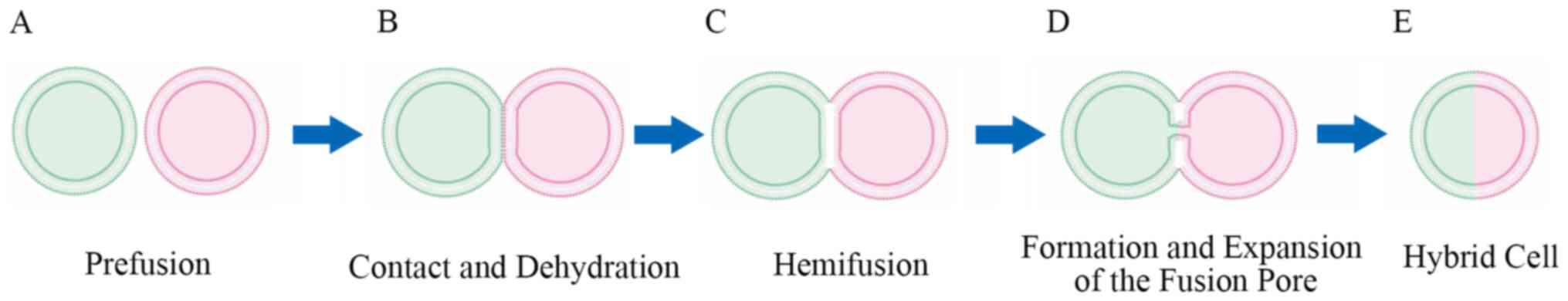
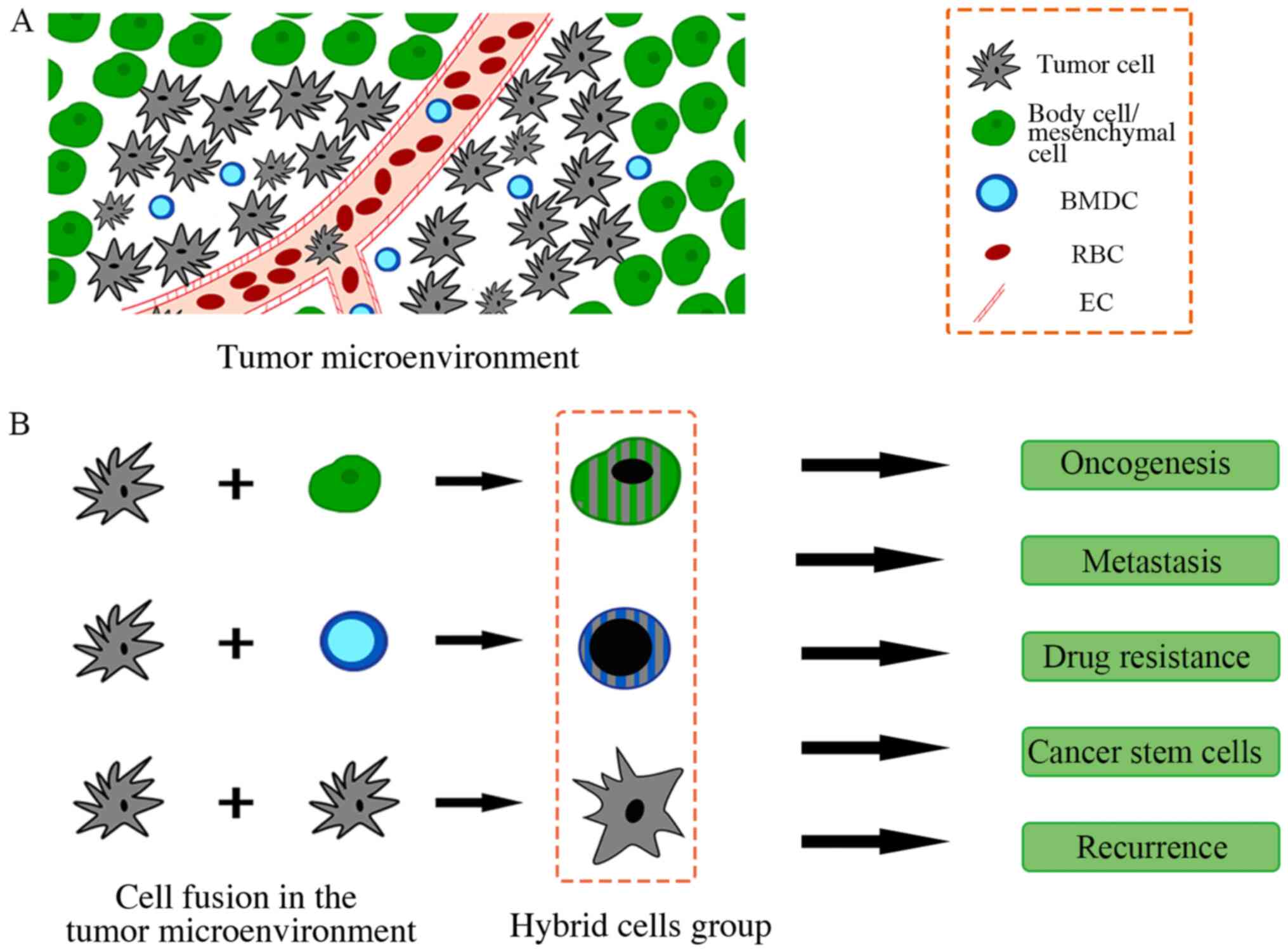
|
1
|
Brukman NG, Uygur B, Podbilewicz B and
Chernomordik LV: How cells fuse. J Cell Biol. 218:1436–1451. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oren-Suissa M and Podbilewicz B: Cell
fusion during development. Trends Cell Biol. 17:537–546. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bastida-Ruiz D, Van Hoesen K and Cohen M:
The dark side of cell fusion. Int J Mol Sci. 17:6382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ku JWK, Chen Y, Lim BJW, Gasser S, Crasta
KC and Gan YH: Bacterial-induced cell fusion is a danger signal
triggering cGAS-STING pathway via micronuclei formation. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 117:15923–15934. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Laberge GS, Duvall E, Haedicke K and
Pawelek J: Leukocyte-cancer cell fusion-genesis of a deadly
journey. Cells. 8:1702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Willkomm L and Bloch W: State of the art
in cell-cell fusion. Methods Mol Biol. 1313:1–19. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zito F, Lampiasi N, Kireev I and Russo R:
United we stand: Adhesion and molecular mechanisms driving cell
fusion across species. Eur J Cell Biol. 95:552–562. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hernández JM and Podbilewicz B: The
hallmarks of cell-cell fusion. Development. 144:4481–4495. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Raj I, Sadat Al Hosseini H, Dioguardi E,
Nishimura K, Han L, Villa A, de Sanctis D and Jovine L: Structural
basis of egg coat-sperm recognition at fertilization. Cell.
169:1315–1326.e17. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Augustine GJ and Weninger K:
Kinetics of complexin binding to the SNARE complex: Correcting
single molecule FRET measurements for hidden events. Biophys J.
93:2178–2187. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Donaldson SH Jr, Lee CT Jr, Chmelka BF and
Israelachvili JN: General hydrophobic interaction potential for
surfactant/lipid bilayers from direct force measurements between
light-modulated bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:15699–15704.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chernomordik LV, Kozlov MM, Leĭkin SL,
Markin VS and Chizmadzhaev IuA: Membrane fusion: Local interactions
and structural rearrangements. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 288:1009–1013.
1986.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chernomordik LV and Kozlov MM: Membrane
hemifusion: Crossing a chasm in two leaps. Cell. 123:375–382. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Skehel JJ and Wiley DC: Receptor binding
and membrane fusion in virus entry: The influenza hemagglutinin.
Annu Rev Biochem. 69:531–569. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eckert DM and Kim PS: Mechanisms of viral
membrane fusion and its inhibition. Annu Rev Biochem. 70:777–810.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weber T, Zemelman BV, McNew JA, Westermann
B, Gmachl M, Parlati F, Söllner TH and Rothman JE: SNAREpins:
Minimal machinery for membrane fusion. Cell. 92:759–772. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Calder LJ and Rosenthal PB: Cryomicroscopy
provides structural snapshots of influenza virus membrane fusion.
Nat Struct Mol Biol. 23:853–858. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Segev N, Avinoam O and Podbilewicz B:
Fusogens. Curr Biol. 28:R378–R380. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mercapide J, Rappa G and Lorico A: The
intrinsic fusogenicity of glioma cells as a factor of
transformation and progression in the tumor microenvironment. Int J
Cancer. 131:334–343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Esnault C, Priet S, Ribet D, Vernochet C,
Bruls T, Lavialle C, Weissenbach J and Heidmann T: A
placenta-specific receptor for the fusogenic, endogenous
retrovirus-derived, human syncytin-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:17532–17537. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fédry J, Liu Y, Péhau-Arnaudet G, Pei J,
Li W, Tortorici MA, Traincard F, Meola A, Bricogne G, Grishin NV,
et al: The ancient gamete fusogen HAP2 is a eukaryotic class II
fusion protein. Cell. 168:904–915.e10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Aguilar PS, Baylies MK, Fleissner A,
Helming L, Inoue N, Podbilewicz B, Wang H and Wong M: Genetic basis
of cell-cell fusion mechanisms. Trends Genet. 29:427–437. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Okabe M: Sperm-egg interaction and
fertilization: Past, present, and future. Biol Reprod. 99:134–146.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Primakoff P and Myles DG: Cell-cell
membrane fusion during mammalian fertilization. FEBS Lett.
581:2174–2180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Runge KE, Evans JE, He ZY, Gupta S,
McDonald KL, Stahlberg H, Primakoff P and Myles DG: Oocyte CD9 is
enriched on the microvillar membrane and required for normal
microvillar shape and distribution. Dev Biol. 304:317–325. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aydin H, Sultana A, Li S, Thavalingam A
and Lee JE: Molecular architecture of the human sperm IZUMO1 and
egg JUNO fertilization complex. Nature. 534:562–565. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ohto U, Ishida H, Krayukhina E, Uchiyama
S, Inoue N and Shimizu T: Structure of IZUMO1-JUNO reveals
sperm-oocyte recognition during mammalian fertilization. Nature.
534:566–569. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mi S, Lee X, Li X, Veldman GM, Finnerty H,
Racie L, LaVallie E, Tang XY, Edouard P, Howes S, et al: Syncytin
is a captive retroviral envelope protein involved in human
placental morphogenesis. Nature. 403:785–789. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gude NM, Roberts CT, Kalionis B and King
RG: Growth and function of the normal human placenta. Thromb Res.
114:397–407. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bjerregaard B, Holck S, Christensen IJ and
Larsson LI: Syncytin is involved in breast cancer-endothelial cell
fusions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 63:1906–1911. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bjerregard B, Ziomkiewicz I, Schulz A and
Larsson LI: Syncytin-1 in differentiating human myoblasts:
Relationship to caveolin-3 and myogenin. Cell Tissue Res.
357:355–362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Søe K, Andersen TL, Hobolt-Pedersen AS,
Bjerregaard B, Larsson LI and Delaisse JM: Involvement of human
endogenous retroviral syncytin-1 in human osteoclast fusion. Bone.
48:837–846. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Antony JM, van Marle G, Opii W,
Butterfield DA, Mallet F, Yong VW, Wallace JL, Deacon RM, Warren K
and Power C: Human endogenous retrovirus glycoprotein-mediated
induction of redox reactants causes oligodendrocyte death and
demyelination. Nat Neurosci. 7:1088–1095. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dupressoir A, Vernochet C, Bawa O, Harper
F, Pierron G, Opolon P and Heidmann T: Syncytin-A knockout mice
demonstrate the critical role in placentation of a fusogenic,
endogenous retrovirus-derived, envelope gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 106:12127–12132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vignery A: Macrophage fusion: The making
of osteoclasts and giant cells. J Exp Med. 202:337–340. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Helming L and Gordon S: Molecular
mediators of macrophage fusion. Trends Cell Biol. 19:514–522. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Saginario C, Sterling H, Beckers C,
Kobayashi R, Solimena M, Ullu E and Vignery A: MFR, a putative
receptor mediating the fusion of macrophages. Mol Cell Biol.
18:6213–6223. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kania JR, KehatStadler T and Kupfer SR:
CD44 antibodies inhibit osteoclast formation. J Bone Miner Res.
12:1155–1164. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yagi M, Miyamoto T, Toyama Y and Suda T:
Role of DC-STAMP in cellular fusion of osteoclasts and macrophage
giant cells. J Bone Miner Metab. 24:355–358. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Horsley V and Pavlath GK: Forming a
multinucleated cell: Molecules that regulate myoblast fusion. Cells
Tissues Organs. 176:67–78. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Quinn ME, Goh Q, Kurosaka M, Gamage DG,
Petrany MJ, Prasad V and Millay DP: Myomerger induces fusion of
non-fusogenic cells and is required for skeletal muscle
development. Nat Commun. 8:156652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mitani Y, Vagnozzi RJ and Millay DP: In
vivo myomaker-mediated heterologous fusion and nuclear
reprogramming. FASEB J. 31:400–411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Boveri T: Concerning the origin of
malignant tumours by Theodor Boveri. Translated and annotated by
Henry Harris. J Cell Sci. 121 (Suppl 1):S1–S84. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun C, Zhao D, Dai X, Chen J, Rong X, Wang
H, Wang A, Li M, Dong J, Huang Q and Lan Q: Fusion of cancer stem
cells and mesenchymal stem cells contributes to glioma
neovascularization. Oncol Rep. 34:2022–2030. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wei HJ, Nickoloff JA, Chen WH, Liu HY, Lo
WC, Chang YT, Yang PC, Wu CW, Williams DF, Gelovani JG and Deng WP:
FOXF1 mediates mesenchymal stem cell fusion-induced reprogramming
of lung cancer cells. Oncotarget. 5:9514–9529. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Melzer C, von der Ohe J and Hass R: In
vitro fusion of normal and neoplastic breast epithelial cells with
human mesenchymal stroma/stem cells partially involves tumor
necrosis factor receptor signaling. Stem Cells. 36:977–989. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Clawson GA, Matters GL, Xin P,
Imamura-Kawasawa Y, Du Z, Thiboutot DM, Helm KF, Neves RI and
Abraham T: Macrophage-tumor cell fusions from peripheral blood of
melanoma patients. PLoS One. 10:e01343202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gast CE, Silk AD, Zarour L, Riegler L,
Burkhart JG, Gustafson KT, Parappilly MS, Roh-Johnson M, Goodman
JR, Olson B, et al: Cell fusion potentiates tumor heterogeneity and
reveals circulating hybrid cells that correlate with stage and
survival. Sci Adv. 4:eaat78282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yu L, Guo W, Zhao S, Wang F and Xu Y:
Fusion between cancer cells and myofibroblasts is involved in
osteosarcoma. Oncol Lett. 2:1083–1087. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Powell AE, Anderson EC, Davies PS, Silk
AD, Pelz C, Impey S and Wong MH: Fusion between intestinal
epithelial cells and macrophages in a cancer context results in
nuclear reprogramming. Cancer Res. 71:1497–1505. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Huang CM, Yan TL, Xu Z, Wang M, Zhou XC,
Jiang EH, Liu K, Shao Z and Shang ZJ: Hypoxia enhances fusion of
oral squamous carcinoma cells and epithelial cells partly via the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of epithelial cells. Biomed Res
Int. 2018:50152032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lu X and Kang Y: Cell fusion as a hidden
force in tumor progression. Cancer Res. 69:8536–8539. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yin L, Hu P, Shi X, Qian W, Zhau HE,
Pandol SJ, Lewis MS, Chung LWK and Wang R: Cancer cell's
neuroendocrine feature can be acquired through cell-cell fusion
during cancer-neural stem cell interaction. Sci Rep. 10:12162020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Dörnen J, Myklebost O and Dittmar T: Cell
fusion of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and breast cancer cells
leads to the formation of hybrid cells exhibiting diverse and
individual (stem cell) characteristics. Int J Mol Sci. 21:96362020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Delespaul L, Merle C, Lesluyes T, Lagarde
P, Le Guellec S, Pérot G, Baud J, Carlotti M, Danet C, Fèvre M, et
al: Fusion-mediated chromosomal instability promotes aneuploidy
patterns that resemble human tumors. Oncogene. 38:6083–6094. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hedley DW, Leary JA and Kirsten F:
Metastatic adenocarcinoma of unknown primary site: Abnormalities of
cellular DNA content and survival. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol.
21:185–189. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Baker SG: A cancer theory kerfuffle can
lead to new lines of research. J Natl Cancer Inst. 107:dju4052014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Mertens F, Johansson B, Höglund M and
Mitelman F: Chromosomal imbalance maps of malignant solid tumors: A
cytogenetic survey of 3185 neoplasms. Cancer Res. 57:2765–2780.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Bjerkvig R, Tysnes BB, Aboody KS, Najbauer
J and Terzis AJ: Opinion: The origin of the cancer stem cell:
Current controversies and new insights. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:899–904.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mohr M, Zaenker KS and Dittmar T: Fusion
in cancer: An explanatory model for aneuploidy, metastasis
formation, and drug resistance. Methods Mol Biol. 1313:21–40. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhou X, Merchak K, Lee W, Grande JP,
Cascalho M and Platt JL: Cell fusion connects oncogenesis with
tumor evolution. Am J Pathol. 185:2049–2060. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Dittmar T, Schwitalla S, Seidel J,
Haverkampf S, Reith G, Meyer-Staeckling S, Brandt BH, Niggemann B
and Zänker KS: Characterization of hybrid cells derived from
spontaneous fusion events between breast epithelial cells
exhibiting stem-like characteristics and breast cancer cells. Clin
Exp Metastas. 28:75–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Goldenberg DM, Rooney RJ, Loo M, Liu D and
Chang CH: In-vivo fusion of human cancer and hamster stromal cells
permanently transduces and transcribes human DNA. PLoS One.
9:e1079272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Su Y, Subedee A, Bloushtain-Qimron N,
Savova V, Krzystanek M, Li L, Marusyk A, Tabassum DP, Zak A,
Flacker MJ, et al: Somatic cell fusions reveal extensive
heterogeneity in basal-like breast cancer. Cell Rep. 11:1549–1563.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Munzarova M, Lauerova L and Capkova J: Are
advanced malignant melanoma cells hybrids between melanocytes and
macrophages? Melanoma Res. 2:127–129. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
He X, Li B, Shao Y, Zhao N, Hsu Y, Zhang Z
and Zhu L: Cell fusion between gastric epithelial cells and
mesenchymal stem cells results in epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition and malignant transformation. BMC Cancer. 15:242015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Faggioli F, Sacco MG, Susani L, Montagna C
and Vezzoni P: Cell fusion is a physiological process in mouse
liver. Hepatology. 48:1655–1664. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Israel BA and Schaeffer WI: Cytoplasmic
suppression of malignancy. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 23:627–632.
1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Seyfried TN: Cancer as a mitochondrial
metabolic disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 3:432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Hsu CC, Tseng LM and Lee HC: Role of
mitochondrial dysfunction in cancer progression. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 241:1281–1295. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Seyfried TN and Shelton LM: Cancer as a
metabolic disease. Nutr Metab (Lond). 7:72010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Platt JL, Zhou X, Lefferts AR and Cascalho
M: Cell fusion in the war on cancer: A perspective on the inception
of malignancy. Int J Mol Sci. 17:11182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Duelli D and Lazebnik Y: Cell fusion: A
hidden enemy? Cancer Cell. 3:445–448. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Weiler J and Dittmar T: Cell fusion in
human cancer: The dark matter hypothesis. Cells. 8:1322019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Mittal V: Epithelial mesenchymal
transition in tumor metastasis. Annu Rev Pathol. 13:395–412. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Pawelek JM and Chakraborty AK: Fusion of
tumour cells with bone marrow-derived cells: A unifying explanation
for metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:377–386. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Kalluri R and Neilson EG:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for
fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 112:1776–1784. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Seyfried TN and Huysentruyt LC: On the
origin of cancer metastasis. Crit Rev Oncog. 18:43–73. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chakraborty AK, Sodi S, Rachkovsky M,
Kolesnikova N, Platt JT, Bolognia JL and Pawelek JM: A spontaneous
murine melanoma lung metastasis comprised of host × tumor hybrids.
Cancer Res. 60:2512–2519. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yilmaz Y, Lazova R, Qumsiyeh M, Cooper D
and Pawelek J: Donor Y chromosome in renal carcinoma cells of a
female BMT recipient: Visualization of putative BMT-tumor hybrids
by FISH. Bone Marrow Transplant. 35:1021–1024. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Fidler IJ: Timeline: The pathogenesis of
cancer metastasis: The ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat
Rev Cancer. 3:453–458. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Jiang E, Yan T, Xu Z and Shang Z: Tumor
microenvironment and cell fusion. Biomed Res Int. 2019:50135922019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Noubissi FK, Harkness T, Alexander CM and
Ogle BM: Apoptosis-induced cancer cell fusion: A mechanism of
breast cancer metastasis. FASEB J. 29:4036–4045. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Choi H and Moon A: Crosstalk between
cancer cells and endothelial cells: Implications for tumor
progression and intervention. Arch Pharm Res. 41:711–724. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kalluri R: The biology and function of
fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:582–598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Wang R, Sun X, Wang CY, Hu P, Chu CY, Liu
S, Zhau HE and Chung LW: Spontaneous cancer-stromal cell fusion as
a mechanism of prostate cancer androgen-independent progression.
PLoS One. 7:e426532012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Clawson GA, Matters GL, Xin P, McGovern C,
Wafula E, dePamphilis C, Meckley M, Wong J, Stewart L, D'Jamoos C,
et al: ‘Stealth dissemination’ of macrophage-tumor cell fusions
cultured from blood of patients with pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 12:e01844512017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Clawson G: The fate of fusions. Cells.
8:132018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Kachalaki S, Ebrahimi M, Mohamed
Khosroshahi L, Mohammadinejad S and Baradaran B: Cancer
chemoresistance; biochemical and molecular aspects: A brief
overview. Eur J Pharm Sci. 89:20–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Vasan N, Baselga J and Hyman DM: A view on
drug resistance in cancer. Nature. 575:299–309. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Miller FR, Mohamed AN and McEachern D:
Production of a more aggressive tumor cell variant by spontaneous
fusion of two mouse tumor subpopulations. Cancer Res. 49:4316–4321.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Nagler C, Hardt C, Zanker KS and Dittmar
T: Co-cultivation of murine BMDCs with 67NR mouse mammary carcinoma
cells give rise to highly drug resistant cells. Cancer Cell Int.
11:212011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Uygur B, Leikina E, Melikov K, Villasmil
R, Verma SK, Vary CPH and Chernomordik LV: Interactions with muscle
cells boost fusion, stemness, and drug resistance of prostate
cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 17:806–820. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Song K, Song Y, Zhao XP, Shen H, Wang M,
Yan TL, Liu K and Shang ZJ: Oral cancer/endothelial cell fusion
experiences nuclear fusion and acquisition of enhanced survival
potential. Exp Cell Res. 328:156–163. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Searles SC, Santosa EK and Bui JD:
Cell-cell fusion as a mechanism of DNA exchange in cancer.
Oncotarget. 9:6156–6173. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Mirzayans R and Murray D: Intratumor
heterogeneity and therapy resistance: Contributions of dormancy,
apoptosis reversal (Anastasis) and cell fusion to disease
recurrence. Int J Mol Sci. 21:13082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Seyfried TN, Arismendi-Morillo G,
Mukherjee P and Chinopoulos C: On the origin of ATP synthesis in
cancer. iScience. 23:1017612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Xu RH, Pelicano H, Zhou Y, Carew JS, Feng
L, Bhalla KN, Keating MJ and Huang P: Inhibition of glycolysis in
cancer cells: A novel strategy to overcome drug resistance
associated with mitochondrial respiratory defect and hypoxia.
Cancer Res. 65:613–621. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Beck B and Blanpain C: Unravelling cancer
stem cell potential. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:727–738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Batlle E and Clevers H: Cancer stem cells
revisited. Nat Med. 23:1124–1134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Dittmar T, Nagler C, Schwitalla S, Reith
G, Niggemann B and Zänker KS: Recurrence cancer stem cells-made by
cell fusion? Med Hypotheses. 73:542–547. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Bartosh TJ, Ullah M, Zeitouni S, Beaver J
and Prockop DJ: Cancer cells enter dormancy after cannibalizing
mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E6447–E6456. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Li G, Kikuchi K, Radka M, Abraham J, Rubin
BP and Keller C: IL-4 receptor blockade abrogates satellite cell:
Rhabdomyosarcoma fusion and prevents tumor establishment. Stem
Cells. 31:2304–2312. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Platt JL and Cascalho M: Cell fusion in
malignancy: A cause or consequence? a provocateur or cure? Cells.
8:5872019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Fais S and Overholtzer M: Cell-in-cell
phenomena in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:758–766. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Koido S, Homma S, Okamoto M, Namiki Y,
Takakura K, Uchiyama K, Kajihara M, Arihiro S, Imazu H, Arakawa H,
et al: Fusions between dendritic cells and whole tumor cells as
anticancer vaccines. Oncoimmunology. 2:e244372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Koido S: Dendritic-tumor fusion cell-based
cancer vaccines. Int J Mol Sci. 17:8282016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Platt JL and Cascalho M: IgM in the
kidney: A multiple personality disorder. Kidney Int. 88:439–441.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Liu WL, Zou MZ, Liu T, Zeng JY, Li X, Yu
WY, Li CX, Ye JJ, Song W, Feng J and Zhang XZ: Expandable
immunotherapeutic nanoplatforms engineered from cytomembranes of
hybrid cells derived from cancer and dendritic cells. Adv Mater.
31:e19004992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Hass R, von der Ohe J and Ungefroren H:
Potential role of MSC/cancer cell fusion and EMT for breast cancer
stem cell formation. Cancers (Basel). 11:14322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Rizvi AZ, Swain JR, Davies PS, Bailey AS,
Decker AD, Willenbring H, Grompe M, Fleming WH and Wong MH: Bone
marrow-derived cells fuse with normal and transformed intestinal
stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:6321–6325. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Davies PS, Powell AE, Swain JR and Wong
MH: Inflammation and proliferation act together to mediate
intestinal cell fusion. PLoS One. 4:e65302009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Garvin S, Oda H, Arnesson LG, Lindström A
and Shabo I: Tumor cell expression of CD163 is associated to
postoperative radiotherapy and poor prognosis in patients with
breast cancer treated with breast-conserving surgery. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 144:1253–1263. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Lindström A, Midtbö K, Arnesson LG, Garvin
S and Shabo I: Fusion between M2-macrophages and cancer cells
results in a subpopulation of radioresistant cells with enhanced
DNA-repair capacity. Oncotarget. 8:51370–51386. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Yeh MH, Chang YH, Tsai YC, Chen SL, Huang
TS, Chiu JF and Ch'ang HJ: Bone marrow derived macrophages fuse
with intestine stromal cells and contribute to chronic fibrosis
after radiation. Radiother Oncol. 119:250–258. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Willenbring H: Therapeutic cell fusion. Br
J Surg. 92:923–924. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|