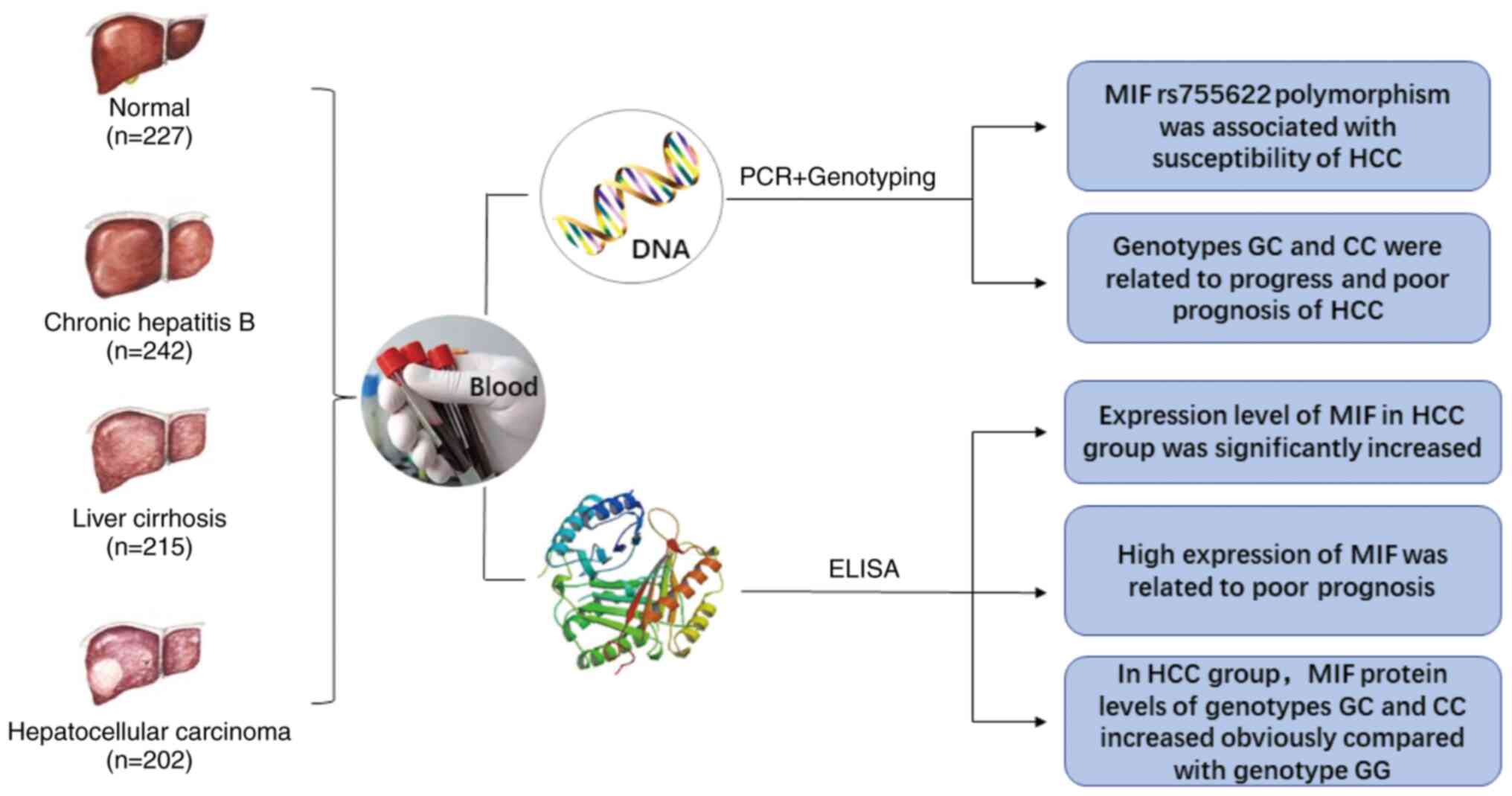
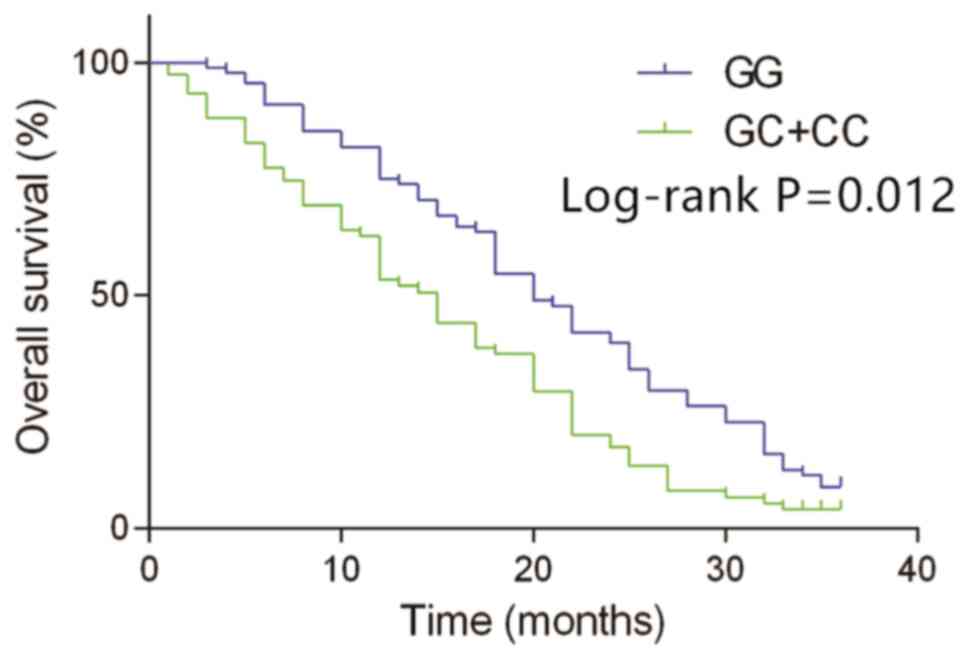
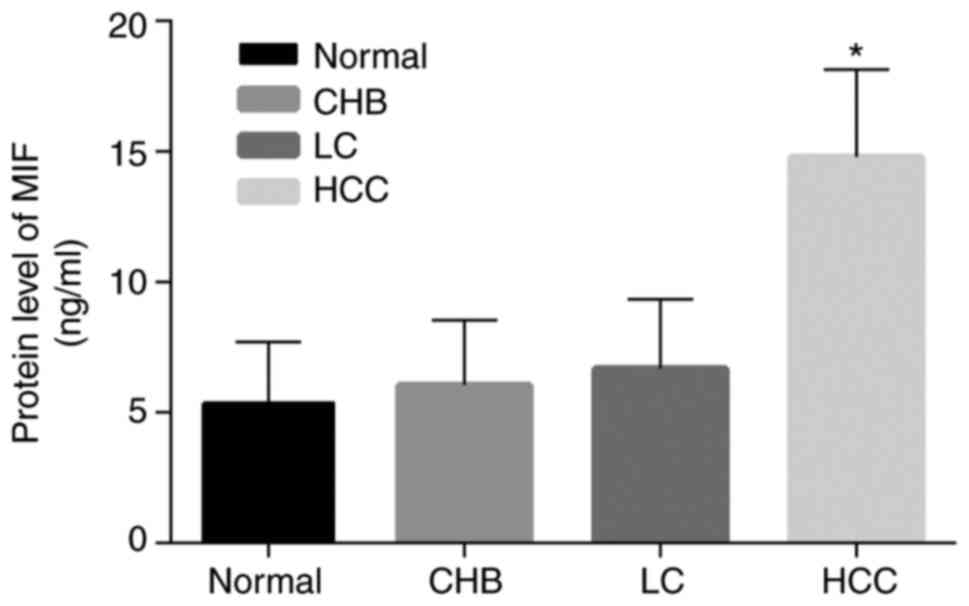
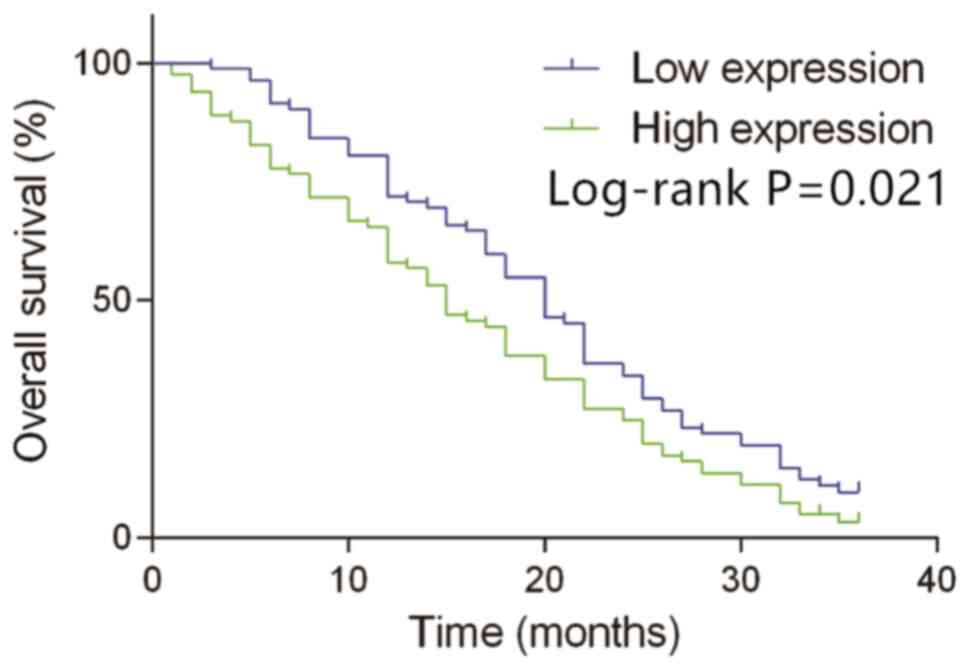
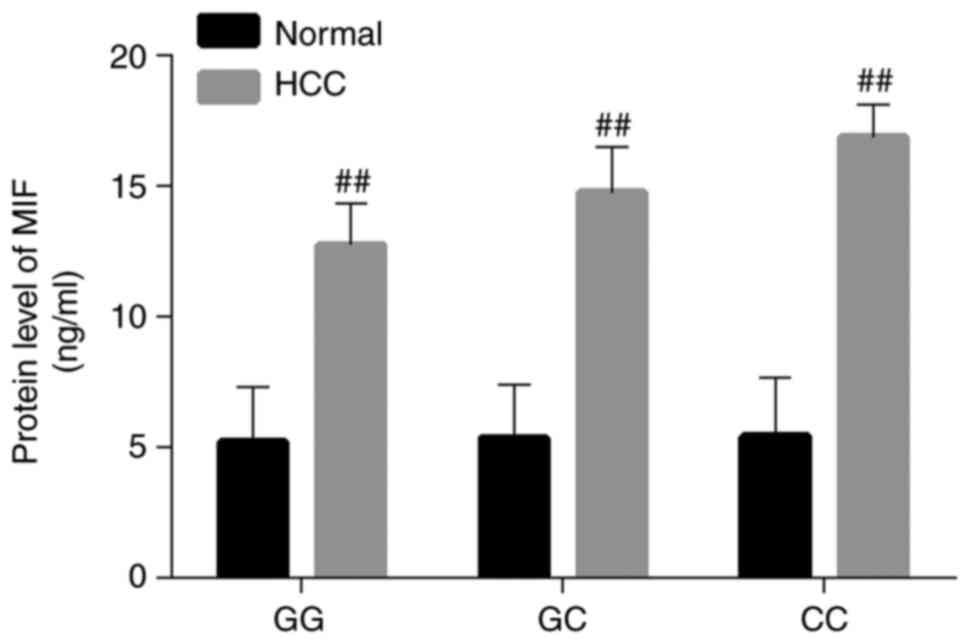
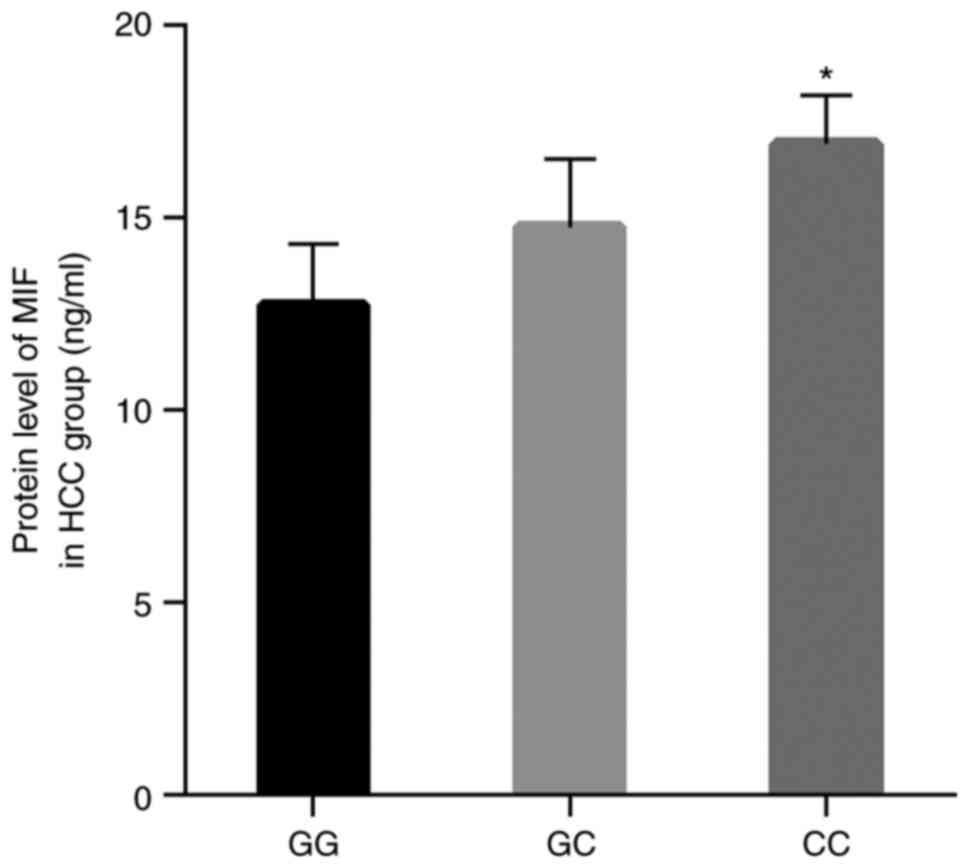
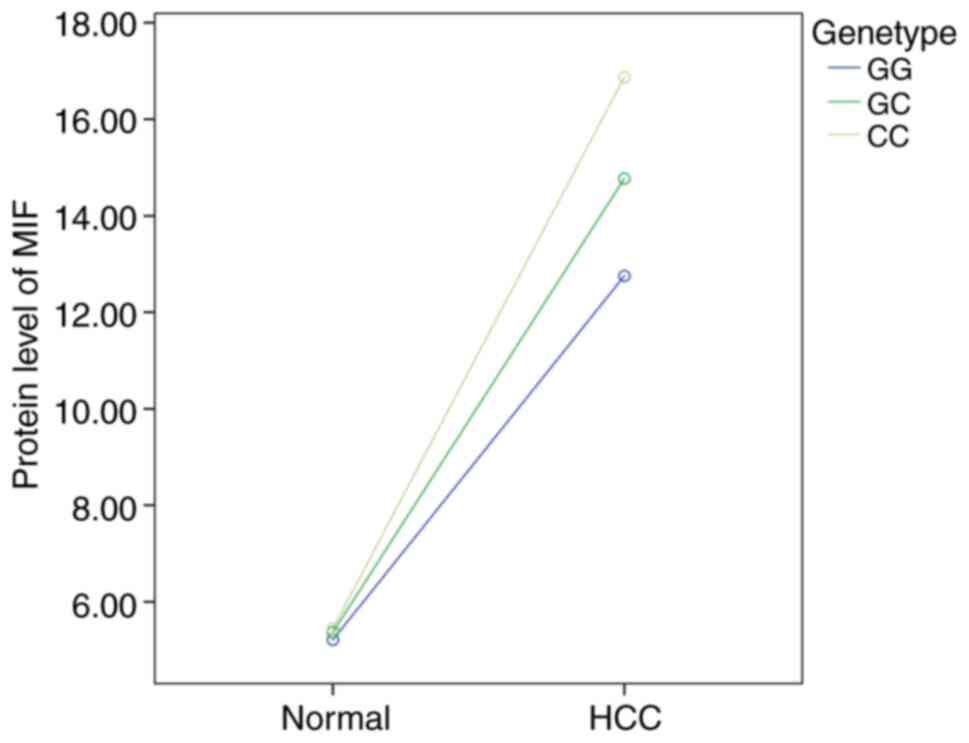
|
1
|
Kulik L and El-Serag HB: Epidemiology and
management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
156:477–491.e1. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pal LR and Moult J: Genetic basis of
common human disease: Insight into the role of missense SNPs from
genome-wide association studies. J Mol Biol. 427:2271–2289. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nie S, Wang H and Wang X: Research
progress on polymorphism of susceptibility genes in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Genet. 41:512–517. 2018.
|
|
5
|
Nobre CC, de Araújo JM, Fernandes TA,
Cobucci RN, Lanza DC, Andrade VS and Fernandes JV: Macrophage
migration inhibitory factor (MIF): Biological activities and
relation with cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 23:235–244. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Grieb G, Merk M, Bernhagen J and Bucala R:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF): A promising
biomarker. Drug News Perspect. 23:257–264. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Illescas O, Gomez-Verjan JC,
Garcia-Velazquez L, Govezensky T and Rodriguez-Sosa M: Macrophage
migration inhibitory factor-173 G/C polymorphism: A global
meta-analysis across the disease spectrum. Front Genet. 9:552018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fukui H, Saito H, Ueno Y, Uto H, Obara K,
Sakaida I, Shibuya A, Seike M, Nagoshi S, Segawa M, et al:
Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for liver cirrhosis
2015. J Gastroenterol. 51:629–650. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hou J, Wang G, Wang F, Cheng J, Ren H,
Zhuang H, Sun J, Li L, Li J, Meng Q, et al: Guideline of prevention
and treatment for chronic hepatitis B (2015 Update). J Clin Transl
Hepatol. 5:297–318. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou J, Sun H, Wang Z, Cong W, Wang J,
Zeng M, Zhou W, Bie P, Liu L, Wen T, et al: Guidelines for the
diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (2019 edition).
Liver Cancer. 9:682–720. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Forner A, Reig ME, de Lope CR and Bruix J:
Current strategy for staging and treatment: The BCLC update and
future prospects. Semin Liver Dis. 30:61–74. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ayuso C, Rimola J, Vilana R, Burrel M,
Darnell A, García-Criado Á, Bianchi L, Belmonte E, Caparroz C,
Barrufet M, et al: Diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC): Current guidelines. Eur J Radiol. 101:72–81. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Meza-Romero R, Benedek G, Leng L, Bucala R
and Vandenbark AA: Predicted structure of MIF/CD74 and RTL1000/CD74
complexes. Metab Brain Dis. 31:249–255. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jankauskas SS, Wong DWL, Bucala R, Djudjaj
S and Boor P: Evolving complexity of MIF signaling. Cell Signal.
57:76–88. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Conroy H. Mawhinney L and Donnelly SC:
Inflammation and cancer: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor
(MIF)-the potential missing link. QJM. 103:831–836. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jäger B, Klatt D, Plappert L, Golpon H,
Lienenklaus S, Barbosa PD, Schambach A and Prasse A: CXCR4/MIF axis
amplifies tumor growth and epithelial-mesenchymal interaction in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Signal. 73:1096722020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Guda MR, Rashid MA, Asuthkar S, Jalasutram
A, Caniglia JL, Tsung AJ and Velpula KK: Pleiotropic role of
macrophage migration inhibitory factor in cancer. Am J Cancer Res.
9:2760–2773. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Penticuff JC, Woolbright BL, Sielecki TM,
Weir SJ and Taylor JA: MIF family proteins in genitourinary cancer:
Tumorigenic roles and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Urol.
16:318–328. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hira E, Ono T, Dhar DK, El-Assal ON,
Hishikawa Y, Yamanoi A and Nagasue N: Overexpression of macrophage
migration inhibitory factor induces angiogenesis and deteriorates
prognosis after radical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer. 103:588–598. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li QT, Feng YM, Ke ZH, Qiu MJ and Xiong
ZF: KCNN4 promotes invasion and metastasis through the MAPK/ERK
pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Investig Med. 68:68–74.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Songlin M, Fei X, Long Y and Yang L: The
effect of miRNA-451 on the proliferation and invasion capacity of
human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines via its regulation on
COX-2 and other cytokines. Oncol Progress. 16:690–693. 2018.
|
|
22
|
Sun B, Nishihira J, Yoshiki T, Kondo M,
Sato Y, Sasaki F and Todo S: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor
promotes tumor invasion and metastasis via the Rho-dependent
pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 11:1050–1058. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pei XJ, Wu TT, Li B, Tian XY, Li Z and
Yang QX: Increased expression of macrophage migration inhibitory
factor and DJ-1 contribute to cell invasion and metastasis of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Med Sci. 11:106–115. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu J, Zhang C, Hu W and Feng Z: Tumor
suppressor p53 and its mutants in cancer metabolism. Cancer Lett.
356:197–203. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mathumai K: Treating p53 mutant
aggregation-associated cancer. Cancers. 10:1542018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ubby I, Krueger C, Rosato R, Qian W, Chang
J and Sabapathy K: Cancer therapeutic targeting using
mutant-p53-specific siRNAs. Oncogene. 38:3415–3427. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fukaya R, Ohta S, Yaguchi T, Matsuzaki Y,
Sugihara E, Okano H, Saya H, Kawakami Y, Kawase T, Yoshida K and
Toda M: MIF maintains the tumorigenic capacity of brain
tumor-initiating cells by directly inhibiting p53. Cancer Res.
76:2813–2823. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kong F, Xuan D, Kong X, Du Y, Li L, Zhu H,
Wang Y, Xie D, Guha S, Li Z, et al: ZFPM2-AS1, a Novel lncRNA,
attenuates the p53 pathway and promotes gastric carcinogenesis by
stabilizing MIF. Oncogene. 37:5982–5996. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ramireddy L, Chen WT, Peng CT, Hu RM, Ke
TW, Chiang HC, Chang SC, Tsai FJ and Lo WY: Association between
genetic polymorphism of the MIF gene and colorectal cancer in
Taiwan. J Clin Lab Anal. 29:268–274. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin S, Wang M, Liu X, Zhu W, Guo Y, Dai Z,
Yang P, Tian T, Dai C, Zheng Y, et al: Association of genetic
polymorphisms in MIF with breast cancer risk in Chinese women. Clin
Exp Med. 17:395–401. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ding GX, Zhou SQ, Xu Z, Feng NH, Song NH,
Wang XJ, Yang J, Zhang W, Wu HF and Hua LX: The association between
MIF-173 G>C polymorphism and prostate cancer in southern
Chinese. J Surg Oncol. 100:106–110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xiang T, Bing Z, Tong Q, Liu S, Peng S,
Yang X and Fan H: The MIF-173G/C gene polymorphism increase
gastrointestinal cancer and hematological malignancy risk: Evidence
from a meta-analysis and FPRP test. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:15949–15957. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yuan T, Tang C, Chen M, Deng S and Chen P:
Influence of the human MIF promoter polymorphism on hepatocellular
carcinoma prognosis. Genet Mol Res. 12:6629–6635. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
O'Reilly C, Doroudian M, Mawhinney L and
Donnelly SC: Targeting MIF in cancer: Therapeutic strategies,
current developments, and future opportunities. Med Res Rev.
36:440–460. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang D, Luo L, Chen W, Chen LZ, Zeng WT,
Li W and Huang XH: Significance of the vascular endothelial growth
factor and the macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the
progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 31:1199–1204.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao YM, Wang L, Dai Z, Wang DD, Hei ZY,
Zhang N, Fu XT, Wang XL, Zhang SC, Qin LX, et al: Validity of
plasma macrophage migration inhibitory factor for diagnosis and
prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 129:2463–2472.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Han Y and Zhang C: Macrophage migration
inhibitory factor plays a pivotal role in hepatocellular carcinoma
and may be a noninvasive imaging target. Medical Hypotheses.
75:530–532. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Oscar I, Gomez-Verjan JC, Lizbeth GV,
Tzipe G and Miriam RS: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor-173
G/C polymorphism: A global meta-analysis across the disease
spectrum. Front Genet. 9:552018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Gnoni A, Santini D, Scartozzi M, Russo A,
Licchetta A, Palmieri V, Lupo L, Faloppi L, Palasciano G, Memeo V,
et al: Hepatocellular carcinoma treatment over sorafenib:
Epigenetics, microRNAs and microenvironment. Is there a light at
the end of the tunnel? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 19:1623–1635.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang K, Pan X, Shu X, Cao H, Chen L, Zou
Y, Deng H, Li G and Xu Q: Relationship between MIF-173 G/C
polymorphism and susceptibility to chronic hepatitis B and
HBV-induced liver cirrhosis. Cell Immunol. 282:113–116. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|