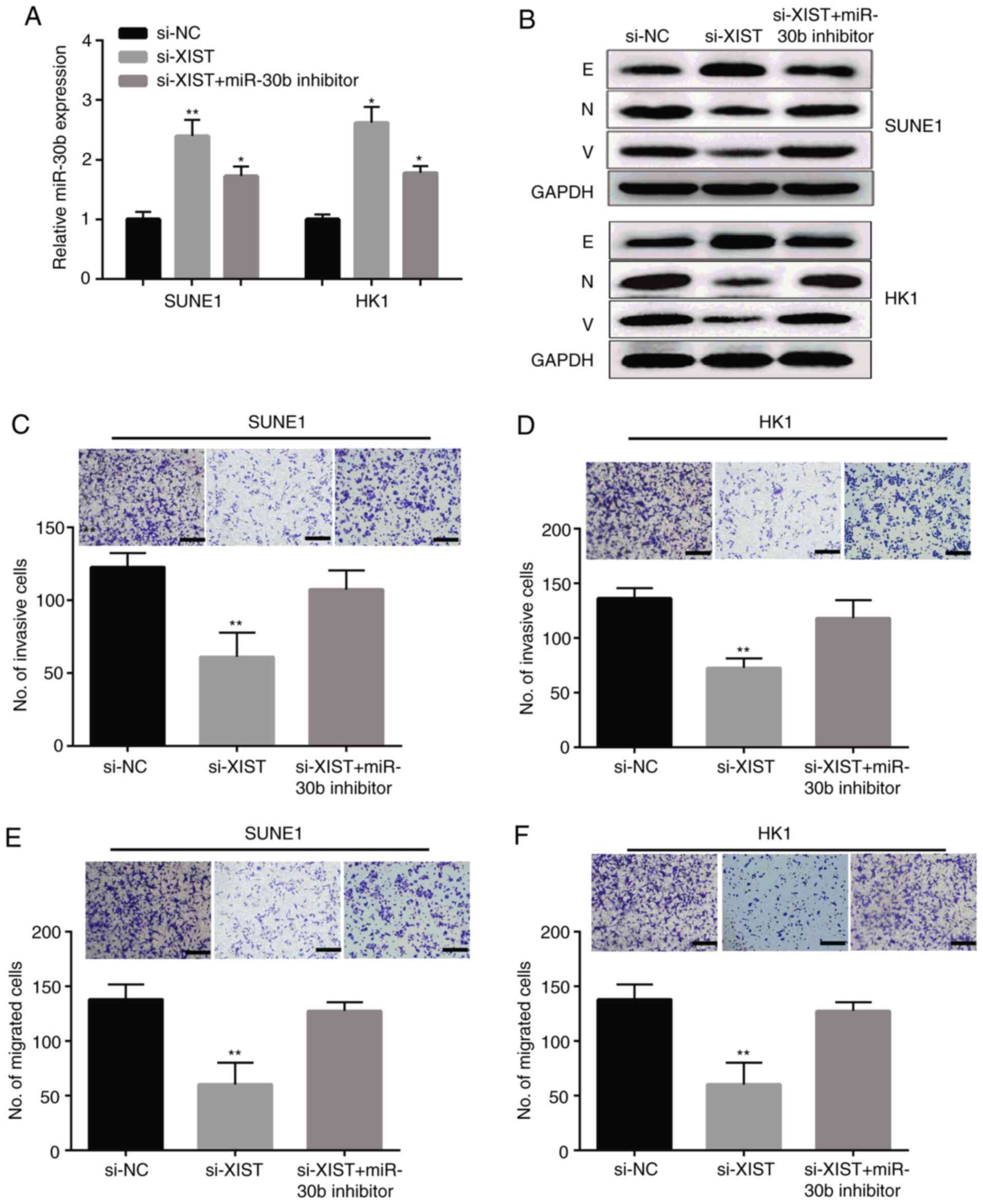
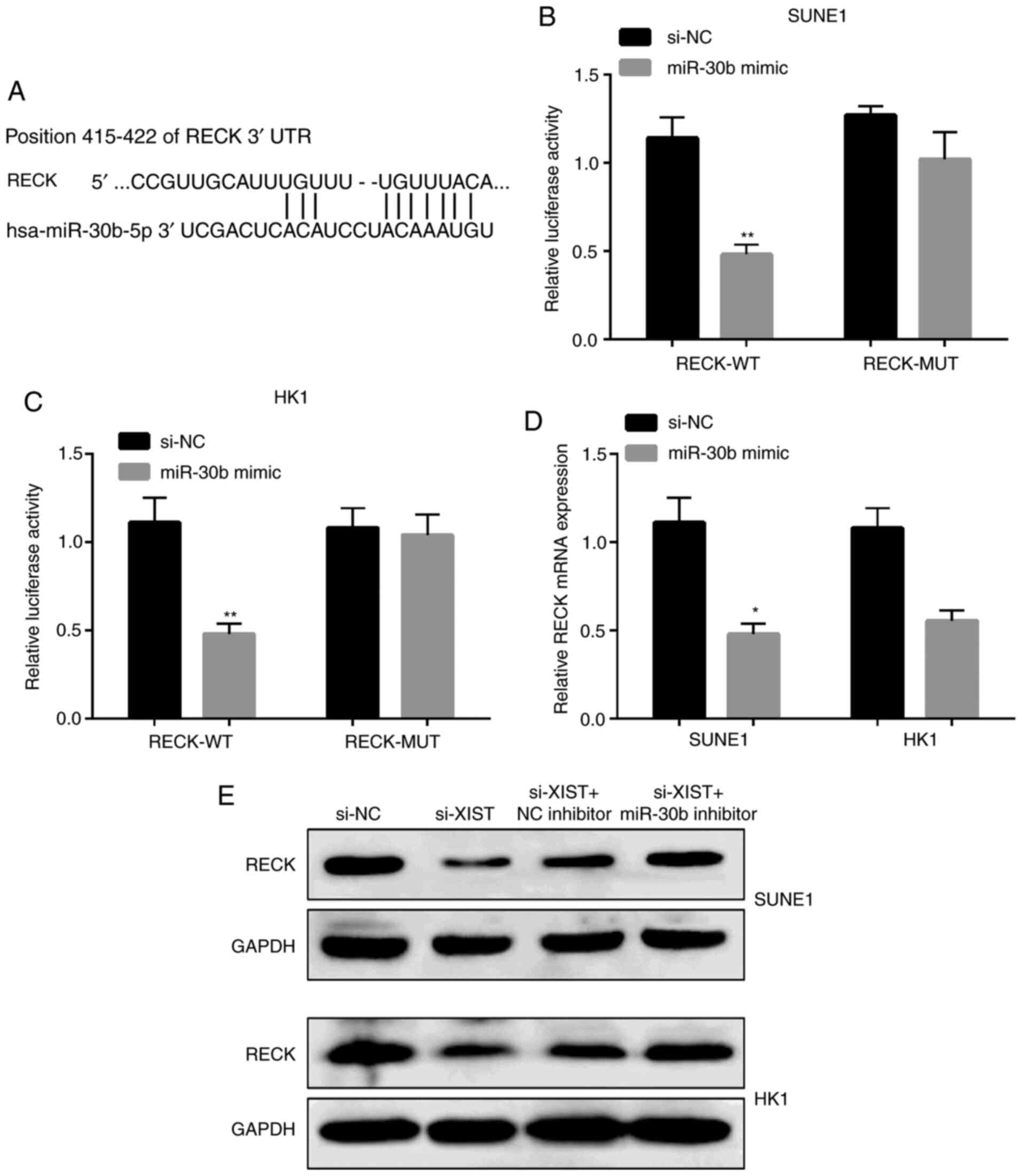
|
1
|
Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, Blanchard P, Sun
Y and Ma J: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 394:64–80. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khoury S and Tran N: Circulating
microRNAs: Potential biomarkers for common malignancies. Biomark
Med. 9:131–151. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang KC, Yang YW, Liu B, Sanyal A,
Corces-Zimmerman R, Chen Y, Lajoie BR, Protacio A, Flynn RA, Gupta
RA, et al: A long noncoding RNA maintains active chromatin to
coordinate homeotic gene expression. Nature. 472:120–124. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Prensner JR and Chinnaiyan AM: The
emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Discov. 1:391–407.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang QQ and Deng YF: Genome-wide analysis
of long non-coding RNA in primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
microarray. Histopathology. 66:1022–1030. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen S, Lv L, Zhan Z, Wang X, You Z, Luo X
and You H: Silencing of long noncoding RNA SRRM2-AS exerts
suppressive effects on angiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via
activating MYLK-mediated cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. J Cell
Physiol. 235:7757–7768. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xue MY and Cao HX: Long non-coding RNA
CASC15 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and
metastasis by downregulating miR-101-3p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:8897–8904. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cheng Q, Xu X, Jiang H, Xu L and Li Q:
Knockdown of long non-coding RNA XIST suppresses nasopharyngeal
carcinoma progression by activating miR-491-5p. J Cell Biochem.
119:3936–3944. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han Q, Li L, Liang H, Li Y, Xie J and Wang
Z: Downregulation of lncRNA X inactive specific transcript (XIST)
suppresses cell proliferation and enhances radiosensitivity by
upregulating mir-29c in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Med Sci
Monit. 23:4798–4807. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gu Z, Hou Z, Zheng L, Wang X, Wu L and
Zhang C: LncRNA DICER1-AS1 promotes the proliferation, invasion and
autophagy of osteosarcoma cells via miR-30b/ATG5. Biomed
Pharmacother. 104:110–118. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brown CJ, Ballabio A, Rupert JL,
Lafreniere RG, Grompe M, Tonlorenzi R and Willard HF: A gene from
the region of the human X inactivation centre is expressed
exclusively from the inactive X chromosome. Nature. 349:38–44.
1991. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ren C, Li X, Wang T, Wang G, Zhao C, Liang
T, Zhu Y, Li M, Yang C, Zhao Y and Zhang GM: Functions and
mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs in ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. 25:566–569. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tantai J, Hu D, Yang Y and Geng J:
Combined identification of long non-coding RNA XIST and HIF1A-AS1
in serum as an effective screening for non-small cell lung cancer.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7887–7895. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yao Y, Ma J, Xue Y, Wang P, Li Z, Liu J,
Chen L, Xi Z, Teng H, Wang Z, et al: Knockdown of long non-coding
RNA XIST exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human glioblastoma
stem cells by up-regulating miR-152. Cancer Lett. 359:75–86. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang YS, Chang CC, Lee SS, Jou YS and
Shih HM: Xist reduction in breast cancer upregulates AKT
phosphorylation via HDAC3-mediated repression of PHLPP1 expression.
Oncotarget. 7:43256–43266. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhuang LK, Yang YT, Ma X, Han B, Wang ZS,
Zhao QY, Wu LQ and Qu ZQ: MicroRNA-92b promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma progression by targeting Smad7 and is mediated by long
non-coding RNA XIST. Cell Death Dis. 7:e22032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He S, Lai R, Chen D, Yan W, Zhang Z, Liu
Z, Ding X and Chen Y: Downregulation of miR-221 inhibits cell
migration and invasion through targeting Methyl-CpG binding domain
protein 2 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Biomed Res
Int. 2015:7516722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gaziel-Sovran A, Segura MF, Di Micco R,
Collins MK, Hanniford D, Vega-Saenz de Miera E, Rakus JF, Dankert
JF, Shang S, Kerbel RS, et al: miR-30b/30d regulation of GalNAc
transferases enhances invasion and immunosuppression during
metastasis. Cancer Cell. 20:104–118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fan X, Wang E, Wang X, Cong X and Chen X:
MicroRNA-21 is a unique signature associated with coronary plaque
instability in humans by regulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 via
reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs. Exp Mol
Pathol. 96:242–249. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mannello F, Tonti GA, Bagnara GP and Papa
S: Role and function of matrix metalloproteinases in the
differentiation and biological characterization of mesenchymal stem
cells. Stem Cells. 24:475–481. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee V, Kwong D, Leung TW, Lam KO, Tong CC
and Lee A: Palliative systemic therapy for recurrent or metastatic
nasopharyngeal carcinoma-How far have we achieved? Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 114:13–23. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ran Y, Wu S and You Y: Demethylation of
E-cadherin gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma could serve as a
potential therapeutic strategy. J Biochem. 149:49–54. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu A, Wu K, Li J, Mo Y, Lin Y, Wang Y,
Shen X, Li S, Li L and Yang Z: Let-7a inhibits migration, invasion
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting HMGA2 in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Transl Med. 13:1052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xiong XD, Ren X, Cai MY, Yang JW, Liu X
and Yang JM: Long non-coding RNAs: An emerging powerhouse in the
battle between life and death of tumor cells. Drug Resist Updat.
26:28–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li L, Chen H, Gao Y, Wang YW, Zhang GQ,
Pan SH, Ji L, Kong R, Wang G, Jia YH, et al: Long noncoding RNA
MALAT1 promotes aggressive pancreatic cancer proliferation and
metastasis via the stimulation of autophagy. Mol Cancer Ther.
15:2232–2243. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dong R, Liu GB, Liu BH, Chen G, Li K,
Zheng S and Dong KR: Targeting long non-coding RNA-TUG1 inhibits
tumor growth and angiogenesis in hepatoblastoma. Cell Death Dis.
7:e22782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Z, Yuan J, Li L, Yang Y, Xu X and
Wang Y: Long non-coding RNA XIST exerts oncogenic functions in
human glioma by targeting miR-137. Am J Transl Res. 9:1845–1855.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma L, Zhou Y, Luo X, Gao H, Deng X and
Jiang Y: Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes cell growth and invasion
through regulating miR-497/MACC1 axis in gastric cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:4125–4135. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen S, Li P, Yang R, Cheng R, Zhang F,
Wang Y, Chen X, Sun Q, Zang W, Du Y, et al: MicroRNA-30b inhibits
cell invasion and migration through targeting collagen triple helix
repeat containing 1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell Int.
15:852015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu ED, Li N, Li BS, Li W, Zhang WJ, Mao
XH, Guo G, Zou QM and Xiao B: miR-30b, down-regulated in gastric
cancer, promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumor growth by targeting
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. PLoS One. 9:e1060492014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang Q, Li Q, Xu T, Jiang H and Xu LG:
miR-491-5p suppresses cell growth and invasion by targeting Notch3
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 35:3541–3547. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu ZL, Wang H, Liu J and Wang ZX:
MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) expression promotes growth, metastasis, and
chemo- or radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by
targeting PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem. 372:35–45. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li J, Li P, Chen T, Gao G, Chen X, Du Y,
Zhang R, Yang R, Zhao W, Dun S, et al: Expression of microRNA-96
and its potential functions by targeting FOXO3 in non-small cell
lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:685–692. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao W, Dong Y, Wu C, Ma Y, Jin Y and Ji
Y: MiR-21 overexpression improves osteoporosis by targeting RECK.
Mol Cell Biochem. 405:125–133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|