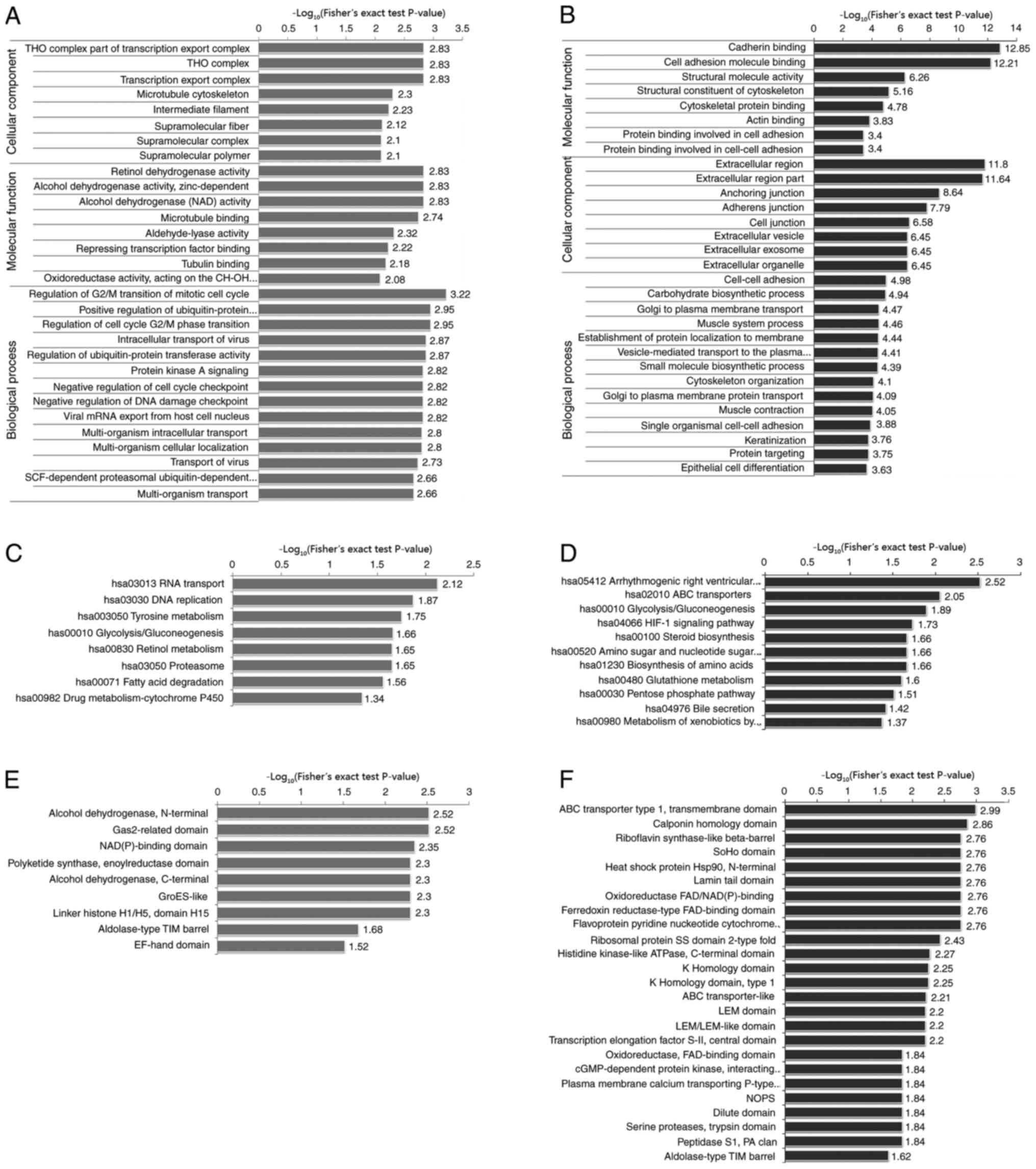
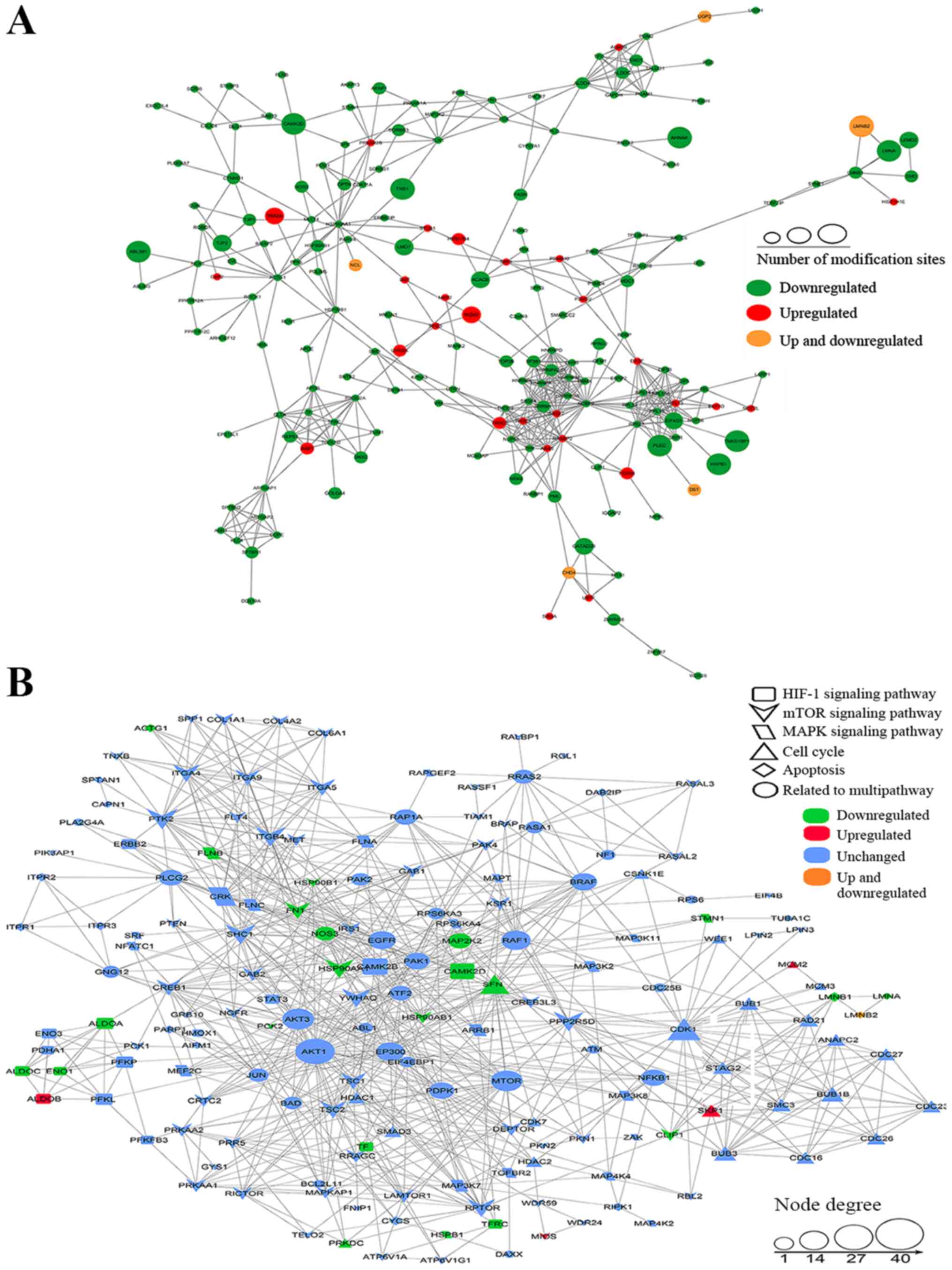
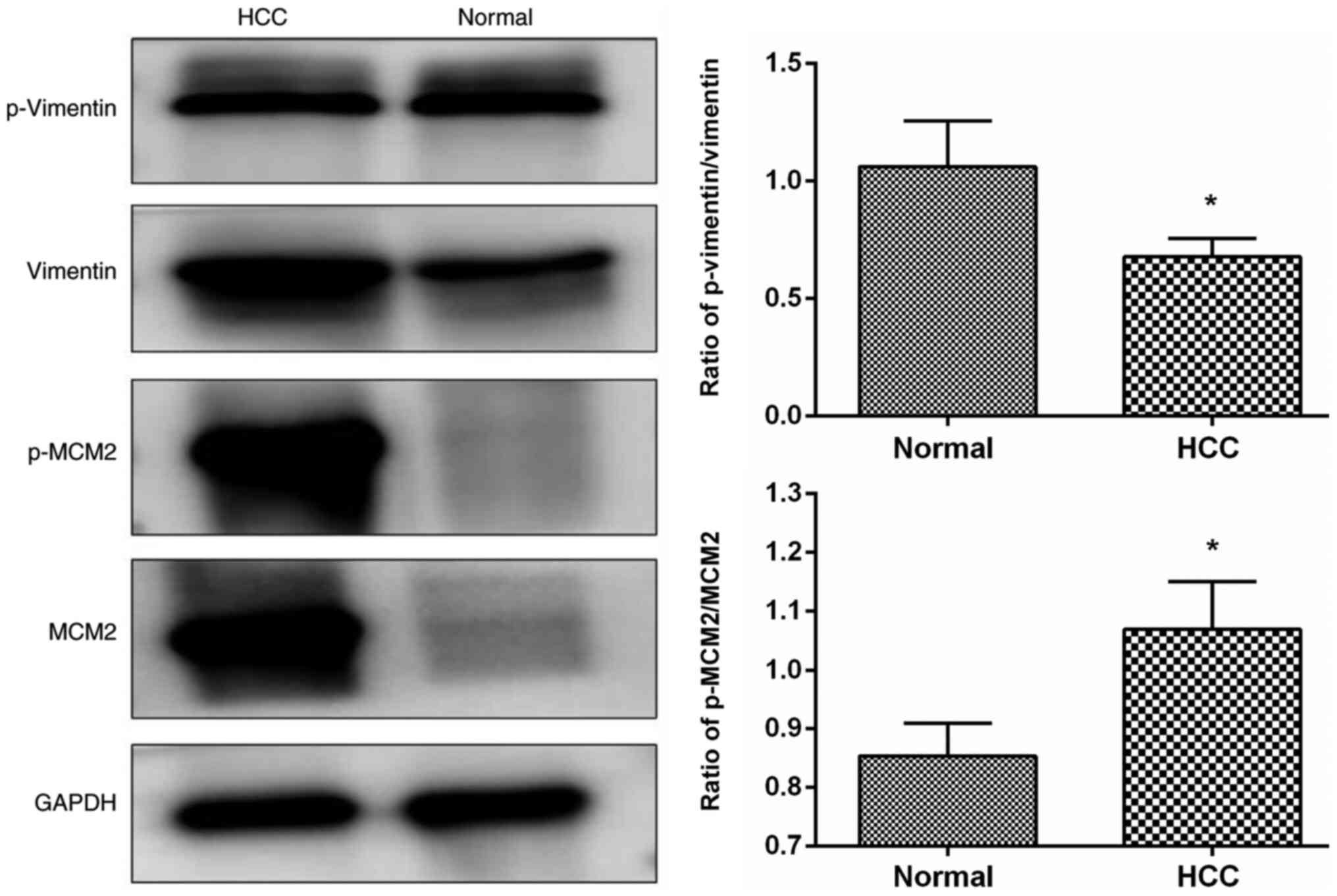
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lafaro KJ, Demirjian AN and Pawlik TM:
Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg Oncol Clin N Am.
24:1–17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roayaie S, Obeidat K, Sposito C, Mariani
L, Bhoori S, Pellegrinelli A, Labow D, Llovet JM, Schwartz M and
Mazzaferro V: Resection of hepatocellular cancer ≤2 cm: Results
from two Western centers. Hepatology. 57:1426–1435. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Armengol C, Sarrias MR and Sala M:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Present and future. Med Clin (Barc).
150:390–397. 2018.(In English, Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen JG, Parkin DM, Chen QG, Lu JH, Shen
QJ, Zhang BC and Zhu YR: Screening for liver cancer: Results of a
randomised controlled trial in Qidong, China. J Med Screen.
10:204–209. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao P, Yang X, Qi S, Liu H, Jiang H,
Hoppmann S, Cao Q, Chua MS, So SK and Cheng Z: Molecular imaging of
hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts with epidermal growth factor
receptor targeted affibody probes. Biomed Res Int. 2013:7590572013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ryan DP and Matthews JM: Protein-protein
interactions in human disease. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 15:441–446.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Satoh J: MicroRNAs and their therapeutic
potential for human diseases: Aberrant microRNA expression in
Alzheimer's disease brains. J Pharmacol Sci. 114:269–275. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu H, Wang Y, Lin S, Deng W, Peng D, Cui Q
and Xue Y: PTMD: A database of human disease-associated
post-translational modifications. Genomics Proteomics
Bioinformatics. 16:244–251. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wan J, Liu H, Chu J and Zhang H: Functions
and mechanisms of lysine crotonylation. J Cell Mol Med.
23:7163–7169. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vu LD, Gevaert K and De Smet I: Protein
language: Post-translational modifications talking to each other.
Trends Plant Sci. 23:1068–1080. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hjerrild M and Gammeltoft S:
Phosphoproteomics toolbox: Computational biology, protein chemistry
and mass spectrometry. FEBS Lett. 580:4764–4770. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B,
Kumar C, Mortensen P and Mann M: Global, in vivo, and site-specific
phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell. 127:635–648.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tomasi ML and Ramani K: SUMOylation and
phosphorylation cross-talk in hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3:202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang F, Song C, Cheng K, Jiang X, Ye M and
Zou H: Perspectives of comprehensive phosphoproteome analysis using
shotgun strategy. Anal Chem. 83:8078–8085. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin X, Huang Y, Sun Y, Tan X, Ouyang J,
Zhao B, Wang Y, Xing X and Liu J: 4E-BP1 Thr46
phosphorylation association with poor prognosis in quantitative
phosphoproteomics of portal vein tumor thrombus revealed that
4E-BP1Thr46 phosphorylation is associated with poor prognosis in
HCC. Cancer Manag Res. 12:103–115. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhai M, Yang Z, Zhang C, Li J, Jia J, Zhou
L, Lu R, Yao Z and Fu Z: APN-mediated phosphorylation of BCKDK
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and proliferation via
the ERK signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 11:3962020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dang Y, Jiang N, Wang H, Chen X, Gao Y,
Zhang X, Qin G, Li Y and Chen R: Proto-oncogene serine/threonine
kinase PIM3 promotes cell migration via modulating Rho GTPase
signaling. J Proteome Res. 19:1298–1309. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fernández-Varo G, Perramón M, Carvajal S,
Oró D, Casals E, Boix L, Oller L, Macías-Muñoz L, Marfà S, Casals
G, et al: Bespoken nanoceria: A new effective treatment in
experimental hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. Jan
21–2020.(Online Ahead of Print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Werth EG, Rajbhandari P, Stockwell BR and
Brown LM: Time course of changes in sorafenib-treated
hepatocellular carcinoma cells suggests involvement of
phosphor-regulated signaling in ferroptosis induction. Proteomics.
20:e20000062020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pinna LA and Meggio F: Protein kinase ck2
(‘casein kinase-2’) and its implication in cell division and
proliferation. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 3:77–97. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Litchfield DW: Protein kinase CK2:
Structure, regulation and role in cellular decisions of life and
death. Biochem J. 369:1–15. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Trembley JH, Wang G, Unger G, Slaton J and
Ahmed K: Protein kinase CK2 in health and disease: CK2: A key
player in cancer biology. Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:1858–1867. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ahmad KA, Wang G, Unger G, Slaton J and
Ahmed K: Protein kinase CK2-a key suppressor of apoptosis. Adv
Enzyme Regul. 48:179–187. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Paculová H and Kohoutek J: The emerging
roles of CDK12 in tumorigenesis. Cell Div. 12:72017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bačević K, Lossaint G, Achour TN, Georget
V, Fisher D and Dulić V: Cdk2 strengthens the intra-S checkpoint
and counteracts cell cycle exit induced by DNA damage. Sci Rep.
7:134292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shah SB, Parmiter D, Constantine C,
Elizalde P, Naldrett M, Karpova TS and Choy JS: Glucose signaling
is connected to chromosome segregation through protein kinase a
phosphorylation of the Dam1 kinetochore subunit in saccharomyces
cerevisiae. Genetics. 211:531–547. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Persaud L, Mighty J, Zhong X, Francis A,
Mendez M, Muharam H, Redenti SM, Das D, Aktas BH and Sauane M:
IL-24 promotes apoptosis through cAMP-dependent PKA pathways in
human breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 19:35612018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Isakov N: Protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms
in cancer, tumor promotion and tumor suppression. Semin Cancer
Biol. 48:36–52. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O and Kolch W:
MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 26:3279–3290.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schaeffer HJ and Weber MJ:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases: Specific messages from
ubiquitous messengers. Mol Cell Biol. 19:2435–2444. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Caunt CJ and Keyse SM: Dual-specificity
MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs): Shaping the outcome of MAP kinase
signalling. FEBS J. 280:489–504. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Steelman LS, Pohnert SC, Shelton JG,
Franklin RA, Bertrand FE and McCubrey JA: JAK/STAT, Raf/MEK/ERK,
PI3K/Akt and BCR-ABL in cell cycle progression and leukemogenesis.
Leukemia. 18:189–218. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ritt DA, Abreu-Blanco MT, Bindu L, Durrant
DE, Zhou M, Specht SI, Stephen AG, Holderfield M and Morrison DK:
Inhibition of Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway signaling by a stress-induced
phospho-regulatory circuit. Mol Cell. 64:875–887. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH and
Theise ND: World Health Organization Classification of Tumours by
International Agency for Research on Cancer WHO classification of
tumours of the digestive system. 3. 4th edition. Lyon, France:
International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2010
|
|
38
|
Perez-Riverol Y, Csordas A, Bai J,
Bernal-Llinares M, Hewapathirana S, Kundu DJ, Inuganti A, Griss J,
Mayer G, Eisenacher M, et al: The PRIDE database and related tools
and resources in 2019: Improving support for quantification data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 47(D1): D442–D450. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cox J and Mann M: MaxQuant enables high
peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass
accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat
Biotechnol. 26:1367–1372. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Schwartz D and Gygi SP: An iterative
statistical approach to the identification of protein
phosphorylation motifs from large-scale data sets. Nat Biotechnol.
23:1391–1398. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lasonder E, Green JL, Camarda G, Talabani
H, Holder AA, Langsley G and Alano P: The Plasmodium falciparum
schizont phosphoproteome reveals extensive phosphatidylinositol and
cAMP-protein kinase A signaling. J Proteome Res. 11:5323–5337.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hunter T and Sefton BM: Transforming gene
product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 77:1311–1315. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ren L, Li C, Wang Y, Teng Y, Sun H, Xing
B, Yang X, Jiang Y and He F: In vivo phosphoproteome analysis
reveals kinome reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 17:1067–1083. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Huttlin EL, Jedrychowski MP, Elias JE,
Goswami T, Rad R, Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Haas W, Sowa ME and Gygi
SP: A tissue-specific atlas of mouse protein phosphorylation and
expression. Cell. 143:1174–1189. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chiotaki R, Polioudaki H and
Theodoropoulos PA: Differential nuclear shape dynamics of invasive
andnon-invasive breast cancer cells are associated with actin
cytoskeleton organization and stability. Biochem Cell Biol.
92:287–295. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cremer M, Küpper K, Wagler B, Wizelman L,
von Hase J, Weiland Y, Kreja L, Diebold J, Speicher MR and Cremer
T: Inheritance of gene density-related higher order chromatin
arrangements in normal and tumor cell nuclei. J Cell Biol.
162:809–820. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Murata S, Nakazawa T, Ohno N, Terada N,
Iwashina M, Mochizuki K, Kondo T, Nakamura N, Yamane T, Iwasa S, et
al: Conservation and alteration of chromosome territory
arrangements in thyroid carcinoma cell nuclei. Thyroid. 17:489–496.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Harnicarová A, Kozubek S, Pacherník J,
Krejci J and Bártová E: Distinct nuclear arrangement of active and
inactive c-myc genes in control and differentiated colon carcinoma
cells. Exp Cell Res. 312:4019–4035. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bártová E, Kozubek S, Kozubek M, Jirsová
P, Lukásová E, Skalníková M, Cafourková A and Koutná I: Nuclear
topography of the c-myc gene in human leukemic cells. Gene.
244:1–11. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Guo T, Lee SS, Ng WH, Zhu Y, Gan CS, Zhu
J, Wang H, Huang S, Sze SK and Kon OL: Global molecular
dysfunctions in gastric cancer revealed by an integrated analysis
of the phosphoproteome and transcriptome. Cell Mol Life Sci.
68:1983–2002. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Thomson M: Evidence of undiscovered cell
regulatory mechanisms: Phosphoproteins and protein kinases in
mitochondria. Cell Mol Life Sci. 59:213–219. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Obeng EA, Stewart C and Abdel-Wahab O:
Altered RNA processing in cancer pathogenesis and therapy. Cancer
Discov. 9:1493–1510. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Primo LMF and Teixeira LK: DNA replication
stress: Oncogenes in the spotlight. Genet Mol Biol. 43 (1 Suppl
1):e201901382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li Y, Bian Y, Wang K and Wan XP: POLE
mutations improve the prognosis of endometrial cancer via
regulating cellular metabolism through AMF/AMFR signal
transduction. BMC Med Genet. 20:2022019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nikolaou KC, Vatandaslar H, Meyer C,
Schmid MW, Tuschl T and Stoffel M: The RNA-binding protein A1CF
regulates hepatic fructose and glycerol metabolism via alternative
RNA splicing. Cell Re. 29:283–300.e8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Musolino V, Palus S, Latouche C, Gliozzi
M, Bosco F, Scarano F, Nucera S, Carresi C, Scicchitano M, von
Haehling S, et al: Cardiac expression of neutrophil
gelatinase-associated lipocalin in a model of cancer
cachexia-induced cardiomyopathy. ESC Heart Fail. 6:89–97. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lu W, Tang X, Huo Y, Xu R, Qi S, Huang J,
Zheng C and Wu CA: Identification and characterization of fructose
1,6-bisphosphate aldolase genes in Arabidopsis reveal a gene family
with diverse responses to abiotic stresses. Gene. 503:65–74. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
van der Linde K, Gutsche N, Leffers HM,
Lindermayr C, Müller B, Holtgrefe S and Scheibe R: Regulation of
plant cytosolic aldolase functions by redox-modifications. Plant
Physiol Biochem. 49:946–957. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Girdler GC, Applewhite DA, Perry WM,
Rogers SL and Röper K: The Gas2 family protein Pigs is a
microtubule +TIP that affects cytoskeleton organisation. J Cell
Sci. 129:121–134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hua YH, Wu CY, Sargsyan K and Lim C:
Sequence-motif detection of NAD(P)-binding proteins: Discovery of a
unique antibacterial drug target. Sci Rep. 4:64712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Agrawal M, Zitnik M and Leskovec J:
Large-scale analysis of disease pathways in the human interactome.
Pac Symp Biocomput. 23:111–122. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Rattray DG and Foster LJ: Dynamics of
protein complex components. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 48:81–85. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yi T, Zhai B, Yu Y, Kiyotsugu Y, Raschle
T, Etzkorn M, Seo HC, Nagiec M, Luna RE, Reinherz EL, et al:
Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis reveals system-wide
signaling pathways downstream of SDF-1/CXCR4 in breast cancer stem
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:E2182–E2190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|