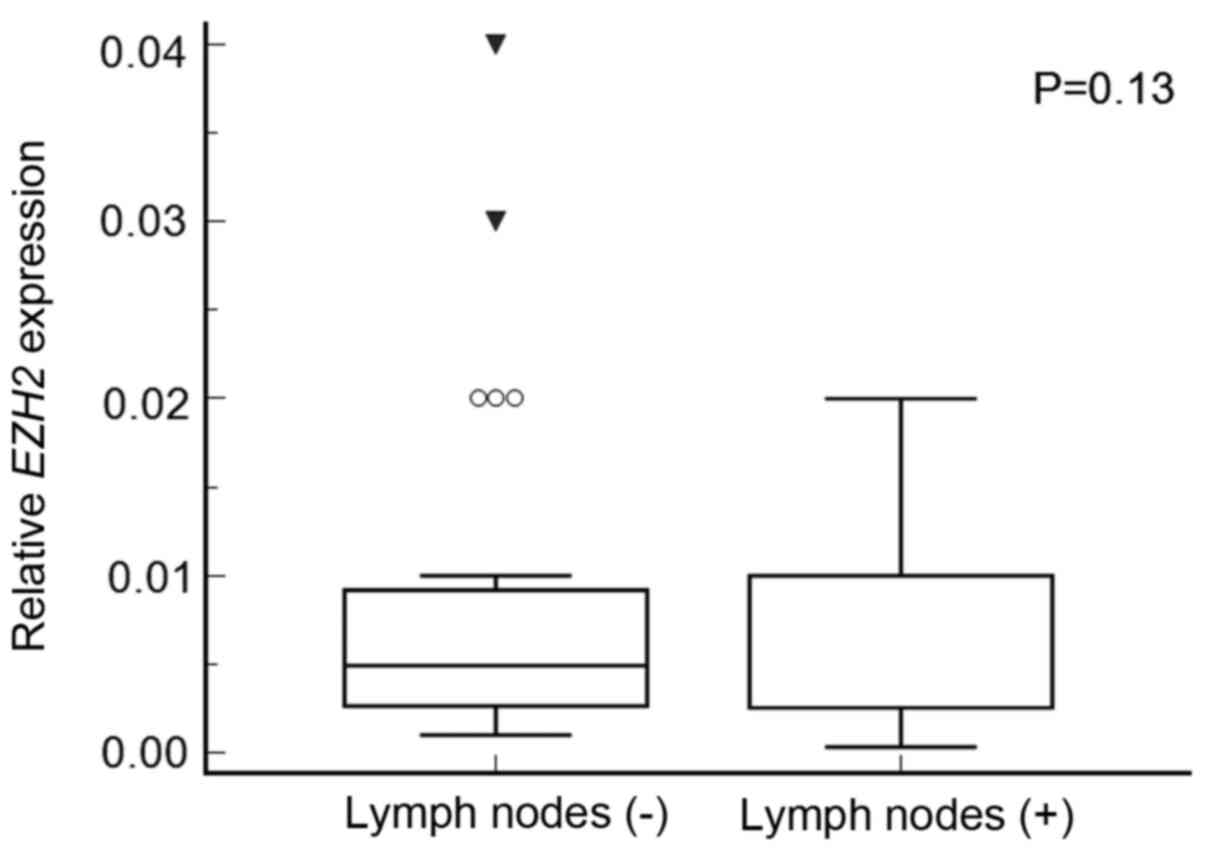
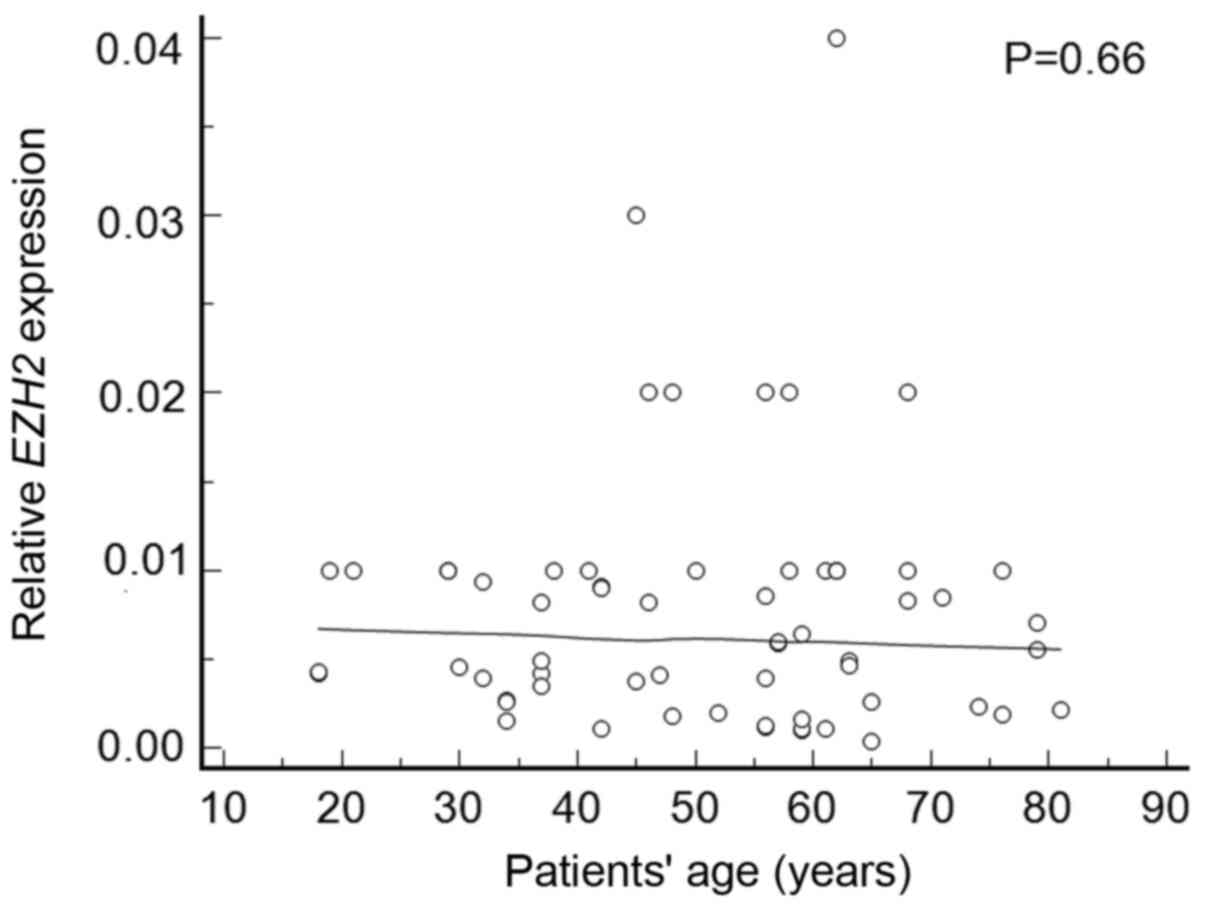
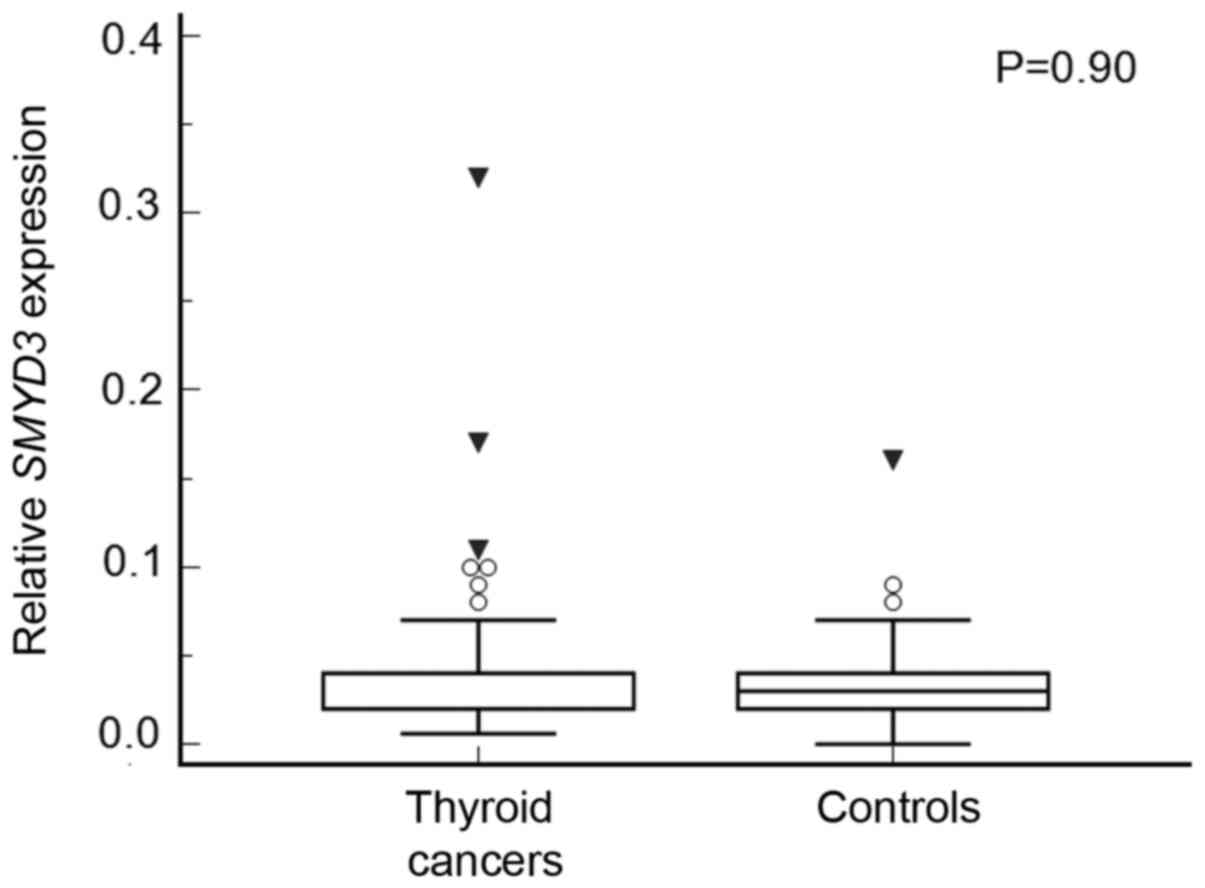
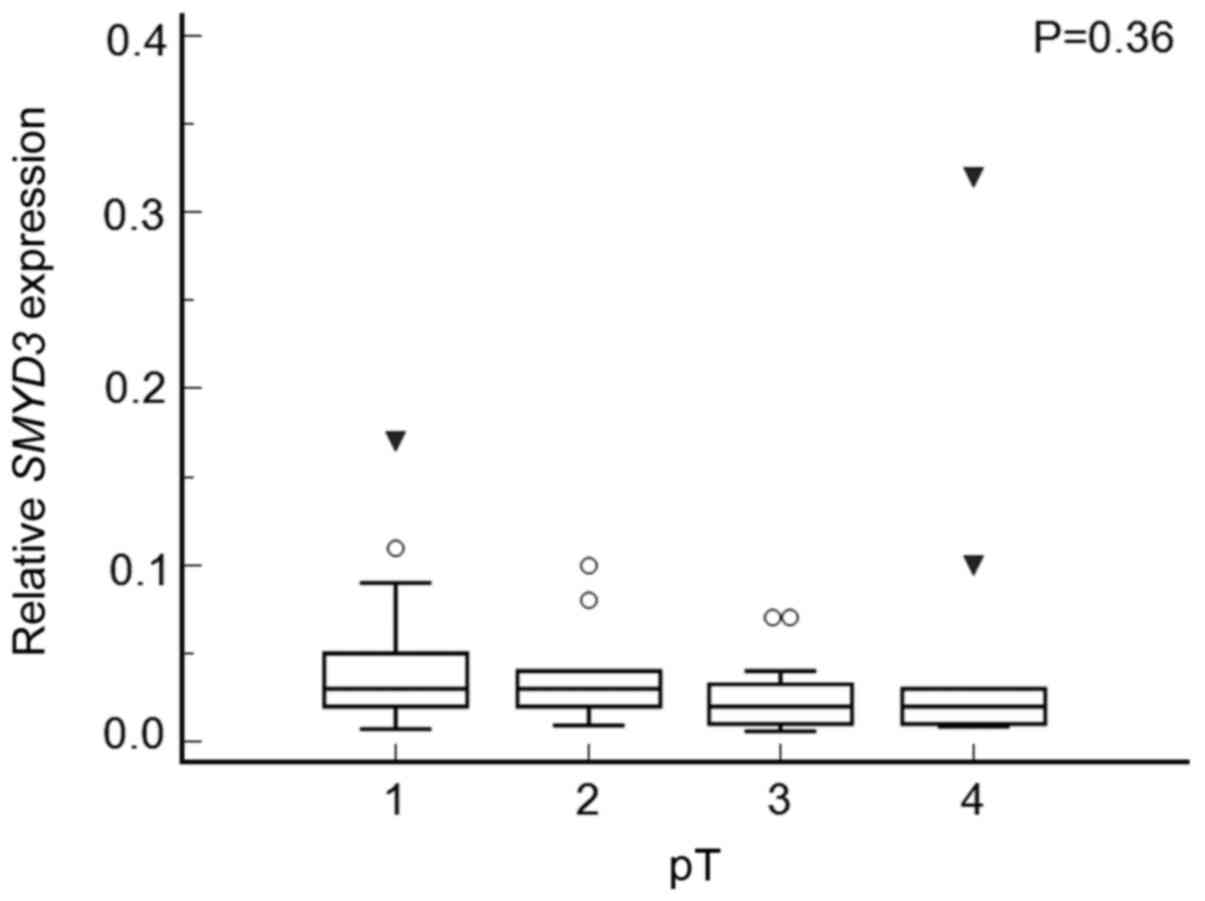
|
1
|
Zou JN, Wang SZ, Yang JS, Luo XG, Xie JH
and Xi T: Knockdown of SMYD3 by RNA interference down-regulates
c-Met expression and inhibits cells migration and invasion induced
by HGF. Cancer Lett. 280:78–85. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kouzarides T: Chromatin modifications and
their function. Cell. 128:693–705. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Giakountis A, Moulos P, Sarris ME, Hatzis
P and Talianidis I: Smyd3-associated regulatory pathways in cancer.
Semin Cancer Biol. 42:70–80. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Varier RA and Timmers HT: Histone lysine
methylation and demethylation pathways in cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1815:75–89. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Spellmon N, Holcomb J, Trescott L,
Sirinupong N and Yang Z: Structure and function of SET and MYND
domain-containing proteins. Int J Mol Sci. 16:1406–1428. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Foreman KW, Brown M, Park F, Emtage S,
Harriss J, Das C, Zhu L, Crew A, Arnold L, Shaaban S and Tucker P:
Structural and functional profiling of the human histone
methyltransferase SMYD3. PLoS One. 6:e222902011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu S, Wu J, Sun B, Zhong C and Ding J:
Structural and biochemical studies of human lysine
methyltransferase Smyd3 reveal the important functional roles of
its post-SET and TPR domains and the regulation of its activity by
DNA binding. Nucleic acids Res. 39:4438–4449. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Van Aller GS, Reynoird N, Barbash O,
Huddleston M, Liu S, Zmoos AF, McDevitt P, Sinnamon R, Le B, Mas G,
et al: Smyd3 regulates cancer cell phenotypes and catalyzes histone
H4 lysine 5 methylation. Epigenetics. 7:340–343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hamamoto R, Furukawa Y, Morita M, Iimura
Y, Silva FP, Li M, Yagyu R and Nakamura Y: SMYD3 encodes a histone
methyltransferase involved in the proliferation of cancer cells.
Nat Cell Biol. 6:731–740. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hamamoto R, Silva FP, Tsuge M, Nishidate
T, Katagiri T, Nakamura Y and Furukawa Y: Enhanced SMYD3 expression
is essential for the growth of breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci.
97:113–118. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu C, Fang X, Ge Z, Jalink M, Kyo S,
Björkholm M, Gruber A, Sjöberg J and Xu D: The telomerase reverse
transcriptase (hTERT) gene is a direct target of the histone
methyltransferase SMYD3. Cancer Res. 67:2626–2631. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo N, Chen R, Li Z, Liu Y, Cheng D, Zhou
Q, Zhou J and Lin Q: Hepatitis C virus core upregulates the
methylation status of the RASSF1A promoter through regulation of
SMYD3 in hilar cholangiocarcinoma cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin.
43:354–361. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tsuge M, Hamamoto R, Silva FP, Ohnishi Y,
Chayama K, Kamatani N, Furukawa Y and Nakamura Y: A variable number
of tandem repeats polymorphism in an E2F-1 binding element in the
5′ flanking region of SMYD3 is a risk factor for human cancers. Nat
Genet. 37:1104–1107. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Luo XG, Ding Y, Zhou QF, Ye L, Wang SZ and
Xi T: SET and MYND domain-containing protein 3 decreases
sensitivity to dexamethasone and stimulates cell adhesion and
migration in NIH3T3 cells. J Biosci Bioeng. 103:444–450. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
AL-Eitan LN and Rababa'h DM: Correlation
between a variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) polymorphism in
SMYD3 gene and breast cancer: A genotype-phenotype study. Gene.
728:1442812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vieira FQ, Costa-Pinheiro P, Almeida-Rios
D, Graça I, Monteiro-Reis S, Simões-Sousa S, Carneiro I, Sousa EJ,
Godinho MI, Baltazar F, et al: SMYD3 contributes to a more
aggressive phenotype of prostate cancer and targets Cyclin D2
through H4K20me3. Oncotarget. 6:13644–13657. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zeng B, Li Z, Chen R, Guo N, Zhou J, Zhou
Q, Lin Q, Cheng D, Liao Q, Zheng L and Gong Y: Epigenetic
regulation of miR-124 by hepatitis C virus core protein promotes
migration and invasion of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells by
targeting SMYD3. FEBS Lett. 586:3271–3278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu Y, Zhu MX, Zhang XD, Xu XE, Wu ZY,
Liao LD, Li LY, Xie YM, Wu JY, Zou HY, et al: SMYD3 stimulates EZR
and LOXL2 transcription to enhance proliferation, migration, and
invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Hum Pathol.
52:153–163. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang SZ, Luo XG, Shen J, Zou JN, Lu YH and
Xi T: Knockdown of SMYD3 by RNA interference inhibits cervical
carcinoma cell growth and invasion in vitro. BMB Rep. 41:294–299.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang Y, Lyu T, Che X, Jia N, Li Q and
Feng W: Overexpression of SMYD3 in ovarian cancer is associated
with ovarian cancer proliferation and apoptosis via methylating
H3K4 and H4K20. J Cancer. 10:4072–4084. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu X, Xu Q, Chen P, Yu C, Ye L, Huang C
and Li T: Effect of SMYD3 on biological behavior and H3K4
methylation in bladder cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 11:8125–8133.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang L, Wang QT, Liu YP, Dong QQ, Hu HJ,
Miao Z, Li S, Liu Y, Zhou H, Zhang TC, et al: ATM signaling pathway
is implicated in the SMYD3-mediated proliferation and migration of
gastric cancer cells. J Gastric Cancer. 17:295–305. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Khatami F and Tavangar SM: Genetic and
epigenetic of medullary thyroid cancer. Iran Biomed J. 22:142–150.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sponziello M, Durante C, Boichard A, Dima
M, Puppin C, Verrienti A, Tamburrano G, Di Rocco G, Redler A,
Lacroix L, et al: Epigenetic-related gene expression profile in
medullary thyroid cancer revealed the overexpression of the histone
methyltransferases EZH2 and SMYD3 in aggressive tumours. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 392:8–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin F, Wu D, Fang D, Chen Y, Zhou H and Ou
C: STAT3-induced SMYD3 transcription enhances chronic lymphocytic
leukemia cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Inflamm Res. 68:739–749.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dai B, Wan W, Zhang P, Zhang Y, Pan C,
Meng G, Xiao X, Wu Z, Jia W, Zhang J and Zhang L: SET and MYND
domain-containing protein 3 is overexpressed in human glioma and
contributes to tumorigenicity. Oncol Rep. 34:2722–2730. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gan L, Yang Y, Li Q, Feng Y, Liu T and Guo
W: Epigenetic regulation of cancer progression by EZH2: From
biological insights to therapeutic potential. Biomark Res.
6:102018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim KH and Roberts CW: Targeting EZH2 in
cancer. Nat Med. 22:128–134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bae WK and Hennighausen L: Canonical and
non-canonical roles of the histone methyltransferase EZH2 in
mammary development and cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 382:593–597.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shen X, Liu Y, Hsu YJ, Fujiwara Y, Kim J,
Mao X, Yuan GC and Orkin SH: EZH1 mediates methylation on histone
H3 lysine 27 and complements EZH2 in maintaining stem cell identity
and executing pluripotency. Mol Cell. 32:491–502. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ezhkova E, Lien WH, Stokes N, Pasolli HA,
Silva JM and Fuchs E: EZH1 and EZH2 cogovern histone H3K27
trimethylation and are essential for hair follicle homeostasis and
wound repair. Genes Dev. 25:485–498. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pal B, Bouras T, Shi W, Vaillant F,
Sheridan JM, Fu N, Breslin K, Jiang K, Ritchie ME, Young M, et al:
Global changes in the mammary epigenome are induced by hormonal
cues and coordinated by Ezh2. Cell Rep. 3:411–426. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Laible G, Wolf A, Dorn R, Reuter G, Nislow
C, Lebersorger A, Popkin D, Pillus L and Jenuwein T: Mammalian
homologues of the Polycomb-group gene Enhancer of zeste mediate
gene silencing in Drosophila heterochromatin and at S. cerevisiae
telomeres. EMBO J. 16:3219–3232. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Masudo K, Suganuma N, Nakayama H, Oshima
T, Rino Y, Iwasaki H, Matsuzu K, Sugino K, Ito K, Kondo T, et al:
EZH2 overexpression as a useful prognostic marker for aggressive
Behaviour in thyroid cancer. In vivo. 32:25–31. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xue L, Yan H, Chen Y, Zhang Q, Xie X, Ding
X, Wang X, Qian Z, Xiao F, Song Z, et al: EZH2 upregulation by ERα
induces proliferation and migration of papillary thyroid carcinoma.
BMC cancer. 19:10942019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Andrusiewicz M, Slowikowski B, Skibinska
I, Wolun-Cholewa M and Dera-Szymanowska A: Selection of reliable
reference genes in eutopic and ectopic endometrium for quantitative
expression studies. Biomed Pharmacother. 78:66–73. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Haddad RI, Nasr C, Bischoff L, Busaidy NL,
Byrd D, Callender G, Dickson P, Duh QY, Ehya H, Goldner W, et al:
NCCN guidelines insights: Thyroid carcinoma, version 2.2018. J Natl
Compr Canc Netw. 16:1429–1440. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang LJ and Cai HQ: miR-1258: A novel
microRNA that controls TMPRSS4 expression is associated with
malignant progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endokrynol
Pol. 71:146–152. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou Q, Chen J, Feng J and Wang J: Long
noncoding RNA PVT1 modulates thyroid cancer cell proliferation by
recruiting EZH2 and regulating thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor
(TSHR). Tumour Biol. 37:3105–3113. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hossain MA, Asa TA, Rahman MM, Uddin S,
Moustafa AA, Quinn JMW and Moni MA: Network-based genetic profiling
reveals cellular pathway differences between follicular thyroid
carcinoma and follicular thyroid adenoma. Int J Environ Res Public
Health. 17:13732020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Fabini E, Manoni E, Ferroni C, Rio AD and
Bartolini M: Small-molecule inhibitors of lysine methyltransferases
SMYD2 and SMYD3: Current trends. Future Med Chem. 11:901–921. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Roman BR, Morris LG and Davies L: The
thyroid cancer epidemic, 2017 perspective. Curr Opin Endocrinol
Diabetes Obes. 24:332–336. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Al-Zahrani AS and Ravichandran K:
Epidemiology of thyroid cancer: A review with special reference to
Gulf cooperation council (GCC) states. Gulf J Oncolog. 17–28.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kinoshita Y, Takasu K, Yuri T, Yoshizawa
K, Emoto Y, Tsubura A and Shikata N: Estrogen receptor-and
progesterone receptor-positive diffuse sclerosing variant of
papillary thyroid carcinoma: A case report. Case Rep Oncol.
6:216–223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang Y, Dong W, Li J, Zhang H, Shan Z and
Teng W: Differential expression patterns and clinical significance
of estrogen receptor-alpha and beta in papillary thyroid carcinoma.
BMC cancer. 14:3832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lu J, Gao J, Zhang J, Sun J, Wu H, Shi X,
Teng L and Liang Z: Association between BRAF V600E mutation and
regional lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Int
J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:793–799. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|