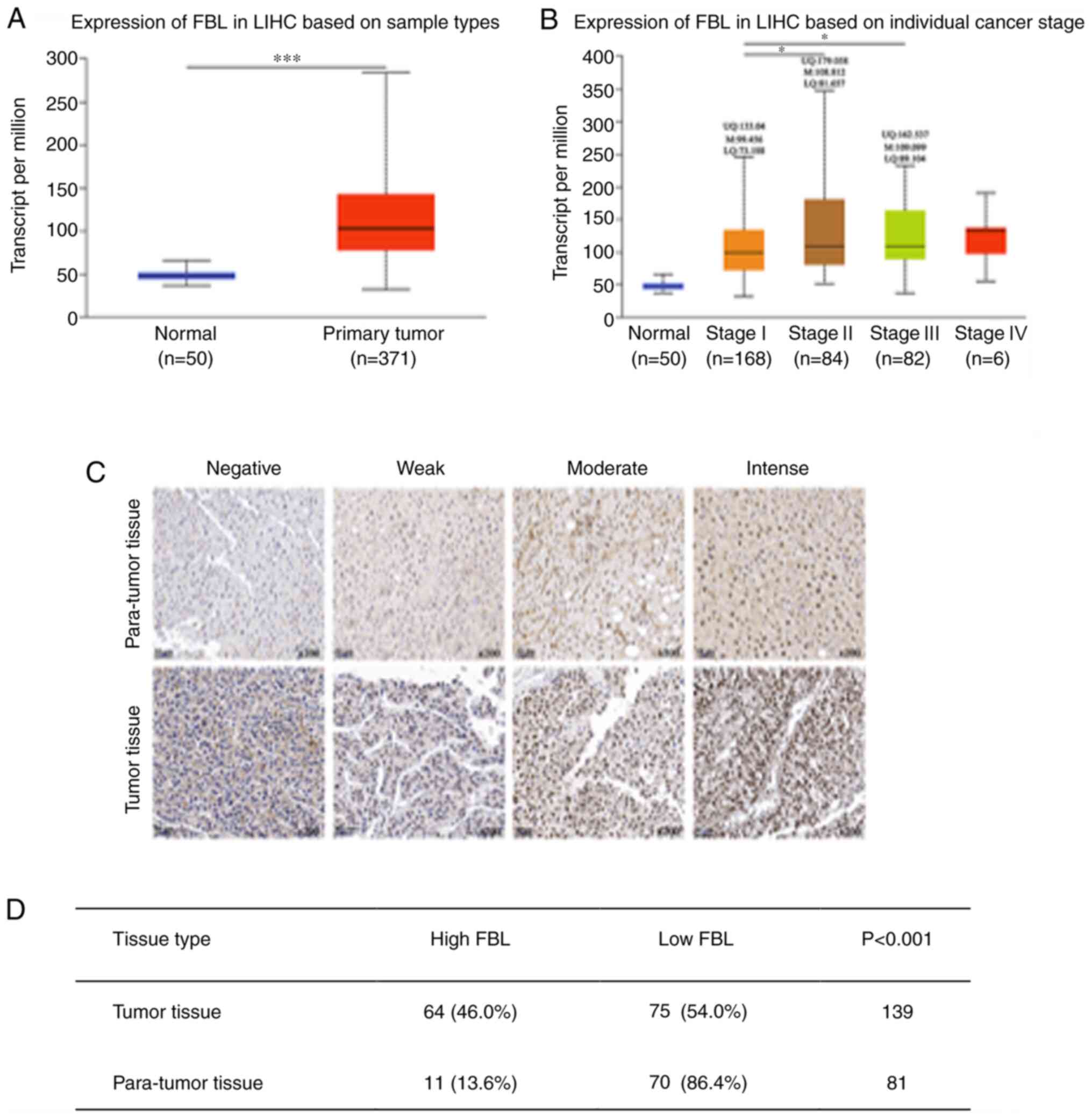
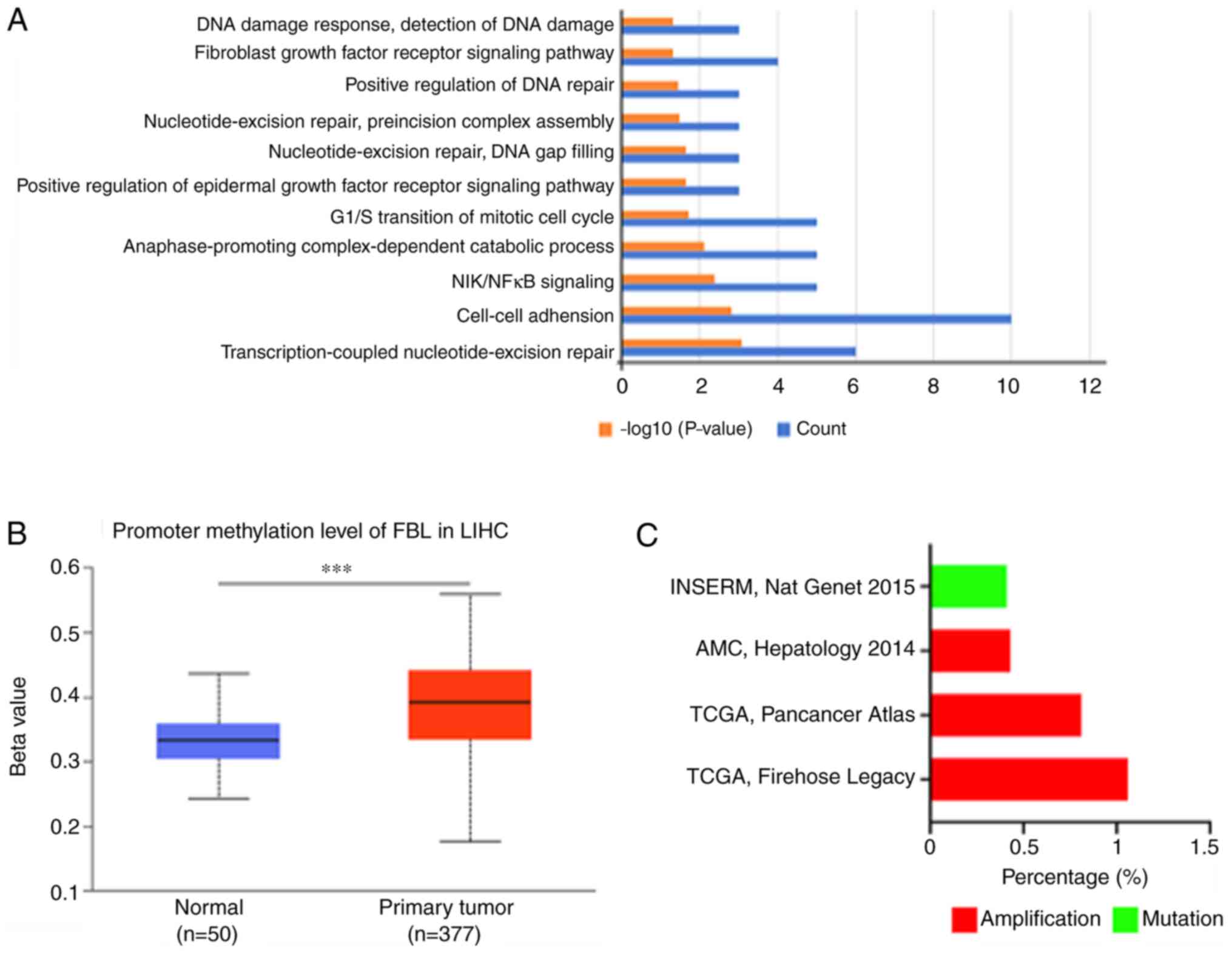
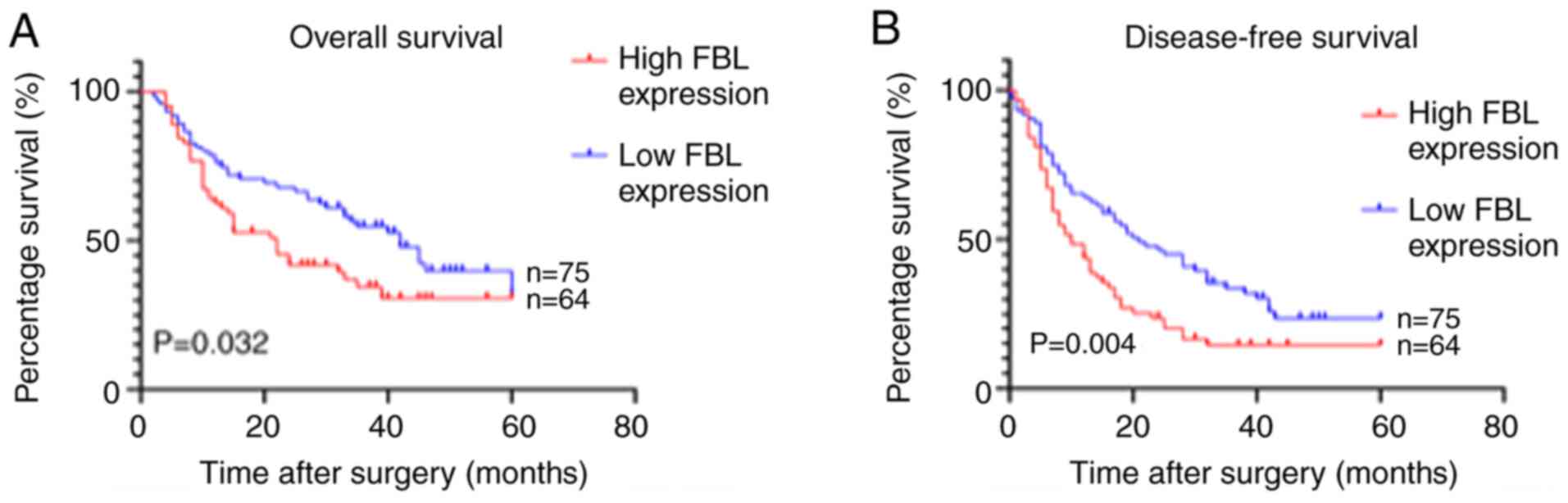
|
1
|
McGlynn KA, Petrick JL and London WT:
Global epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: An emphasis on
demographic and regional variability. Clin Liver Dis. 19:223–238.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Villanueva A: Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
Reply. N Engl J Med. 381:e22019.Reply. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wong RJ, Kim D, Ahmed A and Singal AK:
Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma from more rural and lower
income households have more advanced tumor stage at diagnosis and
significantly higher mortality. Cancer cncr. 33211:2020.
|
|
4
|
Javadian P and Nezhat F: Endometrial
carcinoma and its precursors. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1242:59–72. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Couri T and Pillai A: Goals and targets
for personalized therapy for HCC. Hepatol Int. 13:125–137. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Raoul JL, Forner A, Bolondi L, Cheung TT,
Kloeckner R and de Baere T: Updated use of TACE for hepatocellular
carcinoma treatment: How and when to use it based on clinical
evidence. Cancer Treat Rev. 72:28–36. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Raza A and Sood GK: Hepatocellular
carcinoma review: Current treatment, and evidence-based medicine.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:4115–4127. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fu J and Wang H: Precision diagnosis and
treatment of liver cancer in China. Cancer Lett. 412:283–288. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Llovet JM, Montal R, Sia D and Finn RS:
Molecular therapies and precision medicine for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 15:599–616. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rashed WM, Kandeil MAM, Mahmoud MO and
Ezzat S: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in Egypt: A comprehensive
overview. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 32:52020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Waidmann O: Recent developments with
immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Opin Biol Ther.
18:905–910. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mauro VP and Matsuda D: Translation
regulation by ribosomes: Increased complexity and expanded scope.
RNA Biol. 13:748–755. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gentilella A, Kozma SC and Thomas G: A
liaison between mTOR signaling, ribosome biogenesis and cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1849:812–820. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lawrence MG, Obinata D, Sandhu S, Selth
LA, Wong SQ, Porter LH, Lister N, Pook D, Pezaro CJ, Goode DL, et
al: Patient-derived models of abiraterone- and
enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer reveal sensitivity to
ribosome-directed therapy. Eur Urol. 74:562–572. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mugridge JS and Gross JD: Decapping
enzymes STOP ‘cancer’ ribosomes in their tracks. EMBO J.
37:e1008012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sriram A, Bohlen J and Teleman AA:
Translation acrobatics: how cancer cells exploit alternate modes of
translational initiation. EMBO Rep. 19:e459472018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dunn S, Lombardi O and Cowling VH: c-Myc
co-ordinates mRNA cap methylation and ribosomal RNA production.
Biochem J. 474:377–384. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Monaco PL, Marcel V, Diaz JJ and Catez F:
2′-O-methylation of ribosomal RNA: towards an epitranscriptomic
control of translation? Biomolecules. 8:1062018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sergiev PV, Aleksashin NA, Chugunova AA,
Polikanov YS and Dontsova OA: Structural and evolutionary insights
into ribosomal RNA methylation. Nat Chem Biol. 14:226–235. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Marcel V, Ghayad SE, Belin S, Therizols G,
Morel AP, Solano-Gonzàlez E, Vendrell JA, Hacot S, Mertani HC,
Albaret MA, et al: p53 acts as a safeguard of translational control
by regulating fibrillarin and rRNA methylation in cancer. Cancer
Cell. 24:318–330. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shubina MY, Musinova YR and Sheval EV:
Proliferation, cancer, and aging-novel functions of the nucleolar
methyltransferase fibrillarin? Cell Biol Int. 42:1463–1466. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ayadi L, Galvanin A, Pichot F, Marchand V
and Motorin Y: RNA ribose methylation (2′-O-methylation):
Occurrence, biosynthesis and biological functions. Biochim Biophys
Acta Gene Regul Mech. 1862:253–269. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Erales J, Marchand V, Panthu B, Gillot S,
Belin S, Ghayad SE, Garcia M, Laforêts F, Marcel V, Baudin-Baillieu
A, et al: Evidence for rRNA 2′-O-methylation plasticity: Control of
intrinsic translational capabilities of human ribosomes. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 114:12934–12939. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li L, Miao W, Williams P, Guo C and Wang
Y: SLIRP interacts with helicases to facilitate 2′-O-methylation of
rRNA and to promote translation. J Am Chem Soc. 141:10958–10961.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koh CM, Gurel B, Sutcliffe S, Aryee MJ,
Schultz D, Iwata T, Uemura M, Zeller KI, Anele U, Zheng Q, et al:
Alterations in nucleolar structure and gene expression programs in
prostatic neoplasia are driven by the MYC oncogene. Am J Pathol.
178:1824–1834. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Su H, Xu T, Ganapathy S, Shadfan M, Long
M, Huang TH, Thompson I and Yuan ZM: Elevated snoRNA biogenesis is
essential in breast cancer. Oncogene. 33:1348–1358. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iyer-Bierhoff A and Grummt I: Stop-and-Go:
Dynamics of nucleolar transcription during the cell cycle. Epigenet
Insights. 12:25168657198490902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsoris A and Marlar CA: Use Of The Child
Pugh Score In Liver Disease. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure
Island, FL: 2020
|
|
29
|
Jing JS, Li H, Wang SC, Ma JM, Yu LQ and
Zhou H: NDRG3 overexpression is associated with a poor prognosis in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci Rep.
38:BSR201809072018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schulze K, Imbeaud S, Letouzé E,
Alexandrov LB, Calderaro J, Rebouissou S, Couchy G, Meiller C,
Shinde J, Soysouvanh F, et al: Exome sequencing of hepatocellular
carcinomas identifies new mutational signatures and potential
therapeutic targets. Nat Genet. 47:505–511. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ahn SM, Jang SJ, Shim JH, Kim D, Hong SM,
Sung CO, Baek D, Haq F, Ansari AA, Lee SY, et al: Genomic portrait
of resectable hepatocellular carcinomas: Implications of RB1 and
FGF19 aberrations for patient stratification. Hepatology.
60:1972–1982. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bhandari V, Hoey C, Liu LY, Lalonde E, Ray
J, Livingstone J, Lesurf R, Shiah YJ, Vujcic T, Huang X, et al:
Molecular landmarks of tumor hypoxia across cancer types. Nat
Genet. 51:308–318. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bonneville R, Krook MA, Kautto EA, Miya J,
Wing MR, Chen HZ, Reeser JW, Yu L and Roychowdhury S: Landscape of
microsatellite instability across 39 cancer types. JCO Precis
Oncol. 2017:PO.17.00073. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ding L, Bailey MH, Porta-Pardo E, Thorsson
V, Colaprico A, Bertrand D, Gibbs DL, Weerasinghe A, Huang KL,
Tokheim C, et al Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, :
Perspective on oncogenic processes at the end of the beginning of
cancer genomics. Cell. 173:305–320.e10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ellrott K, Bailey MH, Saksena G, Covington
KR, Kandoth C, Stewart C, Hess J, Ma S, Chiotti KE, McLellan M, et
al MC3 Working Group; Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, :
Scalable open science approach for mutation calling of tumor exomes
using multiple genomic pipelines. Cell Syst. 6:271–281.e7. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gao Q, Liang WW, Foltz SM, Mutharasu G,
Jayasinghe RG, Cao S, Liao WW, Reynolds SM, Wyczalkowski MA, Yao L,
et al Fusion Analysis Working Group; Cancer Genome Atlas Research
Network, : Driver fusions and their implications in the development
and treatment of human cancers. Cell Rep. 23:227–238.e3. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hoadley KA, Yau C, Hinoue T, Wolf DM,
Lazar AJ, Drill E, Shen R, Taylor AM, Cherniack AD, Thorsson V, et
al Cancer Genome Atlas Network, : Cell-of-origin patterns dominate
the molecular classification of 10,000 tumors from 33 types of
cancer. Cell. 173:291–304.e6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu J, Lichtenberg T, Hoadley KA, Poisson
LM, Lazar AJ, Cherniack AD, Kovatich AJ, Benz CC, Levine DA, Lee
AV, et al Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, : An integrated
TCGA pan-cancer clinical data resource to drive high-quality
survival outcome analytics. Cell. 173:400–416.e11. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Poore GD, Kopylova E, Zhu Q, Carpenter C,
Fraraccio S, Wandro S, Kosciolek T, Janssen S, Metcalf J, Song SJ,
et al: Microbiome analyses of blood and tissues suggest cancer
diagnostic approach. Nature. 579:567–574. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sanchez-Vega F, Mina M, Armenia J, Chatila
WK, Luna A, La KC, Dimitriadoy S, Liu DL, Kantheti HS, Saghafinia
S, et al Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, : Oncogenic
signaling pathways in The Cancer Genome Atlas. Cell.
173:321–337.e10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Taylor AM, Shih J, Ha G, Gao GF, Zhang X,
Berger AC, Schumacher SE, Wang C, Hu H, Liu J, et al Cancer Genome
Atlas Research Network, : Genomic and functional approaches to
understanding cancer aneuploidy. Cancer Cell. 33:676–689.e3. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rodriguez-Corona U, Sobol M,
Rodriguez-Zapata LC, Hozak P and Castano E: Fibrillarin from
Archaea to human. Biol Cell. 107:159–174. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ascione A, Fontanella L, Imparato M,
Rinaldi L and De Luca M: Mortality from cirrhosis and
hepatocellular carcinoma in Western Europe over the last 40 years.
Liver Int. 37:1193–1201. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Beal EW, Tumin D, Kabir A, Moris D, Zhang
XF, Chakedis J, Washburn K, Black S, Schmidt CM and Pawlik TM:
Trends in the mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United
States. J Gastrointest Surg. 21:2033–2038. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Weaver AJ, Stafford R, Hale J, Denning D
and Sanabria JR; GBD Collaborators, : Geographical and temporal
variation in the incidence and mortality of
hepato-pancreato-biliary primary malignancies: 1990–2017. J Surg
Res. 245:89–98. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Brandman O and Hegde RS:
Ribosome-associated protein quality control. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
23:7–15. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
van Riggelen J, Yetil A and Felsher DW:
MYC as a regulator of ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis.
Nat Rev Cancer. 10:301–309. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Arthurs C, Murtaza BN, Thomson C, Dickens
K, Henrique R, Patel HRH, Beltran M, Millar M, Thrasivoulou C and
Ahmed A: Expression of ribosomal proteins in normal and cancerous
human prostate tissue. PLoS One. 12:e01860472017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sulima SO, Kampen KR, Vereecke S, Pepe D,
Fancello L, Verbeeck J, Dinman JD and De Keersmaecker K: Ribosomal
lesions promote oncogenic mutagenesis. Cancer Res. 79:320–327.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bellodi C, Kopmar N and Ruggero D:
Deregulation of oncogene-induced senescence and p53 translational
control in X-linked dyskeratosis congenita. EMBO J. 29:1865–1876.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bellodi C, Krasnykh O, Haynes N,
Theodoropoulou M, Peng G, Montanaro L and Ruggero D: Loss of
function of the tumor suppressor DKC1 perturbs p27 translation
control and contributes to pituitary tumorigenesis. Cancer Res.
70:6026–6035. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Rocchi L, Pacilli A, Sethi R, Penzo M,
Schneider RJ, Treré D, Brigotti M and Montanaro L: Dyskerin
depletion increases VEGF mRNA internal ribosome entry site-mediated
translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:8308–8318. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sloan KE, Warda AS, Sharma S, Entian KD,
Lafontaine DLJ and Bohnsack MT: Tuning the ribosome: The influence
of rRNA modification on eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis and
function. RNA Biol. 14:1138–1152. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Nachmani D, Bothmer AH, Grisendi S, Mele
A, Bothmer D, Lee JD, Monteleone E, Cheng K, Zhang Y, Bester AC, et
al: Germline NPM1 mutations lead to altered rRNA 2′-O-methylation
and cause dyskeratosis congenita. Nat Genet. 51:1518–1529. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Amin MA, Matsunaga S, Ma N, Takata H,
Yokoyama M, Uchiyama S and Fukui K: Fibrillarin, a nucleolar
protein, is required for normal nuclear morphology and cellular
growth in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 360:320–326.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bouffard S, Dambroise E, Brombin A,
Lempereur S, Hatin I, Simion M, Corre R, Bourrat F, Joly JS and
Jamen F: Fibrillarin is essential for S-phase progression and
neuronal differentiation in zebrafish dorsal midbrain and retina.
Dev Biol. 437:1–16. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Newton K, Petfalski E, Tollervey D and
Cáceres JF: Fibrillarin is essential for early development and
required for accumulation of an intron-encoded small nucleolar RNA
in the mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 23:8519–8527. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
El Hassouni B, Sarkisjan D, Vos JC,
Giovannetti E and Peters GJ: Targeting the Ribosome Biogenesis Key
Molecule Fibrillarin to Avoid Chemoresistance. Curr Med Chem.
26:6020–6032. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|