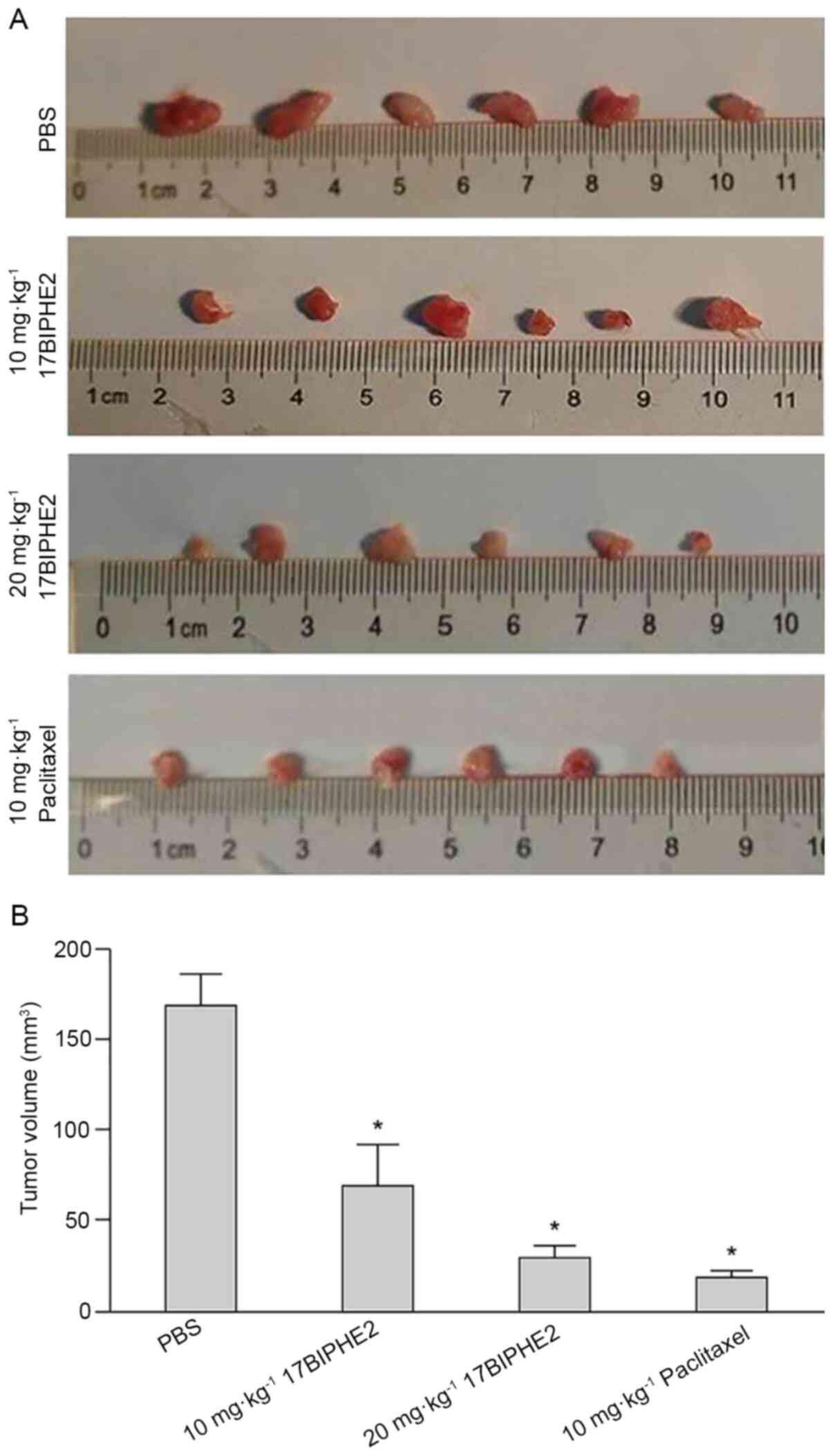
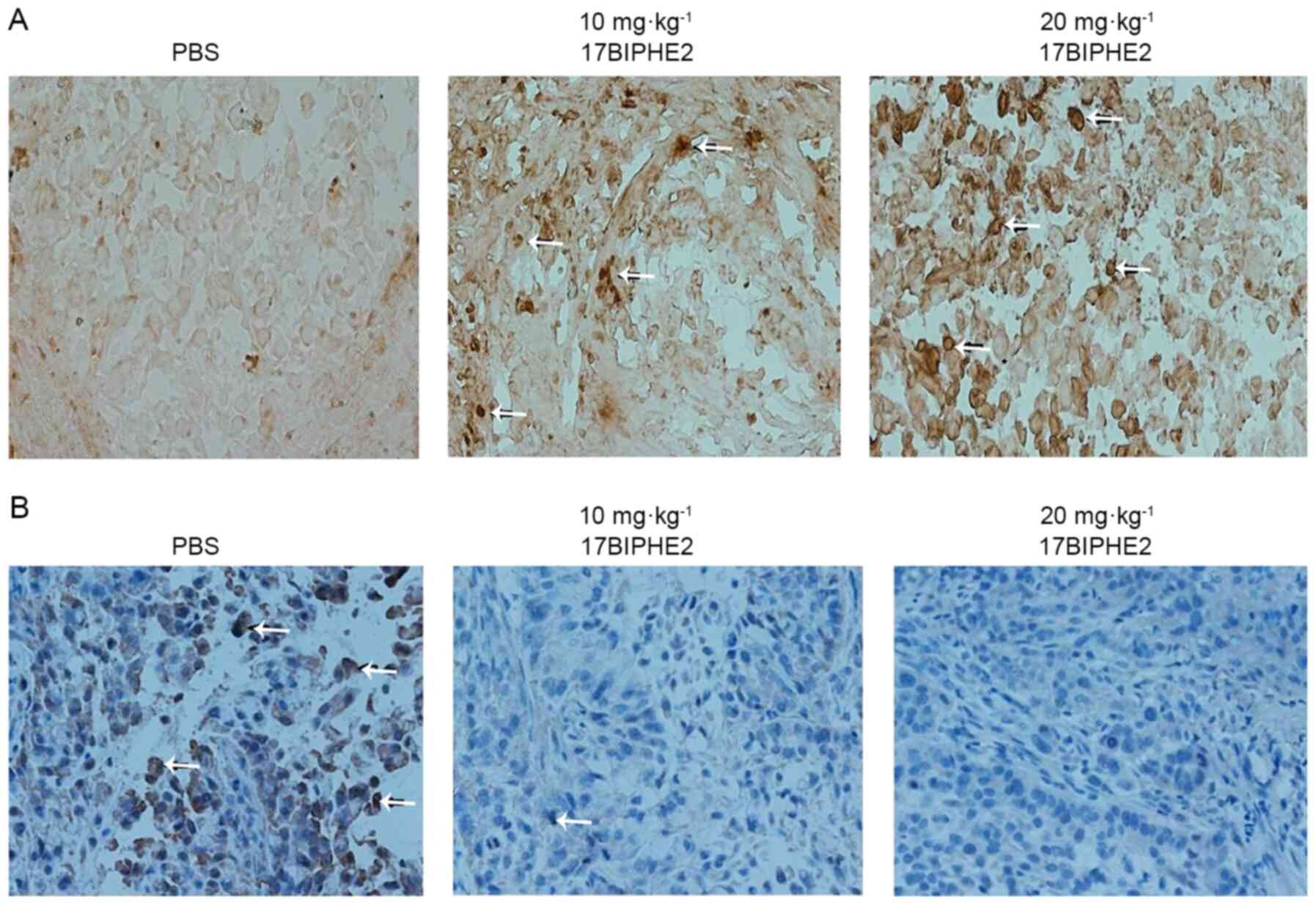
|
1
|
Singh RD, Shandilya R, Bhargava A, Kumar
R, Tiwari R, Chaudhury K, Srivastava RK, Goryacheva IY and Mishra
PK: Quantum dot based nano-biosensors for detection of circulating
cell free miRNAs in lung carcinogenesis: From Biology to Clinical
translation. Front Genet. 9:6162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fahy RJ and Wewers MD: Pulmonary defense
and the human cathelicidin hCAP-18/LL-37. Immunol Res. 31:75–89.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gennaro R and Zanetti M: Structural
features and biological activities of the cathelicidin-derived
antimicrobial peptides. Biopolymers. 55:31–49. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang X, Mishra B, Lushnikova T, Narayana
JL and Wang G: Amino acid composition determines peptide activity
spectrum and hot-spot-based design of merecidin. Adv Biosyst.
2:17002592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang G, Hanke ML, Mishra B, Lushnikova T,
Heim CE, Chittezham Thomas V, Bayles KW and Kielian T:
Transformation of human cathelicidin LL-37 into selective, stable,
and potent antimicrobial compounds. ACS Chem Biol. 9:1997–2002.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zasloff M: Antimicrobial peptides of
multicellular organisms. Nature. 415:389–395. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mader JS, Mookherjee N, Hancock RE and
Bleackley RC: The human host defense peptide LL-37 induces
apoptosis in a calpain- and apoptosis-inducing factor-dependent
manner involving Bax activity. Mol Cancer Res. 7:689–702. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu Z, Zhang F, Bai C, Yao C, Zhong H, Zou
C and Chen X: Sophoridine induces apoptosis and S phase arrest via
ROS-dependent JNK and ERK activation in human pancreatic cancer
cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:1242017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH,
Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M,
Tafuri A, et al: Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth,
malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1773:1263–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Le Chevalier T: Adjuvant chemotherapy for
resectable non-small-cell lung cancer: Where is it going? Ann
Oncol. 21 (Suppl 7):vii196–vii198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hu L, Zhang T, Liu D, Guan G, Huang J,
Proksch P, Chen X and Lin W: Notoamide-type alkaloid induced
apoptosis and autophagy via a P38/JNK signaling pathway in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. RSC Adv. 9:19855–19868. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tian SW, Ren Y, Pei JZ, Ren BC and He Y:
Pigment epithelium-derived factor protects retinal ganglion cells
from hypoxia-induced apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial
dysfunction. Int J Ophthalmol. 10:1046–1054. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kang J, Dietz MJ and Li B: Antimicrobial
peptide LL-37 is bactericidal against Staphylococcus aureus
biofilms. PLoS One. 14:e02166762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ko JK and Zhang Z: LL-37 inhibits
pancreatic cancer development through inhibition of autophagy and
reprogramming of the tumor microenvironment. Pergamon. 110:S5–S6.
2019.
|
|
16
|
Agerberth B, Charo J, Werr J, Olsson B,
Idali F, Lindbom L, Kiessling R, Jörnvall H, Wigzell H and
Gudmundsson GH: The human antimicrobial and chemotactic peptides
LL-37 and alpha-defensins are expressed by specific lymphocyte and
monocyte populations. Blood. 96:3086–3093. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dale BA and Fredericks LP: Antimicrobial
peptides in the oral environment: Expression and function in health
and disease. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 7:119–133. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rico-Mata R, De Leon-Rodriguez LM and
Avila EE: Effect of antimicrobial peptides derived from human
cathelicidin LL-37 on Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. Exp
Parasitol. 133:300–306. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rekha RS, Rao Muvva SS, Wan M, Raqib R,
Bergman P, Brighenti S, Gudmundsson GH and Agerberth B:
Phenylbutyrate induces LL-37-dependent autophagy and intracellular
killing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in human macrophages.
Autophagy. 11:1688–1699. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bucki R, Leszczyńska K, Namiot A and
Sokołowski W: Cathelicidin LL-37: A multitask antimicrobial
peptide. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 58:15–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dosler S and Karaaslan E: Inhibition and
destruction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms by antibiotics and
antimicrobial peptides. Peptides. 62:32–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Amatngalim GD, Nijnik A, Hiemstra PS and
Hancock RE: Cathelicidin Peptide LL-37 Modulates TREM-1 expression
and inflammatory responses to microbial compounds. Inflammation.
34:412–425. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shaykhiev R, Beisswenger C, Kändler K,
Senske J, Püchner A, Damm T, Behr J and Bals R: Human endogenous
antibiotic LL-37 stimulates airway epithelial cell proliferation
and wound closure. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
289:L842–L848. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pan G: Inhibitory effect of antimicrobial
peptide LL-37 on bladder tumor cells (unpublished PhD thesis).
Kunming Medical University; 2015
|
|
25
|
Ren SX, Shen J, Cheng AS, Lu L, Chan RL,
Li ZJ, Wang XJ, Wong CC, Zhang L, Ng SS, et al: FK-16 Derived from
the Anticancer Peptide LL-37 induces caspase-independent apoptosis
and autophagic cell death in colon cancer cells. PLoS One.
8:e636412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Coffelt SB, Waterman RS, Florez L, Höner
zu Bentrup K, Zwezdaryk KJ, Tomchuck SL, LaMarca HL, Danka ES,
Morris CA and Scandurro AB: Ovarian cancers overexpress the
antimicrobial protein hCAP-18 and its derivative LL-37 increases
ovarian cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Int J Cancer.
122:1030–1039. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim JE, Kim HJ, Choi JM, Lee KH, Kim TY,
Cho BK, Jung JY, Chung KY, Cho D and Park HJ: The antimicrobial
peptide human cationic antimicrobial protein-18/cathelicidin LL-37
as a putative growth factor for malignant melanoma. Br J Dermatol.
163:959–967. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Von Haussen J, Koczulla R, Shaykhiev R,
Herr C, Pinkenburg O, Reimer D, Wiewrodt R, Biesterfeld S, Aigner
A, Czubayko F and Bals R: The host defence peptide LL-37/hCAP-18 is
a growth factor for lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. 59:12–23. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chieosilapatham P, Ikeda S, Ogawa H and
Niyonsaba F: Tissue-specific regulation of innate immune responses
by human cathelicidin LL-37. Curr Pharm Des. 24:1079–1091. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ou Hongyu, Zhu Haihong, Zhu Wenjun, et al:
Antimicrobial peptide LL-37 induces apoptosis in AGS cells of
gastric cancer by activating p53 signaling pathway. J Anhui Med
Uni. 56:571–576. 2021.
|
|
31
|
Vandamme D, Landuyt B, Luyten W and
Schoofs L: A comprehensive summary of LL-37, the factotum human
cathelicidin peptide. Cell Immunol. 280:22–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang G: Structures of Human host defense
cathelicidin LL-37 and its smallest antimicrobial peptide KR-12 in
lipid micelles. J Biol Chem. 283:32637–32643. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Doss M, White MR, Tecle T and Hartshorn
KL: Human defensins and LL-37 in mucosal immunity. J Leukoc Biol.
87:79–92. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
An LL, Ma XT, Yang YH, Lin YM, Song YH and
Wu KF: Marked reduction of LL-37/hCAP-18, an antimicrobial peptide,
in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Hematol. 81:45–47.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Choi SY, Kim SJ, Chi BH, Kwon JK and Chang
IH: Modulating the internalization of bacille calmette-guérin by
cathelicidin in bladder cancer cells. Urology. 85:964.e7–964.e12.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ang MK and Mok TSK: Twenty-five years of
Respirology: Advances in lung cancer. Respirology. 25:26–31. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xu N, Jia D, Chen W, Wang H, Liu F, Ge H,
Zhu X, Song Y, Zhang X, Zhang D, et al: FoxM1 is associated with
poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients through
promoting tumor metastasis. PLoS One. 8:e594122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xuan Y, Zhao S, Xiao X, Xiang L and Zheng
HC: Inhibition of chaperone-mediated autophagy reduces tumor growth
and metastasis and promotes drug sensitivity in colorectal cancer.
Mol Med Rep. 23:3602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu WK, Sung JJ, To KF, Yu L, Li HT, Li ZJ,
Chu KM, Yu J and Cho CH: The host defense peptide LL-37 activates
the tumor-suppressing bone morphogenetic protein signaling via
inhibition of proteasome in gastric cancer cells. J Cell Physiol.
223:178–186. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Murray NP, Aedo S, Fuentealba C, Salazar
A, Reyes E, Lopez MA and Minzer S: Circulating prostate cells and
bone marrow micro-metastasis and not treatment modality determine
the risk and time to biochemical failure in low risk prostate
cancer. Arch Esp Urol. 72:1000–1009. 2019.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kaçmaz K
and Linn S: Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the
DNA damage checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem. 73:39–85. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu X, Li J, Huang L, Wang Y, Yang M, Tang
M and Qiu T: Preparation and evaluation of MPEG-PCL polymeric
nanoparticles against gastric cancer. J Wuhan Univ Technol-Mat Sci
Edit. 35:1162–1168. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Tian W, Li B, Zhang X, Dang W, Wang X,
Tang H, Wang L, Cao H and Chen T: Suppression of tumor invasion and
migration in breast cancer cells following delivery of siRNA
against Stat3 with the antimicrobial peptide PR39. Oncol Rep.
28:1362–1368. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhu M, Miao S, Zhou W, Elnesr SS, Dong X
and Zou X: MAPK, AKT/FoxO3a and mTOR pathways are involved in
cadmium regulating the cell cycle, proliferation and apoptosis of
chicken follicular granulosa cells. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf.
214:1120912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bartek J, Lukas C and Lukas J: Checking on
DNA damage in S phase. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 5:792–804. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Al-Ejeh F, Kumar R, Wiegmans A, Lakhani
SR, Brown MP and Khanna KK: Harnessing the complexity of DNA-damage
response pathways to improve cancer treatment outcomes. Oncogene.
29:6085–6098. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Campos A and Clemente-Blanco A: Cell cycle
and DNA repair regulation in the damage response: Protein
phosphatases take over the reins. Int J Mol Sci. 21:4462020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zeng Q: Expression of antimicrobial
peptide LL-37 in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Kunming
Medical University; 2015
|
|
49
|
Su L, Xu G, Shen J, Tuo Y, Zhang X, Jia S,
Chen Z and Su X: Anticancer bioactive peptide suppresses human
gastric cancer growth through modulation of apoptosis and the cell
cycle. Oncol Rep. 23:3–9. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fink SL and Cookson BT: Apoptosis,
pyroptosis, and necrosis: Mechanistic description of dead and dying
eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun. 73:1907–1916. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
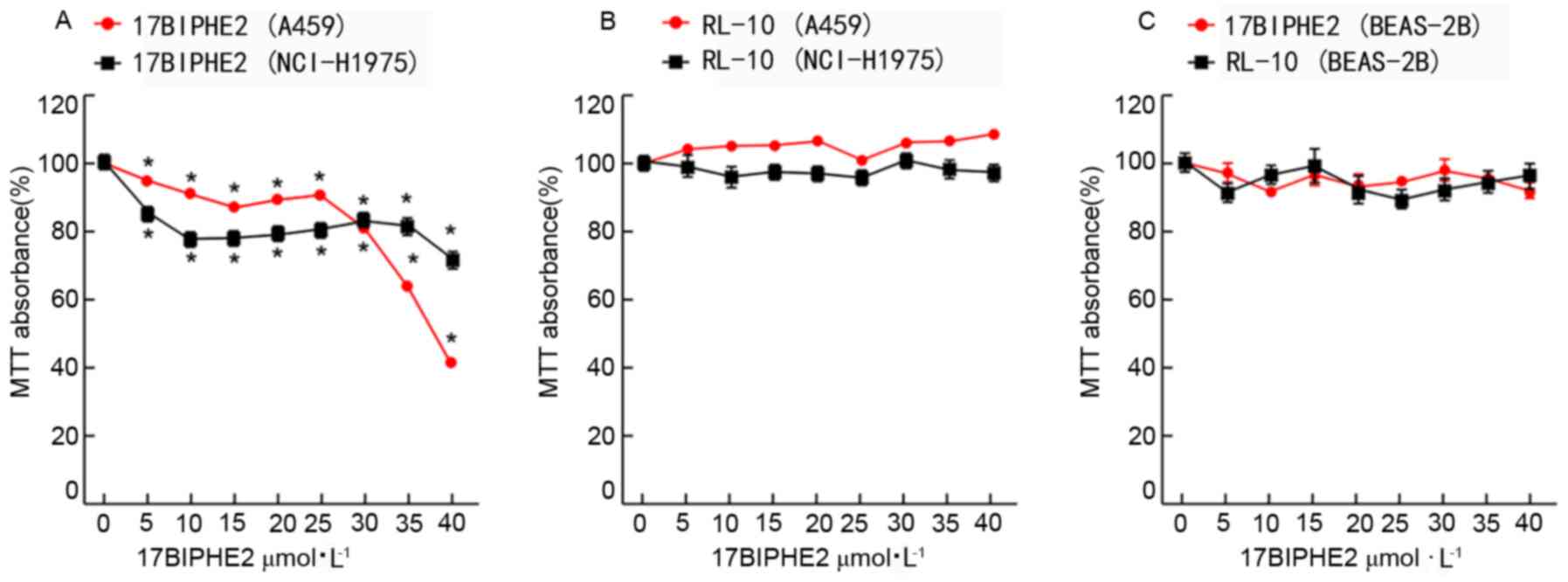
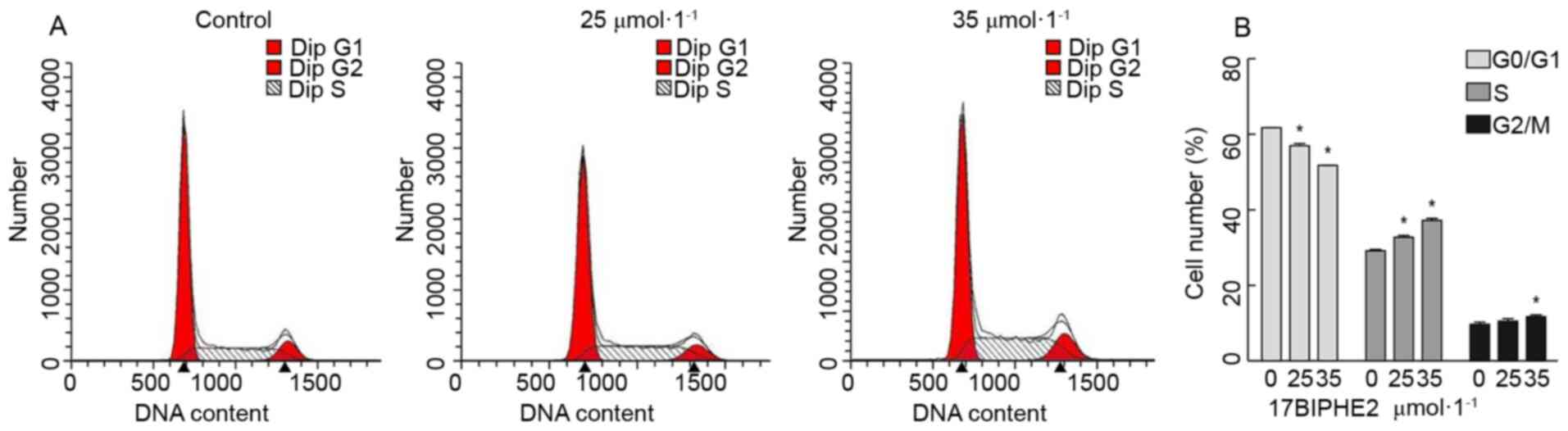
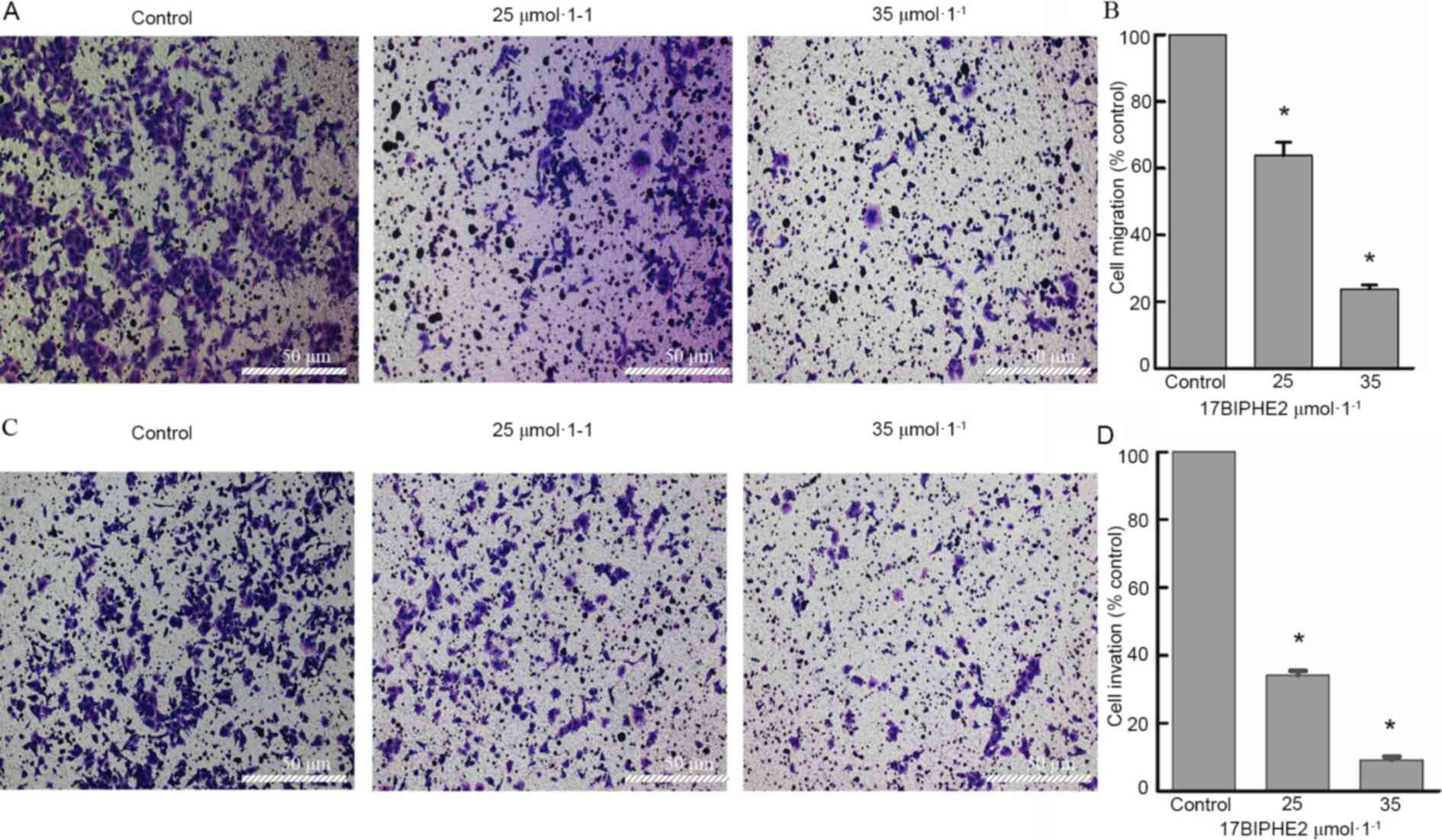
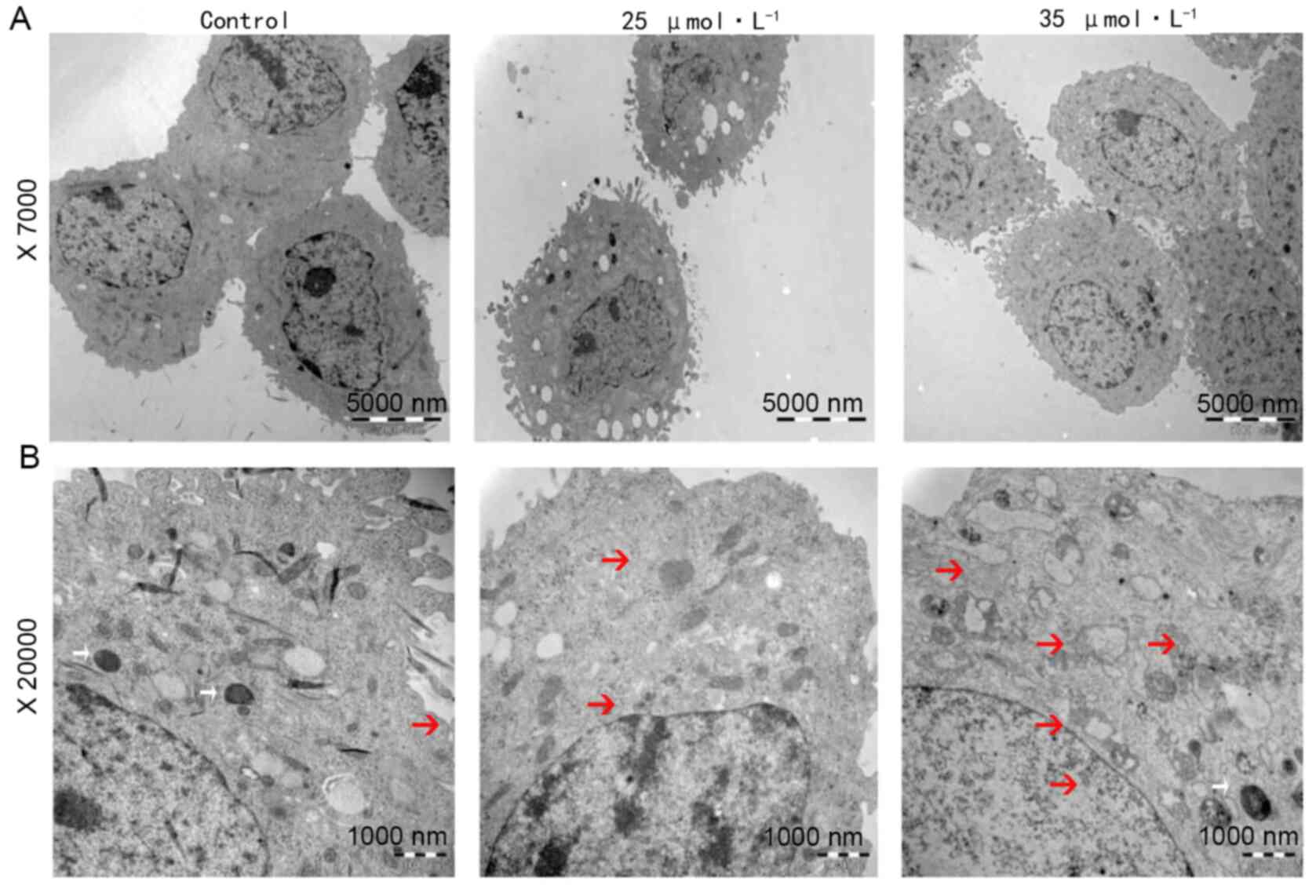
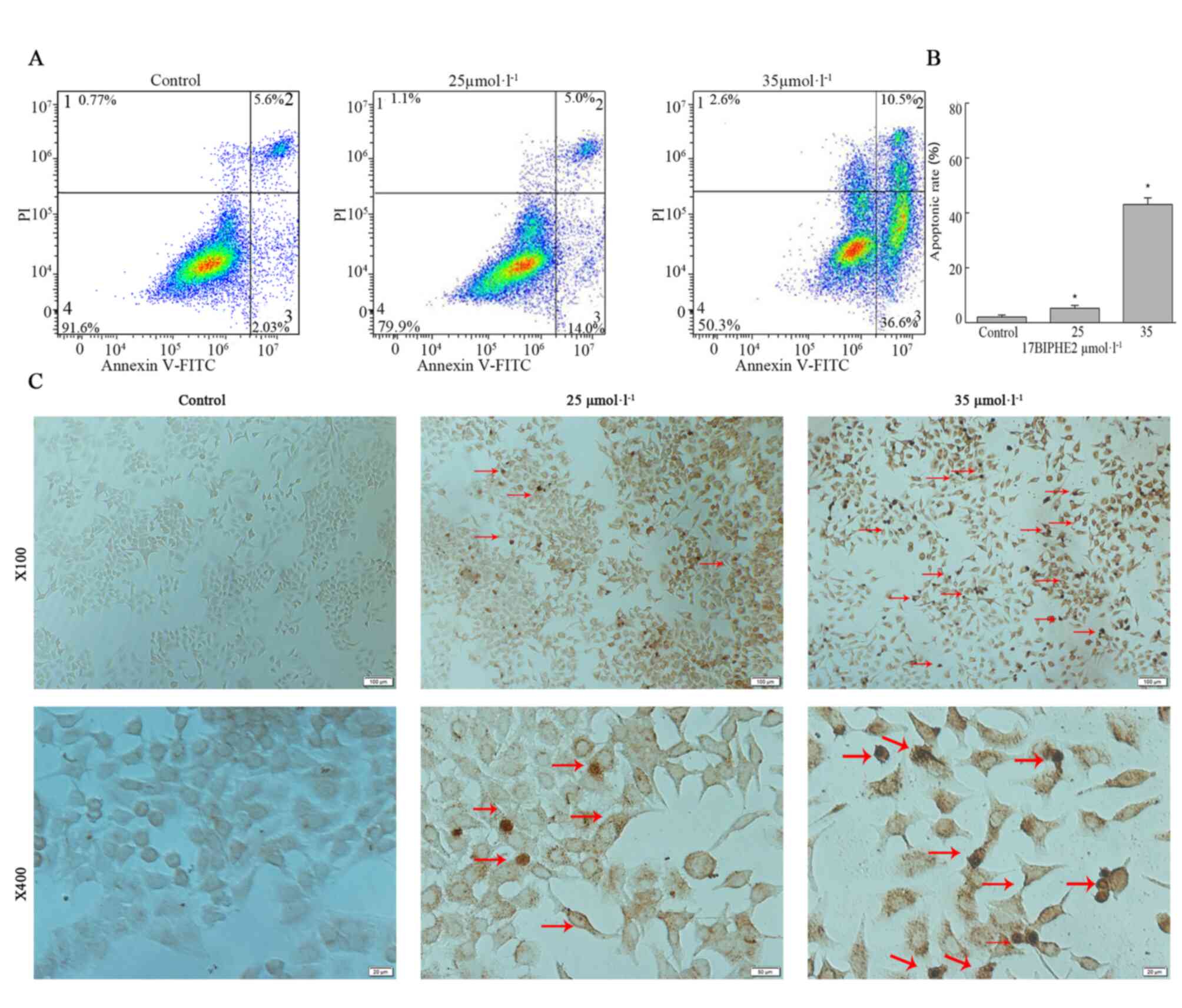
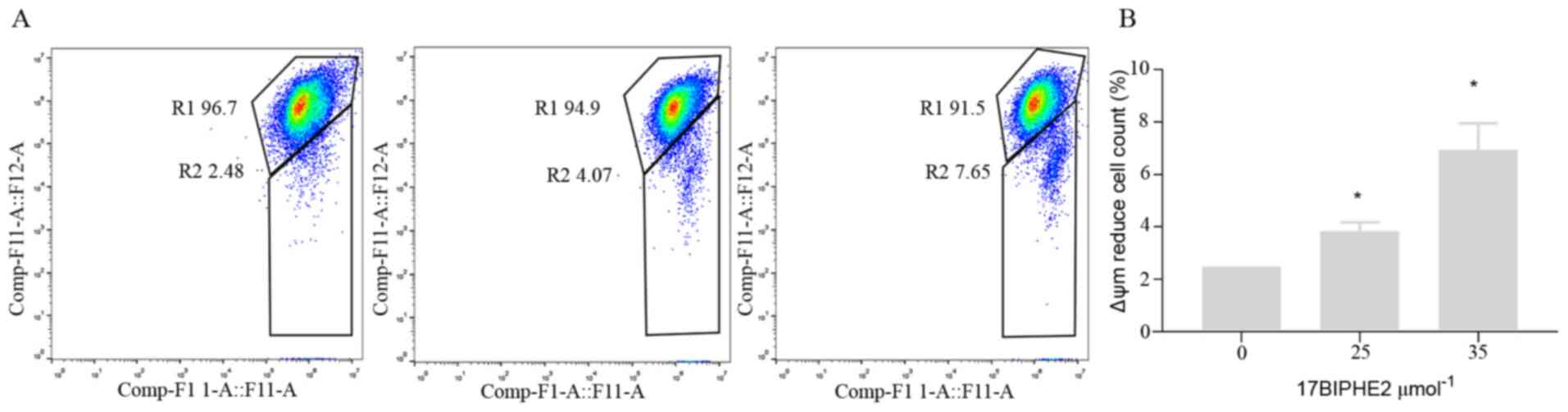
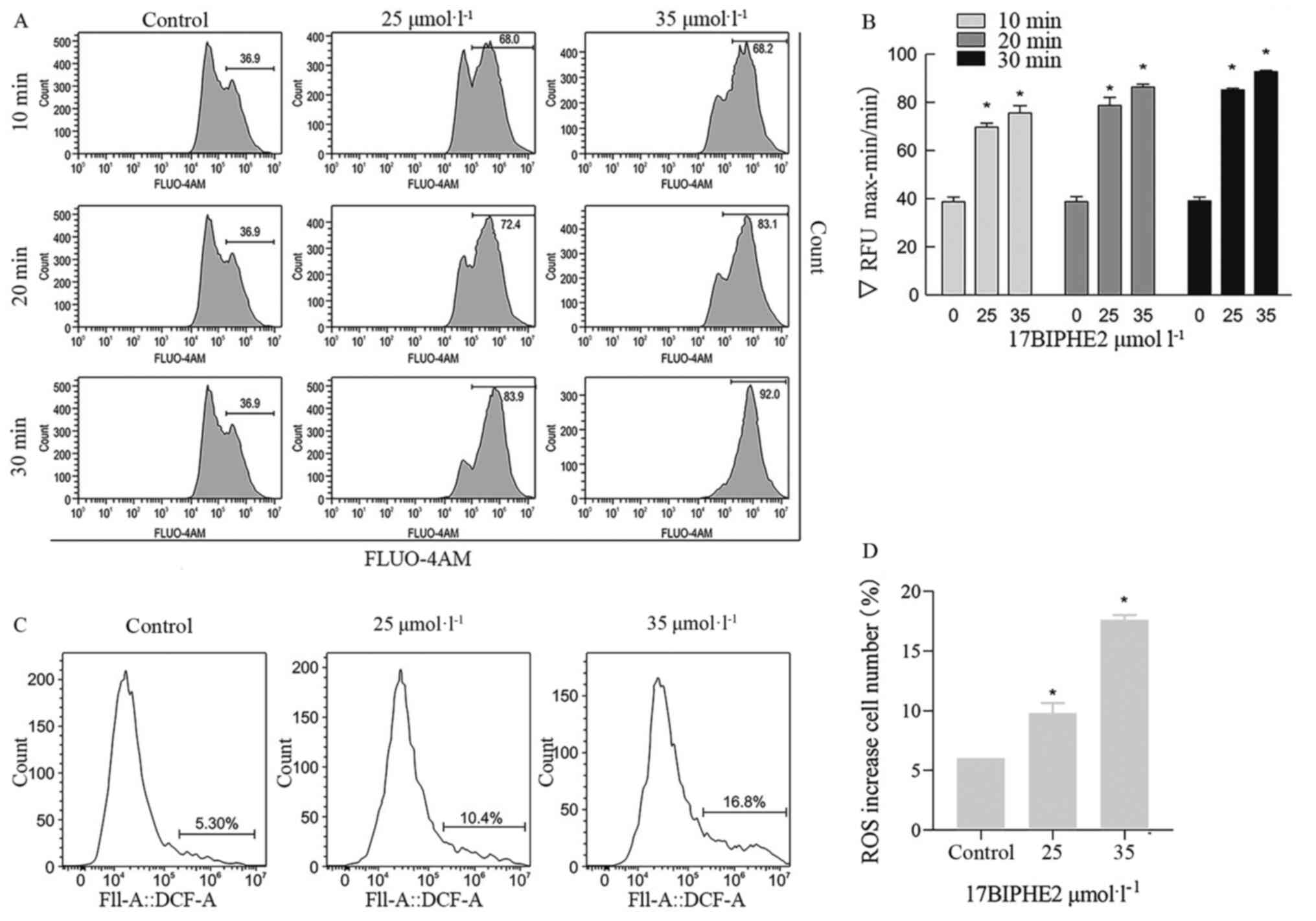
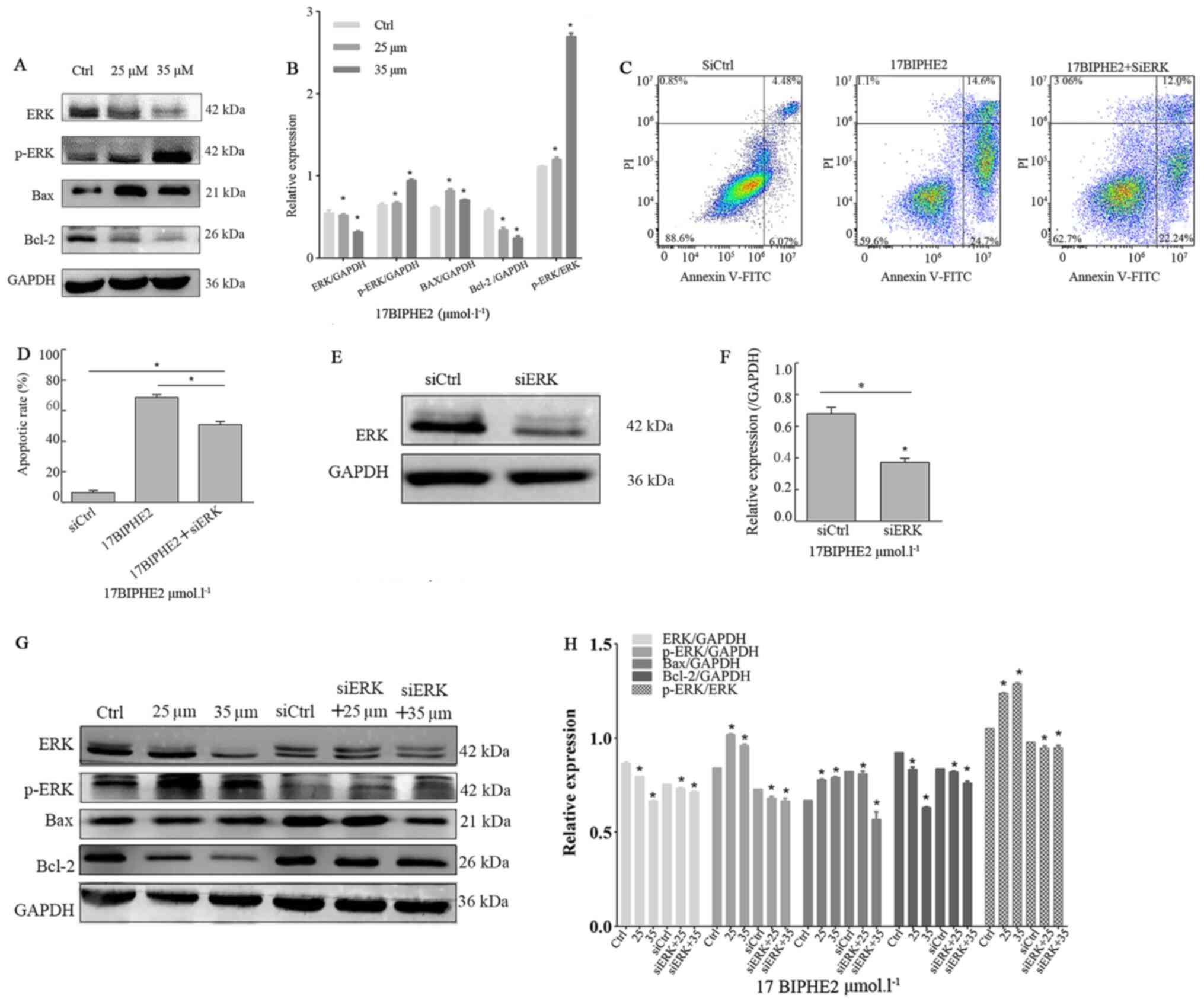
Li Jun: Antimicrobial peptide 17BIPHE2
inhibits lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells and its mechanism. Ningxia
Medical University; 2018
|
|
52
|
Song J, Ham J, Hong T, Song G and Lim W:
Fraxetin suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis
through mitochondria dysfunction in human hepatocellular carcinoma
cell lines Huh7 and Hep3B. Pharmaceutics. 13:1122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chuang KC, Chen FW, Tsai MH and Shieh JJ:
EGR-1 plays a protective role in AMPK inhibitor compound C-induced
apoptosis through ROS-induced ERK activation in skin cancer cells.
Oncol Lett. 21:3042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Schwartz GK and Shah MA: Targeting the
cell cycle: A new approach to cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol.
23:9408–9421. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Dong Y, Yang Y, Wei Y, Gao Y, Jiang W,
Wang G and Wang D: Facile synthetic nano-curcumin encapsulated
Bio-fabricated nanoparticles induces ROS-mediated apoptosis and
migration blocking of human lung cancer cells. Process
Biochemistry. 95:91–98. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Hong Y, Sun Y, Rong X, Li D, Lu Y and Ji
Y: Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells attenuate UVB-induced
apoptosis, ROS, and the Ca2+ level in HLEC cells. Exp
Cell Res. 396:1123212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wang CL, Liu C, Niu LL, Wang LR, Hou LH
and Cao XH: Surfactin-induced apoptosis through ROS-ERS-Ca2+-ERK
pathways in HepG2 cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. 67:1433–1439. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kuriyama I, Miyazaki A, Tsuda Y, Yoshida H
and Mizushina Y: Inhibitory effect of novel somatostatin peptide
analogues on human cancer cell growth based on the selective
inhibition of DNA polymerase β. Bioorg Med Chem. 21:403–411. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Cabrera Zapata LE, Bollo M and Cambiasso
MJ: Estradiol-mediated axogenesis of hypothalamic neurons requires
ERK1/2 and ryanodine receptors-dependent intracellular
Ca2+ rise in male rats. Front Cell Neurosci. 13:1222019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu Y, et al: HSV-2 miR-H4-5p negatively
regulates CDKL2 gene expression, blocking actinomycin D
(ActD)-induced apoptosis in vero cells. Chin J Biochem Mol Bio.
17:9728–9735. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Desagher S and Martinou JC: Mitochondria
as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends in Cell Biol.
10:369–377. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang M, Lu X, Dong X, Hao F, Liu Z, Ni G
and Chen D: pERK1/2 silencing sensitizes pancreatic cancer BXPC-3
cell to gemcitabine-induced apoptosis via regulating Bax and Bcl-2
expression. World J Surg Oncol. 13:662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wang Z, Xu Z, Niu Z, Liang B and Niu J:
Epieriocalyxin A induces cell apoptosis through JNK and ERK1/2
signaling pathways in colon cancer cells. Cell Biochem Biophys.
73:559–564. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|