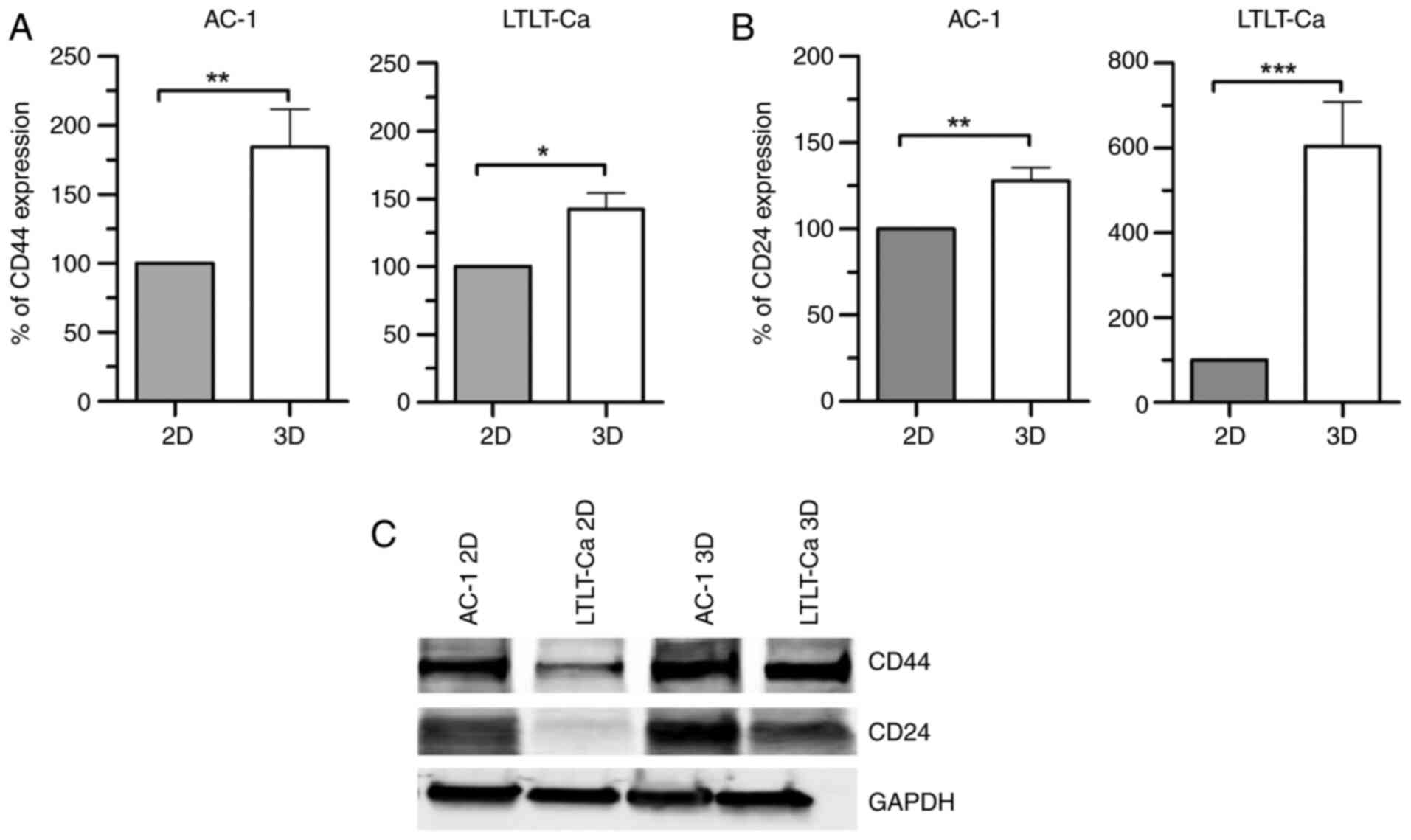
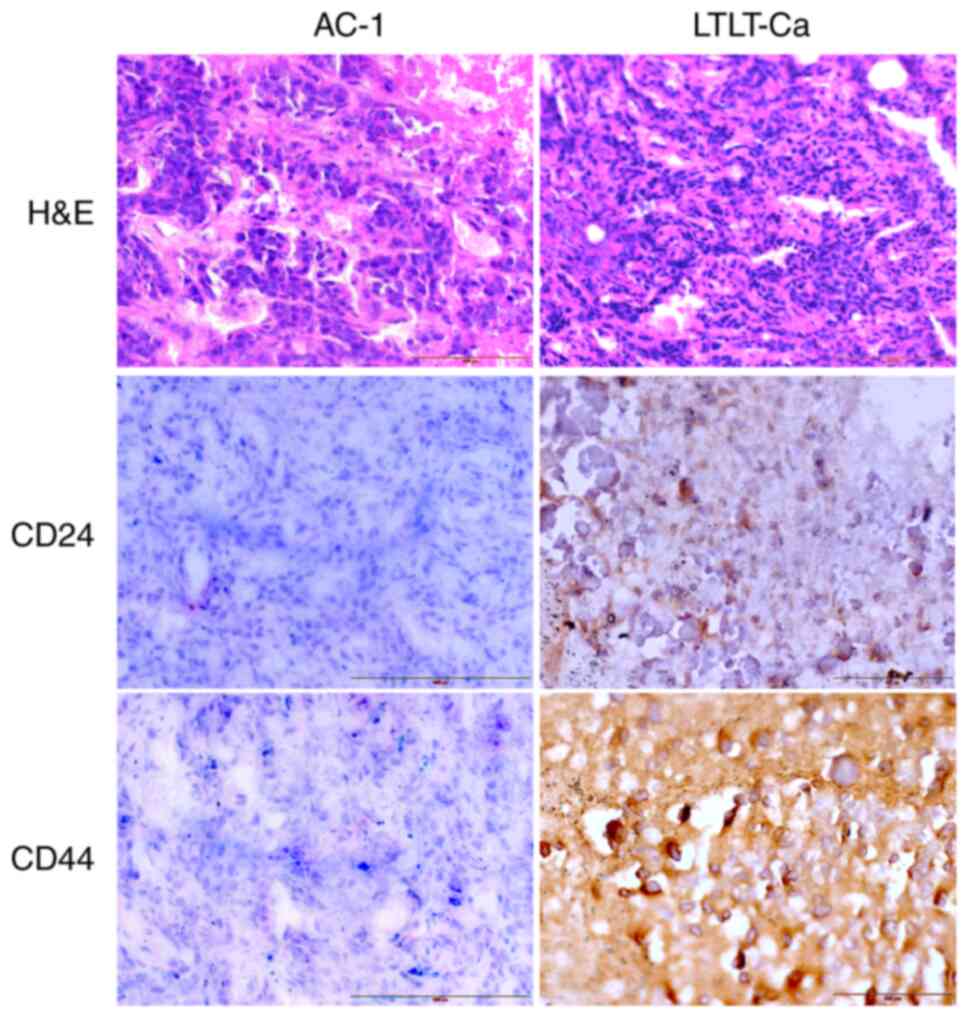
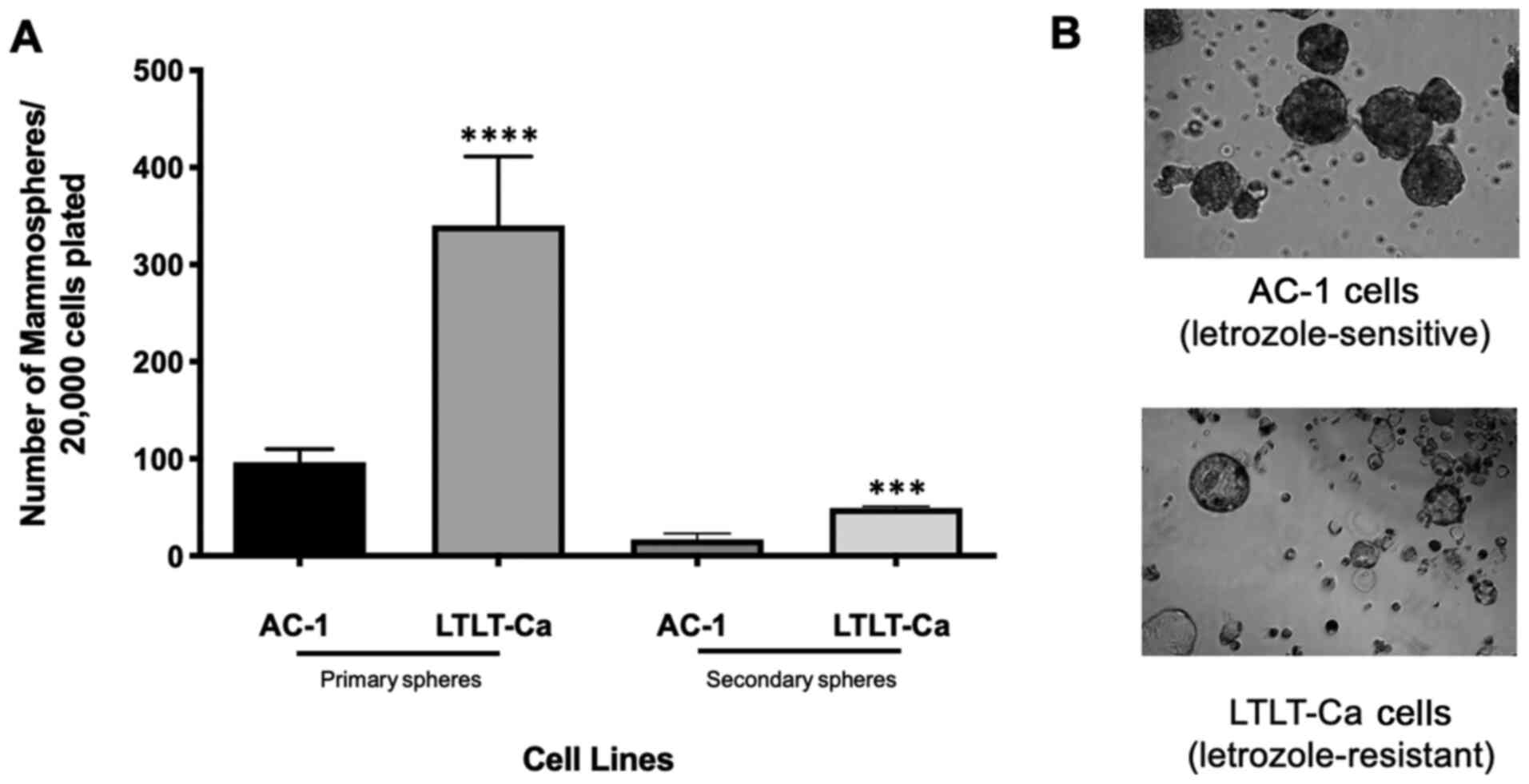
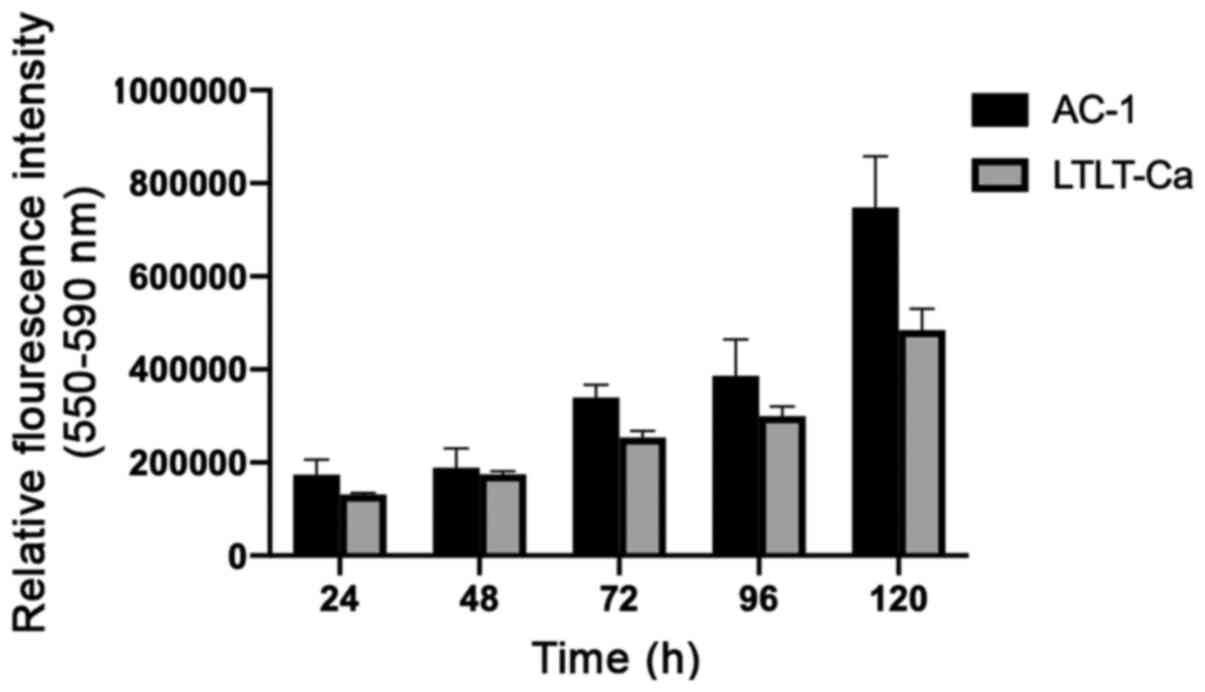
|
1
|
Gilani RA, Kazi AA, Shah P, Schech AJ,
Chumsri S, Sabnis G, Jaiswal AK and Brodie AH: The importance of
her2 signaling in the tumor-initiating cell population in aromatase
inhibitor-resistant breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
135:681–692. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brodie A, Jelovac D, Macedo L, Sabnis G,
Tilghman S and Goloubeva O: Therapeutic observations in MCF-7
aromatase xenografts. Clin Cancer Res. 11:884s–888s.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brodie A, Jelovac D, Sabnis G, Long B,
Macedo L and Goloubeva O: Model systems: Mechanisms involved in the
loss of sensitivity to letrozole. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
95:41–48. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jelovac D, Sabnis G, Long BJ, Macedo L,
Goloubeva OG and Brodie AM: Activation of mitogen-activated protein
kinase in xenografts and cells during prolonged treatment with
aromatase inhibitor letrozole. Cancer Res. 65:5380–5389. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sabnis G and Brodie A: Adaptive changes
results in activation of alternate signaling pathways and
resistance to aromatase inhibitor resistance. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
340:142–147. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sabnis G, Schayowitz A, Goloubeva O,
Macedo L and Brodie A: Trastuzumab reverses letrozole resistance
and amplifies the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to estrogen.
Cancer Res. 69:1416–1428. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tilghman SL, Townley I, Zhong Q, Carriere
PP, Zou J, Llopis SD, Preyan LC, Williams CC, Skripnikova E,
Bratton MR, et al: Proteomic signatures of acquired letrozole
resistance in breast cancer: Suppressed estrogen signaling and
increased cell motility and invasiveness. Mol Cell Proteomics.
12:2440–2455. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsai JH and Yang J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
plasticity in carcinoma metastasis. Genes Dev. 27:2192–2206. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gupta PB, Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA:
Cancer stem cells: Mirage or reality? Nat Med. 15:1010–1012. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, Campbell
LL, Polyak K, Brisken C, Yang J and Weinberg RA: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Al-Hajj M and Clarke MF: Self-renewal and
solid tumor stem cells. Oncogene. 23:7274–7282. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Armstrong AJ, Marengo MS, Oltean S, Kemeny
G, Bitting RL, Turnbull JD, Herold CI, Marcom PK, George DJ and
Garcia-Blanco MA: Circulating tumor cells from patients with
advanced prostate and breast cancer display both epithelial and
mesenchymal markers. Mol Cancer Res. 9:997–1007. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van der Horst G, Bos L and van der Pluijm
G: Epithelial plasticity, cancer stem cells, and the
tumor-supportive stroma in bladder carcinoma. Mol Cancer Res.
10:995–1009. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weiswald LB, Bellet D and Dangles-Marie V:
Spherical cancer models in tumor biology. Neoplasia. 17:1–15. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Serrano M: The ink4a/arf locus in murine
tumorigenesis. Carcinogenesis. 21:865–869. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cicalese A, Bonizzi G, Pasi CE, Faretta M,
Ronzoni S, Giulini B, Brisken C, Minucci S, Di Fiore PP and Pelicci
PG: The tumor suppressor p53 regulates polarity of self-renewing
divisions in mammary stem cells. Cell. 138:1083–1095. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dey D, Saxena M, Paranjape AN, Krishnan V,
Giraddi R, Kumar MV, Mukherjee G and Rangarajan A: Phenotypic and
functional characterization of human mammary stem/progenitor cells
in long term culture. PLoS One. 4:e53292009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Manuel Iglesias J, Beloqui I,
Garcia-Garcia F, Leis O, Vazquez-Martin A, Eguiara A, Cufi S, Pavon
A, Menendez JA, Dopazo J and Martin AG: Mammosphere formation in
breast carcinoma cell lines depends upon expression of e-cadherin.
PLoS One. 8:e772812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gupta A, Mehta R, Alimirah F, Peng X,
Murillo G, Wiehle R and Mehta RG: Efficacy and mechanism of action
of proellex, an antiprogestin in aromatase overexpressing and
letrozole resistant t47d breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 133:30–42. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Capes-Davis A, Reid YA, Kline MC, Storts
DR, Strauss E, Dirks WG, Drexler HG, MacLeod RA, Sykes G, Kohara A,
et al: Match criteria for human cell line authentication: Where do
we draw the line? Int J Cancer. 132:2510–2519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Johnson KP, Yearby LA, Stoute D, Burow ME,
Rhodes LV, Gray M, Carriere P, Tilghman SL, McLachlan JA, Ochieng
J, et al: In vitro and in vivo evaluation of novel anticancer
agents in triple negative breast cancer models. J Health Care Poor
Underserved. 24 (Suppl 1):104–111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Carriere PP, Llopis SD, Naiki AC, Nguyen
G, Phan T, Nguyen MM, Preyan LC, Yearby L, Pratt J, Burks H, et al:
Glyceollin i reverses epithelial to mesenchymal transition in
letrozole resistant breast cancer through zeb1. Int J Environ Res
Public Health. 13:ijerph130100102016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative pcr and
the 2(−delta delta c(t)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pfaffl MW, Lange IG, Daxenberger A and
Meyer HH: Tissue-specific expression pattern of estrogen receptors
(ER): Quantification of ER alpha and ER beta mRNA with real-time
RT-PCR. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 109:345–355. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Creighton CJ, Li X, Landis M, Dixon JM,
Neumeister VM, Sjolund A, Rimm DL, Wong H, Rodriguez A,
Herschkowitz JI, et al: Residual breast cancers after conventional
therapy display mesenchymal as well as tumor-initiating features.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:13820–13825. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dontu G, Abdallah WM, Foley JM, Jackson
KW, Clarke MF, Kawamura MJ and Wicha MS: In vitro propagation and
transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells.
Genes Dev. 17:1253–1270. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Du L, Wang H, He L, Zhang J, Ni B, Wang X,
Jin H, Cahuzac N, Mehrpour M, Lu Y and Chen Q: Cd44 is of
functional importance for colorectal cancer stem cells. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:6751–6760. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ricardo S, Vieira AF, Gerhard R, Leitao D,
Pinto R, Cameselle-Teijeiro JF, Milanezi F, Schmitt F and Paredes
J: Breast cancer stem cell markers cd44, cd24 and aldh1: Expression
distribution within intrinsic molecular subtype. J Clin Pathol.
64:937–946. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li W, Ma H, Zhang J, Zhu L, Wang C and
Yang Y: Unraveling the roles of cd44/cd24 and aldh1 as cancer stem
cell markers in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Sci Rep. 7:138562017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li W, Ma H, Zhang J, Zhu L, Wang C and
Yang Y: Author correction: Unraveling the roles of cd44/cd24 and
aldh1 as cancer stem cell markers in tumorigenesis and metastasis.
Sci Rep. 8:42762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Vazquez-Martin A,
Martin-Castillo B, Cufí S, Del Barco S, Lopez-Bonet E, Brunet J and
Menendez JA: Dynamic emergence of the mesenchymal
cd44(pos)cd24(neg/low) phenotype in her2-gene amplified breast
cancer cells with de novo resistance to trastuzumab (herceptin).
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 397:27–33. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Simpkins SA, Hanby AM, Holliday DL and
Speirs V: Clinical and functional significance of loss of
caveolin-1 expression in breast cancer-associated fibroblasts. J
Pathol. 227:490–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sloan EK, Ciocca DR, Pouliot N, Natoli A,
Restall C, Henderson MA, Fanelli MA, Cuello-Carrión FD, Gago FE and
Anderson RL: Stromal cell expression of caveolin-1 predicts outcome
in breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 174:2035–2043. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Witkiewicz AK, Dasgupta A, Sotgia F,
Mercier I, Pestell RG, Sabel M, Kleer CG, Brody JR and Lisanti MP:
An absence of stromal caveolin-1 expression predicts early tumor
recurrence and poor clinical outcome in human breast cancers. Am J
Pathol. 174:2023–2034. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Trimmer C, Sotgia F, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Balliet RM, Eaton G, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Pavlides S, Howell A,
Iozzo RV, Pestell RG, et al: Caveolin-1 and mitochondrial sod2
(mnsod) function as tumor suppressors in the stromal
microenvironment: A new genetically tractable model for human
cancer associated fibroblasts. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:383–394. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lu Z, Ghosh S, Wang Z and Hunter T:
Downregulation of caveolin-1 function by egf leads to the loss of
e-cadherin, increased transcriptional activity of beta-catenin, and
enhanced tumor cell invasion. Cancer Cell. 4:499–515. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dolled-Filhart M, McCabe A, Giltnane J,
Cregger M, Camp RL and Rimm DL: Quantitative in situ analysis of
beta-catenin expression in breast cancer shows decreased expression
is associated with poor outcome. Cancer Res. 66:5487–5494. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gomes IM, Maia CJ and Santos CR: Steap
proteins: From structure to applications in cancer therapy. Mol
Cancer Res. 10:573–587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xie J, Yang Y, Sun J, Jiao Z, Zhang H and
Chen J: Steap1 inhibits breast cancer metastasis and is associated
with epithelial-mesenchymal transition procession. Clin Breast
Cancer. 19:e195–e207. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Maia CJ, Socorro S, Schmitt F and Santos
CR: Steap1 is over-expressed in breast cancer and down-regulated by
17beta-estradiol in mcf-7 cells and in the rat mammary gland.
Endocrine. 34:108–116. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang G, Huang W, Li W, Chen S, Chen W,
Zhou Y, Peng P and Gu W: Tfpi-2 suppresses breast cancer cell
proliferation and invasion through regulation of erk signaling and
interaction with actinin-4 and myosin-9. Sci Rep. 8:144022018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|