|
1
|
National Cancer Institute: Surveillance,
Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Accessed from. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/common.html2020
|
|
2
|
Nath S and Mukherjee P: MUC1: A
multifaceted oncoprotein with a key role in cancer progression.
Trends Mol Med. 20:332–342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parry S, Silverman HS, McDermott K, Willis
A, Hollingsworth MA and Harris A: Identification of MUC1
proteolytic cleavage sites in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
283:715–720. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siddiqui J, Abe M, Hayes D, Shani E, Yunis
E and Kufe D: Isolation and sequencing of a cDNA coding for the
human DF3 breast carcinoma-associated antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 85:2320–2323. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
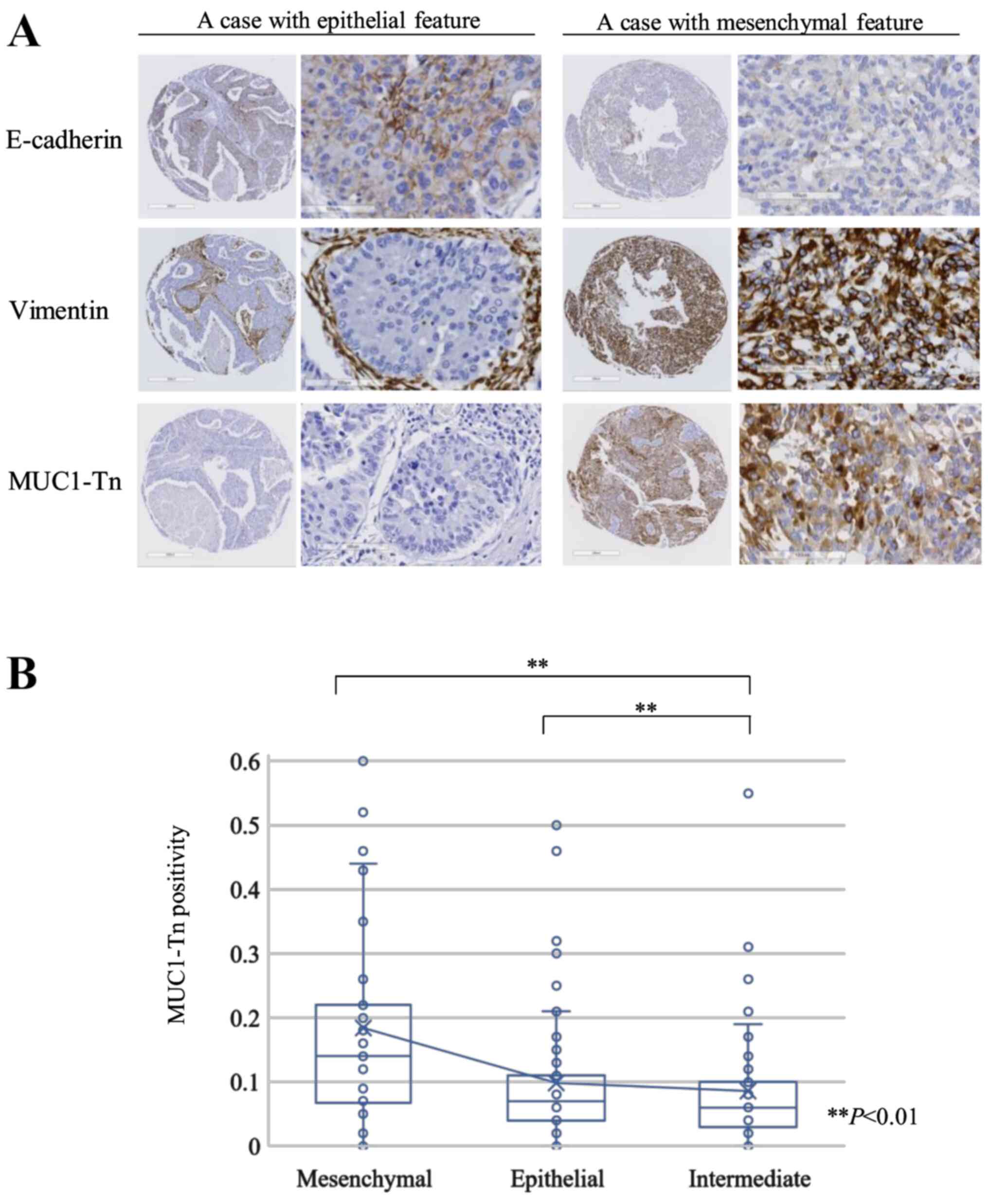
|
Gendler S, Taylor-Papadimitriou J, Duhig
T, Rothbard J and Burchell J: A highly immunogenic region of a
human polymorphic epithelial mucin expressed by carcinomas is made
up of tandem repeats. J Biol Chem. 263:12820–12823. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Qu J, Yu H, Li F, Zhang C, Trad A, Brooks
C, Zhang B, Gong T, Guo Z, Li Y, et al: Molecular basis of antibody
binding to mucin glycopeptides in lung cancer. Int J Oncol.
48:587–594. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fu C, Zhao H, Wang Y, Cai H, Xiao Y, Zeng
Y and Chen H: Tumor-associated antigens: Tn antigen, sTn antigen,
and T antigen. HLA. 88:275–286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ju T and Cummings RD: A unique molecular
chaperone Cosmc required for activity of the mammalian core 1 beta
3-galactosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:16613–16618.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chugh S, Barkeer S, Rachagani S,
Nimmakayala RK, Perumal N, Pothuraju R, Atri P, Mahapatra S, Thapa
I, Talmon GA, et al: Disruption of C1galt1 gene promotes
development and metastasis of pancreatic adenocarcinomas in mice.
Gastroenterology. 155:1608–1624. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Radhakrishnan P, Dabelsteen S, Madsen FB,
Francavilla C, Kopp KL, Steentoft C, Vakhrushev SY, Olsen JV,
Hansen L, Bennett EP, et al: Immature truncated O-glycophenotype of
cancer directly induces oncogenic features. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:E4066–E4075. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guddo F, Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis MI,
Reina C, Vignola AM, Chlouverakis G, Hilkens J, Gatter KC, Harris
AL and Bonsignore G: MUC1 (episialin) expression in non-small cell
lung cancer is independent of EGFR and c-erbB-2 expression and
correlates with poor survival in node positive patients. J Clin
Pathol. 51:667–671. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nagai S, Takenaka K, Sonobe M, Ogawa E,
Wada H and Tanaka F: A novel classification of MUC1 expression is
correlated with tumor differentiation and postoperative prognosis
in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 1:46–51. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kuemmel A, Single K, Bittinger F, Faldum
A, Schmidt LH, Sebastian M, Micke P, Taube C, Buhl R and Wiewrodt
R: TA-MUC1 epitope in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
63:98–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ishikawa N, Hattori N, Yokoyama A and
Kohno N: Utility of KL-6/MUC1 in the clinical management of
interstitial lung diseases. Respir Investig. 50:3–13. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tanaka S, Hattori N, Ishikawa N, Shoda H,
Takano A, Nishino R, Okada M, Arihiro K, Inai K, Hamada H, et al:
Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) is a prognostic biomarker in patients
with surgically resected nonsmall cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer.
130:377–387. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Naito S, Takahashi T, Onoda J, Uemura S,
Ohyabu N, Takemoto H, Yamane S, Fujii I, Nishimura SI and Numata Y:
Generation of novel anti-MUC1 monoclonal antibodies with designed
carbohydrate specificities using MUC1 glycopeptide library. ACS
Omega. 2:7493–7505. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Travis W, Brambilla E, Burke AP, Marx A
and Nicholson AG: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Lung,
Pleura, Thymus and Heart. International Agency for Research on
Cancer; Lyon: 2015
|
|
18
|
Brierley JD, Gospodarowicz MK and
Wittekind C: Union for International Cancer Control (UICC): TNM
Classification of Malignant Tumours. 8th edition. Wiley-Blackwell;
Hoboken, NJ: pp. p2722017
|
|
19
|
Posey AD Jr, Schwab RD, Boesteanu AC,
Steentoft C, Mandel U, Engels B, Stone JD, Madsen TD, Schreiber K,
Haines KM, et al: Engineered CAR-T cells targeting the
cancer-associated Tn-glycoform of the membrane mucin MUC1 control
adenocarcinoma. Immunity. 44:1444–1454. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li T, Mo C, Qin X, Li S, Liu Y and Liu Z:
Glycoprofiling of early gastric cancer using lectin microarray
technology. Clin Lab. 64:153–161. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Konno A, Hoshino Y, Terashima S, Motoki R
and Kawaguchi T: Carbohydrate expression profile of colorectal
cancer cells is relevant to metastatic pattern and prognosis. Clin
Exp Metastasis. 19:61–70. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Byrd JC and Bresalier RS: Mucins and mucin
binding proteins in colorectal cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
23:77–99. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Welinder C, Baldetorp B, Blixt O, Grabau D
and Jansson B: Primary breast cancer tumours contain high amounts
of IgA1 immunoglobulin: An immunohistochemical analysis of a
possible carrier of the tumour-associated Tn antigen. PLoS One.
8:e617492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pinto R, Carvalho AS, Conze T, Magalhães
A, Picco G, Burchell JM, Taylor-Papadimitriou J, Reis CA, Almeida
R, Mandel U, et al: Identification of new cancer biomarkers based
on aberrant mucin glycoforms by in situ proximity ligation. J Cell
Mol Med. 16:1474–1484. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ju T, Lanneau GS, Gautam T, Wang Y, Xia B,
Stowell SR, Willard MT, Wang W, Xia JY, Zuna RE, et al: Human tumor
antigens Tn and sialyl Tn arise from mutations in Cosmc. Cancer
Res. 68:1636–1646. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Häuselmann I and Borsig L: Altered
tumor-cell glycosylation promotes metastasis. Front Oncol.
4:282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Higashi N, Fujioka K, Denda-Nagai K,
Hashimoto S, Nagai S, Sato T, Fujita Y, Morikawa A, Tsuiji M,
Miyata-Takeuchi M, et al: The macrophage C-type lectin specific for
galactose/N-acetylgalactosamine is an endocytic receptor expressed
on monocyte-derived immature dendritic cells. J Biol Chem.
277:20686–20693. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ju T, Wang Y, Aryal RP, Lehoux SD, Ding X,
Kudelka MR, Cutler C, Zeng J, Wang J, Sun X, et al: Tn and
sialyl-Tn antigens, aberrant O-glycomics as human disease markers.
Proteomics Clin Appl. 7:618–631. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Napoletano C, Rughetti A, Agervig Tarp MP,
Coleman J, Bennett EP, Picco G, Sale P, Denda-Nagai K, Irimura T,
Mandel U, et al: Tumor-associated Tn-MUC1 glycoform is internalized
through the macrophage galactose-type C-type lectin and delivered
to the HLA class I and II compartments in dendritic cells. Cancer
Res. 67:8358–8367. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kölbl AC, Jeschke U, Friese K and
Andergassen U: The role of TF- and Tn-antigens in breast cancer
metastasis. Histol Histopathol. 31:613–621. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Matsubara T, Tagawa T, Takada K, Toyokawa
G, Shimokawa M, Kozuma Y, Akamine T, Haro A, Osoegawa A and Mori M:
Clinical and prognostic significance of the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in stage IA lung adenocarcinoma: A propensity
score-matched analysis. Clin Lung Cancer. 20:e504–e513. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Warburg O: On the origin of cancer cells.
Science. 123:309–314. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Peixoto A, Fernandes E, Gaiteiro C, Lima
L, Azevedo R, Soares J, Cotton S, Parreira B, Neves M, Amaro T, et
al: Hypoxia enhances the malignant nature of bladder cancer cells
and concomitantly antagonizes protein O-glycosylation extension.
Oncotarget. 7:63138–63157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Aubert S, Fauquette V, Hémon B, Lepoivre
R, Briez N, Bernard D, Van Seuningen I, Leroy X and Perrais M:
MUC1, a new hypoxia inducible factor target gene, is an actor in
clear renal cell carcinoma tumor progression. Cancer Res.
69:5707–5715. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kaira K, Okumura T, Nakagawa K, Ohde Y,
Takahashi T, Murakami H, Naito T, Endo M, Kondo H, Nakajima T, et
al: MUC1 expression in pulmonary metastatic tumors: A comparison of
primary lung cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 18:439–447. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hollingsworth MA and Swanson BJ: Mucins in
cancer: Protection and control of the cell surface. Nat Rev Cancer.
4:45–60. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kufe DW: Mucins in cancer: Function,
prognosis and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:874–885. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|