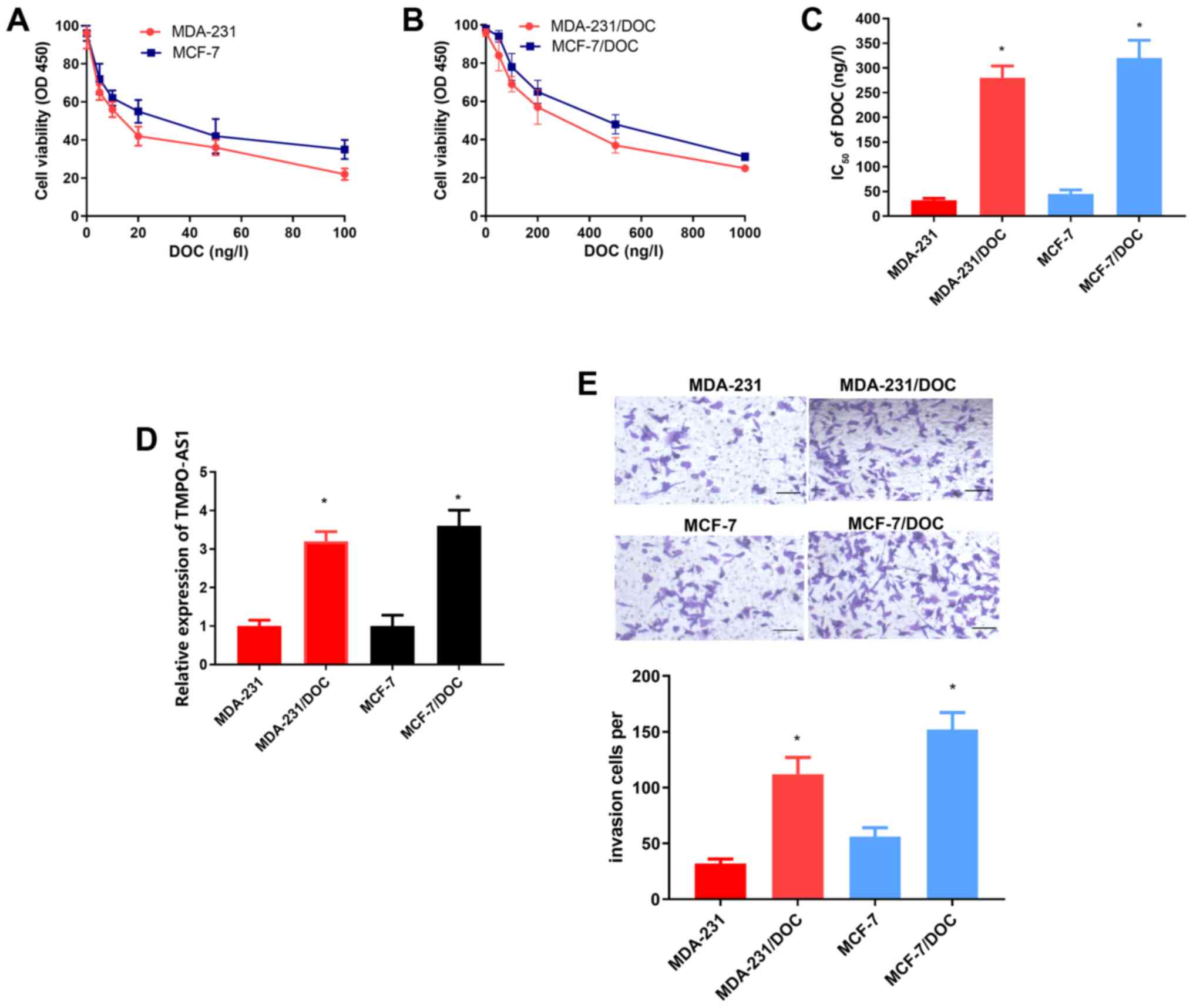
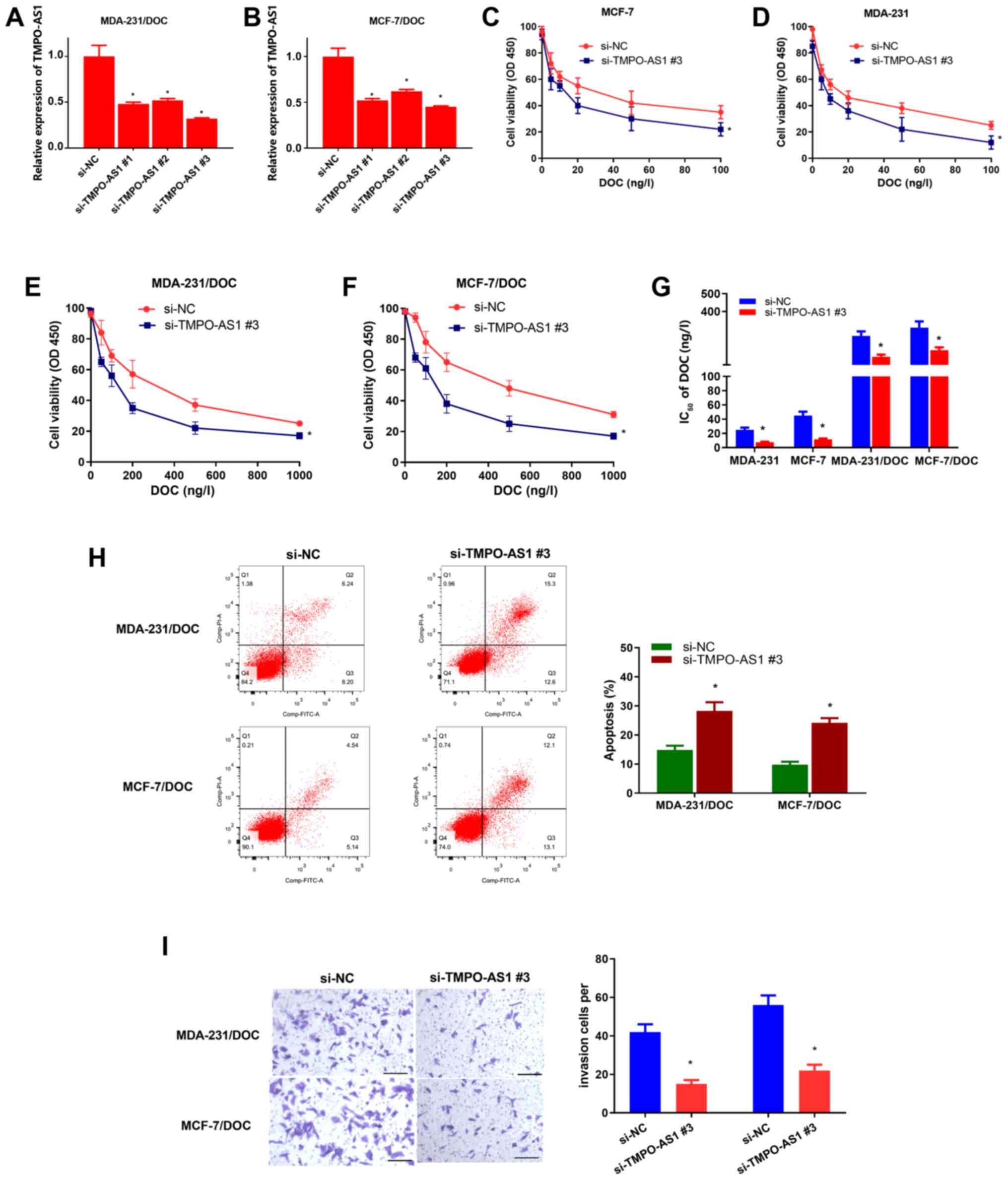
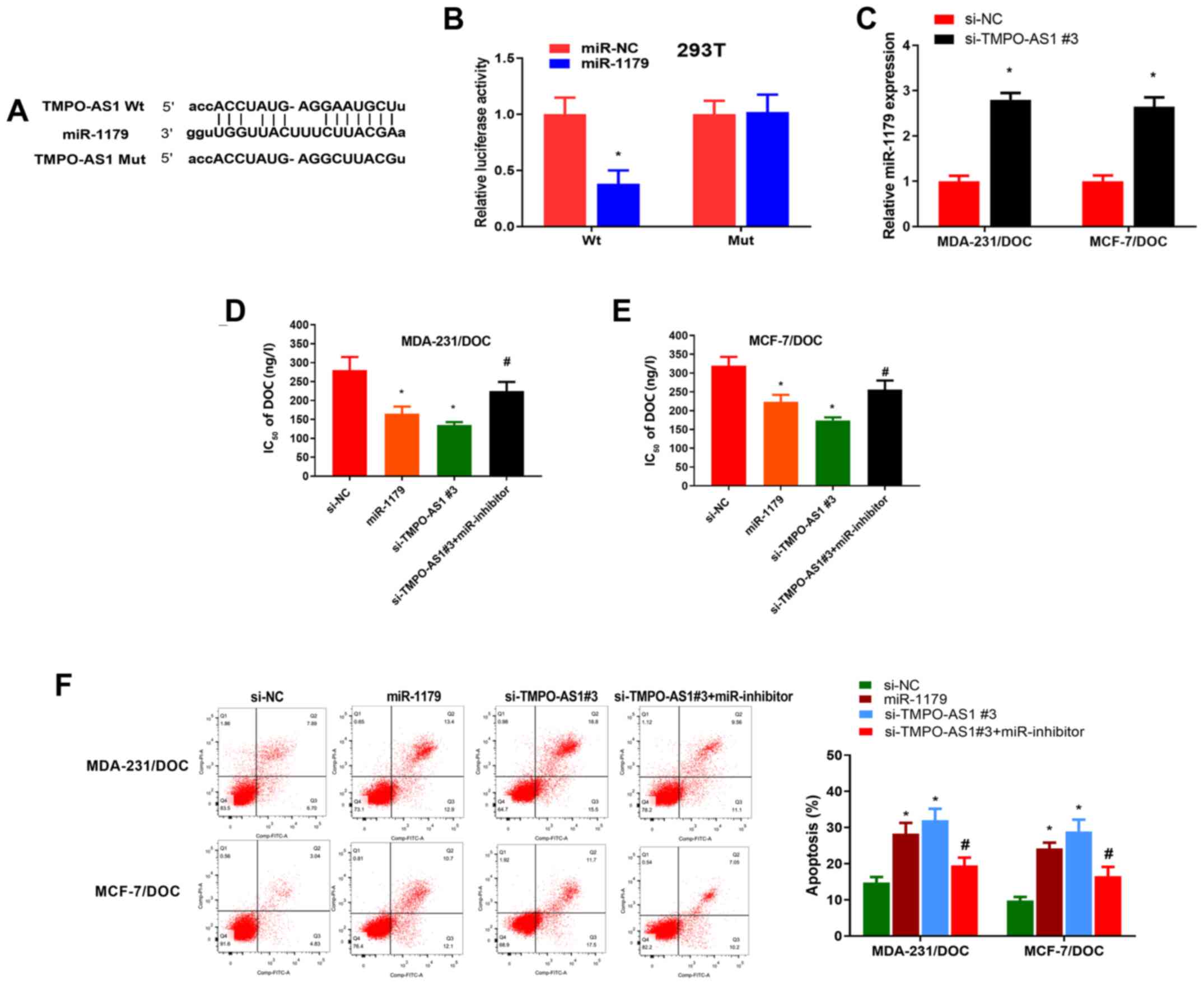
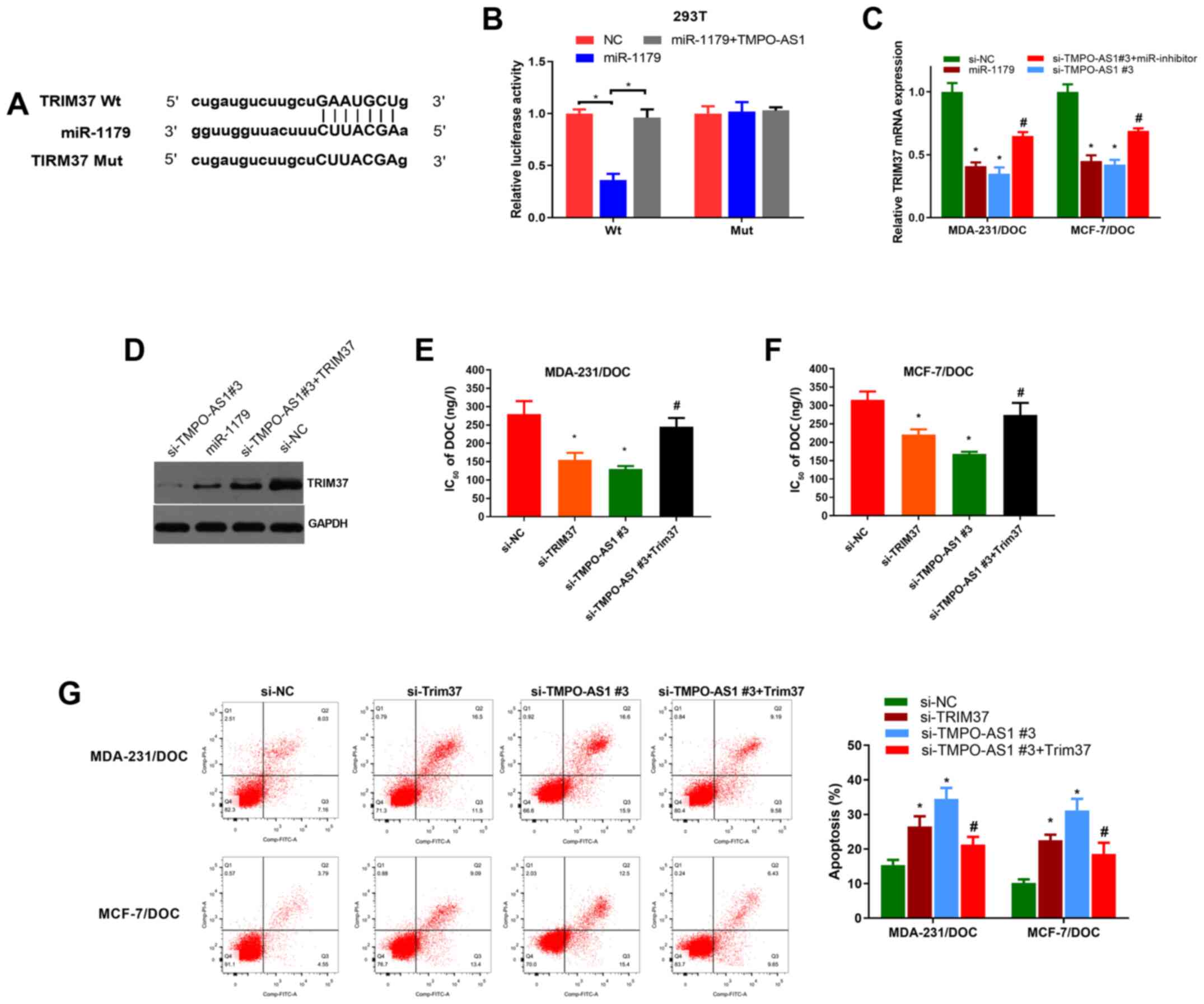
|
1
|
Merino Bonilla JA, Torres Tabanera M and
Ros Mendoza LH: Breast cancer in the 21st century: From early
detection to new therapies. Radiologia. 59:368–379. 2017.(In
English, Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fan L, Strasser Weippl K, Li JJ, St Louis
J, Finkelstein DM, Yu KD, Chen WQ, Shao ZM and Goss PE: Breast
cancer in China. Lancet Oncol. 15:e279–e289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Goetz MP, Gradishar WJ, Anderson BO,
Abraham J, Aft R, Allison KH, Blair SL, Burstein HJ, Dang C, Elias
AD, et al: NCCN guidelines insights: Breast cancer, version 3.2018.
J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 17:118–126. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang M, Li Y, Shen X, Ruan Y, Lu Y, Jin X,
Song P, Guo Y, Zhang X, Qu H, et al: CLDN6 promotes chemoresistance
through GSTP1 in human breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
36:1572017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jarroux J, Morillon A and Pinskaya M:
History, discovery, and classification of lncRNAs. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1008:1–46. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huarte M: The emerging role of lncRNAs in
cancer. Nat Med. 21:1253–1261. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peng WX, Koirala P and Mo YY:
LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene.
36:5661–5667. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiao J, Lv Y, Jin F, Liu Y, Ma Y, Xiong Y,
Liu L, Zhang S, Sun Y, Tipoe GL, et al: LncRNA HANR promotes
tumorigenesis and increase of chemoresistance in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:1926–1938. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han P, Li JW, Zhang BM, Lv JC, Li YM, Gu
XY, Yu ZW, Jia YH, Bai XF, Li L, et al: The lncRNA CRNDE promotes
colorectal cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance via
miR-181a-5p-mediated regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol
Cancer. 16:92017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
YiRen H, YingCong Y, Sunwu Y, Keqin L,
Xiaochun T, Senrui C, Ende C, XiZhou L and Yanfan C: Long noncoding
RNA MALAT1 regulates autophagy associated chemoresistance via
miR-23b-3p sequestration in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 16:1742017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fang Z, Zhao J, Xie W, Sun Q, Wang H and
Qiao B: LncRNA UCA1 promotes proliferation and cisplatin resistance
of oral squamous cell carcinoma by sunppressing miR-184 expression.
Cancer Med. 6:2897–2908. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li DS, Ainiwaer JL, Sheyhiding I, Zhang Z
and Zhang LW: Identification of key long non-coding RNAs as
competing endogenous RNAs for miRNA-mRNA in lung adenocarcinoma.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:2285–2295. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peng F, Wang R, Zhang Y, Zhao Z, Zhou W,
Chang Z, Liang H, Zhao W, Qi L, Guo Z and Gu Y: Differential
expression analysis at the individual level reveals a lncRNA
prognostic signature for lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer.
16:982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang W, Su X, Yan W, Kong Z, Wang D,
Huang Y, Zhai Q, Zhang X, Wu H, Li Y, et al: Overexpression of
AR-regulated lncRNA TMPO-AS1 correlates with tumor progression and
poor prognosis in prostate cancer. Prostate. 78:1248–1261. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bhatnagar S and Green MR: TRIMming down
tumor suppressors in breast cancer. Cell Cycle. 14:1345–1346. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu Y, Yang Y and Liu Y, Hao Y, Zhang Y, Hu
Y, Jiang L, Gong Y, Wu K and Liu Y: Upregulation of PAG1/Cbp
contributes to adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promoted
tumor progression and chemoresistance in breast cancer. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 494:719–727. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guttman M and Rinn JL: Modular regulatory
principles of large non-coding RNAs. Nature. 482:339–346. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gooding AJ, Zhang B, Gunawardane L, Beard
A, Valadkhan S and Schiemann WP: The lncRNA BORG facilitates the
survival and chemoresistance of triple-negative breast cancers.
Oncogene. 38:2020–2041. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dong H, Wang W, Mo S, Chen R, Zou K, Han
J, Zhang F and Hu J: SP1-induced lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 expression
promotes chemoresistance of breast cancer by epigenetic regulation
of MyD88. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:2022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang R, Zhang T, Yang Z, Jiang C and Seng
J: Long non-coding RNA FTH1P3 activates paclitaxel resistance in
breast cancer through miR-206/ABCB1. J Cell Mol Med. 22:4068–4075.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang B, Li Y, Qu X, Zhu H, Tan Y, Fan Q,
Jiang Y, Liao M and Wu X: Long noncoding RNA cancer susceptibility
candidate 9 promotes doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer by binding
to enhancer of zeste homolog 2. Int J Mol Med. 42:2801–2810.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wei L, Liu Y, Zhang H, Ma Y, Lu Z, Gu Z
and Ding C: TMPO-AS1, a novel E2F1-regulated lncRNA, contributes to
the proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma cells via modulating
miR-326/SOX12 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 12:12403–12414. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ding B, Lou W, Xu L and Fan W: Non-coding
RNA in drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci Rep.
38:BSR201809152018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun ZY, Jian YK, Zhu HY and Li B:
lncRNAPVT1 targets miR-152 to enhance chemoresistance of
osteosarcoma to gemcitabine through activating c-MET/PI3K/AKT
pathway. Pathol Res Pract. 215:555–563. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu F, Zha G, Wu Y, Cai W and Ao J:
Overexpressing lncRNA SNHG16 inhibited HCC proliferation and
chemoresistance by functionally sponging hsa-miR-93. Onco Targets
Ther. 11:8855–8863. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gang X, Yuan M and Zhang J: Long
non-coding RNA TMPO-AS1 promotes cervical cancer cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion by regulating
miR-143-3p/ZEB1 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 12:1587–1599. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li WJ, Xie XX, Bai J, Wang C, Zhao L and
Jiang DQ: Increased expression of miR-1179 inhibits breast cancer
cell metastasis by modulating Notch signaling pathway and
correlates with favorable prognosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:8374–8382. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin C, Hu Z, Yuan G, Su H, Zeng Y, Guo Z,
Zhong F, Jiang K and He S: MicroRNA-1179 inhibits the
proliferation, migration and invasion of human pancreatic cancer
cells by targeting E2F5. Chem Biol Interact. 291:65–71. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang J, Yu C, Chen M, Tian S and Sun C:
Over-expression of TRIM37 promotes cell migration and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 464:1120–1127. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hu CE and Gan J: TRIM37 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Mol Med
Rep. 15:1057–1062. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bhatnagar S, Gazin C, Chamberlain L, Ou J,
Zhu X, Tushir JS, Virbasius CM, Lin L, Zhu LJ, Wajapeyee N and
Green MR: TRIM37 is a new histone H2A ubiquitin ligase and breast
cancer oncoprotein. Nature. 516:116–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|