblasts. Hepatology. 38:879–889.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fukui T, Kishimoto M, Nakajima A,
Yamashina M, Nakayama S, Kusuda T, Sakaguchi Y, Yoshida K, Uchida
K, Nishio A, et al: The specific linker phosphorylation of Smad2/3
indicates epithelial stem cells in stomach; particularly increasing
in mucosae of Helicobacter-associated gastritis. J Gastroenterol.
46:456–468. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Miller JR and Moon RT: Signal transduction
through beta-catenin and specification of cell fate during
embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 10:2527–2539. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Brabletz T, Jung A and Kirchner T:
Beta-catenin and the morphogenesis of colorectal cancer. Virchows
Arch. 441:1–11. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Edelman GM, Gallin WJ, Delouvée A,
Cunningham BA and Thiery JP: Early epochal maps of two different
cell adhesion molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 80:4384–4388.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tepass U, Truong K, Godt D, Ikura M and
Peifer M: Cadherins in embryonic and neural morphogenesis. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 1:91–100. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hirohashi S: Inactivation of the
E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion system in human cancers. Am J
Pathol. 153:333–339. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Muta H, Noguchi M, Kanai Y, Ochiai A,
Nawata H and Hirohashi S: E-cadherin gene mutations in signet ring
cell carcinoma of the stomach. Jpn J Cancer Res. 87:843–848. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Saito A, Kanai Y, Maesawa C, Ochiai A,
Torii A and Hirohashi S: Disruption of E-cadherin-mediated cell
adhesion systems in gastric cancers in young patients. Jpn J Cancer
Res. 90:993–999. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Weidner N, Moore DH II and Vartanian R:
Correlation of Ki-67 antigen expression with mitotic figure index
and tumor grade in breast carcinomas using the novel
‘paraffin’-reactive MIB1 antibody. Hum Pathol. 25:337–342. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jung A, Schrauder M, Oswald U, Knoll C,
Sellberg P, Palmqvist R, Niedobitek G, Brabletz T and Kirchner T:
The invasion front of human colorectal adenocarcinomas shows
co-localization of nuclear beta-catenin, cyclin D1, and p16INK4A
and is a region of low proliferation. Am J Pathol. 159:1613–1617.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Palmqvist R, Rutegârd JN, Bozoky B,
Landberg G and Stenling R: Human colorectal cancers with an intact
p16/cyclin D1/pRb pathway have up-regulated p16 expression and
decreased proliferation in small invasive tumor clusters. Am J
Pathol. 157:1947–1953. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Palmqvist R, Sellberg P, Oberg A, Tavelin
B, Rutegård JN and Stenling R: Low tumour cell proliferation at the
invasive margin is associated with a poor prognosis in Dukes' stage
B colorectal cancers. Br J Cancer. 79:577–581. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Takahashi Y, Fukui T, Kishimoto M, Suzuki
R, Mitsuyama T, Sumimoto K, Okazaki T, Sakao M, Sakaguchi Y,
Yoshida K, et al: Phosphorylation of Smad2/3 at the specific linker
threonine residue indicates slow-cycling esophageal stem-like cells
before re-entry to the cell cycle. Dis Esophagus. 29:107–115. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li XQ, Yang XL, Zhang G, Wu SP, Deng XB,
Xiao SJ, Liu QZ, Yao KT and Xiao GH: Nuclear β-catenin accumulation
is associated with increased expression of Nanog protein and
predicts poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl
Med. 11:1142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang G, Wang W, Yao C, Zhang S, Liang L,
Han M, Ren J, Qi X, Zhang X, Wang S, et al: Radiation-resistant
cancer stem-like cell properties are regulated by PTEN through the
activity of nuclear β-catenin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 8:74661–74672. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Espersen ML, Olsen J, Linnemann D, Høgdall
E and Troelsen JT: Clinical implications of intestinal stem cell
markers in colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 14:63–71.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Srinivasan T, Walters J, Bu P, Than EB,
Tung KL, Chen KY, Panarelli N, Milsom J, Augenlicht L, Lipkin SM,
et al: NOTCH signaling regulates asymmetric cell fate of fast- and
slow-cycling colon cancer-initiating cells. Cancer Res.
76:3411–3421. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Boman BM, Fields JZ, Cavanaugh KL, Guetter
A and Runquist OA: How dysregulated colonic crypt dynamics cause
stem cell overpopulation and initiate colon cancer. Cancer Res.
68:3304–3313. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|