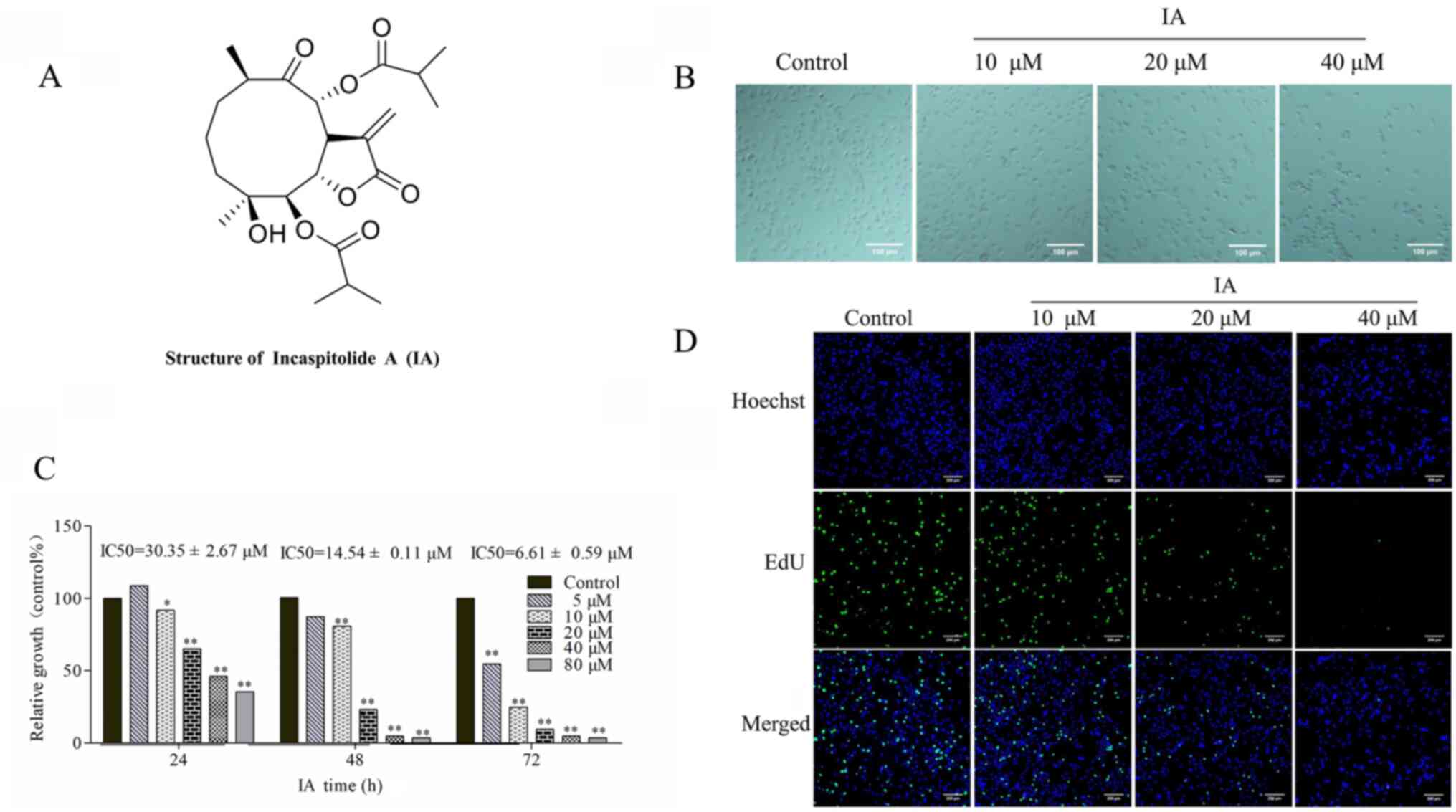
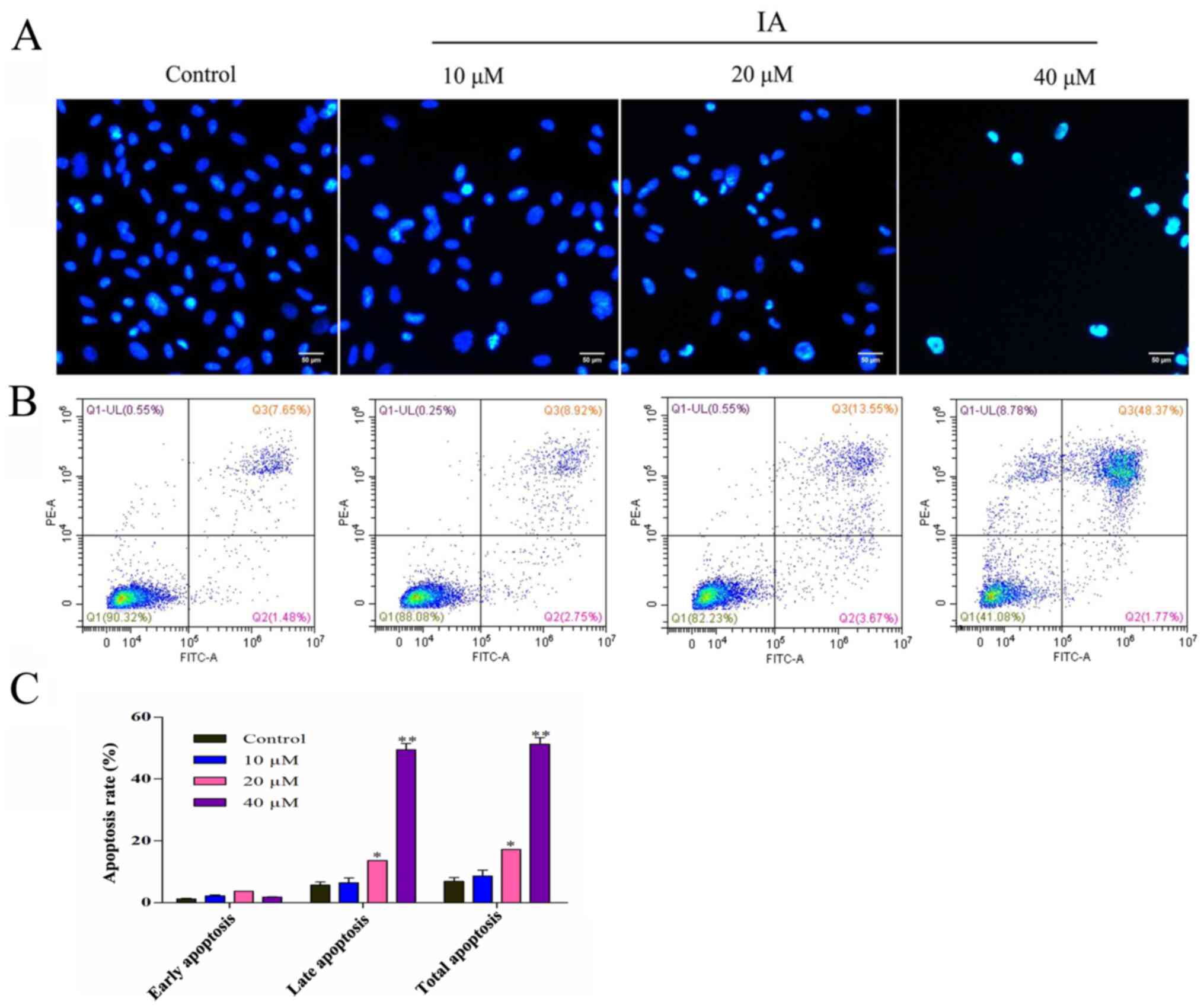
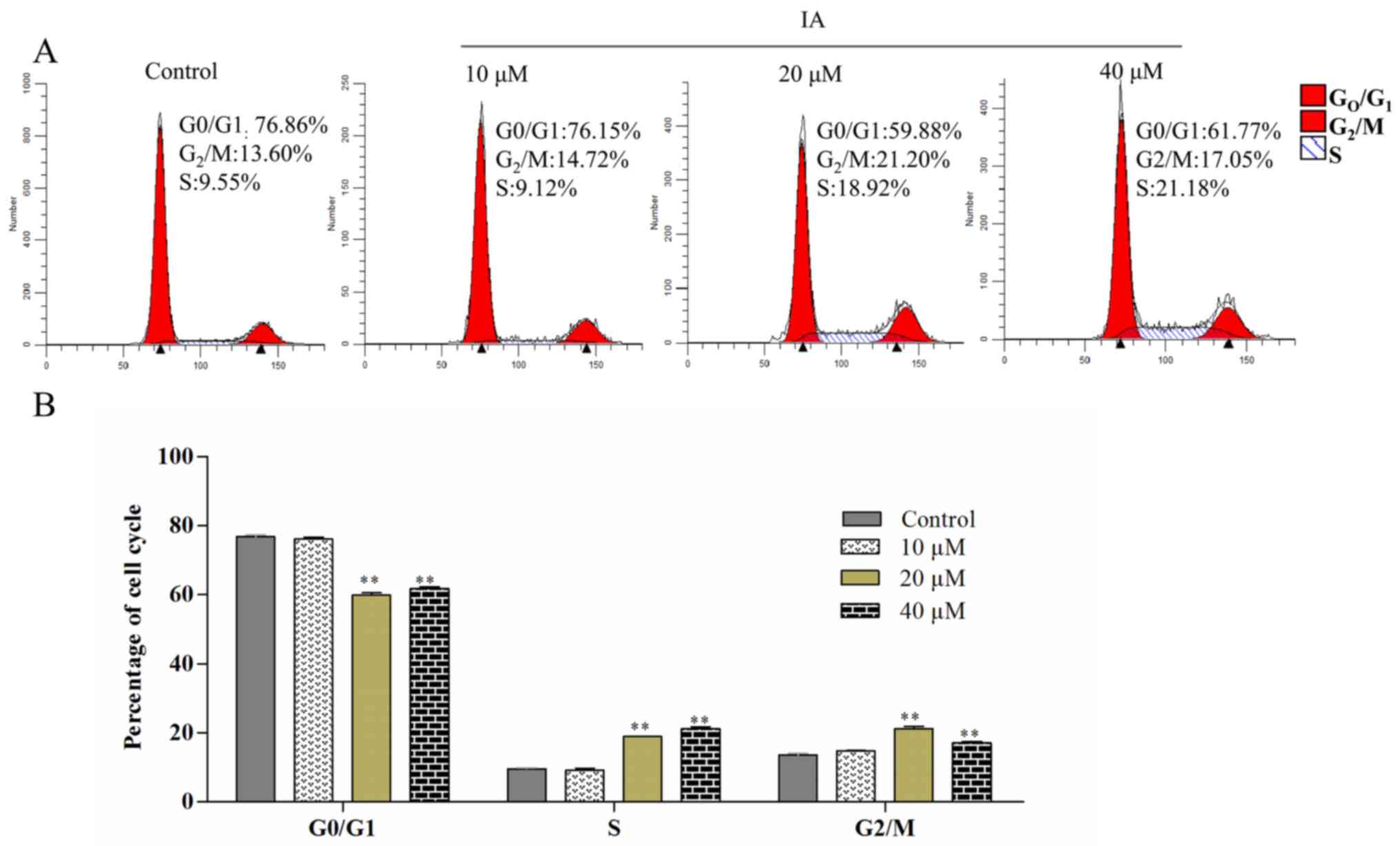
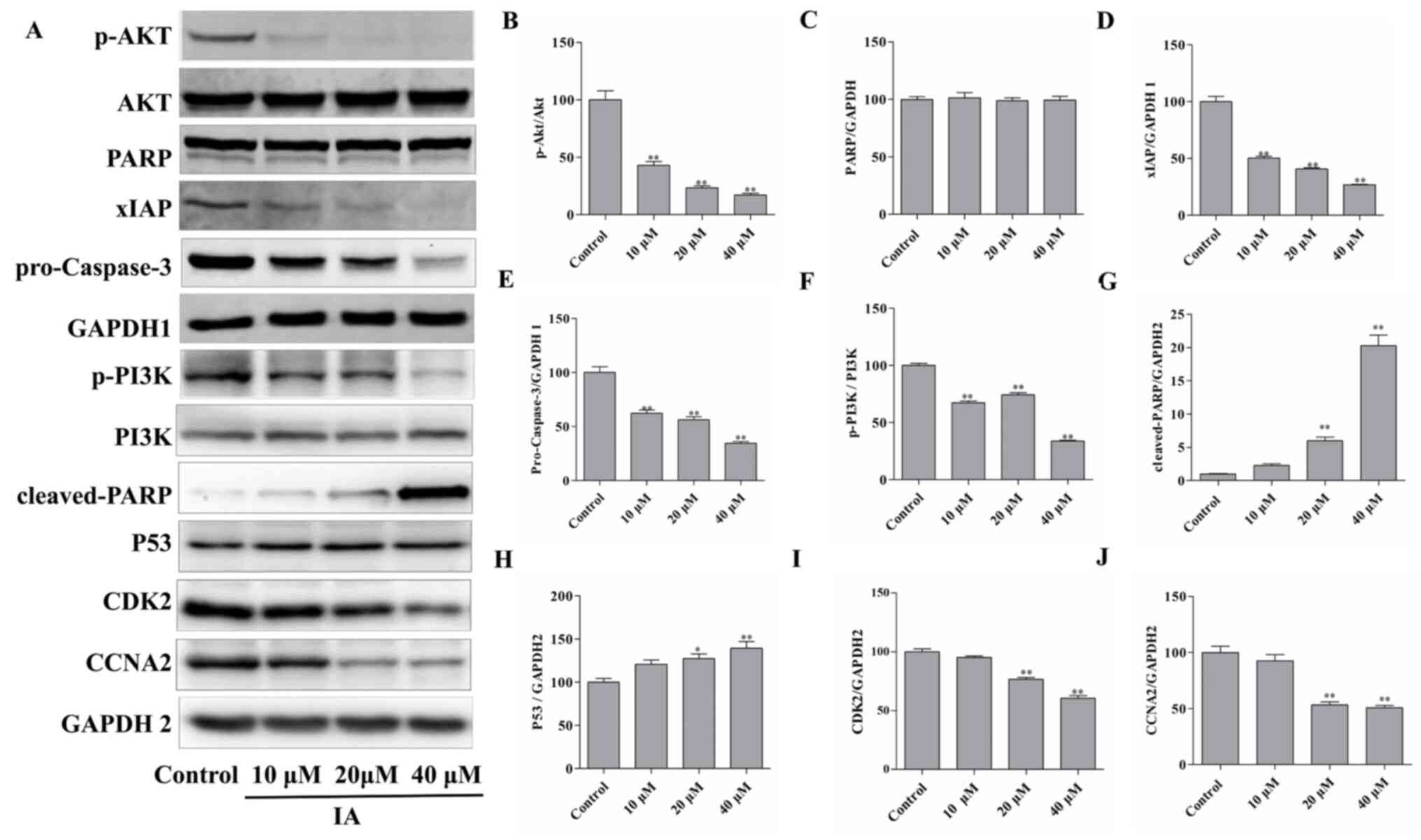
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Darnel AD, Behmoaram E, Vollmer RT, Corcos
J, Bijian K, Sircar K, Su J, Jiao J, Alaoui-Jamali MA and Bismar
TA: Fascin regulates prostate cancer cell invasion and is
associated with metastasis and biochemical failure in prostate
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1376–1383. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang J, Park JS, Wei Y, Rajurkar M, Cotton
JL, Fan Q, Lewis BC, Ji H and Mao J: TRIB2 acts downstream of
Wnt/TCF in liver cancer cells to regulate YAP and C/EBPα function.
Mol Cell. 51:211–225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tye BK: MCM proteins in DNA replication.
Annu Rev Biochem. 68:649–686. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Matsuda T and Saika K: Comparison of time
trends in prostate cancer incidence (1973–2002) in Asia, from
cancer incidence in five continents, Vols IV–IX. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
39:468–469. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu X, Yu C, Bi Y and Zhang ZJ: Trends and
age-period-cohort effect on incidence and mortality of prostate
cancer from 1990 to 2017 in China. Public Health. 172:70–80. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu X, Albertsen PC, Andriole GL, Roobol
MJ, Schröder FH and Vickers AJ: Risk-based prostate cancer
screening. Eur Urol. 61:652–661. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kallifatidis G, Hoy JJ and Lokeshwar BL:
Bioactive natural products for chemoprevention and treatment of
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Semin Cancer Biol.
40-41:160–169. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z and Kong D:
Cellular signaling perturbation by natural products. Cell Signal.
21:1541–1547. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Editorial Committee of Flora of China, .
Flora of China. 75. Beijing, China: Science Press; pp. 2961979
|
|
11
|
Kim MR, Hwang BY, Jeong ES, Lee YM, Yoo
HS, Chung YB, Hong JT and Moon DC: Cytotoxic germacranolide
sesquiterpene lactones from Carpesium triste var.
manshuricum. Arch Pharm Res. 30:556–560. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li XW, Weng L, Gao X, Zhao Y, Pang F, Liu
JH, Zhang HF and Hu JF: Antiproliferative and apoptotic
sesquiterpene lactones from Carpesium faberi. Bioorg Med
Chem Lett. 21:366–372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dang H, Li H, Ma C, Wang Y, Tian J, Deng
L, Wang D, Jing X, Luo K, Xing W, et al: Identification of
Carpesium cernuum extract as a tumor migration inhibitor
based on its biological response profiling in breast cancer cells.
Phytomedicine. 64:1530722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Koppula S, Kim WJ, Jiang J, Shim DW, Oh
NH, Kim TJ, Kang TB and Lee KH: Carpesium macrocephalum
attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in macrophages
by regulating the NF-κB/IκB-α, Akt, and STAT signaling pathways. Am
J Chin Med. 41:927–943. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim EJ, Jin HK, Kim YK, Lee HY, Lee SY,
Lee KR, Zee OP, Han JW and Lee HW: Suppression by a sesquiterpene
lactone from Carpesium divaricatum of inducible nitric oxide
synthase by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Biochem
Pharmacol. 61:903–910. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
State Administration of Traditional
Chinese Medicine. Chinese materia medica. Shanghai Scientific and
Technical Publishers; Shanghai, China: pp. 7601999
|
|
17
|
Chung IM and Moon HI: Antiplasmodial
activities of sesquiterpene lactone from Carpesium cernum. J
Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 24:131–135. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim JJ, Chung IM, Jung JC, Kim MY and Moon
HI: In vivo antiplasmodial activity of 11(13)-dehydroivaxillin from
Carpesium ceruum. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 24:247–250. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang JP, Wang GW, Tian XH, Yang YX, Liu
QX, Chen LP, Li HL and Zhang WD: The genus Carpesium: A review of
its ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J
Ethnopharmacol. 163:173–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma JP, Tan CH and Zhu DY: Glycosidic
constituents from Carpesium cernuum L. J Asian Nat Prod Res.
10:565–569. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang GW, Qin JJ, Cheng XR, Shen YH, Shan
L, Jin HZ and Zhang WD: Inula sesquiterpenoids: Structural
diversity, cytotoxicity and anti-tumor activity. Expert Opin
Investig Drugs. 23:317–345. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang FY, Li XQ, Qi S, Yao S, Ke CQ, Tang
CP, Liu HC, Geng MY and Ye Y: Sesquiterpene lactones from Inula
cappa. Phytochem Lett. 5:639–642. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu JW, Tang CP, Cai YY, Ke CQ, Lin LG, Yao
S and Ye Y: Cytotoxic germacrane-type sesquiterpene lactones from
the whole plant of Inula cappa. Chin Chem Lett. 28:927–930.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yan C, Zhang WQ, Sun M, Liang W, Wang TY,
Zhang YD and Ding X: Carpescernolides A and B, rare oxygen
bridge-containing Sesquiterpenes lactones from Carpesium
cernuum. Tetrahedron Lett. 59:4063–4066. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang T, Si JG, Zhang QB, Ding G and Zou
ZM: New highly oxygenated germacranolides from Carpesium
divaricatum and their cytotoxic activity. Sci Rep. 6:272372016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bohlmann F, Singh P and Jakupovic J:
Further ineupatorolide-like germacranolides from Inula
cuspidata. Phytochemistry. 21:157–160. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang R, Dong ZY, Lan XZ, Liao ZH and Chen
M: Sweroside alleviated LPS-induced inflammation via SIRT1
mediating NF-κB and FOXO1 signaling pathways in RAW264.7 cells.
Molecules. 24:8722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mao J, Yi M, Tao Y, Huang Y and Chen M:
Costunolide isolated from Vladimiria souliei inhibits the
proliferation and induces the apoptosis of HepG2 cells. Mol Med
Rep. 19:1372–1379. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yin PH, Liu X, Qiu YY, Cai JF, Qin JM, Zhu
HR and Li Q: Anti-tumor activity and apoptosis-regulation
mechanisms of bufalin in various cancers: New hope for cancer
patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:5339–5343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guo Y, Balasubramanian B, Zhao ZH and Liu
WC: Marine algal polysaccharides alleviate aflatoxin B1-induced
bursa of Fabricius injury by regulating redox and apoptotic
signaling pathway in broilers. Poult Sci. 100:844–857. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu WC, Guo Y, Zhao ZH, Jha R and
Balasubramanian B: Algae-derived polysaccharides promote growth
performance by improving antioxidant capacity and intestinal
barrier function in broiler chickens. Front Vet Sci. 7:6013362020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rao L and White E: Bcl-2 and the ICE
family of apoptotic regulators: Making a connection. Curr Opin
Genet Dev. 7:52–58. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jin D, Yang JP, Hu JH, Wang LN and Zou J:
MCP-1 stimulates spinal microglia via PI3K/Akt pathway in bone
cancer pain. Brain Res. 1599:158–167. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Petrulea MS, Plantinga TS, Smit JW,
Georgescu CE and Netea-Maier RT: PI3K/Akt/mTOR: A promising
therapeutic target for non-medullary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer
Treat Rev. 41:707–713. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pramanik KC, Kudugunti SK, Fofaria NM,
Moridani MY and Srivastava SK: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester
suppresses melanoma tumor growth by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/XIAP
pathway. Carcinogenesis. 34:2061–2070. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vyas VK, Ghate M and Goel A: Pharmacophore
modeling, virtual screening, docking and in silico ADMET analysis
of protein kinase B (PKB β) inhibitors. J Mol Graph Model.
42:17–25. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Deveraux QL, Takahashi R, Salvesen GS and
Reed JC: X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell-death
proteases. Nature. 388:300–304. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sasaki H, Sheng Y, Kotsuji F and Tsang BK:
Down-regulation of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein induces
apoptosis in chemoresistant human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res.
60:5659–5666. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Han B, Jiang P, Li Z, Yu Y, Huang T, Ye X
and Li X: Coptisine-induced apoptosis in human colon cancer cells
(HCT-116) is mediated by PI3K/Akt and mitochondrial-associated
apoptotic pathway. Phytomedicine. 48:152–160. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, Steelman
LS, Shelton JG, Blalock WL, Franklin RA and McCubrey JA:
Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression,
apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: A target for cancer
chemotherapy. Leukemia. 17:590–603. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang W, Shang X, Zhang C, Gao X, Robinson
B and Liu J: The effects of carvedilol on cardiac function and the
AKT/XIAP signaling pathway in diabetic cardiomyopathy rats.
Cardiology. 136:204–211. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|