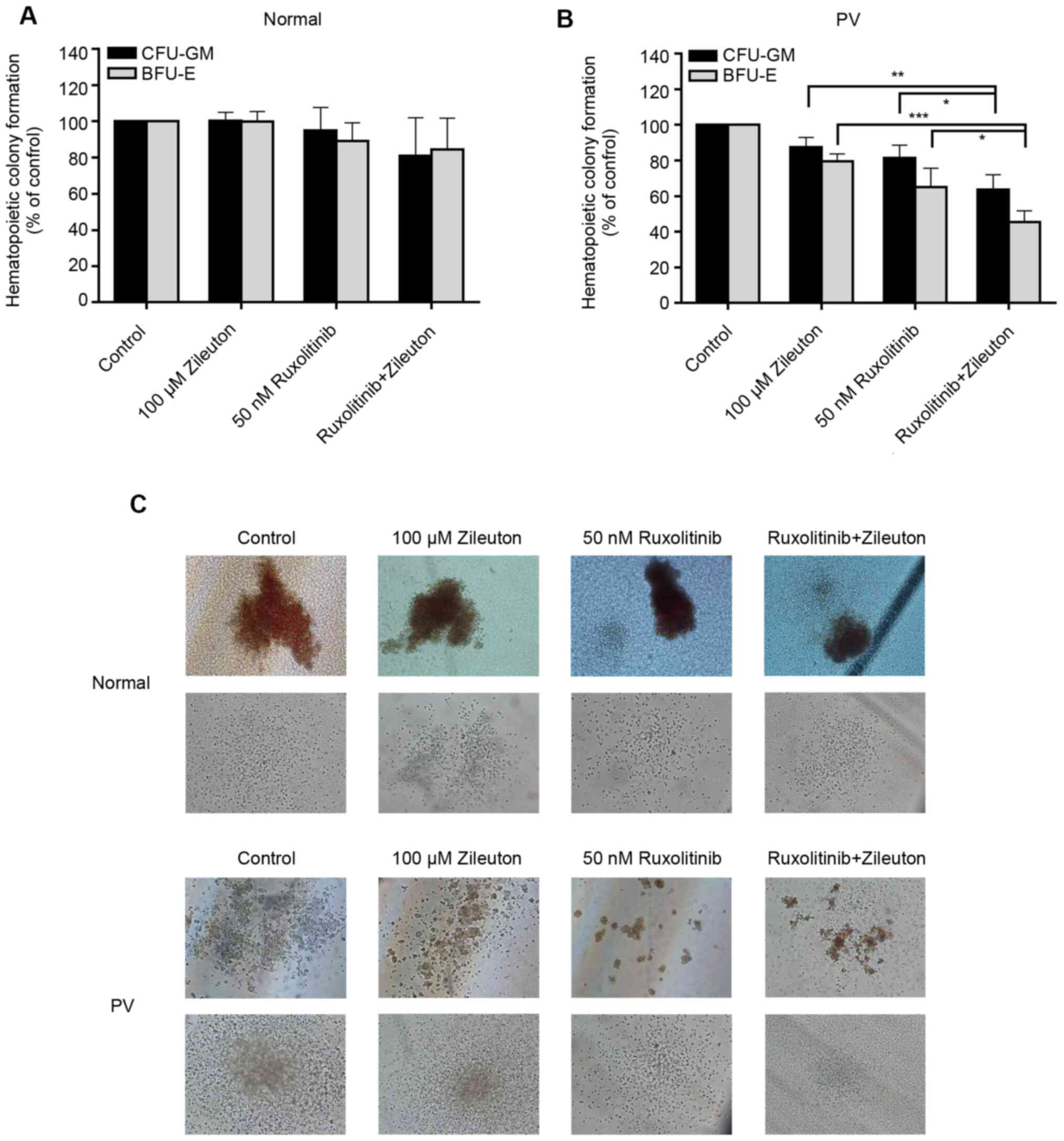
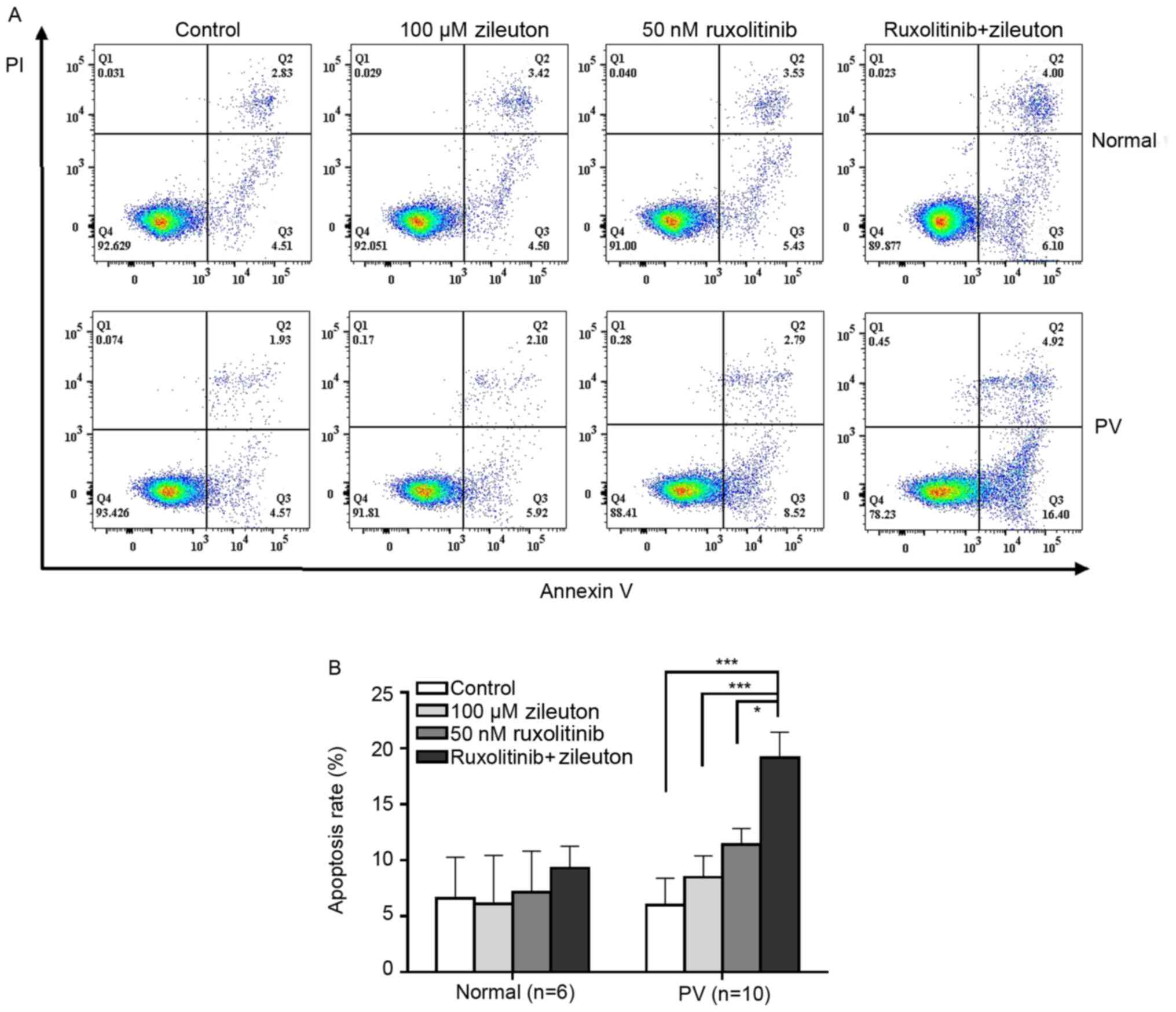
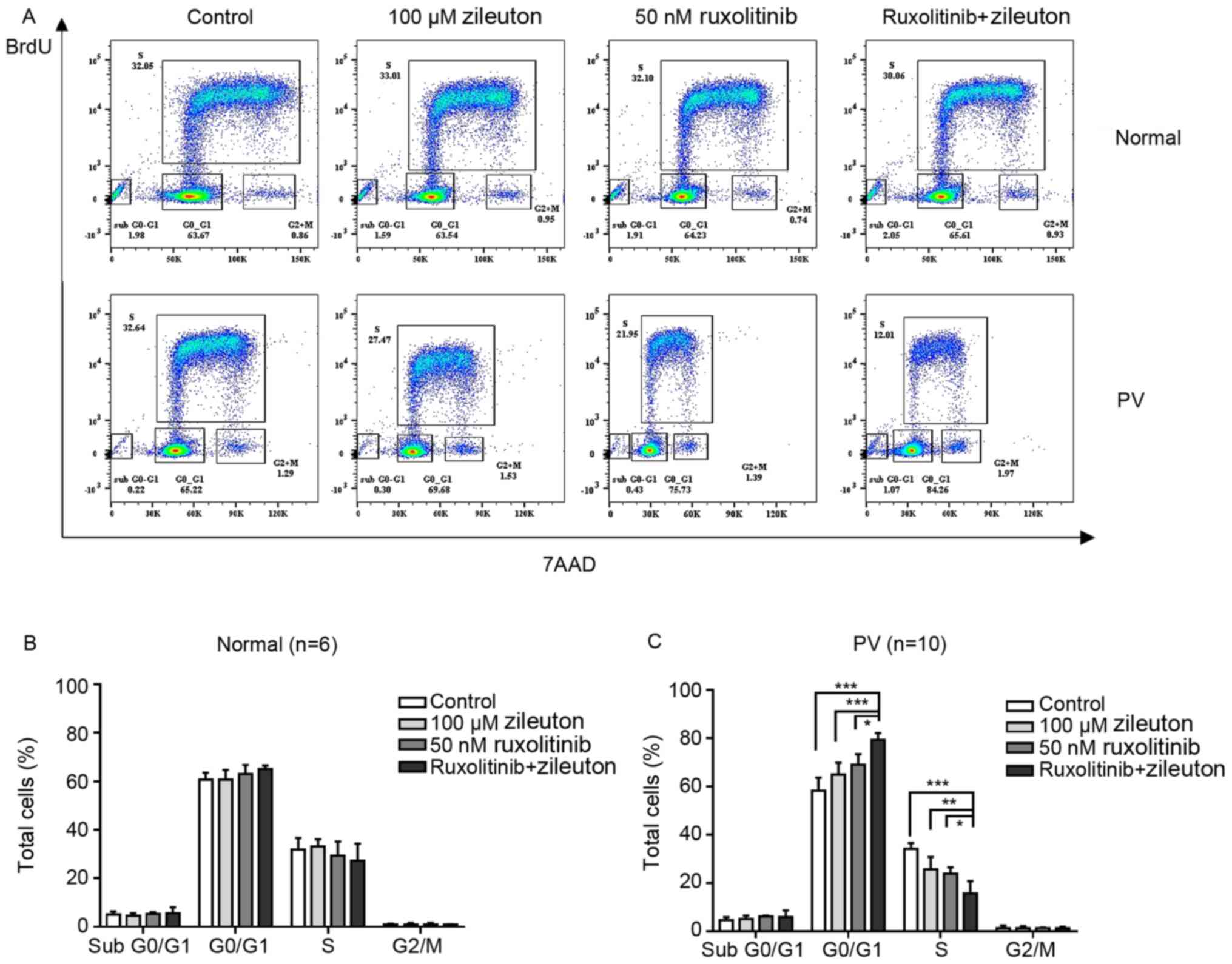
|
1
|
Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J,
Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, Bloomfield CD, Cazzola M and Vardiman JW:
The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification
of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 127:2391–2405.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, East C,
Fourouclas N, Swanton S, Vassiliou GS, Bench AJ, Boyd EM, Curtin N,
et al: Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human
myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 365:1054–1061. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
James C, Ugo V, Le Couédic JP, Staerk J,
Delhommeau F, Lacout C, Garçon L, Raslova H, Berger R,
Bennaceur-Griscelli A, et al: A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading
to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature.
434:1144–1148. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jones AV, Kreil S, Zoi K, Waghorn K,
Curtis C, Zhang L, Score J, Seear R, Chase AJ, Grand FH, et al:
Widespread occurrence of the JAK2 V617F mutation in chronic
myeloproliferative disorders. Blood. 106:2162–2168. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, Teo
SS, Tiedt R, Passweg JR, Tichelli A, Cazzola M and Skoda RC: A
gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders.
N Engl J Med. 352:1779–1790. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Deininger M, Radich J, Burn TC, Huber R
and Verstovsek S: The effect of long-term ruxolitinib treatment on
JAK2p.V617F allele burden in patients with myelofibrosis. Blood.
126:1551–1554. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cervantes F and Pereira A: Does
ruxolitinib prolong the survival of patients with myelofibrosis?
Blood. 129:832–837. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Needleman P, Turk J, Jakschik BA, Morrison
AR and Lefkowith JB: Arachidonic acid metabolism. Ann Rev Biochem.
55:69–102. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peters-Golden M and Henderson WR Jr:
Leukotrienes. N Engl J Med. 357:1841–1854. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pidgeon GP, Lysaght J, Krishnamoorthy S,
Reynolds JV, O'Byrne K, Nie D and Honn KV: Lipoxygenase metabolism:
Roles in tumor progression and survival. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:503–524. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang D and Dubois RN: Eicosanoids and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:181–193. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bishayee K and Khuda-Bukhsh AR:
5-lipoxygenase antagonist therapy: A new approach towards targeted
cancer chemotherapy. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
45:709–719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moore GY and Pidgeon GP: Cross-talk
between cancer cells and the tumour microenvironment: The role of
the 5-lipoxygenase pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 18:2362017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen Y, Shan Y, Lu M, DeSouza N, Guo Z,
Hoffman R, Liang A and Li S: Alox5 blockade eradicates
JAK2V617F-induced polycythemia Vera in mice. Cancer Res.
77:164–174. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mehta J, Wang H, Iqbal SU and Mesa R:
Epidemiology of myeloproliferative neoplasms in the United States.
Leuk Lymphoma. 55:595–600. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hoffman R, Prchal JT, Samuelson S, Ciurea
SO and Rondelli D: Philadelphia chromosome-negative
myeloproliferative disorders: Biology and treatment. Biol Blood
Marrow Transplant. 13 (Suppl 1):S64–S72. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mascarenhas J: A concise update on risk
factors, therapy, and outcome of leukemic transformation of
myeloproliferative neoplasms. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 16
(Suppl):S124–S129. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Silvennoinen O and Hubbard SR: Molecular
insights into regulation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Blood. 125:3388–3392. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, Ebert BL,
Wernig G, Huntly BJ, Boggon TJ, Wlodarska I, Clark JJ, Moore S, et
al: Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia
Vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with
myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell. 7:387–397. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Verstovsek S, Mesa RA, Gotlib J, Levy RS,
Gupta V, DiPersio JF, Catalano JV, Deininger M, Miller C, Silver
RT, et al: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ruxolitinib
for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med. 366:799–807. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hasselbalch HC and Bjørn ME: Ruxolitinib
versus standard therapy for the treatment of polycythemia Vera. N
Engl J Med. 372:16702015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pardanani A, Harrison C, Cortes JE,
Cervantes F, Mesa RA, Milligan D, Masszi T, Mishchenko E, Jourdan
E, Vannucchi AM, et al: Safety and efficacy of fedratinib in
patients with primary or secondary myelofibrosis: A randomized
clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 1:643–651. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kiladjian J, Verstovsek S, Griesshammer M,
Masszi T, Durrant S, Passamonti F, Harrison CN, Pane F, Zachee P,
Kirito K, et al: Results from the 208-week (4-year) Follow-up of
RESPONSE Trial, a Phase 3 study comparing ruxolitinib (Rux) with
best available therapy (BAT) for the treatment of polycythemia Vera
(PV). Blood. 130 (Suppl 1):S3222017.
|
|
25
|
Verstovsek S, Gotlib J, Mesa RA, Vannucchi
AM, Kiladjian JJ, Cervantes F, Harrison CN, Paquette R, Sun W, Naim
A, et al: Long-term survival in patients treated with ruxolitinib
for myelofibrosis: COMFORT-I and -II pooled analyses. J Hematol
Oncol. 10:1562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Harrison CN, Vannucchi AM, Kiladjian JJ,
Al-Ali HK, Gisslinger H, Knoops L, Cervantes F, Jones MM, Sun K,
McQuitty M, et al: Long-term findings from COMFORT-II, a phase 3
study of ruxolitinib vs. best available therapy for myelofibrosis.
Leukemia. 31:7752016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Verstovsek S, Mesa RA, Gotlib J, Gupta V,
DiPersio JF, Catalano JV, Deininger MW, Miller CB, Silver RT,
Talpaz M, et al: Long-term treatment with ruxolitinib for patients
with myelofibrosis: 5-year update from the randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 COMFORT-I trial. J
Hematol Oncol. 10:552017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Harrison C, Kiladjian JJ, Al-Ali HK,
Gisslinger H, Waltzman R, Stalbovskaya V, McQuitty M, Hunter DS,
Levy R, Knoops L, et al: JAK inhibition with ruxolitinib versus
best available therapy for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med.
366:787–798. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Avis I, Hong SH, Martínez A, Moody T, Choi
YH, Trepel J, Das R, Jett M and Mulshine JL: Five-lipoxygenase
inhibitors can mediate apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines
through complex eicosanoid interactions. FASEB J. 15:2007–2009.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Melstrom LG, Bentrem DJ, Salabat MR,
Kennedy TJ, Ding XZ, Strouch M, Rao SM, Witt RC, Ternent CA,
Talamonti MS, et al: Overexpression of 5-lipoxygenase in colon
polyps and cancer and the effect of 5-LOX inhibitors in vitro and
in a murine model. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6525–6530. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hennig R, Ding XZ, Tong WG, Schneider MB,
Standop J, Friess H, Büchler MW, Pour PM and Adrian TE:
5-Lipoxygenase and leukotriene B(4) receptor are expressed in human
pancreatic cancers but not in pancreatic ducts in normal tissue. Am
J Pathol. 161:421–428. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hoque A, Lippman SM, Wu TT, Xu Y, Liang
ZD, Swisher S, Zhang H, Cao L, Ajani JA and Xu XC: Increased
5-lipoxygenase expression and induction of apoptosis by its
inhibitors in esophageal cancer: A potential target for prevention.
Carcinogenesis. 26:785–791. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Matsuyama M, Yoshimura R, Mitsuhashi M,
Hase T, Tsuchida K, Takemoto Y, Kawahito Y, Sano H and Nakatani T:
Expression of lipoxygenase in human prostate cancer and growth
reduction by its inhibitors. Int J Oncol. 24:821–827.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hyde CA and Missailidis S: Inhibition of
arachidonic acid metabolism and its implication on cell
proliferation and tumour-angiogenesis. Int Immunopharmacol.
9:701–715. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ding XZ, Iversen P, Cluck MW, Knezetic JA
and Adrian TE: Lipoxygenase inhibitors abolish proliferation of
human pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
261:218–223. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wen Z, Liu H, Li M, Li B, Gao W, Shao Q,
Fan B, Zhao F, Wang Q, Xie Q, et al: Increased metabolites of
5-lipoxygenase from hypoxic ovarian cancer cells promote
tumor-associated macrophage infiltration. Oncogene. 34:1241–1252.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hassan S and Carraway RE: Involvement of
arachidonic acid metabolism and EGF receptor in neurotensin-induced
prostate cancer PC3 cell growth. Regul Pept. 133:105–114. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Karlage KL, Mogalian E, Jensen A and
Myrdal PB: Inhalation of an ethanol-based zileuton formulation
provides a reduction of pulmonary adenomas in the A/J mouse model.
AAPS PharmSciTech. 11:168–173. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Romano M, Catalano A, Nutini M, D'Urbano
E, Crescenzi C, Claria J, Libner R, Davi G and Procopio A:
5-Lipoxygenase regulates malignant mesothelial cell survival:
Involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor. FASEB J.
15:2326–2336. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ye YN, Wu WK, Shin VY, Bruce IC, Wong BC
and Cho CH: Dual inhibition of 5-LOX and COX-2 suppresses colon
cancer formation promoted by cigarette smoke. Carcinogenesis.
26:827–834. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Levental KR, Yu H, Kass L, Lakins JN,
Egeblad M, Erler JT, Fong SF, Csiszar K, Giaccia A, Weninger W, et
al: Matrix crosslinking forces tumor progression by enhancing
integrin signaling. Cell. 139:891–906. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Cox TR, Lang G,
Bird D, Koong A, Le QT and Giaccia AJ: Hypoxia-induced lysyl
oxidase is a critical mediator of bone marrow cell recruitment to
form the premetastatic niche. Cancer Cell. 15:35–44. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kirschmann DA, Seftor EA, Fong SF, Nieva
DR, Sullivan CM, Edwards EM, Sommer P, Csiszar K and Hendrix MJ: A
molecular role for lysyl oxidase in breast cancer invasion. Cancer
Res. 62:4478–4483. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Graham SM, Vass JK, Holyoake TL and Graham
GJ: Transcriptional analysis of quiescent and proliferating CD34+
human hemopoietic cells from normal and chronic myeloid leukemia
sources. Stem Cells. 25:3111–3120. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Roos J, Oancea C, Heinssmann M, Khan D,
Held H, Kahnt AS, Capelo R, La Buscato E, Proschak E, Puccetti E,
et al: 5-Lipoxygenase is a candidate target for therapeutic
management of stem cell-like cells in acute myeloid leukemia.
Cancer Res. 74:5244–5255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen Y, Hu Y, Zhang H, Peng C and Li S:
Loss of the Alox5 gene impairs leukemia stem cells and prevents
chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet. 41:783–792. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ruiz-Herguido C, Guiu J, D'Altri T,
Inglés-Esteve J, Dzierzak E, Espinosa L and Bigas A: Hematopoietic
stem cell development requires transient Wnt/β-catenin activity. J
Exp Med. 209:1457–1468. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hu Y, Chen Y, Douglas L and Li S:
Beta-catenin is essential for survival of leukemic stem cells
insensitive to kinase inhibition in mice with BCR-ABL-induced
chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 23:109–116. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhao C, Blum J, Chen A, Kwon HY, Jung SH,
Cook JM, Lagoo A and Reya T: Loss of beta-catenin impairs the
renewal of normal and CML stem cells in vivo. Cancer Cell.
12:528–541. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Heidel FH, Bullinger L, Feng Z, Wang Z,
Neff TA, Stein L, Kalaitzidis D, Lane SW and Armstrong SA: Genetic
and pharmacologic inhibition of beta-catenin targets
imatinib-resistant leukemia stem cells in CML. Cell Stem Cell.
10:412–424. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lucas CM, Harris RJ, Giannoudis A,
Mcdonald E and Clark RE: Low leukotriene B4 receptor 1 leads to
ALOX5 downregulation at diagnosis of chronic myeloid leukemia.
Haematologica. 99:1710–1715. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dolinska M, Piccini A, Wong WM, Gelali E,
Johansson AS, Klang J, Xiao P, Yektaei-Karin E, Strömberg UO,
Mustjoki S, et al: Leukotriene signaling via ALOX5 and cysteinyl
leukotriene receptor 1 is dispensable for in vitro growth of
CD34+ CD38− stem and progenitor cells in
chronic myeloid leukemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 490:378–384.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|