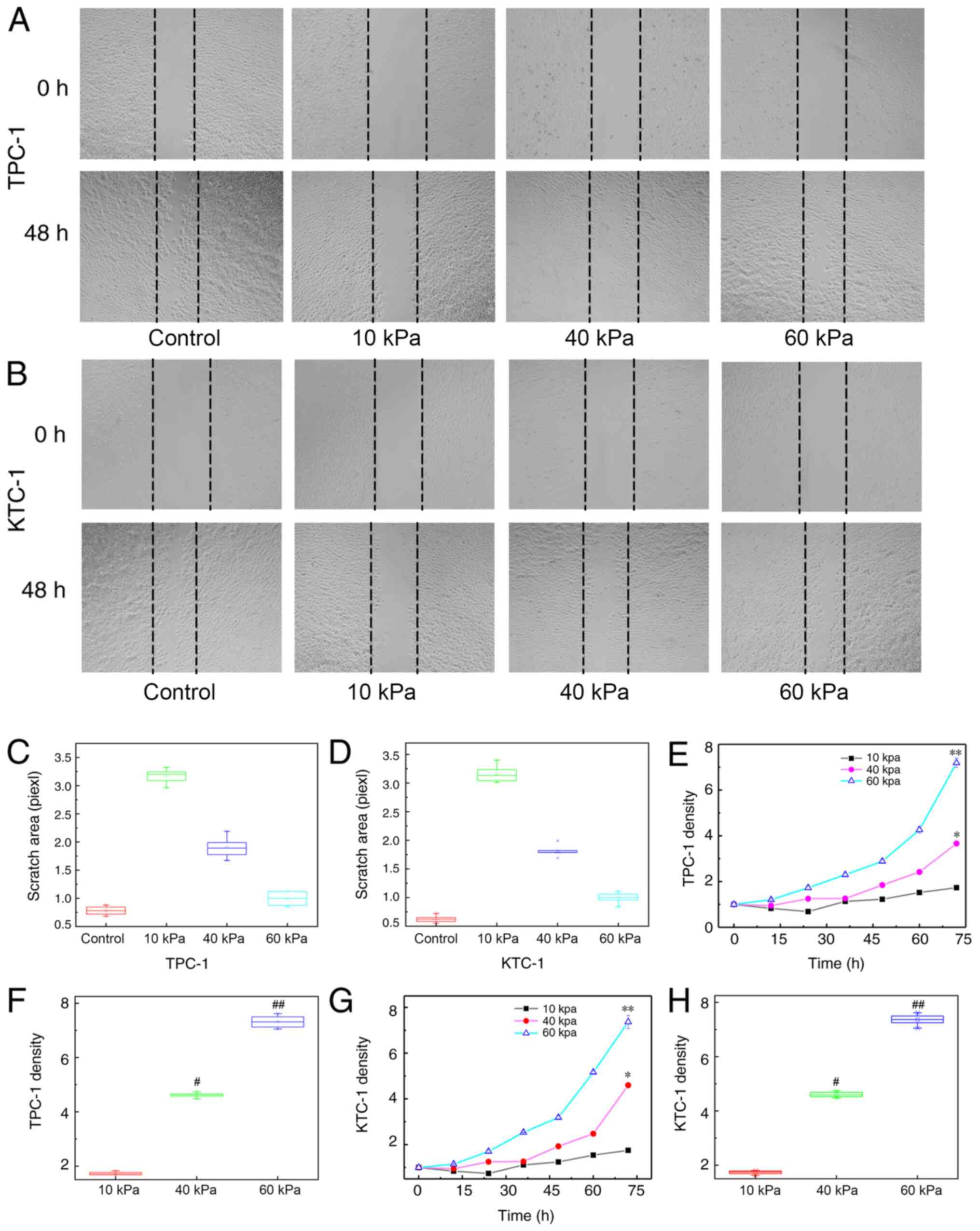
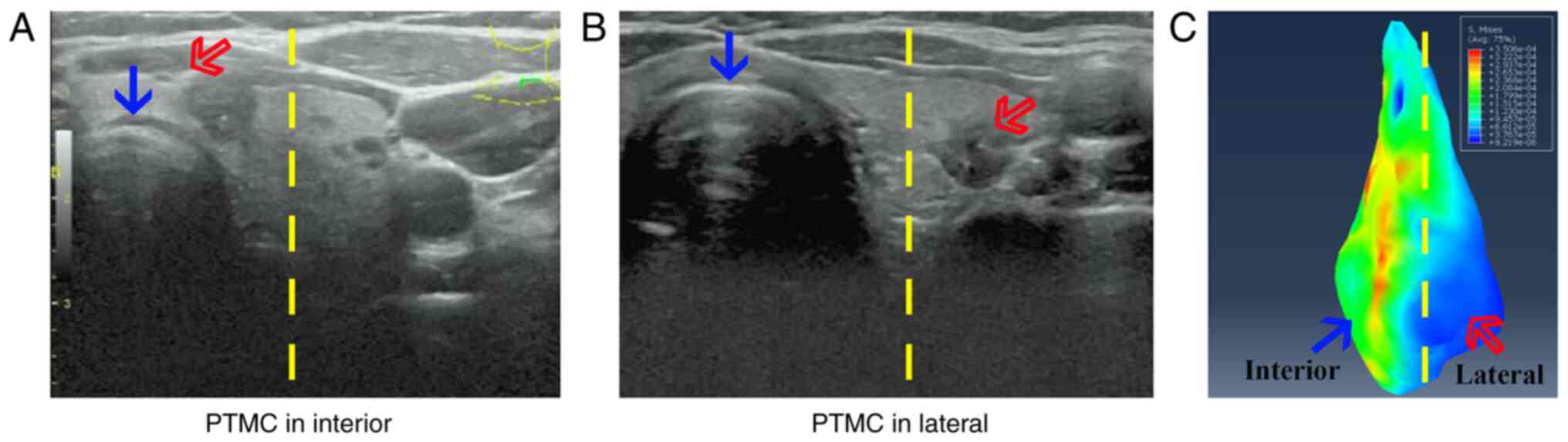
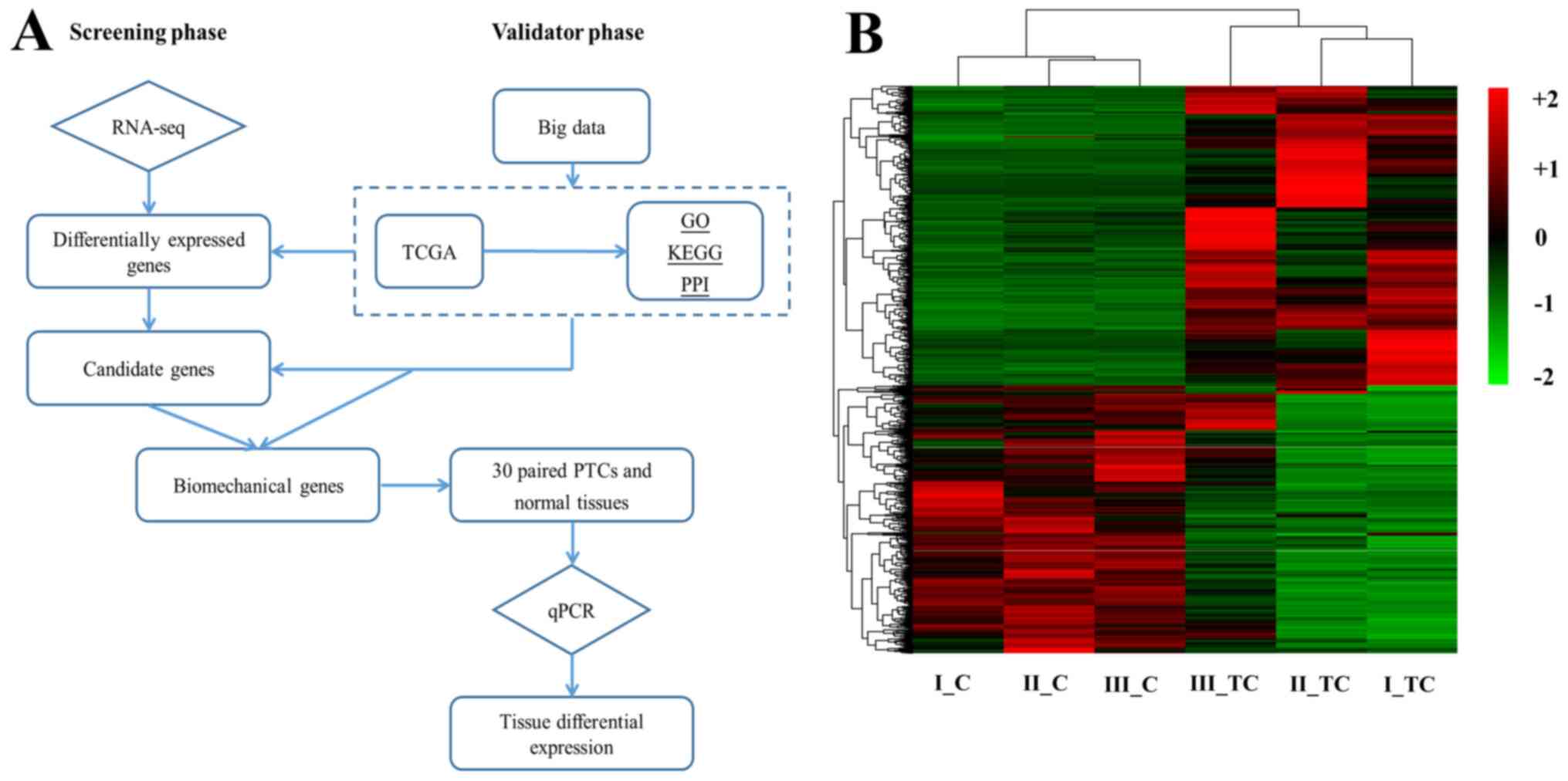
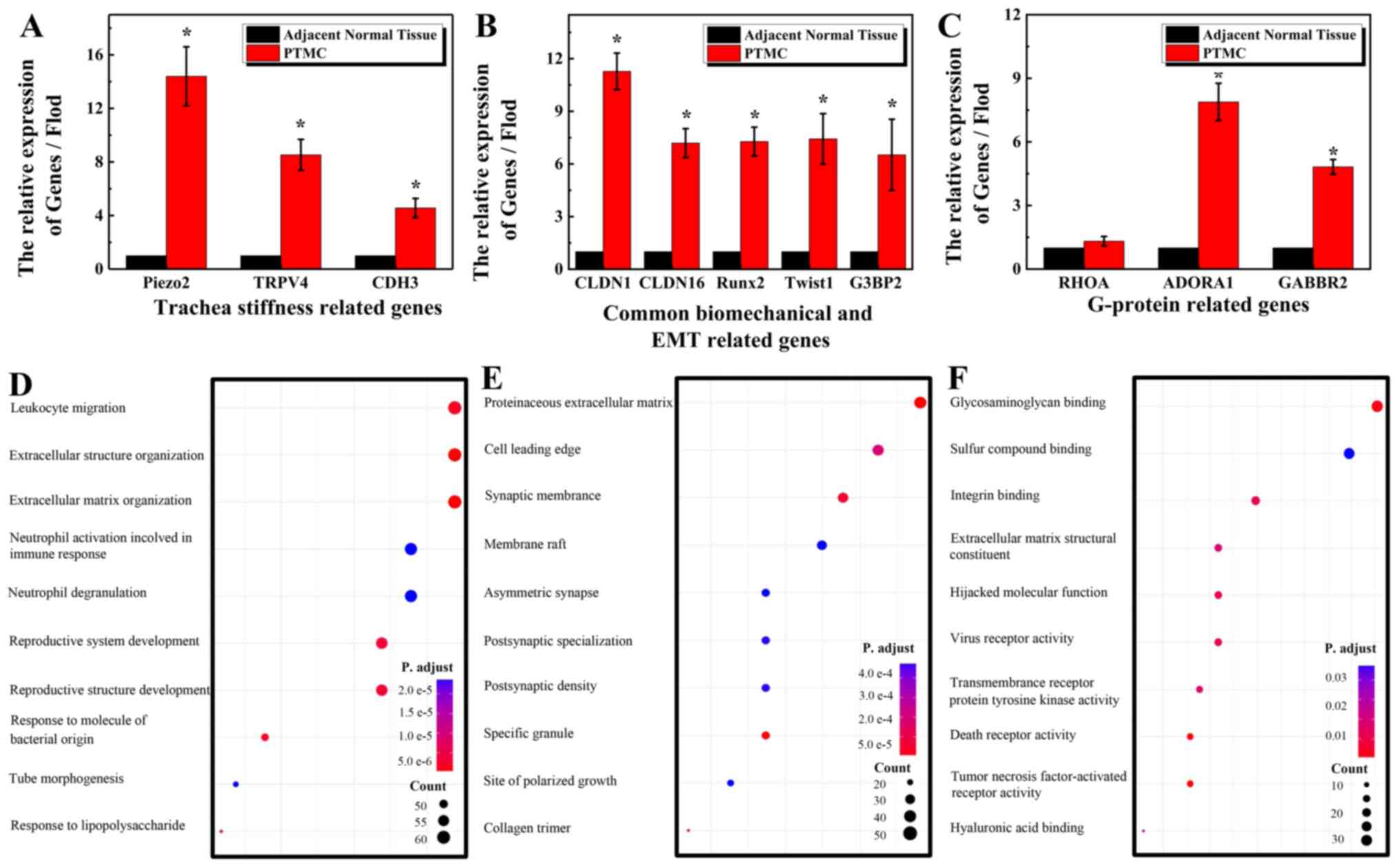
|
1
|
Brooks SA, Lomax-Browne HJ, Carter TM,
Kinch CE and Hall DM: Molecular interactions in cancer cell
metastasis. Acta Histochem. 112:3–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kausch I and Böhle A: Molecular aspects of
bladder cancer III. Prognostic markers of bladder cancer. Eur Urol.
41:15–29. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang R, Ma M, Dong G, Yao RR, Li JH,
Zheng QD, Dong YY, Ma H, Gao DM, Cui JF, et al: Increased matrix
stiffness promotes tumor progression of residual hepatocellular
carcinoma after insufficient heat treatment. Cancer Sci.
108:1778–1786. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Levental KR, Yu H, Kass L, Lakins JN,
Egeblad M, Erler JT, Fong SF, Csiszar K, Giaccia A, Weninger W, et
al: Matrix crosslinking forces tumor progression by enhancing
integrin signaling. Cell. 139:891–906. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. Feb 4–2021.(Epub ahead
of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
La Vecchia C, Malvezzi M, Bosetti C,
Garavello W, Bertuccio P, Levi F and Negri E: Thyroid cancer
mortality and incidence: A global overview. Int J Cancer.
136:2187–2195. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liang W and Sun F: Identification of key
genes of papillary thyroid cancer using integrated bioinformatics
analysis. J Endocrinol Invest. 41:1237–1245. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cui D, Zhao Y and Xu J: Activated
CXCL5-CXCR2 axis promotes the migration, invasion and EMT of
papillary thyroid carcinoma cells via modulation of β-catenin
pathway. Biochimie. 148:1–11. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jasim S, Baranski TJ, Teefey SA and
Middleton WD: Investigating the effect of thyroid nodule location
on the risk of thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 30:401–407. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brauckhoff M and Dralle H: Cervicovisceral
resection in invasive thyroid tumors. Chirurg. 80:88–98. 2009.(In
German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Machens A, Hinze R and Dralle H: Surgery
on the cervicovisceral axis for invasive thyroid cancer.
Langenbecks Arch Surg. 386:318–323. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim JW, Roh JL, Gong G, Cho KJ, Choi SH,
Nam SY and Kim SY: Treatment outcomes and risk factors for
recurrence after definitive surgery of locally invasive
well-differentiated papillary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid.
26:262–270. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He S, Liu C, Li X, Ma S, Huo B and Ji B:
Dissecting collective cell behavior in polarization and alignment
on micropatterned substrates. Biophys J. 109:489–500. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yao P and Xin WH: Experimental study on
the goiter's effect on the stress relaxation of thyroid. Chin J
Control Endemic Dis. 19:79–80. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Trabelsi O, del Palomar AP,
López-Villalobos JL, Ginel A and Doblaré M: Experimental
characterization and constitutive modeling of the mechanical
behavior of the human trachea. Med Eng Phys. 32:76–82. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Haddad RI, Nasr C, Bischoff L, Busaidy NL,
Byrd D, Callender G, Dickson P, Duh QY, Ehya H, Goldner W, et al:
NCCN guidelines insights: Thyroid carcinoma, version 2.2018. J Natl
Compr Canc Netw. 16:1429–1440. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cabanillas ME, McFadden DG and Durante C:
Thyroid cancer. Lancet. 388:2783–2795. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Robinson MD, Mccarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Statist Soc B. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
20
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M,
Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork
P, et al: The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction
networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39((Database Issue)): D561–D568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Adamcsek B, Palla G, Farkas IJ, Derényi I
and Vicsek T: CFinder: Locating cliques and overlapping modules in
biological networks. Bioinformatics. 22:1021–1023. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Peng Y, Chen Y, Qin X, Li S and Liu Y:
Unveiling the mechanotransduction mechanism of substrate
stiffness-modulated cancer cell motility via ROCK1 and ROCK2
differentially regulated manner. FASEB J. 33:644.42019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liang J, Zhang XL, Yuan JW, Zhang HR, Liu
D, Hao J, Ji W, Wu XZ and Chen D: Cucurbitacin B inhibits the
migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by altering the
biomechanical properties of cells. Phytother Res. 33:618–630.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pardo-Pastor C, Rubio-Moscardo F,
Vogel-González M, Serra SA, Afthinos A, Mrkonjic S, Destaing O,
Abenza JF, Fernández-Fernández JM, Trepat X, et al: Piezo2 channel
regulates RhoA and actin cytoskeleton to promote cell
mechanobiological responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:1925–1930.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
McKenzie AJ, Hicks SR, Svec KV, Naughton
H, Edmunds ZL and Howe AK: The mechanical microenvironment
regulates ovarian cancer cell morphology, migration, and spheroid
disaggregation. Sci Rep. 8:72282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Woo SH, Lukacs V, de Nooij JC, Zaytseva D,
Criddle CR, Francisco A, Jessell TM, Wilkinson KA and Patapoutian
A: Piezo2 is the principal mechanotransduction channel for
proprioception. Nat Neurosci. 18:1756–1762. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Coste B, Mathur J, Schmidt M, Earley TJ,
Ranade S, Petrus MJ, Dubin AE and Patapoutian A: Piezo1 and Piezo2
are essential components of distinct mechanically activated cation
channels. Science. 330:55–60. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ferrari LF, Bogen O, Green P and Levine
JD: Contribution of Piezo2 to endothelium-dependent pain. Mol Pain.
11:652015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nonomura K, Woo SH, Chang RB, Gillich A,
Qiu Z, Francisco AG, Ranade SS, Liberles SD and Patapoutian A:
Piezo2 senses airway stretch and mediates lung inflation-induced
apnoea. Nature. 541:176–181. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang H, Liu C, Zhou RM, Yao J, Li XM, Shen
Y, Cheng H, Yuan J, Yan B and Jiang Q: Piezo2 protein: A novel
regulator of tumor angiogenesis and hyperpermeability. Oncotarget.
7:44630–44643. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kameda Y, Nishimaki T, Chisaka O, Iseki S
and Sucov HM: Expression of the epithelial marker E-cadherin by
thyroid C cells and their precursors during murine development. J
Histochem Cytochem. 55:1075–1088. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Taniuchi K, Nakagawa H, Hosokawa M,
Nakamura T, Eguchi H, Ohigashi H, Ishikawa O, Katagiri T and
Nakamura Y: Overexpressed P-cadherin/CDH3 promotes motility of
pancreatic cancer cells by interacting with p120ctn and activating
rho-family GTPases. Cancer Res. 65:3092–3099. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Albergaria A, Resende C, Nobre AR, Ribeiro
AS, Sousa B, Machado JC, Seruca R, Paredes J and Schmitt F:
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β (C/EBPβ) isoforms as
transcriptional regulators of the pro-invasive CDH3/P-cadherin gene
in human breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e557492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|