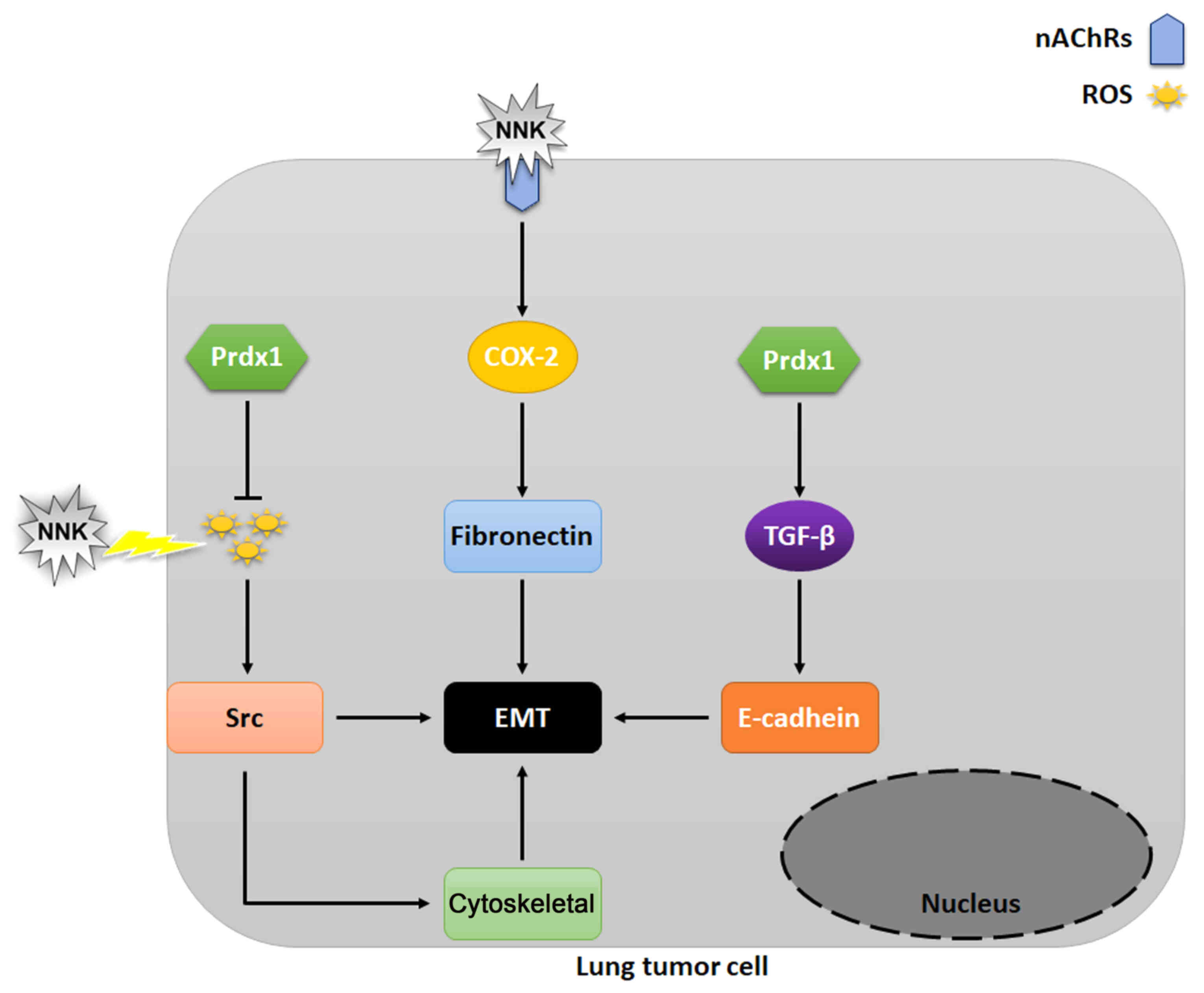
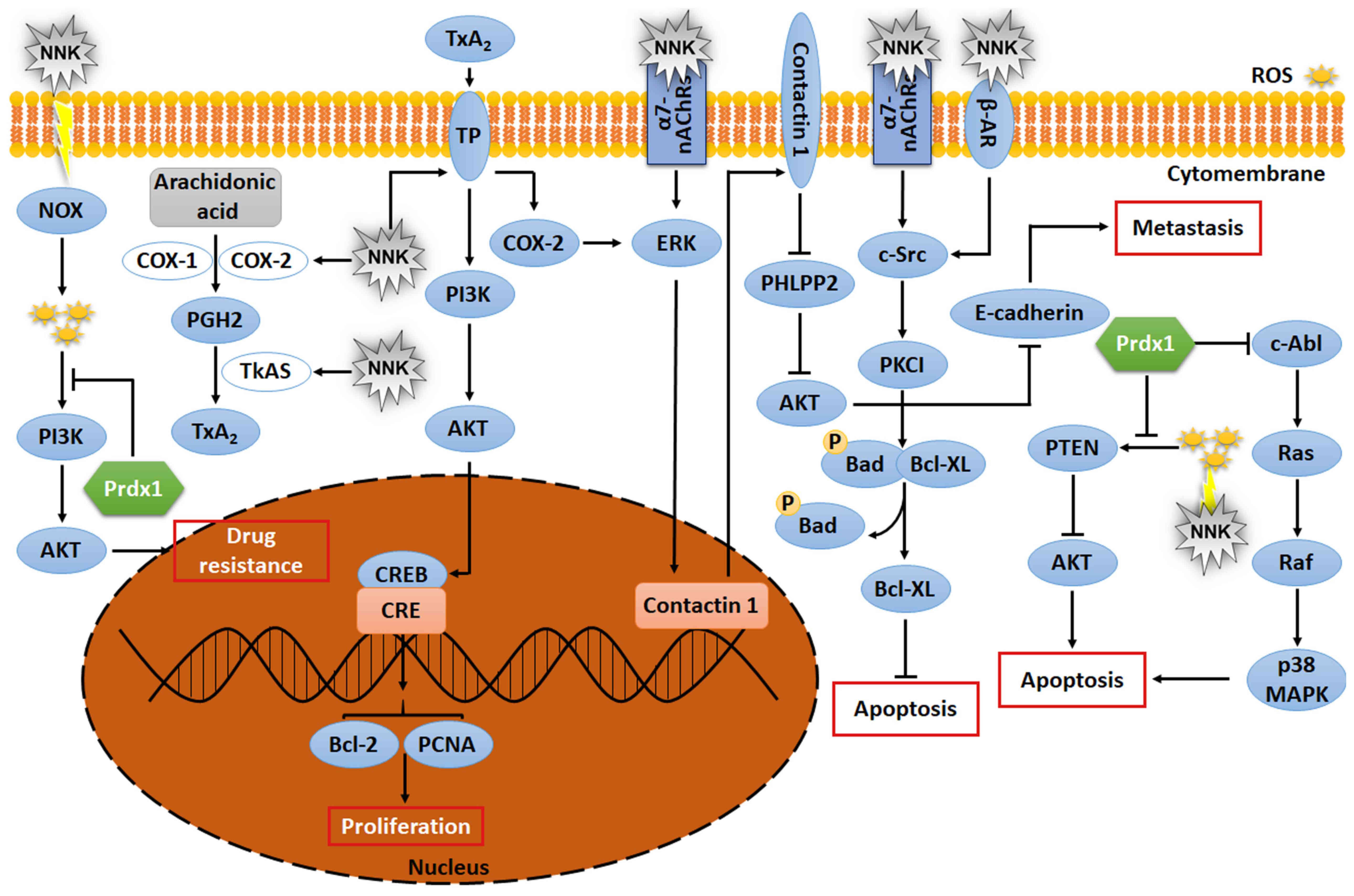
|
1
|
Proctor RN: Tobacco and the global lung
cancer epidemic. Nat Rev Cancer. 1:82–86. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thun M, Peto R, Boreham J and Lopez AD:
Stages of the cigarette epidemic on entering its second century.
Tob Control. 21:96–101. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
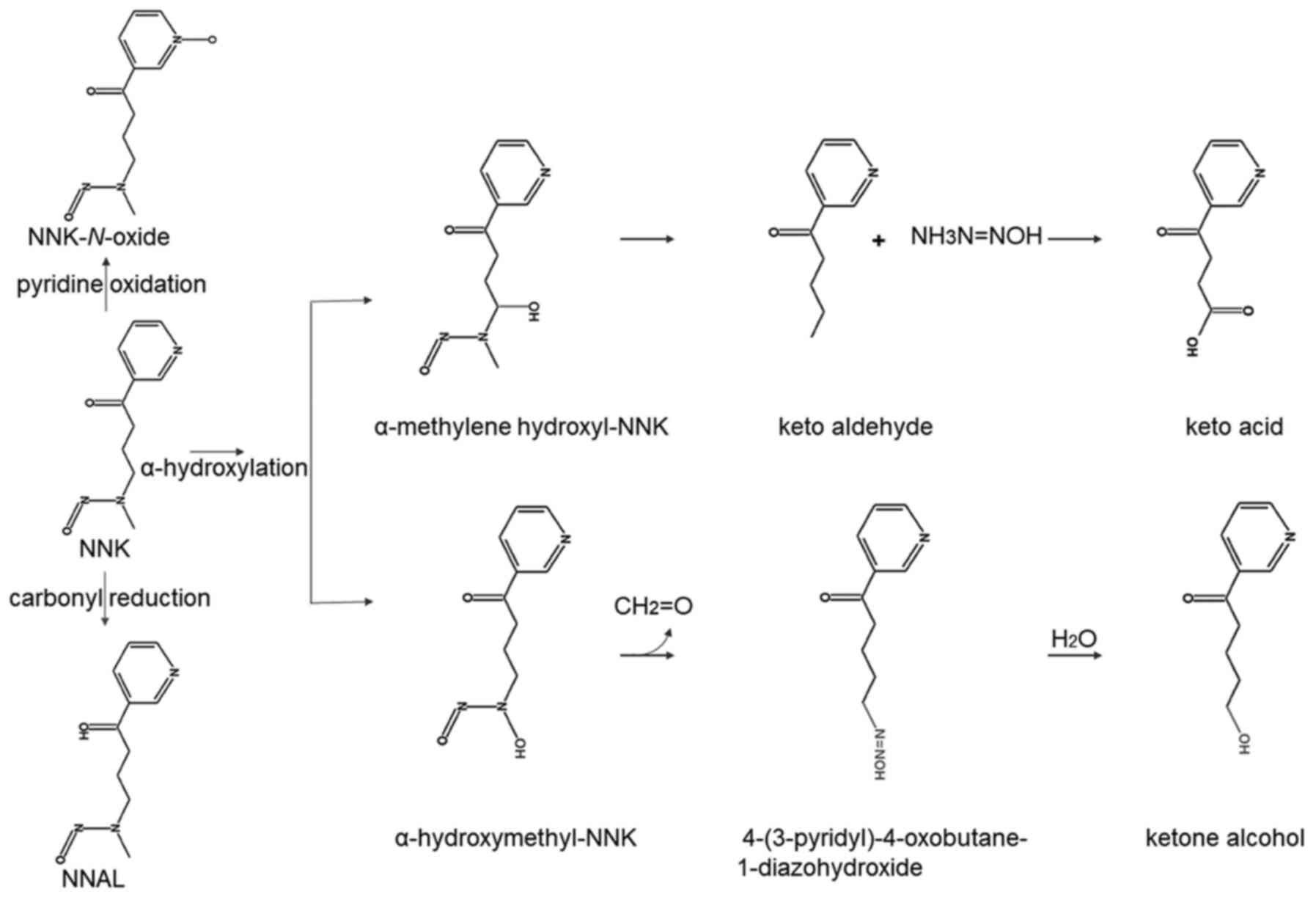
4
|
Witschi H: Carcinogenic activity of
cigarette smoke gas phase and its modulation by beta-carotene and
N-acetylcysteine. Toxicol Sci. 84:81–87. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
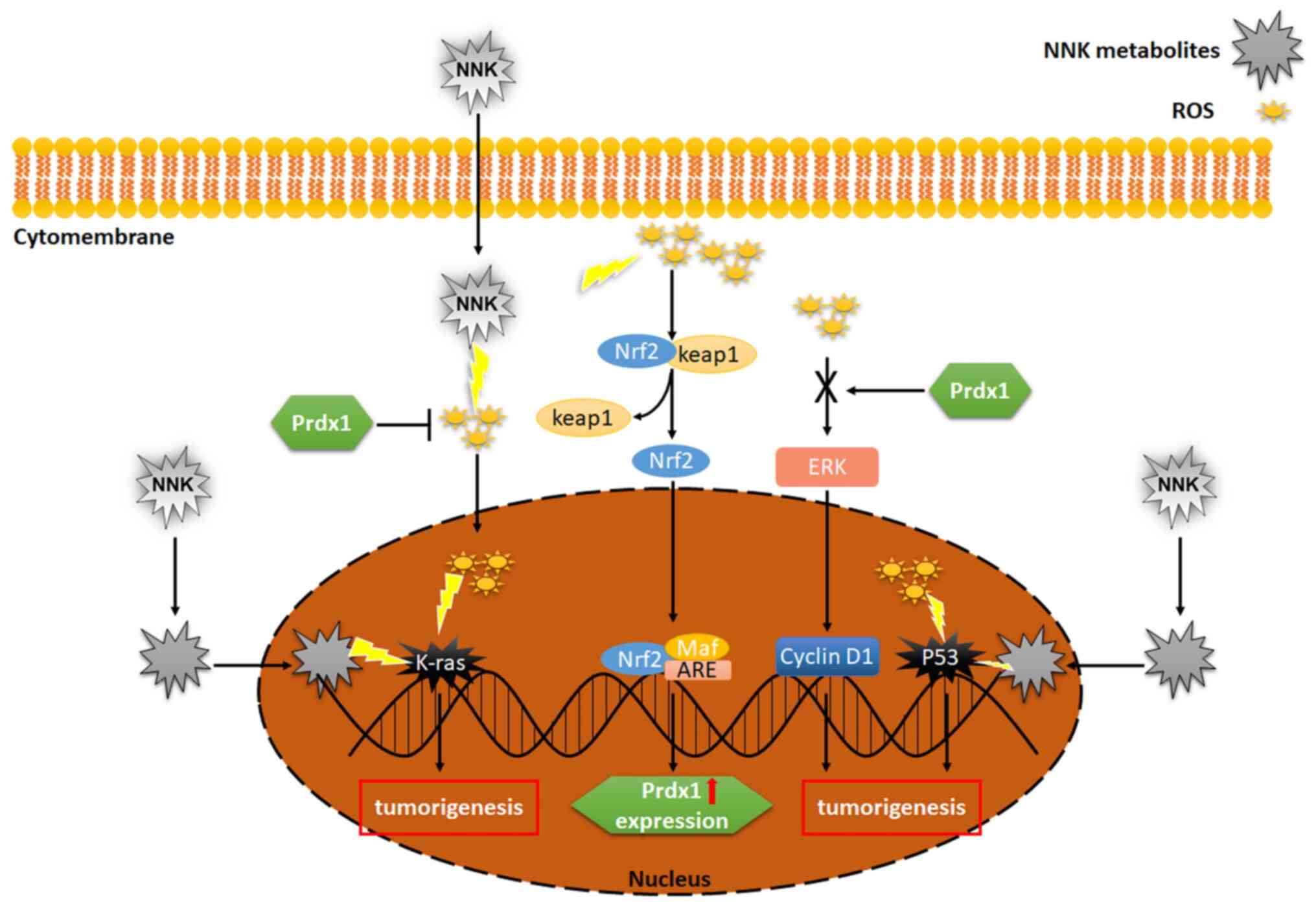
|
5
|
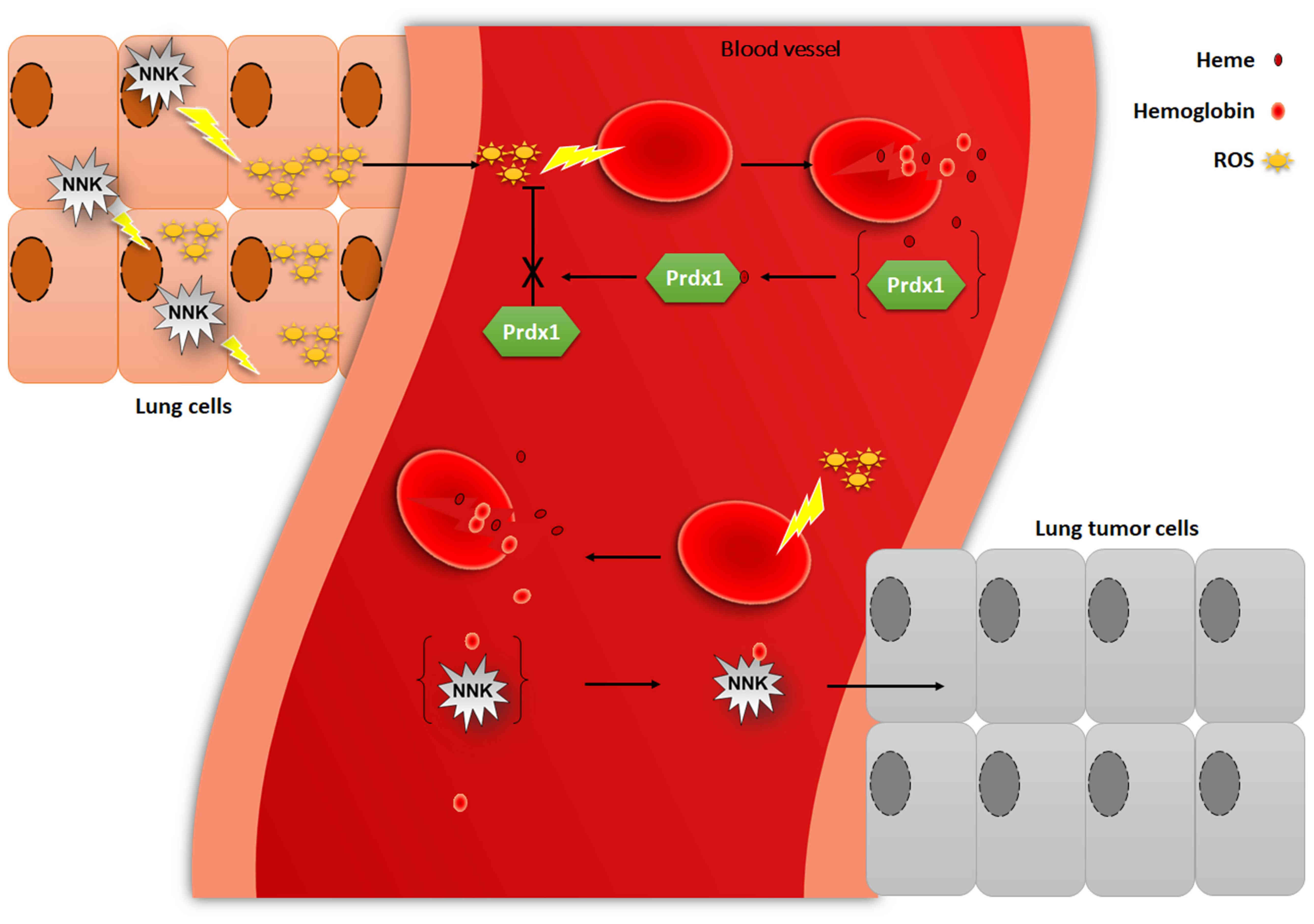
Jin Z, Gao F, Flagg T and Deng X:
Tobacco-specific nitrosamine
4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone promotes functional
cooperation of Bcl2 and c-Myc through phosphorylation in regulating
cell survival and proliferation. J Biol Chem. 279:40209–40219.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maser E: Significance of reductases in the
detoxification of the tobacco-specific carcinogen NNK. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 25:235–237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yalcin E and de la Monte S: Tobacco
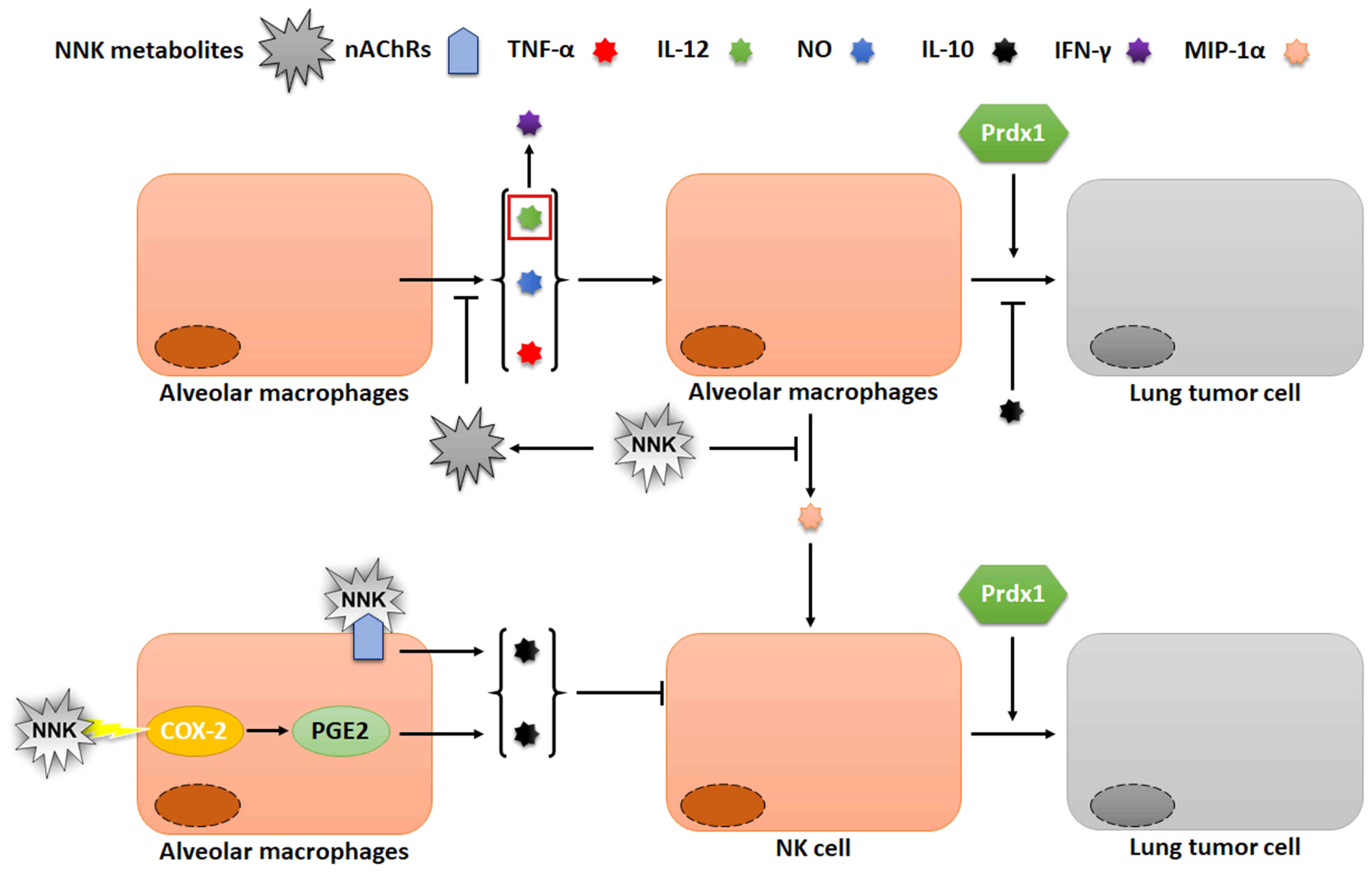
nitrosamines as culprits in disease: Mechanisms reviewed. J Physiol
Biochem. 72:107–120. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yeh SL, Wang WY, Huang CS and Hu ML:
Flavonoids suppresses the enhancing effect of beta-carotene on DNA
damage induced by 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone
(NNK) in A549 cells. Chem Biol Interact. 160:175–182. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lehtonen ST, Svensk AM, Soini Y, Pääkkö P,
Hirvikoski P, Kang SW, Säily M and Kinnula VL: Peroxiredoxins, a
novel protein family in lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 111:514–521.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gorrini C, Harris IS and Mak TW:
Modulation of oxidative stress as an anticancer strategy. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 12:931–947. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rhee SG and Kil IS: Multiple functions and
regulation of mammalian peroxiredoxins. Annu Rev Biochem.
86:749–775. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bajor M, Zych AO, Graczyk-Jarzynka A,
Muchowicz A, Firczuk M, Trzeciak L, Gaj P, Domagala A, Siernicka M,
Zagozdzon A, et al: Targeting peroxiredoxin 1 impairs growth of
breast cancer cells and potently sensitises these cells to
prooxidant agents. Br J Cancer. 119:873–884. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Han YH, Zhang YQ, Jin MH, Jin YH, Qiu MY,
Li WL, He C, Yu LY, Hyun JW, Lee J, et al: Peroxiredoxin I
deficiency increases keratinocyte apoptosis in a skin tumor model
via the ROS-p38 MAPK pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
529:635–641. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hampton MB, Vick KA, Skoko JJ and Neumann
CA: Peroxiredoxin involvement in the initiation and progression of
human cancer. Antioxid Redox Signal. 28:591–608. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen MF, Chen WC, Wu CT, Lin PY, Shau H,
Liao SK, Yang CT and Lee KD: p53 status is a major determinant of
effects of decreasing peroxiredoxin I expression on tumor growth
and response of lung cancer cells to treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 66:1461–1472. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hirata N, Yamada S, Sekino Y and Kanda Y:
Tobacco nitrosamine NNK increases ALDH-positive cells via ROS-Wnt
signaling pathway in A549 human lung cancer cells. J Toxicol Sci.
42:193–204. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shi GQ, Zhou WS, Li M, Ren F and Han YW:
Characterization and expression analysis of peroxiredoxin genes in
NNK-induced V79 cells. Biomed Environ Sci. 30:224–228.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Immenschuh S and Baumgart-Vogt E:
Peroxiredoxins, oxidative stress, and cell proliferation. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 7:768–777. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Akopyan G and Bonavida B: Understanding
tobacco smoke carcinogen NNK and lung tumorigenesis. Int J Oncol.
29:745–752. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hecht SS, Hochalter JB, Villalta PW and
Murphy SE: 2′-Hydroxylation of nicotine by cytochrome P450 2A6 and
human liver microsomes: Formation of a lung carcinogen precursor.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:12493–12497. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peterson LA: Context matters: Contribution
of specific DNA adducts to the genotoxic properties of the
tobacco-specific nitrosamine NNK. Chem Res Toxicol. 30:420–433.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ashmore JH, Luo S, Watson CJW and Lazarus
P: Carbonyl reduction of NNK by recombinant human lung enzymes:
Identification of HSD17β12 as the reductase important in (R)-NNAL
formation in human lung. Carcinogenesis. 39:1079–1088. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Leslie EM, Ghibellini G, Nezasa K and
Brouwer KL: Biotransformation and transport of the tobacco-specific
carcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) in
bile duct-cannulated wild-type and Mrp2/Abcc2-deficient (TR) Wistar
rats. Carcinogenesis. 28:2650–2656. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Richter E, Friesenegger S, Engl J and
Tricker AR: Use of precision-cut tissue slices in organ culture to
study metabolism of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone
(NNK) and 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL) by
hamster lung, liver and kidney. Toxicology. 144:83–91. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rhee SG, Kang SW, Chang TS, Jeong W and
Kim K: Peroxiredoxin, a novel family of peroxidases. IUBMB Life.
52:35–41. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Neumann CA, Cao J and Manevich Y:
Peroxiredoxin 1 and its role in cell signaling. Cell Cycle.
8:4072–4078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ding C, Fan X and Wu G: Peroxiredoxin 1-an
antioxidant enzyme in cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 21:193–202. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Park YH, Kim SU, Lee BK, Kim HS, Song IS,
Shin HJ, Han YH, Chang KT, Kim JM, Lee DS, et al: Prx I suppresses
K-ras-driven lung tumorigenesis by opposing redox-sensitive
ERK/cyclin D1 pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal. 19:482–496. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chang TS, Jeong W, Choi SY, Yu S, Kang SW
and Rhee SG: Regulation of peroxiredoxin I activity by
Cdc2-mediated phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 277:25370–25376. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Poole LB: The basics of thiols and
cysteines in redox biology and chemistry. Free Radic Biol Med.
80:148–157. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Watanabe Y, Ishimori K and Uchida T: Dual
role of the active-center cysteine in human peroxiredoxin 1:
Peroxidase activity and heme binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
483:930–935. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gozzelino R, Jeney V and Soares MP:
Mechanisms of cell protection by heme oxygenase-1. Annu Rev
Pharmacol Toxicol. 50:323–354. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guo Y, Patil NK, Luan L, Bohannon JK and
Sherwood ER: The biology of natural killer cells during sepsis.
Immunology. 153:190–202. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Aktaş ON, Öztürk AB, Erman B, Erus S,
Tanju S and Dilege Ş: Role of natural killer cells in lung cancer.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 144:997–1003. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li S, Wang R, Zhang M, Wang L and Cheng S:
Proteomic analysis of non-small cell lung cancer tissue
interstitial fluids. World J Surg Oncol. 11:1732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen MF, Keng PC, Shau H, Wu CT, Hu YC,
Liao SK and Chen WC: Inhibition of lung tumor growth and
augmentation of radiosensitivity by decreasing peroxiredoxin I
expression. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 64:581–591. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu D, Mao P, Huang Y, Liu Y, Liu X, Pang
X and Li Y: Proteomic analysis of lung tissue in a rat acute lung
injury model: Identification of PRDX1 as a promoter of
inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2014:4693582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brenner DR, Fanidi A, Grankvist K, Muller
DC, Brennan P, Manjer J, Byrnes G, Hodge A, Severi G, Giles GG, et
al: Inflammatory cytokines and lung cancer risk in 3 prospective
studies. Am J Epidemiol. 185:86–95. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
DeCotiis C, Hu Y, Greenberg AK, Huie M,
Tsay JC, Pass H, Goldberg JD and Rom WN: Inflammatory cytokines and
non-small cell lung cancer in a CT-scan screening cohort:
Background review of the literature. Cancer Biomark. 16:219–233.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chang JW, Lee SH, Jeong JY, Chae HZ, Kim
YC, Park ZY and Yoo YJ: Peroxiredoxin-I is an autoimmunogenic tumor
antigen in non-small cell lung cancer. FEBS Lett. 579:2873–2877.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Finkel T and Holbrook NJ: Oxidants,
oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature. 408:239–247.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Moloney JN and Cotter TG: ROS signalling
in the biology of cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 80:50–64. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Macip S, Igarashi M, Berggren P, Yu J, Lee
SW and Aaronson SA: Influence of induced reactive oxygen species in
p53-mediated cell fate decisions. Mol Cell Biol. 23:8576–8585.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Moll HP, Pranz K, Musteanu M, Grabner B,
Hruschka N, Mohrherr J, Aigner P, Stiedl P, Brcic L, Laszlo V, et
al: Afatinib restrains K-RAS-driven lung tumorigenesis. Sci Transl
Med. 10:eaao23012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Aran V and Omerovic J: Current approaches
in NSCLC targeting K-RAS and EGFR. Int J Mol Sci. 20:57012019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Scheffler M, Ihle MA, Hein R,
Merkelbach-Bruse S, Scheel AH, Siemanowski J, Brägelmann J, Kron A,
Abedpour N, Ueckeroth F, et al: K-ras mutation subtypes in NSCLC
and associated Co-occuring mutations in other oncogenic pathways. J
Thorac Oncol. 14:606–616. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Peeper DS, Upton TM, Ladha MH, Neuman E,
Zalvide J, Bernards R, DeCaprio JA and Ewen ME: Ras signalling
linked to the cell-cycle machinery by the retinoblastoma protein.
Nature. 386:177–181. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Slebos RJ, Kibbelaar RE, Dalesio O,
Kooistra A, Stam J, Meijer CJ, Wagenaar SS, Vanderschueren RG, van
Zandwijk N, Mooi WJ, et al: K-ras oncogene activation as a
prognostic marker in adenocarcinoma of the lung. N Engl J Med.
323:561–565. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Proulx LI, Paré G and Bissonnette EY:
Alveolar macrophage cytotoxic activity is inhibited by
4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK), a
carcinogenic component of cigarette smoke. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 56:831–838. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rioux N and Castonguay A: The induction of
cyclooxygenase-1 by a tobacco carcinogen in U937 human macrophages
is correlated to the activation of NF-kappaB. Carcinogenesis.
21:1745–1751. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang Y, Narayanapillai SC, Hu Q, Fujioka N
and Xing C: Detection and quantification of
4-hydroxy-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (HPB) from smoker albumin and
its potential as a surrogate biomarker of tobacco-specific
nitrosamines exposure and bioactivation. Toxicol Lett. 311:11–16.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Peterson LA, Carmella SG and Hecht SS:
Investigations of metabolic precursors to hemoglobin and DNA
adducts of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone.
Carcinogenesis. 11:1329–1333. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hecht SS, Stepanov I and Carmella SG:
Exposure and metabolic activation biomarkers of carcinogenic
tobacco-specific nitrosamines. Acc Chem Res. 49:106–114. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hecht SS, Trushin N, Rigotty J, Carmella
SG, Borukhova A, Akerkar S, Desai D, Amin S and Rivenson A:
Inhibitory effects of 6-phenylhexyl isothiocyanate on
4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone metabolic activation
and lung tumorigenesis in rats. Carcinogenesis. 17:2061–2067. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tsiftsoglou AS, Tsamadou AI and
Papadopoulou LC: Heme as key regulator of major mammalian cellular
functions: Molecular, cellular, and pharmacological aspects.
Pharmacol Ther. 111:327–345. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Severance S and Hamza I: Trafficking of
heme and porphyrins in metazoa. Chem Rev. 109:4596–4616. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shimizu T, Lengalova A, Martínek V and
Martínková M: Heme: Emergent roles of heme in signal transduction,
functional regulation and as catalytic centres. Chem Soc Rev.
48:5624–5657. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Khan AA and Quigley JG: Control of
intracellular heme levels: Heme transporters and heme oxygenases.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:668–682. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Roumenina LT, Rayes J, Lacroix-Desmazes S
and Dimitrov JD: Heme: Modulator of plasma systems in hemolytic
diseases. Trends Mol Med. 22:200–213. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Vlasova II: Peroxidase activity of human
hemoproteins: Keeping the fire under control. Molecules.
23:25612018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Peralta IN, Cogoi L, Filip R and Anesini
C: Prevention of hydrogen peroxide-induced red blood cells lysis by
Ilex paraguariensis aqueous extract: Participation of phenolic and
xanthine compounds. Phytother Res. 27:192–198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hahl P, Hunt R, Bjes ES, Skaff A,
Keightley A and Smith A: Identification of oxidative modifications
of hemopexin and their predicted physiological relevance. J Biol
Chem. 292:13658–13671. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Therriault MJ, Proulx LI, Castonguay A and
Bissonnette EY: Immunomodulatory effects of the tobacco-specific
carcinogen, NNK, on alveolar macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol.
132:232–238. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Liu Y and Cao X: The origin and function
of tumor-associated macrophages. Cell Mol Immunol. 12:1–4. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Proulx LI, Castonguay A and Bissonnette
EY: Cytokine production by alveolar macrophages is down regulated
by the alpha-methylhydroxylation pathway of
4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK).
Carcinogenesis. 25:997–1003. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Proulx LI, Gaudreault M, Turmel V, Augusto
LA, Castonguay A and Bissonnette EY:
4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone, a component of
tobacco smoke, modulates mediator release from human bronchial and
alveolar epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 140:46–53. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Mashimo M: Dual roles of α7 nicotinic
acetylcholine receptors expressed in immune cells in T cell
differentiation-α7 nAChRs exert different actions between
antigen-presenting cells and CD4(+) T cells. Yakugaku Zasshi.
140:1421–1425. 2020.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Schuller HM, Jull BA, Sheppard BJ and
Plummer HK: Interaction of tobacco-specific toxicants with the
neuronal alpha(7) nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and its
associated mitogenic signal transduction pathway: Potential role in
lung carcinogenesis and pediatric lung disorders. Eur J Pharmacol.
393:265–277. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Rahim SS, Khan N, Boddupalli CS, Hasnain
SE and Mukhopadhyay S: Interleukin-10 (IL-10) mediated suppression
of IL-12 production in RAW 264.7 cells also involves c-rel
transcription factor. Immunology. 114:313–321. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zirnheld AL, Villard M, Harrison AM,
Kosiewicz MM and Alard P: β-Catenin stabilization in NOD dendritic
cells increases IL-12 production and subsequent induction of
IFN-γ-producing T cells. J Leukoc Biol. 106:1349–1358. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chakraborty K, Zhou Z, Wakamatsu N and
Guerrero-Plata A: Interleukin-12p40 modulates human
metapneumovirus-induced pulmonary disease in an acute mouse model
of infection. PLoS One. 7:e371732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Guo Y, Cao W and Zhu Y: Immunoregulatory
functions of the IL-12 family of cytokines in antiviral systems.
Viruses. 11:7722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Trinchieri G: Interleukin-12 and the
regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev
Immunol. 3:133–146. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Caligiuri MA: Human natural killer cells.
Blood. 112:461–469. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kinnula VL, Lehtonen S, Kaarteenaho-Wiik
R, Lakari E, Pääkkö P, Kang SW, Rhee SG and Soini Y: Cell specific
expression of peroxiredoxins in human lung and pulmonary
sarcoidosis. Thorax. 57:157–164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Tae Lim Y, Sup Song D, Joon Won T, Lee YJ,
Yoo JS, Eun Hyung K, Won Yoon J, Park SY and Woo Hwang K:
Peroxiredoxin-1, a possible target in modulating inflammatory
cytokine production in macrophage like cell line RAW264.7.
Microbiol Immunol. 56:411–419. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Mennecier G, Torres LN, Cogliati B,
Sanches DS, Mori CM, Latorre AO, Chaible LM, Mackowiak II, Nagamine
MK, Da Silva TC, et al: Chronic exposure of lung alveolar
epithelial type II cells to tobacco-specific carcinogen NNK results
in malignant transformation: A new in vitro lung carcinogenesis
model. Mol Carcinog. 53:392–402. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Yilmaz M and Christofori G: EMT, the
cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:15–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Vu T, Jin L and Datta PK: Effect of
cigarette smoking on epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in
lung cancer. J Clin Med. 5:442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Mehdi MZ, Pandey NR, Pandey SK and
Srivastava AK: H2O2-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and PKB
requires tyrosine kinase activity of insulin receptor and c-Src.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 7:1014–1020. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Shen J, Xu L, Owonikoko TK, Sun SY, Khuri
FR, Curran WJ and Deng X: NNK promotes migration and invasion of
lung cancer cells through activation of c-Src/PKCι/FAK loop. Cancer
Lett. 318:106–113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhang H, Liu H, Borok Z, Davies KJ, Ursini
F and Forman HJ: Cigarette smoke extract stimulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Src activation. Free
Radic Biol Med. 52:1437–1442. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Shintani Y, Okimura A, Sato K, Nakagiri T,
Kadota Y, Inoue M, Sawabata N, Minami M, Ikeda N, Kawahara K, et
al: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is a determinant of
sensitivity to chemoradiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Ann
Thorac Surg. 92:1794–1804. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Tseng YC, Tsai YH, Tseng MJ, Hsu KW, Yang
MC, Huang KH, Li AF, Chi CW, Hsieh RH, Ku HH and Yeh TS:
Notch2-induced COX-2 expression enhancing gastric cancer
progression. Mol Carcinog. 51:939–951. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Ocaña OH, Córcoles R, Fabra A,
Moreno-Bueno G, Acloque H, Vega S, Barrallo-Gimeno A, Cano A and
Nieto MA: Metastatic colonization requires the repression of the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition inducer Prrx1. Cancer Cell.
22:709–724. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Reichert M, Takano S, von Burstin J, Kim
SB, Lee JS, Ihida-Stansbury K, Hahn C, Heeg S, Schneider G, Rhim
AD, et al: The Prrx1 homeodomain transcription factor plays a
central role in pancreatic regeneration and carcinogenesis. Genes
Dev. 27:288–300. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R and Thompson
EW: The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: New insights in
signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 172:973–981.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Ha B, Kim EK, Kim JH, Lee HN, Lee KO, Lee
SY and Jang HH: Human peroxiredoxin 1 modulates TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through its peroxidase activity.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 421:33–37. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Xu J, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res.
19:156–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yang Y, Pan X, Lei W, Wang J and Song J:
Transforming growth factor-beta1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition and apoptosis via a cell cycle-dependent mechanism.
Oncogene. 25:7235–7244. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Derynck R and Akhurst RJ: Differentiation
plasticity regulated by TGF-beta family proteins in development and
disease. Nat Cell Biol. 9:1000–1004. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Gotzmann J, Huber H, Thallinger C,
Wolschek M, Jansen B, Schulte-Hermann R, Beug H and Mikulits W:
Hepatocytes convert to a fibroblastoid phenotype through the
cooperation of TGF-beta1 and Ha-Ras: Steps towards invasiveness. J
Cell Sci. 115:1189–1202. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Ushio-Fukai M and Nakamura Y: Reactive
oxygen species and angiogenesis: NADPH oxidase as target for cancer
therapy. Cancer Lett. 266:37–52. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Jiang F, Qiu Q, Khanna A, Todd NW, Deepak
J, Xing L, Wang H, Liu Z, Su Y, Stass SA and Katz RL: Aldehyde
dehydrogenase 1 is a tumor stem cell-associated marker in lung
cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 7:330–338. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Huang RY, Li MY, Hsin MK, Underwood MJ, Ma
LT, Mok TS, Warner TD and Chen GG: 4-Methylnitrosamino-
1-3-pyridyl-1-butanone (NNK) promotes lung cancer cell survival by
stimulating thromboxane A2 and its receptor. Oncogene. 30:106–116.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hung YH and Hung WC:
4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1- (3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) enhances
invasiveness of lung cancer cells by up-regulating contactin-1 via
the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor/ERK signaling pathway.
Chem Biol Interact. 179:154–159. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Yan J, Wong N, Hung C, Chen WX and Tang D:
Contactin-1 reduces E-cadherin expression via activating AKT in
lung cancer. PLoS One. 8:e654632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Jin Z, Xin M and Deng X: Survival function
of protein kinase C{iota} as a novel nitrosamine
4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone-activated bad
kinase. J Biol Chem. 280:16045–16052. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Wang KC, Liu YC, El-Shazly M, Shih SP, Du
YC, Hsu YM, Lin HY, Chen YC, Wu YC, Yang SC and Lu MC: The
antioxidant from ethanolic extract of Rosa cymosa fruits
activates phosphatase and tensin homolog in vitro and in vivo: A
new insight on its antileukemic effect. Int J Mol Sci. 20:19352019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Neumann CA and Fang Q: Are peroxiredoxins
tumor suppressors? Curr Opin Pharmacol. 7:375–380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Nauseef WM: Biological roles for the NOX
family NADPH oxidases. J Biol Chem. 283:16961–16965. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Ge GZ, Xu TR and Chen C: Tobacco
carcinogen NNK-induced lung cancer animal models and associated
carcinogenic mechanisms. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
47:477–487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Hong WG, Kim JY, Cho JH, Hwang SG, Song
JY, Lee E, Chang TS, Um HD and Park JK: AMRI-59 functions as a
radiosensitizer via peroxiredoxin I-targeted ROS accumulation and
apoptotic cell death induction. Oncotarget. 8:114050–114064. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|