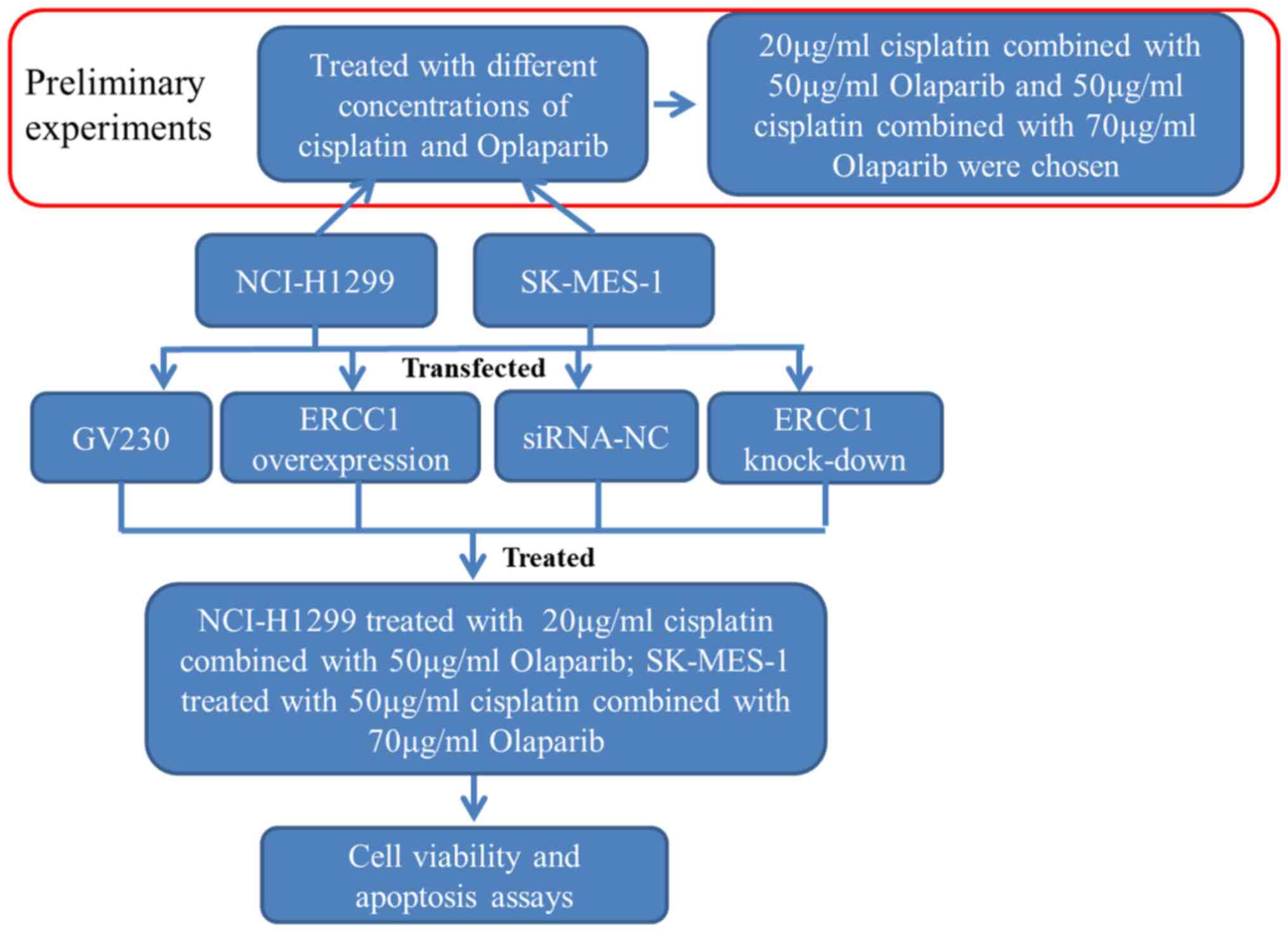
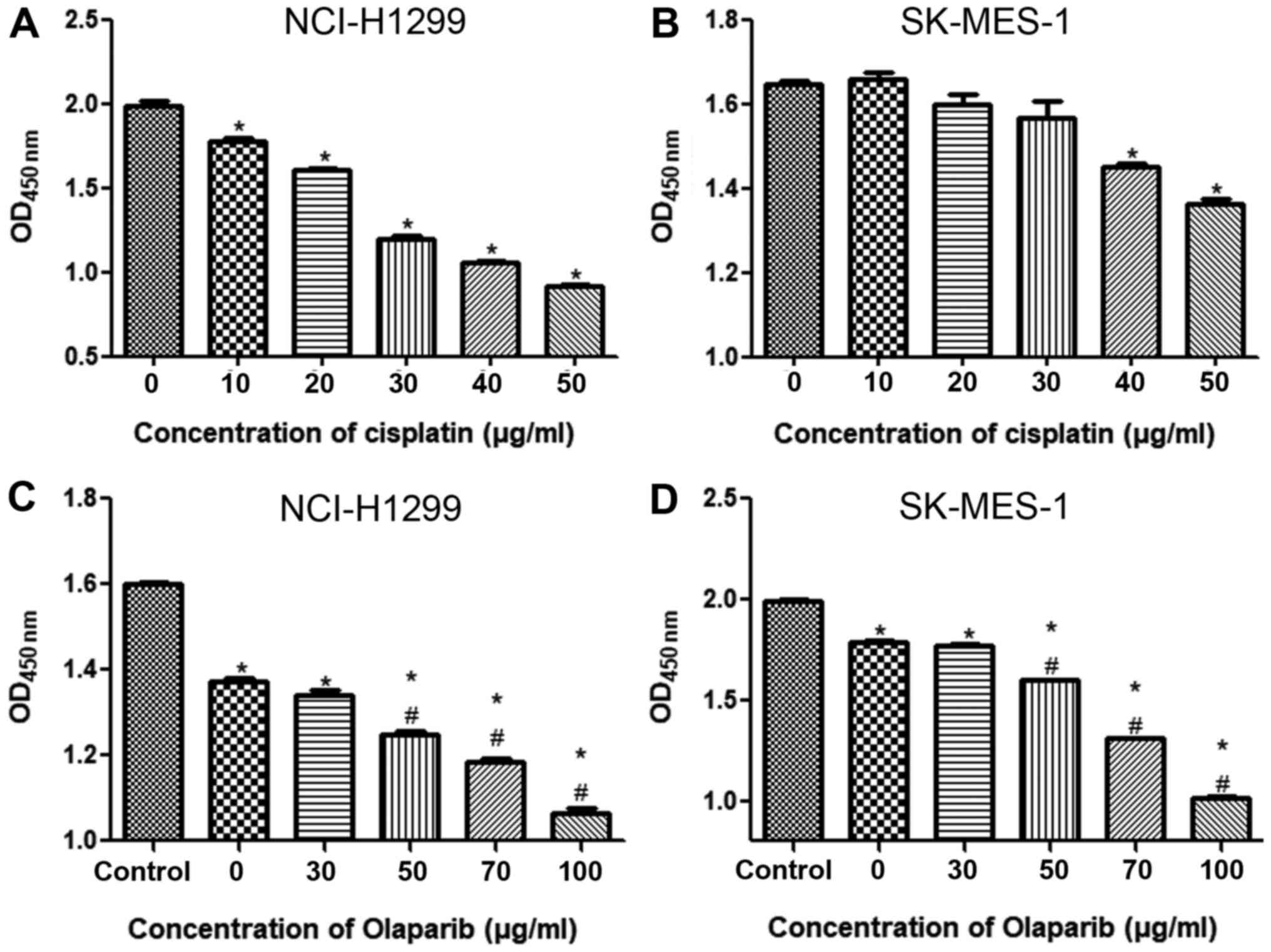
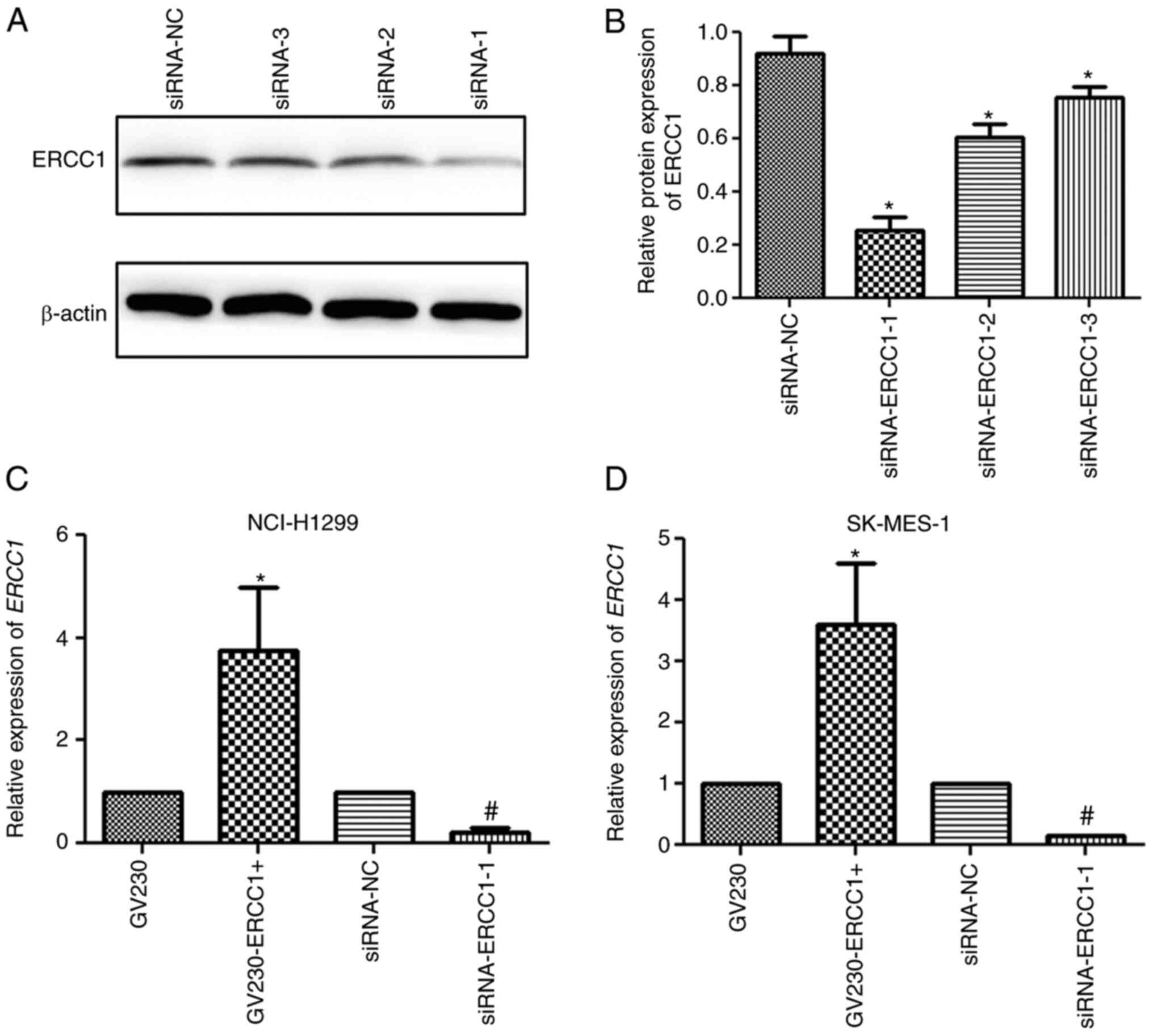
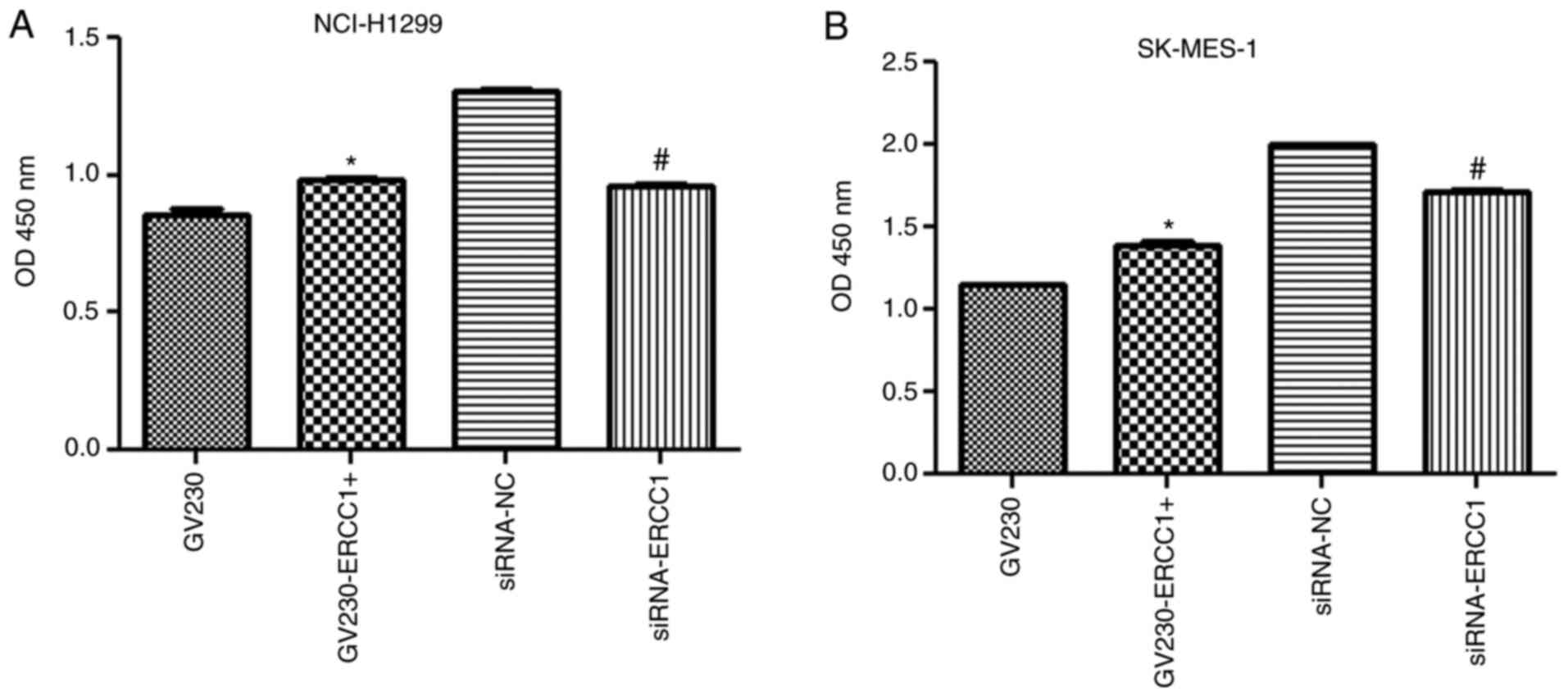
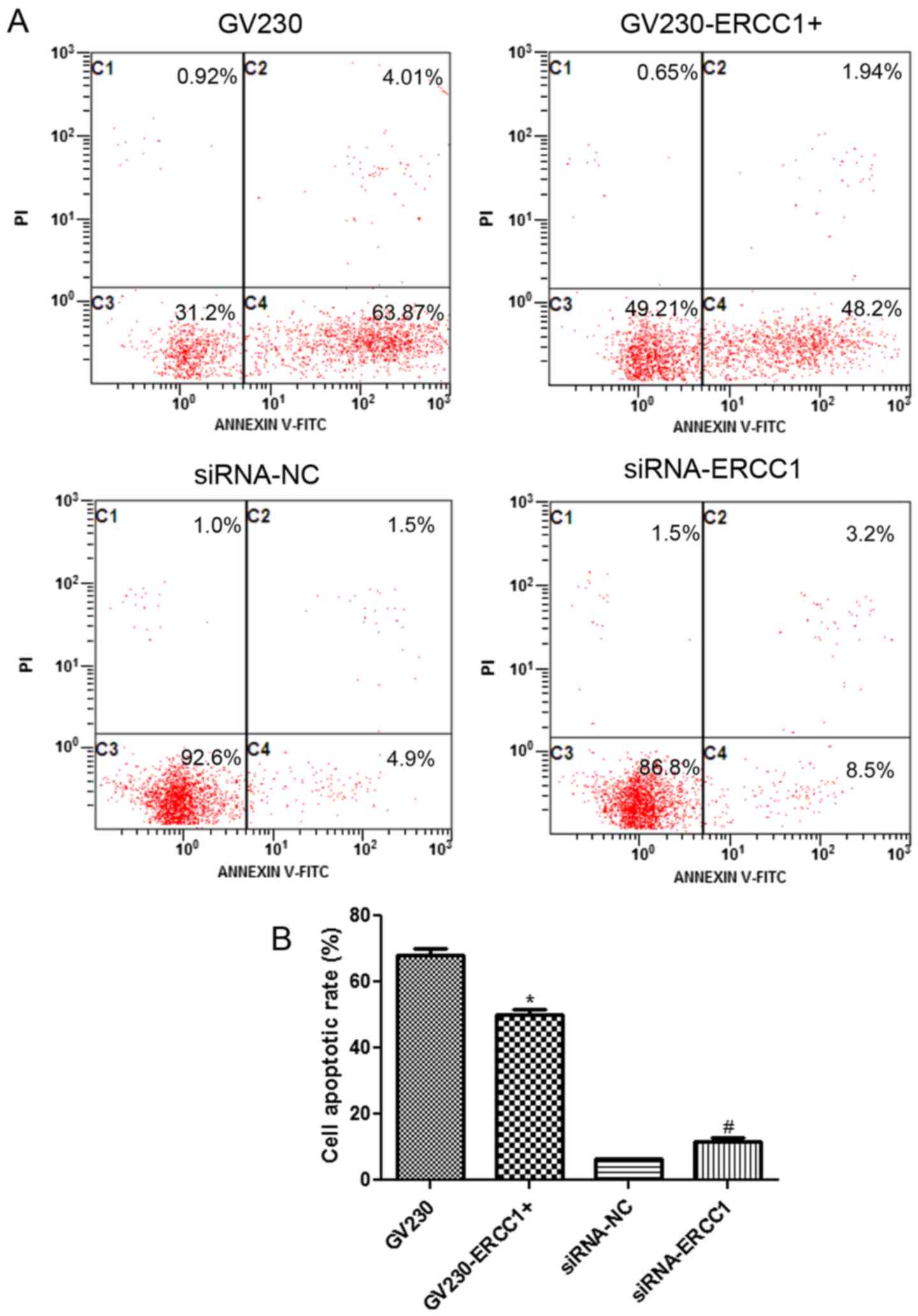
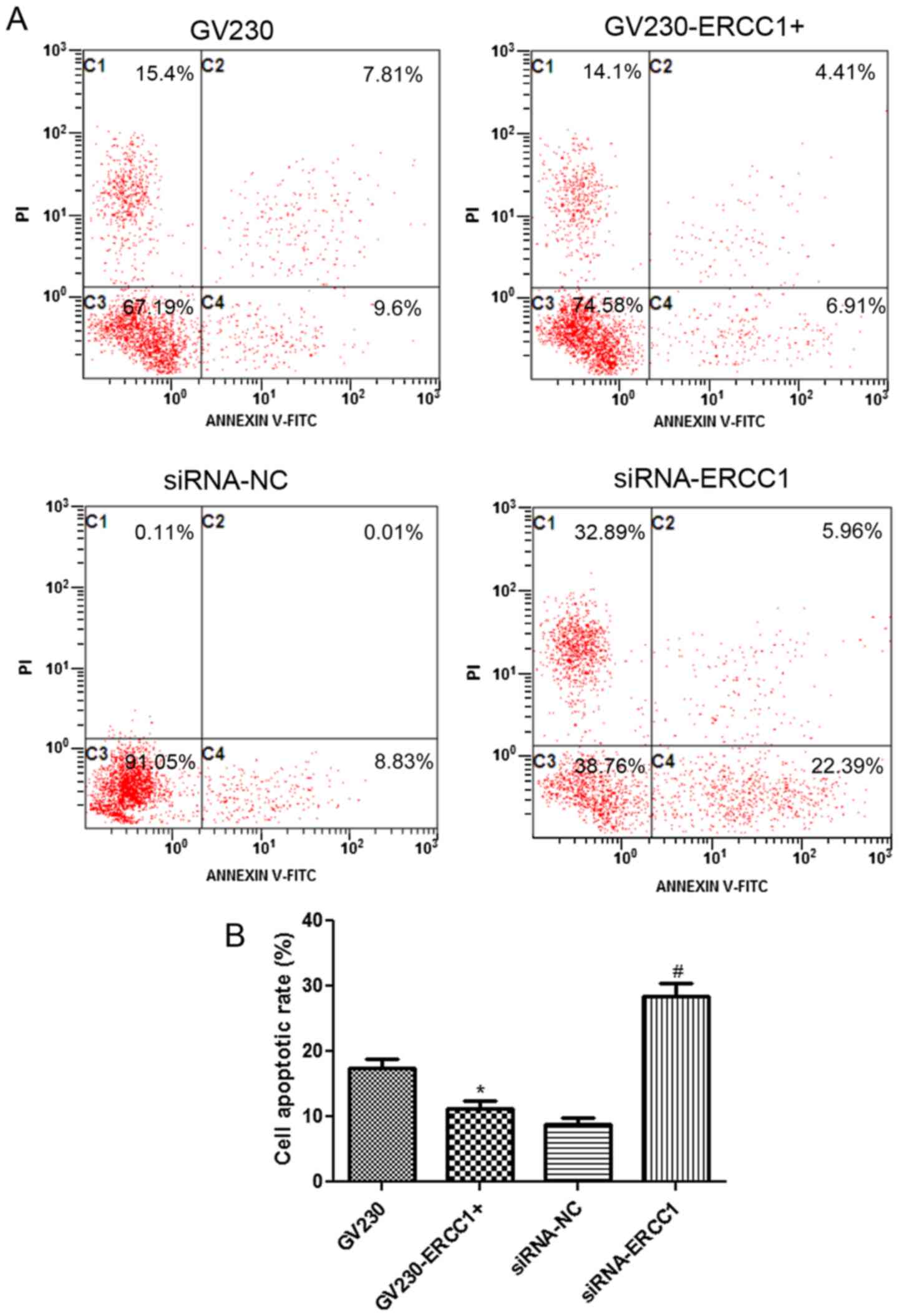
|
1
|
Bade BC and Dela Cruz CS: Lung Cancer
2020: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Prevention. Clin Chest Med.
41:1–24. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ardizzoni A, Boni L, Tiseo M, Fossella FV,
Schiller JH, Paesmans M, Radosavljevic D, Paccagnella A, Zatloukal
P, Mazzanti P, et al CISCA (CISplatin versus CArboplatin)
Meta-analysis Group, : Cisplatin- versus carboplatin-based
chemotherapy in first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell
lung cancer: An individual patient data meta-analysis. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 99:847–857. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yin JY, Huang Q, Zhao YC, Zhou HH and Liu
ZQ: Meta-analysis on pharmacogenetics of platinum-based
chemotherapy in non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. PLoS
One. 7:e381502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jassem J, Skokowski J, Dziadziuszko R,
Jassem E, Szymanowska A, Rzyman W and Roszkiewicz A: Results of
surgical treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: Validation of the
new postoperative pathologic TNM classification. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 119:1141–1146. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Choi J, Oh JY, Lee YS, Min KH, Shim JJ,
Choi SI, Park DW, Park CK, Kang EJ, Yong HS, et al: Clinical
efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy in stage IB (<4 cm) non-small
cell lung cancer patients with high-risk factors. Korean J Intern
Med. Aug 21–2020.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.3904/kjim.2020.011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Martin LP, Hamilton TC and Schilder RJ:
Platinum resistance: he role of DNA repair pathways. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:1291–1295. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Damia G and Broggini M: Platinum
resistance in ovarian cancer: Role of DNA repair. Cancers (Basel).
11:112019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lazic A, Popović J, Paunesku T, Woloschak
GE and Stevanović M: Insights into platinum-induced peripheral
neuropathy-current perspective. Neural Regen Res. 15:1623–1630.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang D and Lippard SJ: Cellular processing
of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 4:307–320. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kirschner K and Melton DW: Multiple roles
of the ERCC1-XPF endonuclease in DNA repair and resistance to
anticancer drugs. Anticancer Res. 30:3223–3232. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Selvakumaran M, Pisarcik DA, Bao R, Yeung
AT and Hamilton TC: Enhanced cisplatin cytotoxicity by disturbing
the nucleotide excision repair pathway in ovarian cancer cell
lines. Cancer Res. 63:1311–1316. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen S, Zhang J, Wang R, Luo X and Chen H:
The platinum-based treatments for advanced non-small cell lung
cancer, is low/negative ERCC1 expression better than high/positive
ERCC1 expression? A meta-analysis. Lung Cancer. 70:63–70. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu G and Lippard SJ: Photoaffinity
labeling reveals nuclear proteins that uniquely recognize
cisplatin-DNA interstrand cross-links. Biochemistry. 48:4916–4925.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gandhi L, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S,
Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, Domine M, Clingan P, Hochmair MJ,
Powell SF, et al KEYNOTE-189 investigators, : Pembrolizumab plus
chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J
Med. 378:2078–2092. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Le DT, Uram JN, Wang H, Bartlett BR,
Kemberling H, Eyring AD, Skora AD, Luber BS, Azad NS, Laheru D, et
al: PD-1 blockade in tumors with mismatch-repair deficiency. N Engl
J Med. 372:2509–2520. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Robson M, Im SA, Senkus E, Xu B, Domchek
SM, Masuda N, Delaloge S, Li W, Tung N, Armstrong A, et al:
Olaparib for metastatic breast cancer in patients with a germline
BRCA mutation. N Engl J Med. 377:523–533. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sahoo S, Meijles DN, Al Ghouleh I, Tandon
M, Cifuentes-Pagano E, Sembrat J, Rojas M, Goncharova E and Pagano
PJ: MEF2C-MYOCD and leiomodin1 suppression by miRNA-214 promotes
smooth muscle cell phenotype switching inpulmonary arterial
Hypertension. PLoS One. 11:e01537802016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Patel AJ, Richter A, Drayson MT and
Middleton GW: The role of B lymphocytes in the immuno-biology of
non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 69:325–342.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ferrara MG, Di Noia V, D'Argento E, Vita
E, Damiano P, Cannella A, Ribelli M, Pilotto S, Milella M, Tortora
G, et al: Oncogene-addicted non-small-cell lung cancer: Treatment
opportunities and future perspectives. Cancers (Basel). 12:122020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhou J, Kang Y, Chen L, Wang H, Liu J,
Zeng S and Yu L: The drug-resistance mechanisms of five
platinum-based antitumor agents. Front Pharmacol. 11:3432020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mesquita KA, Alabdullah M, Griffin M, Toss
MS, Fatah TM, Alblihy A, Moseley P, Chan SY, Rakha EA and
Madhusudan S: ERCC1-XPF deficiency is a predictor of olaparib
induced synthetic lethality and platinum sensitivity in epithelial
ovarian cancers. Gynecol Oncol. 153:416–424. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Postel-Vinay S and Soria JC: ERCC1 as
predictor of platinum benefit in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 35:384–386. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oza AM, Cibula D, Benzaquen AO, Poole C,
Mathijssen RH, Sonke GS, Colombo N, Špaček J, Vuylsteke P, Hirte H,
et al: Olaparib combined with chemotherapy for recurrent
platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer: A randomised phase 2 trial.
Lancet Oncol. 16:87–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ledermann JA and Pujade-Lauraine E:
Olaparib as maintenance treatment for patients with
platinum-sensitive relapsed ovarian cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol. May
22–2019.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1177/1758835919849753.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Johnson N, Li YC, Walton ZE, Cheng KA, Li
D, Rodig SJ, Moreau LA, Unitt C, Bronson RT, Thomas HD, et al:
Compromised CDK1 activity sensitizes BRCA-proficient cancers to
PARP inhibition. Nat Med. 17:875–882. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vilar E, Bartnik CM, Stenzel SL, Raskin L,
Ahn J, Moreno V, Mukherjee B, Iniesta MD, Morgan MA, Rennert G, et
al: MRE11 deficiency increases sensitivity to poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase inhibition in microsatellite unstable colorectal
cancers. Cancer Res. 71:2632–2642. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Weil MK and Chen AP: PARP inhibitor
treatment in ovarian and breast cancer. Curr Probl Cancer. 35:7–50.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xie KJ, He HE, Sun AJ, Liu XB, Sun LP and
Dong XJ: Expression of ERCC1, MSH2 and PARP1 in non-small cell lung
cancer and prognostic value in patients treated with platinum-based
chemotherapy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:2591–2596. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Roos WP and Kaina B: DNA damage-induced
cell death: From specific DNA lesions to the DNA damage response
and apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 332:237–248. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pierceall WE, Olaussen KA, Rousseau V,
Brambilla E, Sprott KM, Andre F, Pignon JP, Le Chevalier T, Pirker
R, Jiang C, et al: Cisplatin benefit is predicted by
immunohistochemical analysis of DNA repair proteins in squamous
cell carcinoma but not adenocarcinoma: Theranostic modeling by
NSCLC constituent histological subclasses. Ann Oncol. 23:2245–2252.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guo ZP, Hu YC, Xie Y, Jin F, Song ZQ, Liu
XD, Ma T and Zhou PK: MLN4924 suppresses the BRCA1 complex and
synergizes with PARP inhibition in NSCLC cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 483:223–229. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Paul I, Savage KI, Blayney JK, Lamers E,
Gately K, Kerr K, Sheaff M, Arthur K, Richard DJ, Hamilton PW, et
al: PARP inhibition induces BAX/BAK-independent synthetic lethality
of BRCA1-deficient non-small cell lung cancer. J Pathol.
224:564–574. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|