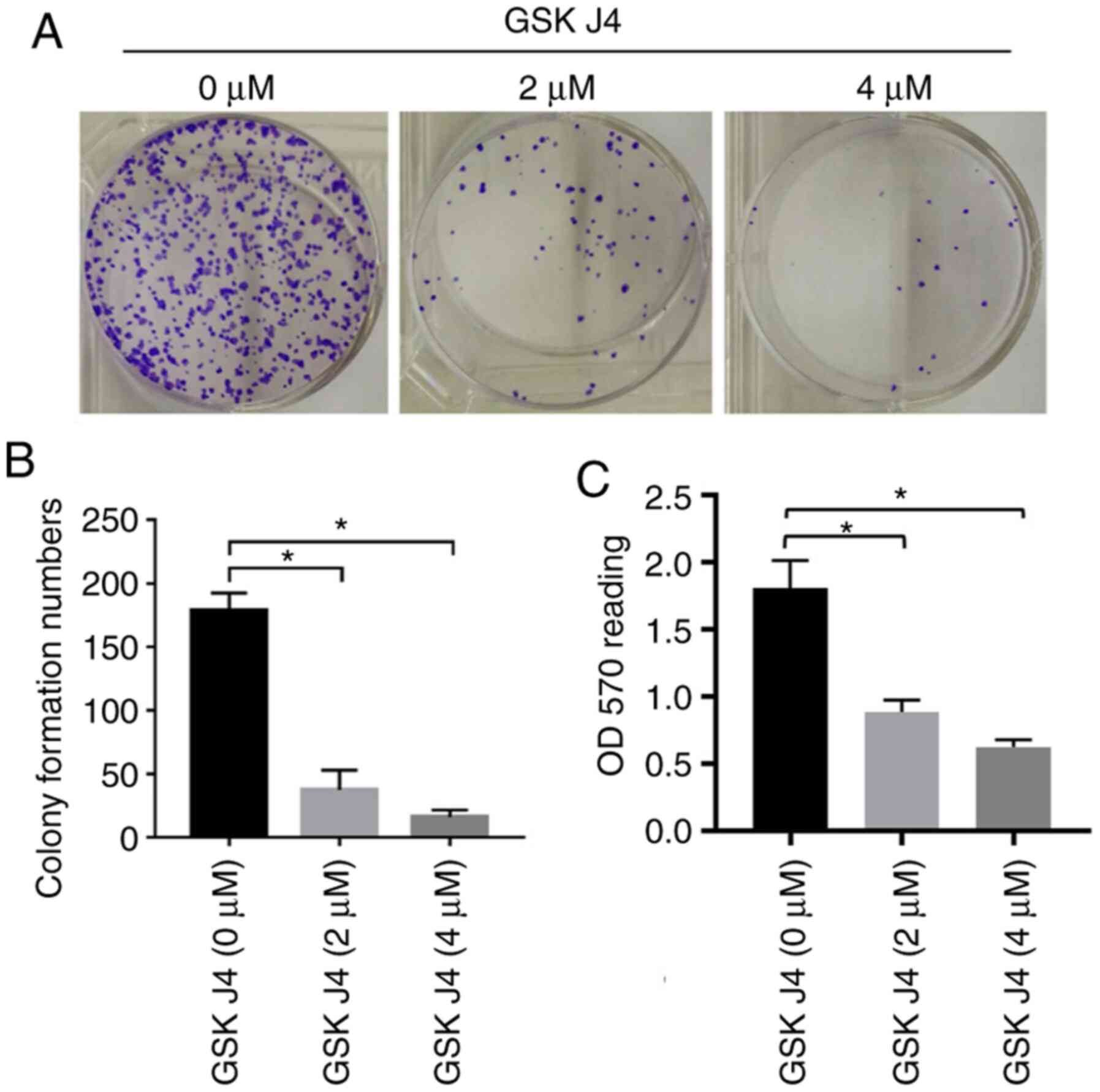
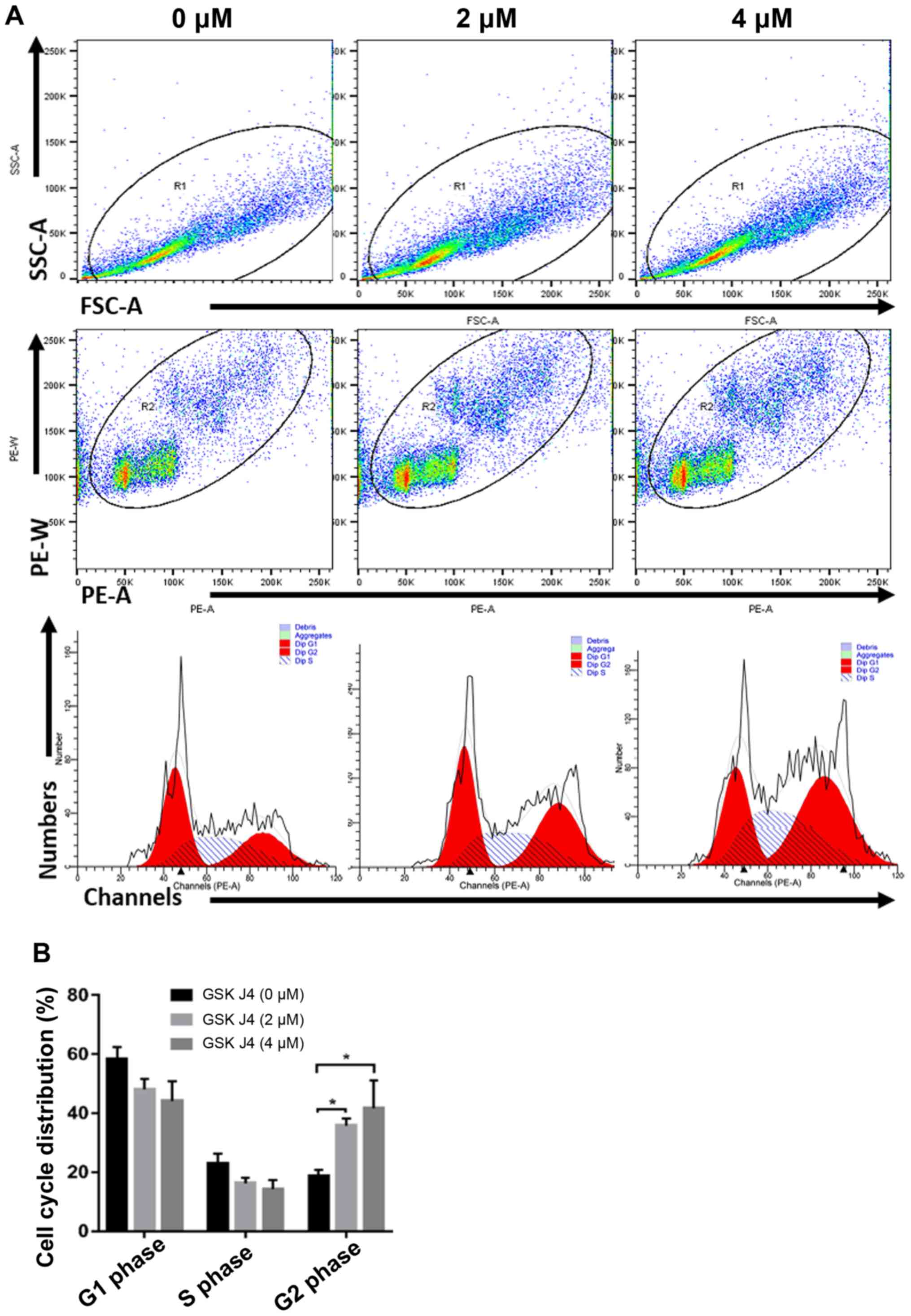
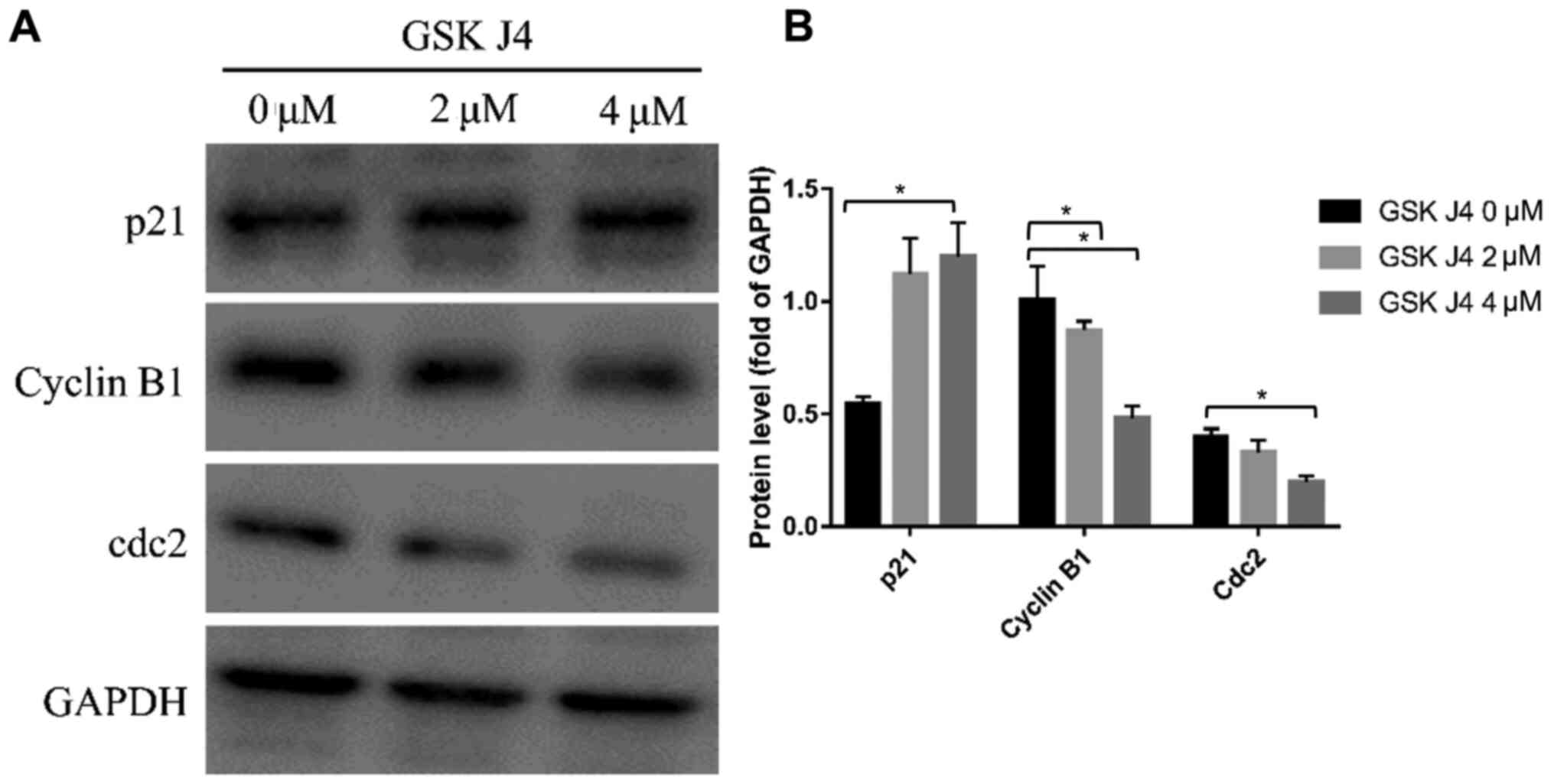
|
1
|
Chen C, Wu M, Zhang W, Lu W, Zhang M,
Zhang Z, Zhang X and Yuan Z: MicroRNA-939 restricts Hepatitis B
virus by targeting Jmjd3-mediated and C/EBPα-coordinated chromatin
remodeling. Sci Rep. 6:359742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang J, Gan L, Wu Z, Yan S, Liu X and Guo
W: The influence of marital status on the stage at diagnosis,
treatment, and survival of adult patients with gastric cancer: A
population-based study. Oncotarget. 8:22385–22405. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yoo C, Ryu MH, Na YS, Ryoo BY, Lee CW and
Kang YK: Vorinostat in combination with capecitabine plus cisplatin
as a first-line chemotherapy for patients with metastatic or
unresectable gastric cancer: Phase II study and biomarker analysis.
Br J Cancer. 114:1185–1190. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Padmanabhan N, Ushijima T and Tan P: How
to stomach an epigenetic insult: The gastric cancer epigenome. Nat
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:467–478. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Liang J and Hou P: Hypermethylation
in gastric cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 448:124–132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang M and Du X: Noncoding RNAs in
gastric cancer: Research progress and prospects. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:6610–6618. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang WY, Gu JL and Zhen TM: Recent
advances of histone modification in gastric cancer. J Cancer Res
Ther. 10 (Suppl):240–245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun DF, Zhang YJ, Tian XQ, Chen YX and
Fang JY: Inhibition of mTOR signalling potentiates the effects of
trichostatin A in human gastric cancer cell lines by promoting
histone acetylation. Cell Biol Int. 38:50–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Akiyama Y, Koda Y, Byeon SJ, Shimada S,
Nishikawaji T, Sakamoto A, Chen Y, Kojima K, Kawano T, Eishi Y, et
al: Reduced expression of SET7/9, a histone mono-methyltransferase,
is associated with gastric cancer progression. Oncotarget.
7:3966–3983. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang ZJ, Yang JL, Wang YP, Lou JY, Chen J,
Liu C and Guo LD: Decreased histone H2B monoubiquitination in
malignant gastric carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 19:8099–8107.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu X, Liu J, Xu X, Zhang C and Dai D:
Genome-wide analysis of histone modifications by ChIP-chip to
identify silenced genes in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 33:2567–2574.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun M, Nie F, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Hou J, He
D, Xie M, Xu L, De W, Wang Z, et al: lncRNA HOXA11-AS Promotes
Proliferation and Invasion of Gastric Cancer by Scaffolding the
Chromatin Modification Factors PRC2, LSD1, and DNMT1. Cancer Res.
76:6299–6310. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Meng CF, Zhu XJ, Peng G and Dai DQ:
Re-expression of methylation-induced tumor suppressor gene
silencing is associated with the state of histone modification in
gastric cancer cell lines. World J Gastroenterol. 13:6166–6171.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song IS, Ha GH, Kim JM, Jeong SY, Lee HC,
Kim YS, Kim YJ, Kwon TK and Kim NS: Human ZNF312b oncogene is
regulated by Sp1 binding to its promoter region through DNA
demethylation and histone acetylation in gastric cancer. Int J
Cancer. 129:2124–2133. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Audia JE and Campbell RM: Histone
Modifications and Cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
8:a0195212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Perrigue PM, Najbauer J and Barciszewski
J: Histone demethylase JMJD3 at the intersection of cellular
senescence and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1865:237–244.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Q, Hou L, Ding G, Li Y, Wang J, Qian B,
Sun J and Wang Q: KDM6B induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and enhances clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis through the
activation of SLUG. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:6334–6344.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xiang Y, Zhu Z, Han G, Lin H, Xu L and
Chen CD: JMJD3 is a histone H3K27 demethylase. Cell Res.
17:850–857. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Shen L, Stupack DG, Bai N, Xun J,
Ren G, Han J, Li L, Luo Y, Xiang R, et al: JMJD3 promotes survival
of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma subtypes via distinct mechanisms.
Oncotarget. 7:29387–29399. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH and
Theise ND: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Digestive System.
3. 4th edition. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon:
2010
|
|
22
|
Otto T and Sicinski P: Cell cycle proteins
as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:93–115.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shmakova A, Batie M, Druker J and Rocha S:
Chromatin and oxygen sensing in the context of JmjC histone
demethylases. Biochem J. 462:385–395. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen S, Ma J, Wu F, Xiong LJ, Ma H, Xu W,
Lv R, Li X, Villen J, Gygi SP, et al: The histone H3 Lys 27
demethylase JMJD3 regulates gene expression by impacting
transcriptional elongation. Genes Dev. 26:1364–1375. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao W, Li Q, Ayers S, Gu Y, Shi Z, Zhu Q,
Chen Y, Wang HY and Wang RF: Jmjd3 inhibits reprogramming by
upregulating expression of INK4a/Arf and targeting PHF20 for
ubiquitination. Cell. 152:1037–1050. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Poreba E, Broniarczyk JK and
Gozdzicka-Jozefiak A: Epigenetic mechanisms in virus-induced
tumorigenesis. Clin Epigenetics. 2:233–247. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Anderton JA, Bose S, Vockerodt M,
Vrzalikova K, Wei W, Kuo M, Helin K, Christensen J, Rowe M, Murray
PG, et al: The H3K27me3 demethylase, KDM6B, is induced by
Epstein-Barr virus and over-expressed in Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Oncogene. 30:2037–2043. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen J: The Cell-Cycle Arrest and
Apoptotic Functions of p53 in Tumor Initiation and Progression.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 6:a0261042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Enyindah-Asonye G, Li Y, Xin W, Singer NG,
Gupta N, Fung J and Lin F: CD6 Receptor Regulates Intestinal
Ischemia/Reperfusion-induced Injury by Modulating Natural
IgM-producing B1a Cell Self-renewal. J Biol Chem. 292:661–671.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Y, Singer NG, Whitbred J, Bowen MA, Fox
DA and Lin F: CD6 as a potential target for treating multiple
sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:2687–2692. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yan N, Xu L, Wu X, Zhang L, Fei X, Cao Y
and Zhang F: GSKJ4, an H3K27me3 demethylase inhibitor, effectively
suppresses the breast cancer stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 359:405–414.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sedrak H, El-Garem N, Naguib M, El-Zawahry
H, Esmat M and Rashed L: Vascular endothelial growth factor before
and after locoregional treatment and its relation to treatment
response in hepatocelluar carcinoma patients. Asian Pacific Journal
of Tropical Biomedicine. 5:1005–1009. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ha SD, Cho W and Kim SO: HDAC8 Prevents
Anthrax Lethal Toxin-induced Cell Cycle Arrest through Silencing
PTEN in Human Monocytic THP-1 Cells. Toxins (Basel). 9:E1622017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kennedy R and Klein U: Aberrant Activation
of NF-κB Signalling in Aggressive Lymphoid Malignancies. Cells.
7:E1892018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Staudt LM: Oncogenic activation of
NF-kappaB. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2:a0001092010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tang B, Qi G, Tang F, Yuan S, Wang Z,
Liang X, Li B, Yu S, Liu J, Huang Q, et al: Aberrant JMJD3
Expression Upregulates Slug to Promote Migration, Invasion, and
Stem Cell-Like Behaviors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res.
76:6520–6532. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yin X, Yang S, Zhang M and Yue Y: The role
and prospect of JMJD3 in stem cells and cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 118:1093842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Aguirre-Gamboa R, Gomez-Rueda H,
Martínez-Ledesma E, Martínez-Torteya A, Chacolla-Huaringa R,
Rodriguez-Barrientos A, Tamez-Peña JG and Treviño V: SurvExpress:
An online biomarker validation tool and database for cancer gene
expression data using survival analysis. PLoS One. 8:e742502013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Goswami CP and Nakshatri H: PROGgeneV2:
Enhancements on the existing database. BMC Cancer. 14:9702014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Goldman M, Craft B, Swatloski T, Cline M,
Morozova O, Diekhans M, Haussler D and Zhu J: The UCSC Cancer
Genomics Browser: Update 2015. Nucleic Acids Res. 43D:D812–D817.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res.
45W:W98–W102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: UALCAN: A Portal for Facilitating Tumor Subgroup Gene
Expression and Survival Analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vasaikar SV, Straub P, Wang J and Zhang B:
LinkedOmics: Analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer
types. Nucleic Acids Res. 46D:D956–D963. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|