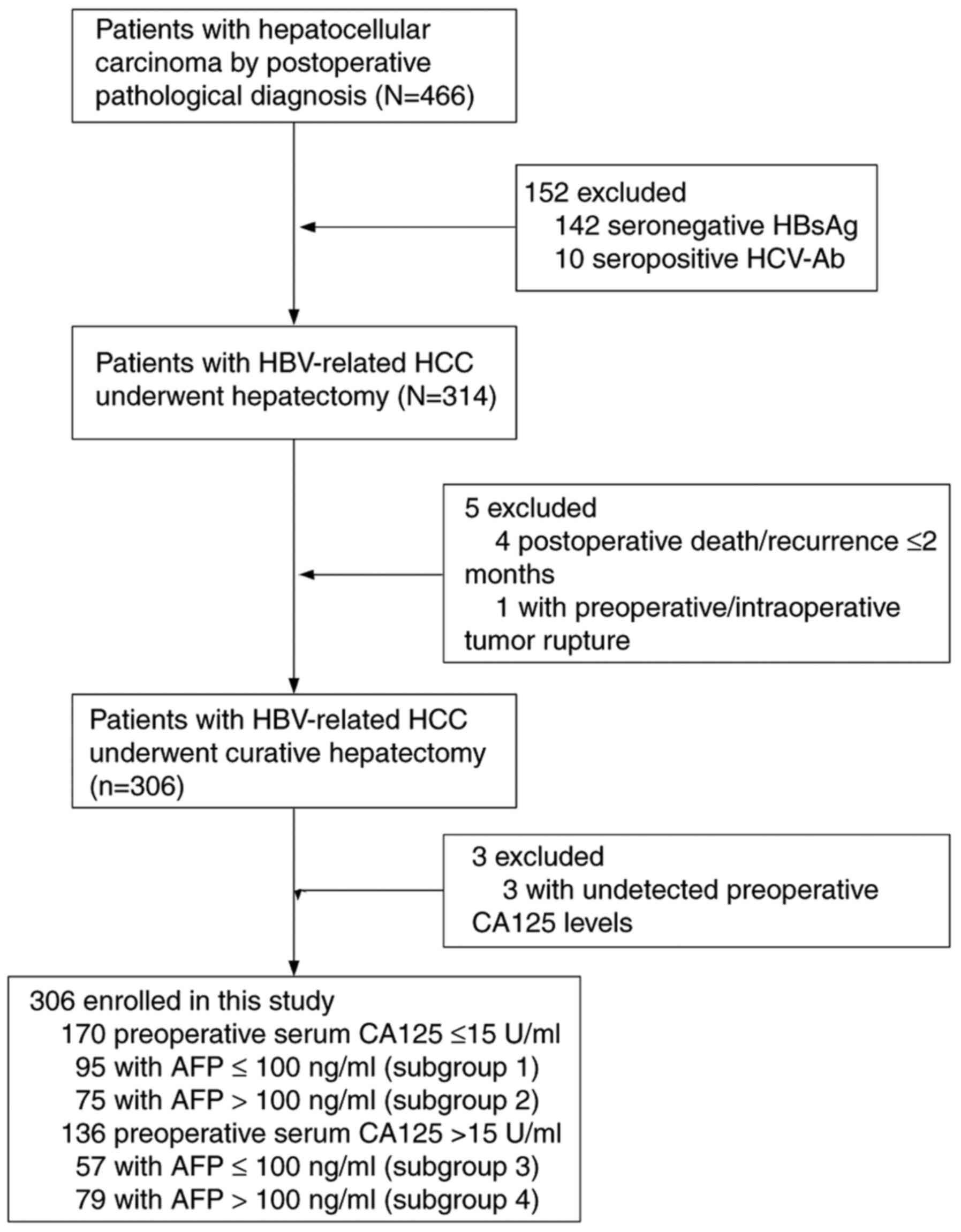
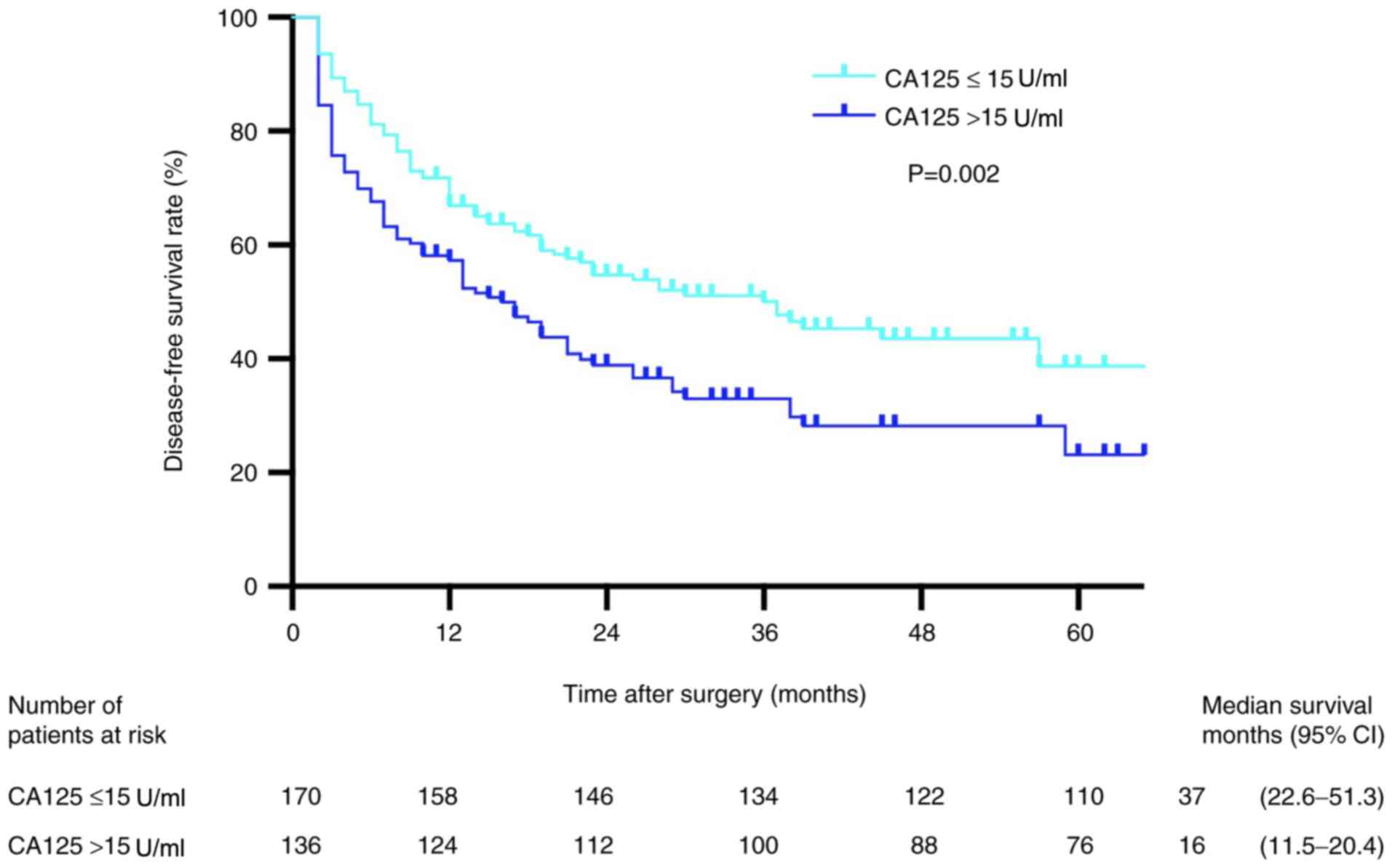
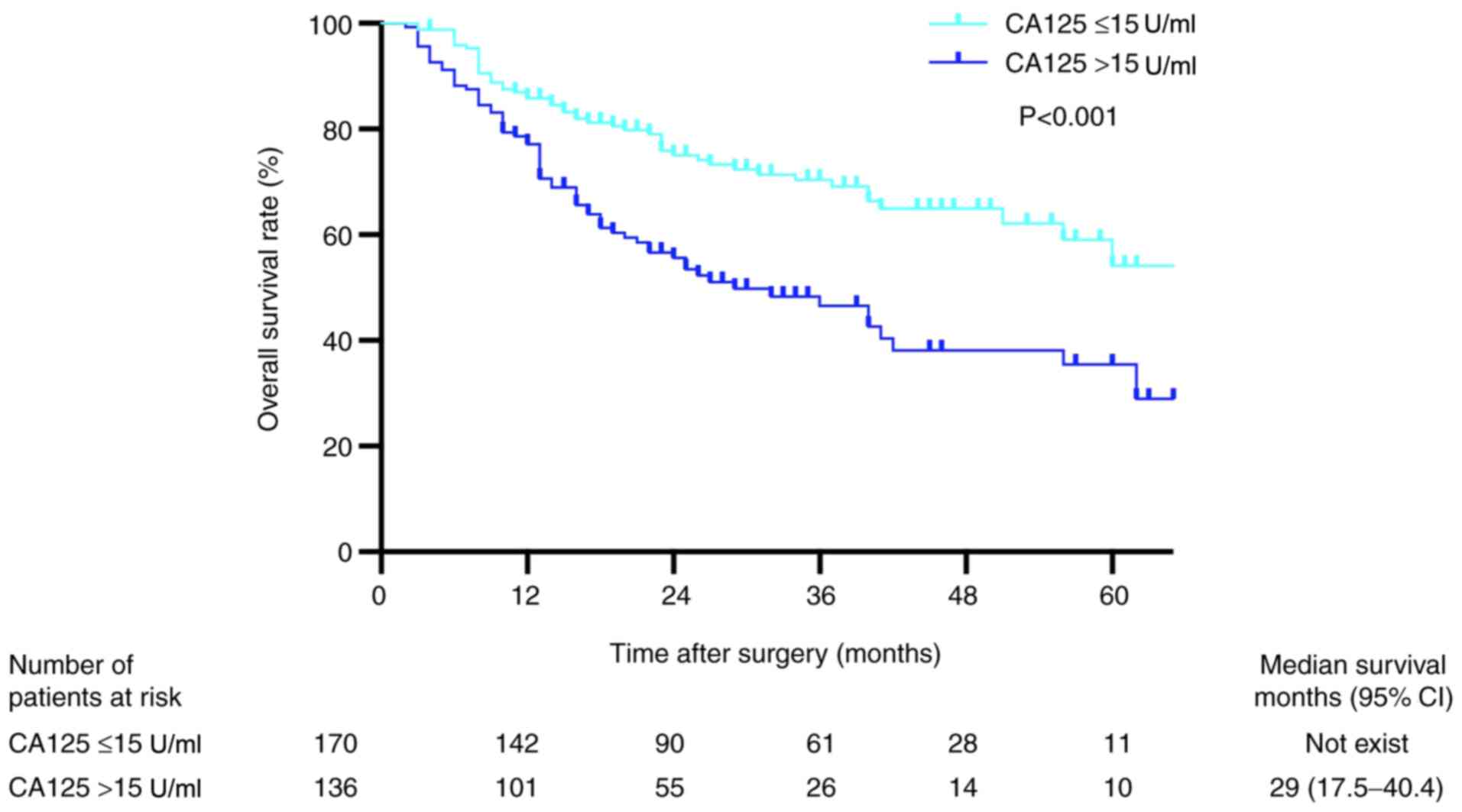
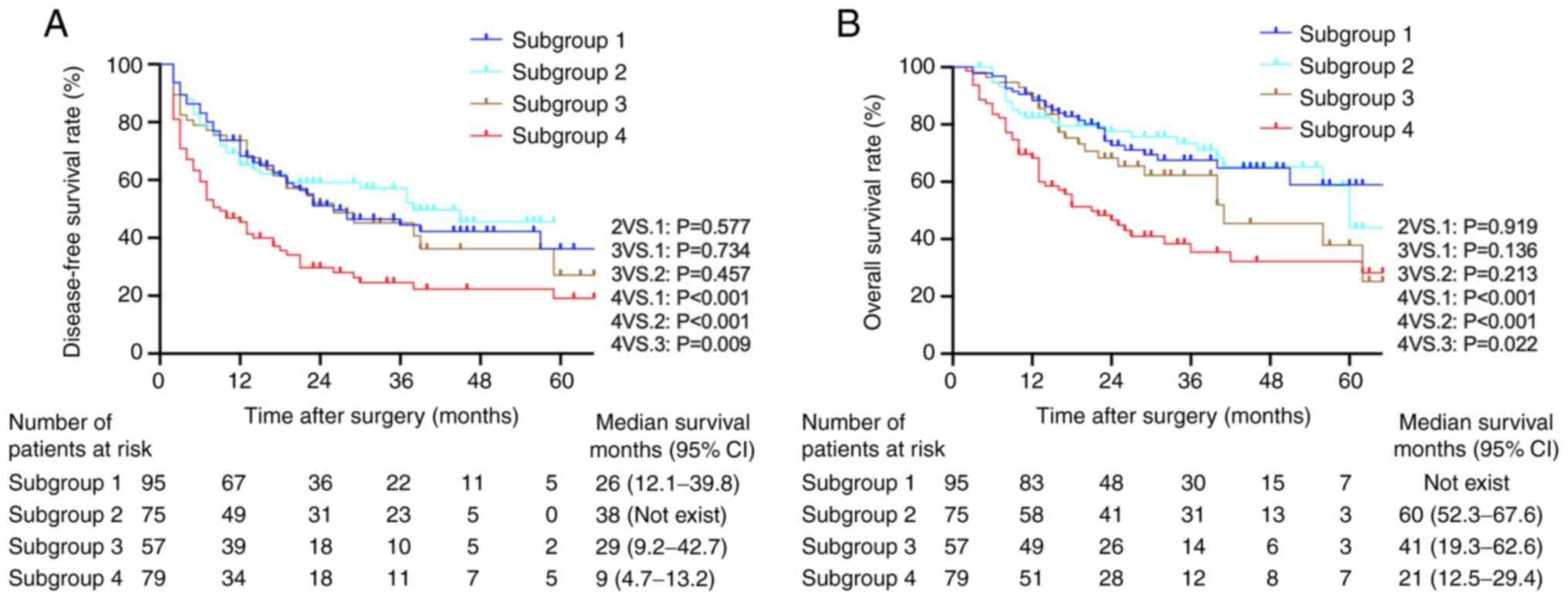
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zamor PJ, deLemos AS and Russo MW: Viral
hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma: Etiology and management. J
Gastrointest Oncol. 8:229–242. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nguyen VT, Law MG and Dore GJ: Hepatitis
B-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiological characteristics
and disease burden. J Viral Hepat. 16:453–463. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bruix J, Gores GJ and Mazzaferro V:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut.
63:844–855. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Miura JT, Johnston FM, Tsai S, Eastwood D,
Banerjee A, Christians KK, Turaga KK and Gamblin TC: Surgical
resection versus ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma</=3 cm: A
population-based analysis. HPB (Oxford). 17:896–901. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rahbari NN, Mehrabi A, Mollberg NM, Müller
SA, Koch M, Büchler MW and Weitz J: Hepatocellular carcinoma:
Current management and perspectives for the future. Ann Surg.
253:453–469. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Akamatsu N and Kokudo N: Liver
transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma from living-donor vs.
Deceased donor. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 5:422–428. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hyun MH, Lee YS, Kim JH, Lee CU, Jung YK,
Seo YS, Yim HJ, Yeon JE and Byun KS: Hepatic resection compared to
chemoembolization in intermediate- to advanced-stage hepatocellular
carcinoma: A meta-analysis of high-quality studies. Hepatology.
68:977–993. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Trevisani F, Bucci L and Garuti F: Is it
time to extend criteria for hepatic resection in the treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma? Hepatology. 64:2257–2258. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bast RC Jr, Feeney M, Lazarus H, Nadler
LM, Colvin RB and Knapp RC: Reactivity of a monoclonal antibody
with human ovarian carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 68:1331–1337. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bast RC Jr, Klug TL, St John E, Jenison E,
Niloff JM, Lazarus H, Berkowitz RS, Leavitt T, Griffiths CT, Parker
L, et al: A radioimmunoassay using a monoclonal antibody to monitor
the course of epithelial ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 309:883–887.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang Y, Zeng J, Liu T, Lin X, Guo P, Zeng
J, Zhou W and Liu J: Prognostic significance of elevated
preoperative serum CA125 levels after curative hepatectomy for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 13:4559–4567. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen K, Gentry-Maharaj A, Burnell M,
Steentoft C, Marcos-Silva L, Mandel U, Jacobs I, Dawnay A, Menon U
and Blixt O: Microarray Glycoprofiling of CA125 improves
differential diagnosis of ovarian cancer. J Proteome Res.
12:1408–1418. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li Y, Li DJ, Chen J, Liu W, Li JW, Jiang
P, Zhao X, Guo F, Li XW and Wang SG: Application of Joint Detection
of AFP, CA19-9, CA125 and CEA in identification and diagnosis of
cholangiocarcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:3451–3455. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu LX, Li XF, Chen HF, Zhu YC, Wang WX, Xu
CW, Xie DF, Wan Y and Du KQ: Combined detection of CEA and CA125
for the diagnosis for lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-grand). 64:67–70. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Devarbhavi H, Kaese D, Williams AW, Rakela
J, Klee GG and Kamath PS: Cancer antigen 125 in patients with
chronic liver disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 77:538–541. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bergmann JF, Bidart JM, George M,
Beaugrand M, Levy VG and Bohuon C: Elevation of CA 125 in patients
with benign and malignant ascites. Cancer. 59:213–217. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lopez JB, Balasegaram M and Thambyrajah V:
Serum CA 125 as a marker of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biol
Markers. 11:178–182. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Piñero F, Dirchwolf M and Pessôa MG:
Biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma: Diagnosis, prognosis and
treatment response assessment. Cells. 9:13702020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liang C, Qin Y, Zhang B, Ji S, Shi S, Xu
W, Liu J, Xiang J, Liang D, Hu Q, et al: Oncogenic KRAS Targets
MUC16/CA125 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer Res.
15:201–212. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pradjatmo H and Pradjatmo H: Impact of
preoperative serum levels of CA 125 on epithelial ovarian cancer
survival. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:1881–1886. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Isaksson S, Jönsson P, Monsef N,
Brunnström H, Bendahl PO, Jönsson M, Staaf J and Planck M: CA 19-9
and CA 125 as potential predictors of disease recurrence in
resectable lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 12:e01862842017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou S, Wang Z, Li M and Wu L: Elevated
preoperative serum CA125 predicts larger tumor diameter in patients
with hepatocellular carcinoma and low AFP levels. Biomed Res Int.
2019:69596372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chong CC, Lee KF, Ip PC, Wong JS, Cheung
SY, Wong J, Ho SC and Lai PB: Pre-operative predictors of
post-hepatectomy recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma: Can we
predict earlier? Surgeon. 10:260–266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Terrault NA, Bzowej NH, Chang KM, Hwang
JP, Jonas MM and Murad MH; American Association for the Study of
Liver Diseases, : AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic
hepatitis B. Hepatology. 63:261–283. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Haridas D, Chakraborty S, Ponnusamy MP,
Lakshmanan I, Rachagani S, Cruz E, Kumar S, Das S, Lele SM,
Anderson JM, et al: Pathobiological implications of MUC16
expression in pancreatic cancer. PLoS One. 6:e268392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lakshmanan I, Ponnusamy MP, Das S,
Chakraborty S, Haridas D, Mukhopadhyay P, Lele SM and Batra SK:
MUC16 induced rapid G2/M transition via interactions with JAK2 for
increased proliferation and anti-apoptosis in breast cancer cells.
Oncogene. 31:805–817. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lakshmanan I, Salfity S, Seshacharyulu P,
Rachagani S, Thomas A, Das S, Majhi PD, Nimmakayala RK, Vengoji R,
Lele SM, et al: MUC16 Regulates TSPYL5 for lung cancer cell growth
and chemoresistance by suppressing p53. Clin Cancer Res.
23:3906–3917. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Klug TL, Bast RC Jr, Niloff JM, Knapp RC
and Zurawski VR Jr: Monoclonal antibody immunoradiometric assay for
an antigenic determinant (CA 125) associated with human epithelial
ovarian carcinomas. Cancer Res. 44:1048–1053. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Trevisani F, Garuti F and Neri A:
Alpha-fetoprotein for diagnosis, prognosis, and transplant
selection. Semin Liver Dis. 39:163–177. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu L, Wang Z, Jiang S, Shao B, Liu J,
Zhang S, Zhou Y, Zhou Y and Zhang Y: Perioperative allogenenic
blood transfusion is associated with worse clinical outcomes for
hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 8:e642612013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rao TD, Tian H, Ma X, Yan X, Thapi S,
Schultz N, Rosales N, Monette S, Wang A, Hyman DM, et al:
Expression of the carboxy-terminal portion of MUC16/CA125 induces
transformation and tumor invasion. PLoS One. 10:e01266332015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Das S, Rachagani S, Torres-Gonzalez MP,
Lakshmanan I, Majhi PD, Smith LM, Wagner KU and Batra SK:
Carboxyl-terminal domain of MUC16 imparts tumorigenic and
metastatic functions through nuclear translocation of JAK2 to
pancreatic cancer cells. Oncotarget. 6:5772–5787. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Giannakouros P, Matte I, Rancourt C and
Piche A: Transformation of NIH3T3 mouse fibroblast cells by MUC16
mucin (CA125) is driven by its cytoplasmic tail. Int J Oncol.
46:91–98. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim N, Hong Y, Kwon D and Yoon S: Somatic
mutaome profile in human cancer tissues. Genomics Inform.
11:239–244. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen SH, Hung WC, Wang P, Paul C and
Konstantopoulos K: Mesothelin binding to CA125/MUC16 promotes
pancreatic cancer cell motility and invasion via MMP-7 activation.
Sci Rep. 3:18702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Higashi M, Yamada N, Yokoyama S, Kitamoto
S, Tabata K, Koriyama C, Batra SK and Yonezawa S: Pathobiological
implications of MUC16/CA125 expression in intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma-mass forming type. Pathobiology. 79:101–116.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cotton S, Azevedo R, Gaiteiro C, Ferreira
D, Lima L, Peixoto A, Fernandes E, Neves M, Neves D, Amaro T, et
al: Targeted O-glycoproteomics explored increased sialylation and
identified MUC16 as a poor prognosis biomarker in advanced-stage
bladder tumours. Mol Oncol. 11:895–912. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Belisle JA, Horibata S, Jennifer GA,
Petrie S, Kapur A, André S, Gabius HJ, Rancourt C, Connor J,
Paulson JC and Patankar MS: Identification of Siglec-9 as the
receptor for MUC16 on human NK cells, B cells, and monocytes. Mol
Cancer. 9:1182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gubbels JA, Felder M, Horibata S, Belisle
JA, Kapur A, Holden H, Petrie S, Migneault M, Rancourt C, Connor JP
and Patankar MS: MUC16 provides immune protection by inhibiting
synapse formation between NK and ovarian tumor cells. Mol Cancer.
9:112010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Reinartz S, Failer S, Schuell T and Wagner
U: CA125 (MUC16) gene silencing suppresses growth properties of
ovarian and breast cancer cells. Eur J Cancer. 48:1558–1569. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Peng SY, Chen WJ, Lai PL, Jeng YM, Sheu JC
and Hsu HC: High alpha-fetoprotein level correlates with high
stage, early recurrence and poor prognosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma: Significance of hepatitis virus infection, age, p53 and
beta-catenin mutations. Int J Cancer. 112:44–50. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Edula RG, Muthukuru S, Moroianu S, Wang Y,
Lingiah V, Fung P and Pyrsopoulos NT: CA-125 significance in
cirrhosis and correlation with disease severity and portal
hypertension: A retrospective study. J Clin Transl Hepatol.
6:241–246. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Singhal A, Lander E, Karachristos A, Daly
E, Dowling P, Patel V, Maloo M and Jain A: Elevation of CA 125 and
CA 19-9 in patients with end-stage liver disease. Int J Biol
Markers. 27:e147–e151. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|