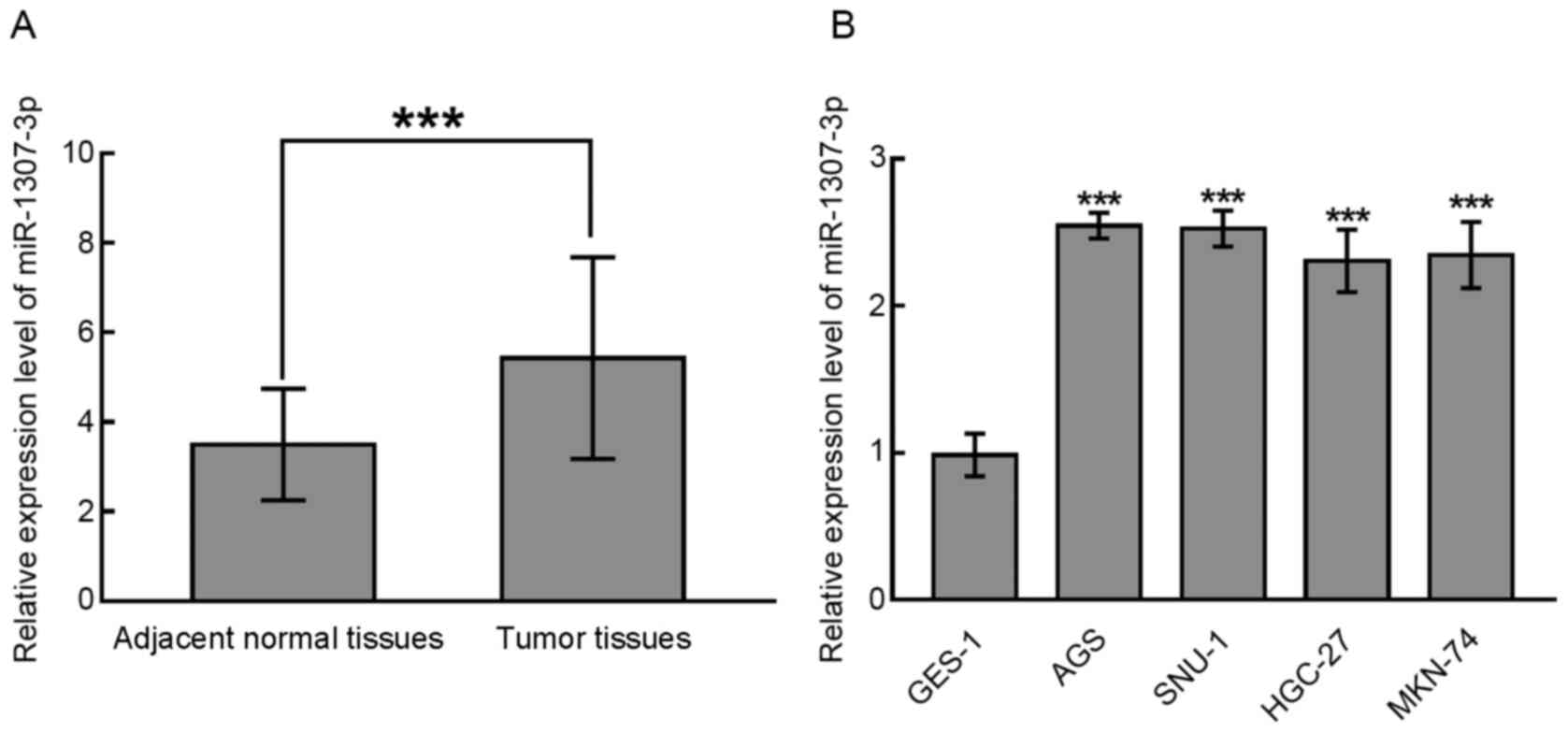
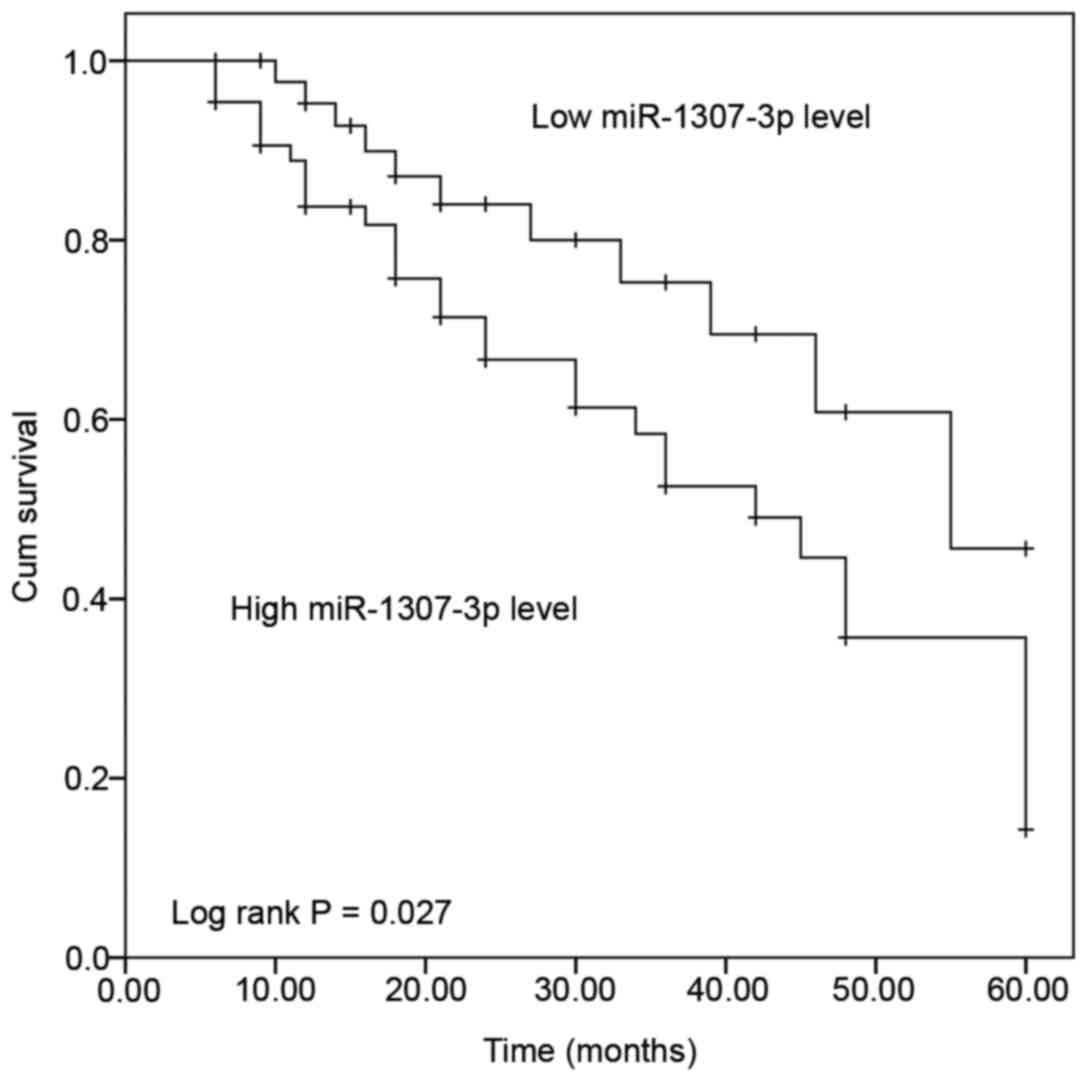
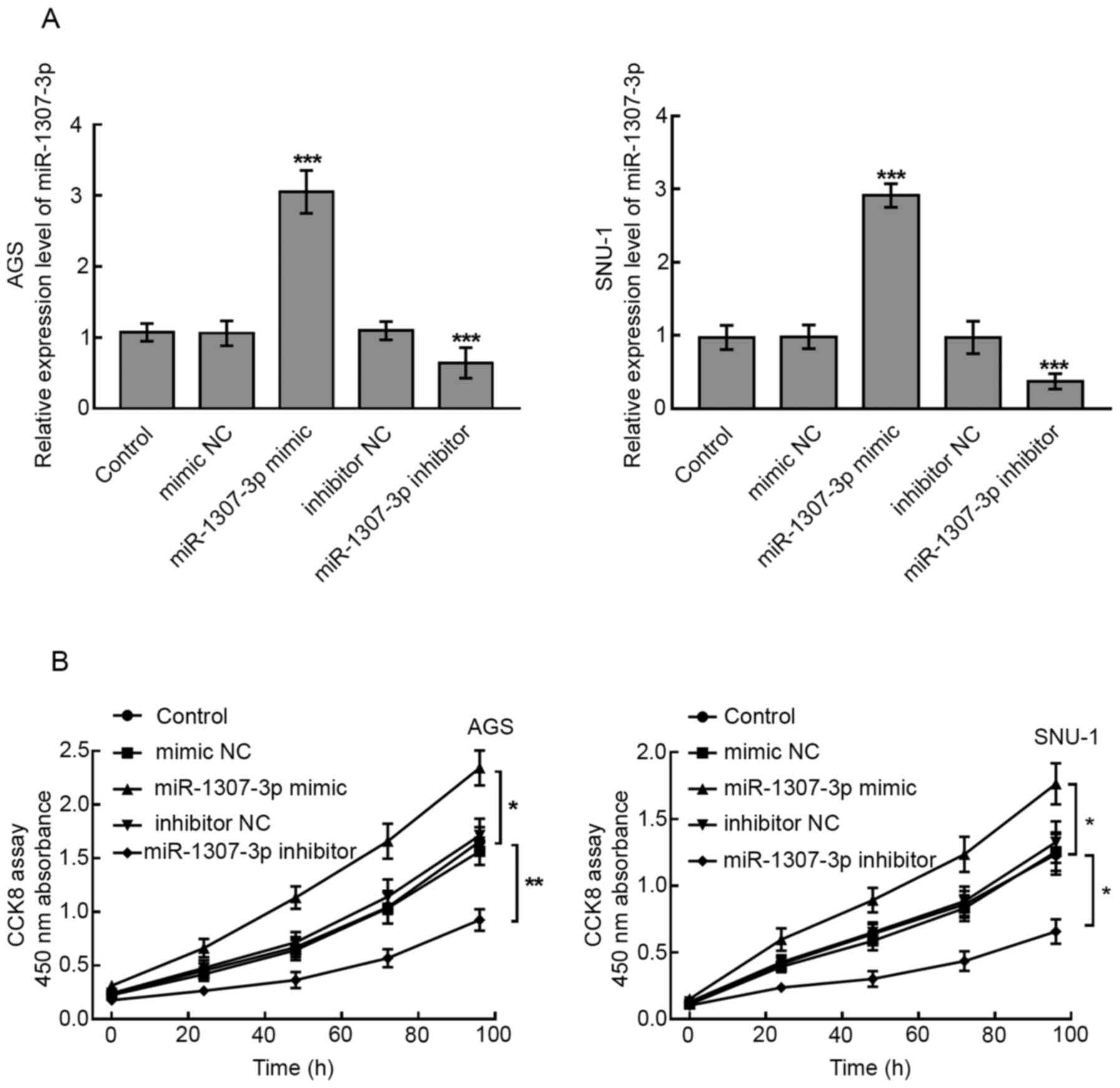
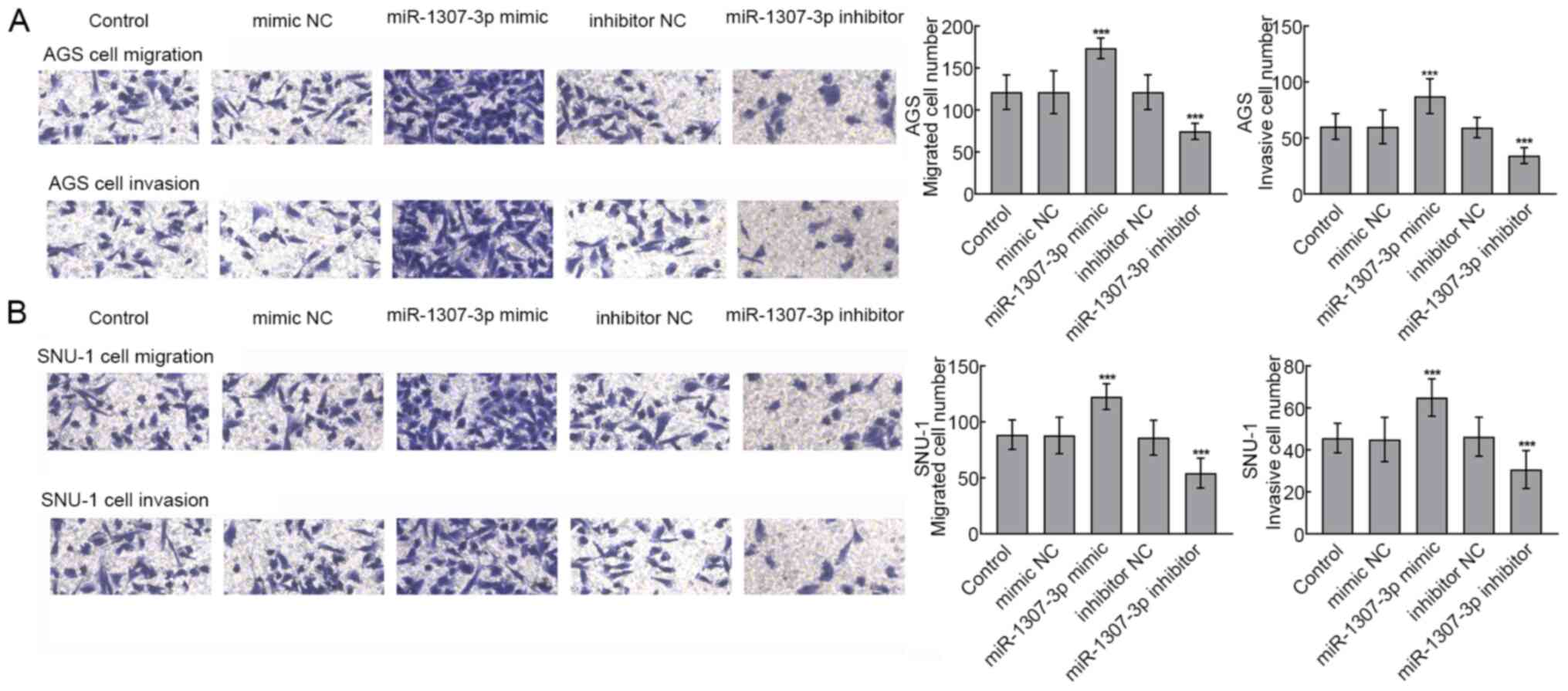
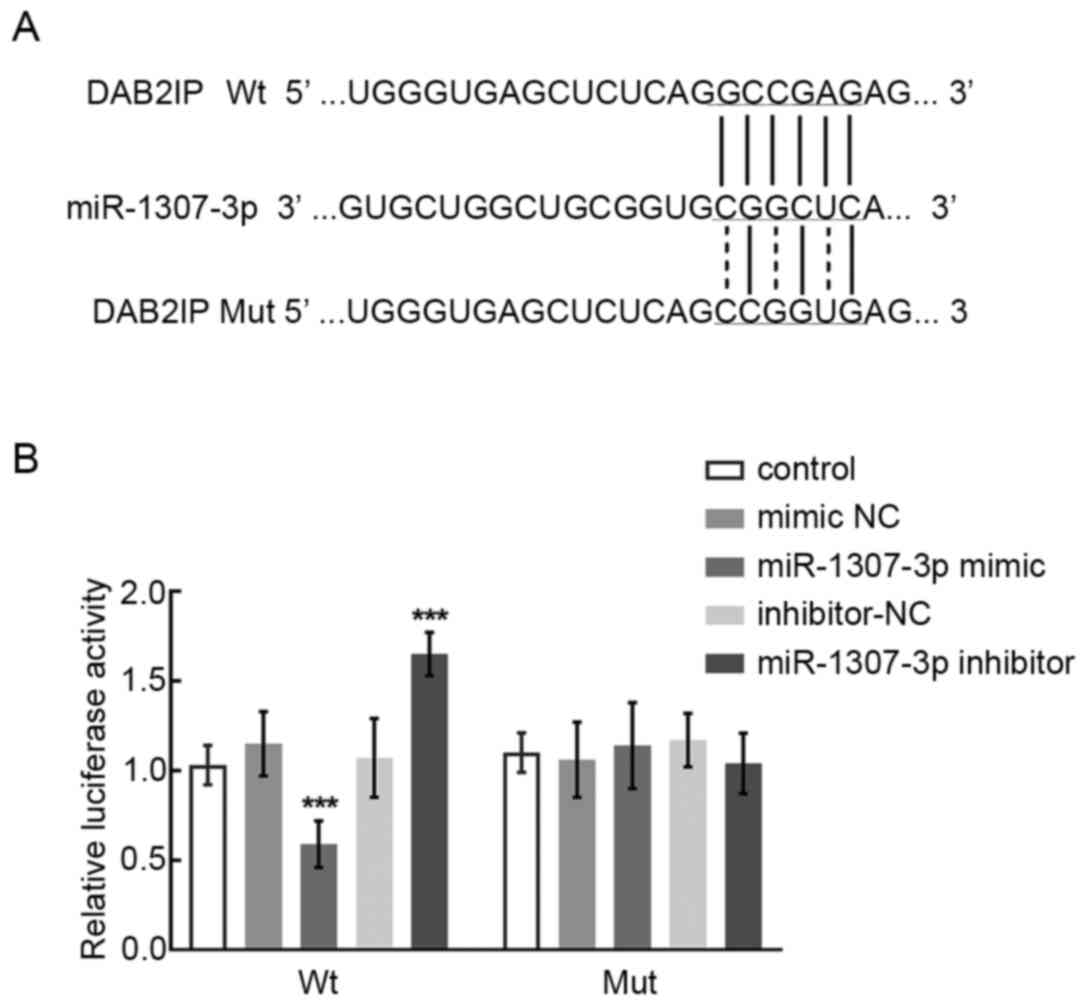
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Balakrishnan M, George R, Sharma A and
Graham DY: Changing Trends in Stomach Cancer Throughout the World.
Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 19:362017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Global Burden of Disease Cancer
Collaboration, ; Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, Barregard L,
Bhutta ZA, Brenner H, Dicker DJ, Chimed-Orchir O, Dandona R,
Dandona L, et al: Global, regional, and national cancer incidence,
mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and
disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015:
A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA
Oncol. 3:524–548. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
de Martel C, Ferlay J, Franceschi S,
Vignat J, Bray F, Forman D and Plummer M: Global burden of cancers
attributable to infections in 2008: A review and synthetic
analysis. Lancet Oncol. 13:607–615. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
de Martel C, Forman D and Plummer M:
Gastric cancer: Epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterol Clin
North Am. 42:219–240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yasui W, Yokozaki H, Fujimoto J, Naka K,
Kuniyasu H and Tahara E: Genetic and epigenetic alterations in
multistep carcinogenesis of the stomach. J Gastroenterol. 35 (Suppl
12):111–115. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stock M and Otto F: Gene deregulation in
gastric cancer. Gene. 360:1–19. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang WC and Zhang XF, Peng J, Li XF, Wang
AL, Bie YQ, Shi LH, Lin MB and Zhang XF: Survival Mechanisms and
Influence Factors of Circulating Tumor Cells. BioMed Res Int.
2018:63047012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Karimi P, Islami F, Anandasabapathy S,
Freedman ND and Kamangar F: Gastric cancer: Descriptive
epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 23:700–713. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hoffman Y, Bublik DR, Ugalde AP, Elkon R,
Biniashvili T, Agami R, Oren M and Pilpel Y: 3′UTR Shortening
Potentiates MicroRNA-Based Repression of Pro-differentiation Genes
in Proliferating Human Cells. PLoS Genet. 12:e10058792016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim S and Jeong S: Mutation hotspots in
the β-catenin gene: Lessons from the human cancer genome databases.
Mol Cells. 42:8–16. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ahmed FE: Role of miRNA in carcinogenesis
and biomarker selection: A methodological view. Expert Rev Mol
Diagn. 7:569–603. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brenner B, Hoshen MB, Purim O, David MB,
Ashkenazi K, Marshak G, Kundel Y, Brenner R, Morgenstern S, Halpern
M, et al: MicroRNAs as a potential prognostic factor in gastric
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 17:3976–3985. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wei Y, Wang Y, Zang A, Wang Z, Fang G and
Hong D: MiR-4766-5p inhibits the development and progression of
gastric cancer by targeting NKAP. OncoTargets Ther. 12:8525–8536.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen H, Yang Y, Wang J, Shen D, Zhao J and
Yu Q: miR-130b-5p promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of
gastric cancer cells via targeting RASAL1. Oncol Lett.
15:6361–6367. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen S, Wang L, Yao B, Liu Q and Guo C:
miR-1307-3p promotes tumor growth and metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by repressing DAB2 interacting protein. Biomed
Pharmacother. 117:1090552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Han S, Zou H, Lee JW, Han J, Kim HC, Cheol
JJ, Kim LS and Kim H: miR-1307-3p stimulates breast cancer
development and progression by targeting SMYD4. J Cancer.
10:441–448. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zheng Y, Zheng Y, Lei W, Xiang L and Chen
M: miR-1307-3p overexpression inhibits cell proliferation and
promotes cell apoptosis by targeting ISM1 in colon cancer. Mol Cell
Probes. 48:1014452019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kalinowski FC, Brown RA, Ganda C, Giles
KM, Epis MR, Horsham J and Leedman PJ: microRNA-7: A tumor
suppressor miRNA with therapeutic potential. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 54:312–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yadav S, Shekhawat M, Jahagirdar D and
Kumar Sharma N: Natural and artificial small RNAs: A promising
avenue of nucleic acid therapeutics for cancer. Cancer Biol Med.
14:242–253. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shin VY and Chu KM: MiRNA as potential
biomarkers and therapeutic targets for gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:10432–10439. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qiu T, Wang K, Li X and Jin J: miR-671-5p
inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation and promotes cell
apoptosis by targeting URGCP. Exp Ther Med. 16:4753–4758.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu T, Gong L, Li W, Zuo Q, Cai D, Mao H,
Wang L, Lin J and Xiao B: MiR-30a suppresses metastasis of gastric
adenocarcinoma via targeting FAPα. Cancer Biomark. 27:471–484.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ding L, Zhang S, Xu M, Zhang R, Sui P and
Yang Q: MicroRNA-27a contributes to the malignant behavior of
gastric cancer cells by directly targeting PH domain and
leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase 2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
36:452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nakamura S, Kanda M and Kodera Y:
Incorporating molecular biomarkers into clinical practice for
gastric cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 19:757–771. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li L, Mou YP, Wang YY, Wang HJ and Mou XZ:
miR-199a-3p targets ETNK1 to promote invasion and migration in
gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis. Pathol
Res Pract. 215:1525112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun L, Yao Y, Lu T, Shang Z, Zhan S, Shi
W, Pan G, Zhu X and He S: DAB2IP downregulation enhances the
proliferation and metastasis of human gastric cancer cells by
derepressing the ERK1/2 pathway. Gastroenterol Res Pract.
2018:29682522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu L, Xu C, Hsieh JT, Gong J and Xie D:
DAB2IP in cancer. Oncotarget. 7:3766–3776. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nakamura R, Omori T, Mayanagi S, Irino T,
Wada N, Kawakubo H, Kameyama K and Kitagawa Y: Risk of lymph node
metastasis in undifferentiated-type mucosal gastric carcinoma.
World J Surg Oncol. 17:322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mikami K, Hirano Y, Futami K and Maekawa
T: Expansion of lymph node metastasis in mixed-type submucosal
invasive gastric cancer. Asian J Surg. 41:462–466. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bausys R, Bausys A, Vysniauskaite I,
Maneikis K, Klimas D, Luksta M, Strupas K and Stratilatovas E: Risk
factors for lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer patients:
Report from Eastern Europe country- Lithuania. BMC Surg.
17:1082017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|