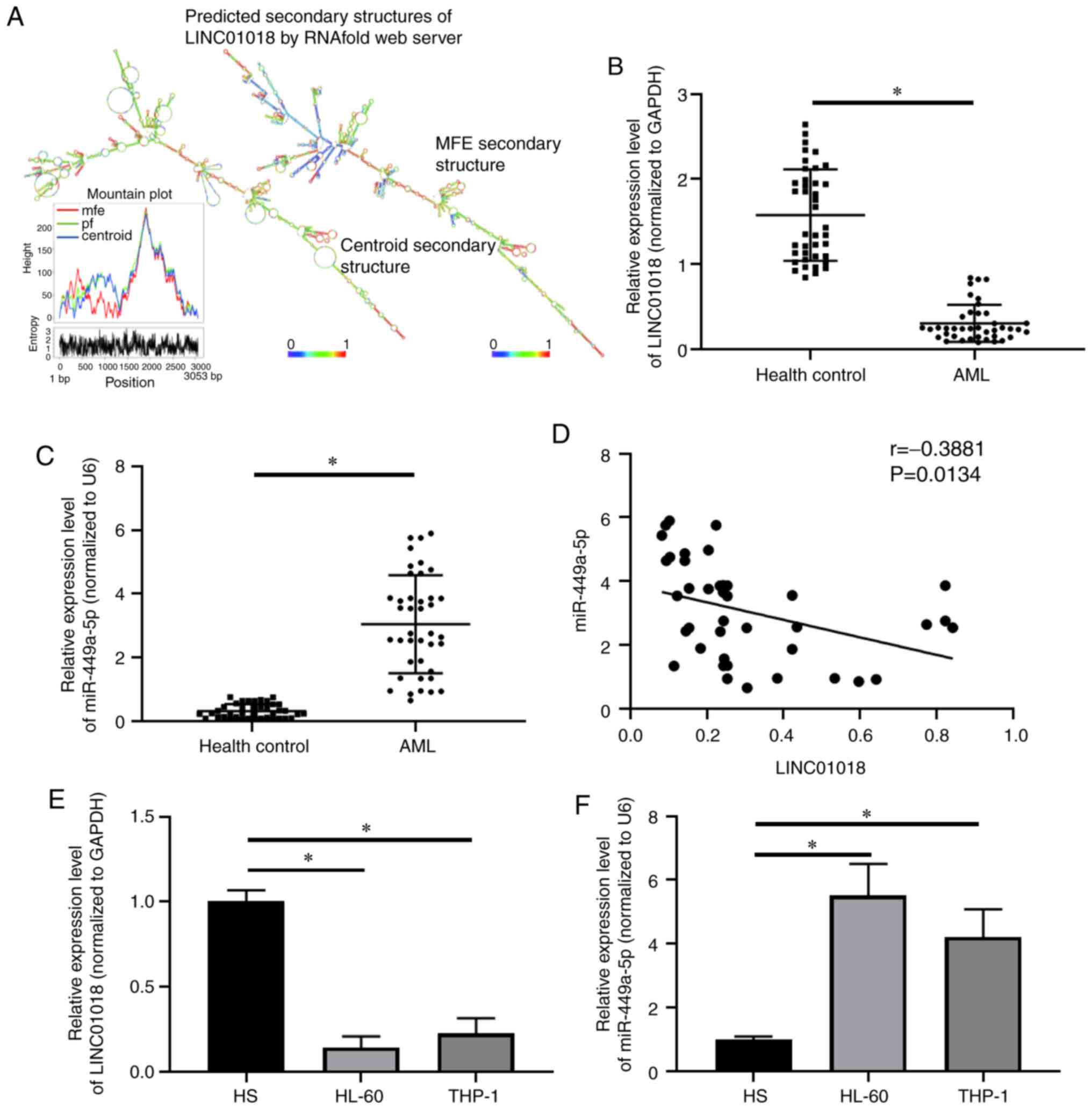
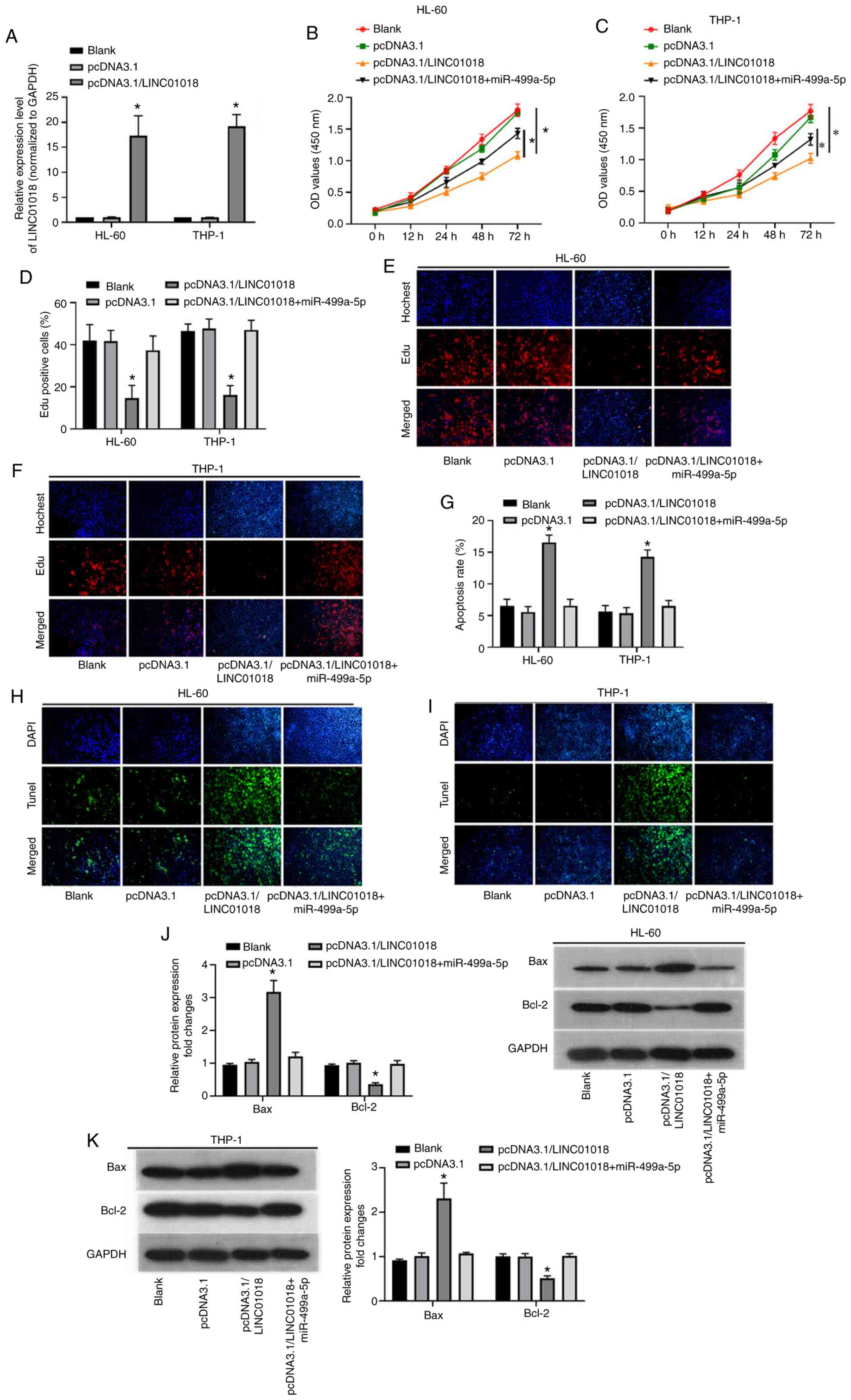
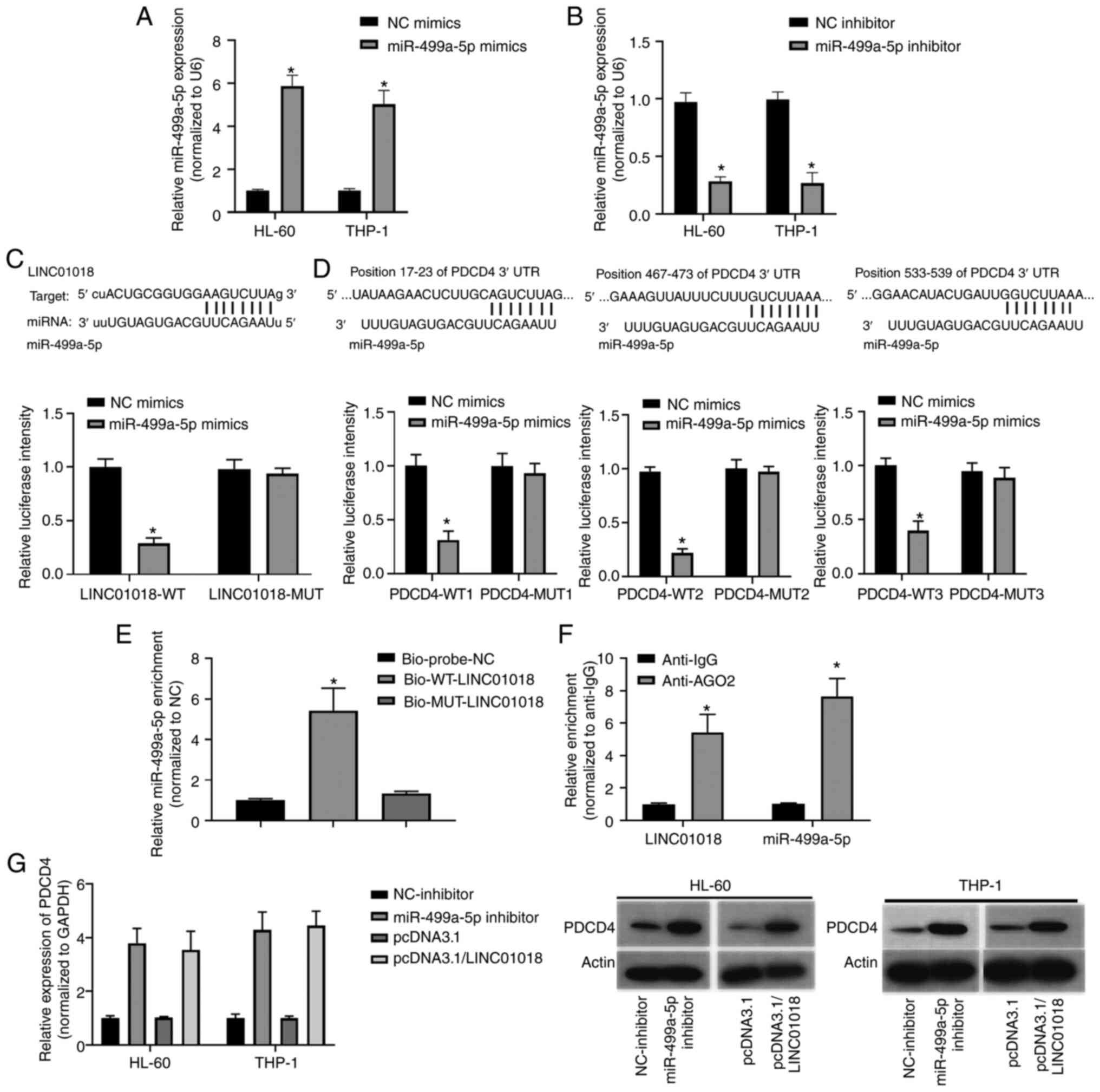
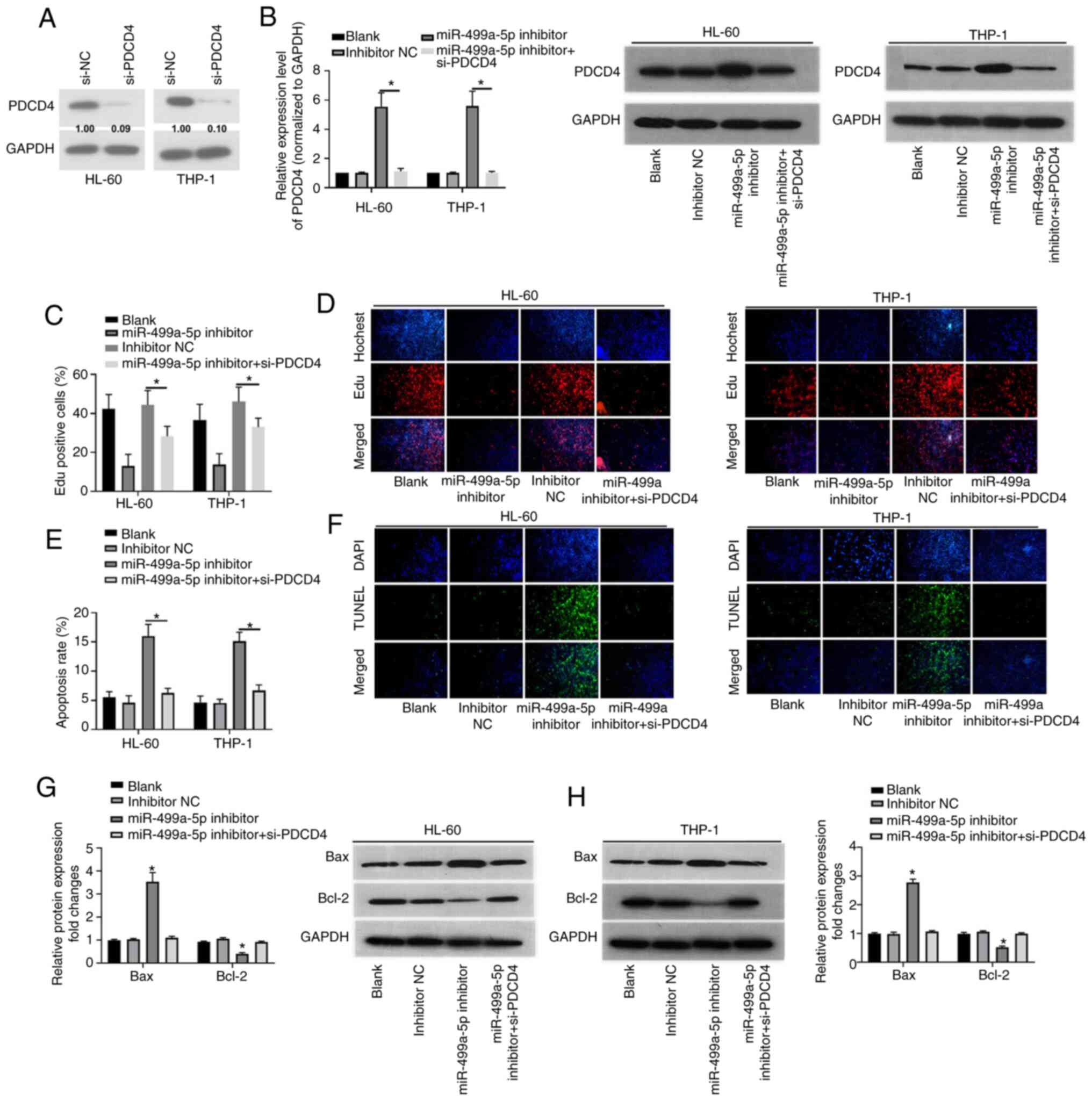
|
1
|
De Kouchkovsky I and Abdul-Hay M: ‘Acute
myeloid leukemia: A comprehensive review and 2016 update’. Blood
Cancer J. 6:e4412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shah A, Andersson TM, Rachet B, Björkholm
M and Lambert PC: Survival and cure of acute myeloid leukaemia in
England, 1971–2006: A population-based study. Br J Haematol.
162:509–516. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Davila J, Slotkin E and Renaud T: Relapsed
and refractory pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: Current and
emerging treatments. Paediatr Drugs. 16:151–168. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Meyers J, Yu Y, Kaye JA and Davis KL:
Medicare fee-for-service enrollees with primary acute myeloid
leukemia: An analysis of treatment patterns, survival, and
healthcare resource utilization and costs. Appl Health Econ Health
Policy. 11:275–286. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shi Z, Tiwari AK, Patel AS, Fu LW and Chen
ZS: Roles of sildenafil in enhancing drug sensitivity in cancer.
Cancer Res. 71:3735–3738. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang JX, Rastetter RH and Wilhelm D:
Non-coding RNAs: An introduction. Adv Exp Med Biol. 886:13–32.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dong X, Chen K, Cuevas-Diaz Duran R, You
Y, Sloan SA, Zhang Y, Zong S, Cao Q, Barres BA and Wu JQ:
Comprehensive identification of long non-coding RNAs in purified
cell types from the brain reveals functional LncRNA in OPC fate
determination. PLoS Genet. 11:e10056692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wrang X, Chen H, Bai J and He A: MicroRNA:
An important regulator in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Biol Int.
41:936–945. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lei L, Xia S, Liu D, Li X, Feng J, Zhu Y,
Hu J, Xia L, Guo L, Chen F, et al: Genome-wide characterization of
lncRNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. Brief Bioinform. 19:627–635.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jarroux J, Morillon A and Pinskaya M:
History, discovery, and classification of lncRNAs. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1008:1–46. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Puvvula PK: LncRNAs regulatory networks in
cellular senescence. Int J Mol Sci. 20:26152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maruyama R and Suzuki H: Long noncoding
RNA involvement in cancer. BMB Rep. 45:604–611. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang Z, Zhou L, Wu LM, Lai MC, Xie HY,
Zhang F and Zheng SS: Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR
predicts tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients
following liver transplantation. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:1243–1250.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kogo R, Shimamura T, Mimori K, Kawahara K,
Imoto S, Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Suzuki A, Komune S, et al:
Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates polycomb-dependent chromatin
modification and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal
cancers. Cancer Res. 71:6320–6326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim K, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Johnson
G, Frank J, Burghardt R, Kim S and Safe S: HOTAIR is a negative
prognostic factor and exhibits pro-oncogenic activity in pancreatic
cancer. Oncogene. 32:1616–1625. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ji P, Diederichs S, Wang W, Böing S,
Metzger R, Schneider PM, Tidow N, Brandt B, Buerger H, Bulk E, et
al: MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin beta4 predict
metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncogene. 22:8031–8041. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miao Y, Sui J, Xu SY, Liang GY, Pu YP and
Yin LH: Comprehensive analysis of a novel four-lncRNA signature as
a prognostic biomarker for human gastric cancer. Oncotarget.
8:75007–75024. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ruan X, Li P, Chen Y, Shi Y, Pirooznia M,
Seifuddin F, Suemizu H, Ohnishi Y, Yoneda N, Nishiwaki M, et al: In
vivo functional analysis of non-conserved human lncRNAs associated
with cardiometabolic traits. Nat Commun. 11:452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shang H, Sun L, Braun T, Si Q and Tong J:
Association between miR-124 rs531564 and miR-100 rs1834306
polymorphisms and cervical cancer: A meta-analysis. Eur J Gynaecol
Oncol. 40:925–931. 2019.
|
|
20
|
Song SJ, Ito K, Ala U, Kats L, Webster K,
Sun SM, Manova-Todorova K, Teruya-Feldstein J, Avigan DE, Delwel R
and Pandolfi PP: The oncogenic microRNA miR-22 targets the TET2
tumor suppressor to promote hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal
and transformation. Cell Stem Cell. 13:87–101. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bousquet M, Quelen C, Rosati R, Mansat-De
Mas V, La Starza R, Bastard C, Lippert E, Talmant P,
Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Leroux D, et al: Myeloid cell differentiation
arrest by miR-125b-1 in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid
leukemia with the t(2;11)(p21;q23) translocation. J Exp Med.
205:2499–2506. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
He S, Li Z, Yu Y, Zeng Q, Cheng Y, Ji W,
Xia W and Lu S: Exosomal miR-499a-5p promotes cell proliferation,
migration and EMT via mTOR signaling pathway in lung
adenocarcinoma. Exp Cell Res. 379:203–213. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hou YY, Lee JH, Chen HC, Yang CM, Huang
SJ, Liou HH, Chi CC, Tsai KW and Ger LP: The association between
miR-499a polymorphism and oral squamous cell carcinoma progression.
Oral Dis. 21:195–206. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi Q, Feng K, Xia L, Wang C and Zhu J:
Combined use of Serum miR-499a-5p and CA199 increases the
diagnostic sensitivity of pancreatic cancer. Clin Lab. 65:2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Manabe A, Coustan-Smith E, Kumagai M, Behm
FG, Raimondi SC, Pui CH and Campana D: Interleukin-4 induces
programmed cell death (apoptosis) in cases of high-risk acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 83:1731–1737. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Long J, Yin Y, Guo H, Li S, Sun Y, Zeng C
and Zhu W: The mechanisms and clinical significance of PDCD4 in
colorectal cancer. Gene. 680:59–64. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Q and Yang HS: The role of Pdcd4 in
tumour suppression and protein translation. Biol Cell. May
28–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou H and Huang S: Role of mTOR signaling
in tumor cell motility, invasion and metastasis. Curr Protein Pept
Sci. 12:30–42. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fehler O, Singh P, Haas A, Ulrich D,
Müller JP, Ohnheiser J and Klempnauer KH: An evolutionarily
conserved interaction of tumor suppressor protein Pdcd4 with the
poly(A)-binding protein contributes to translation suppression by
Pdcd4. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:11107–11118. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liwak U, Thakor N, Jordan LE, Roy R, Lewis
SM, Pardo OE, Seckl M and Holcik M: Tumor suppressor PDCD4
represses internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation of
antiapoptotic proteins and is regulated by S6 kinase 2. Mol Cell
Biol. 32:1818–1829. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wedeken L, Singh P and Klempnauer KH:
Tumor suppressor protein Pdcd4 inhibits translation of p53 mRNA. J
Biol Chem. 286:42855–42862. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Y, Zhou Q and Ma JJ: High expression
of lnc-CRNDE presents as a biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia and
promotes the malignant progression in acute myeloid leukemia cell
line U937. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:763–770. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang S, Xu M, Sun Z, Yu X, Deng Y and
Chang H: LINC01018 confers a novel tumor suppressor role in
hepatocellular carcinoma through sponging microRNA-182-5p. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 317:G116–G126. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu L, Ren W and Chen K: MiR-34a promotes
apoptosis and inhibits autophagy by targeting HMGB1 in acute
myeloid leukemia cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 41:1981–1992. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
So AY, Sookram R, Chaudhuri AA,
Minisandram A, Cheng D, Xie C, Lim EL, Flores YG, Jiang S, Kim JT,
et al: Dual mechanisms by which miR-125b represses IRF4 to induce
myeloid and B-cell leukemias. Blood. 124:1502–1512. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu H and Wen Q: Downregulation of miR135a
predicts poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia and regulates
leukemia progression via modulating HOXA10 expression. Mol Med Rep.
18:1134–1140. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang S, Zhang Q, Shi G and Yin J:
MiR-182-5p regulates BCL2L12 and BCL2 expression in acute myeloid
leukemia as a potential therapeutic target. Biomed Pharmacother.
97:1189–1194. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gu X, Dong M, Liu Z, Yang J and Shi Y:
MiR-499a-5p inhibits proliferation, invasion, migration, and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and enhances radiosensitivity of
cervical cancer cells via targeting eIF4E. Onco Targets Ther.
13:2913–2924. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang Z, Li C, Fan XY and Liu LJ: Circular
RNA circ_0079593 promotes glioma development through regulating
KPNA2 expression by sponging miR-499a-5p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 24:1288–1301. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhao L, Jiang P, Zheng H, Chen P and Yang
M: Downregulation of miR-499a-5p predicts a poor prognosis of
patients with non-small cell lung cancer and restrains the
tumorigenesis by targeting fibroblast growth factor 9. Technol
Cancer Res Treat. 19:15330338209570012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Espadinha AS, Prouzet-Mauléon V, Claverol
S, Lagarde V, Bonneu M, Mahon FX and Cardinaud B: A tyrosine
kinase-STAT5-miR21-PDCD4 regulatory axis in chronic and acute
myeloid leukemia cells. Oncotarget. 8:76174–76188. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gu J, Zhu X, Li Y, Dong D, Yao J, Lin C,
Huang K, Hu H and Fei J: miRNA-21 regulates arsenic-induced
anti-leukemia activity in myelogenous cell lines. Med Oncol.
28:211–218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ozpolat B, Akar U, Steiner M,
Zorrilla-Calancha I, Tirado-Gomez M, Colburn N, Danilenko M,
Kornblau S and Berestein GL: Programmed cell death-4 tumor
suppressor protein contributes to retinoic acid-induced terminal
granulocytic differentiation of human myeloid leukemia cells. Mol
Cancer Res. 5:95–108. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Riccioni R, Lulli V, Castelli G, Biffoni
M, Tiberio R, Pelosi E, Lo-Coco F and Testa U: miR-21 is
overexpressed in NPM1-mutant acute myeloid leukemias. Leuk Res.
39:221–228. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Simmons HM, Ruis BL, Kapoor M, Hudacek AW
and Conklin KF: Identification of NOM1, a nucleolar, eIF4A binding
protein encoded within the chromosome 7q36 breakpoint region
targeted in cases of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Gene.
347:137–145. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang JJ, Wang ZY, Chen R, Xiong J, Yao YL,
Wu JH and Li GX: Macrophage-secreted exosomes delivering miRNA-21
inhibitor can regulate BGC-823 cell proliferation. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:4203–4209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|