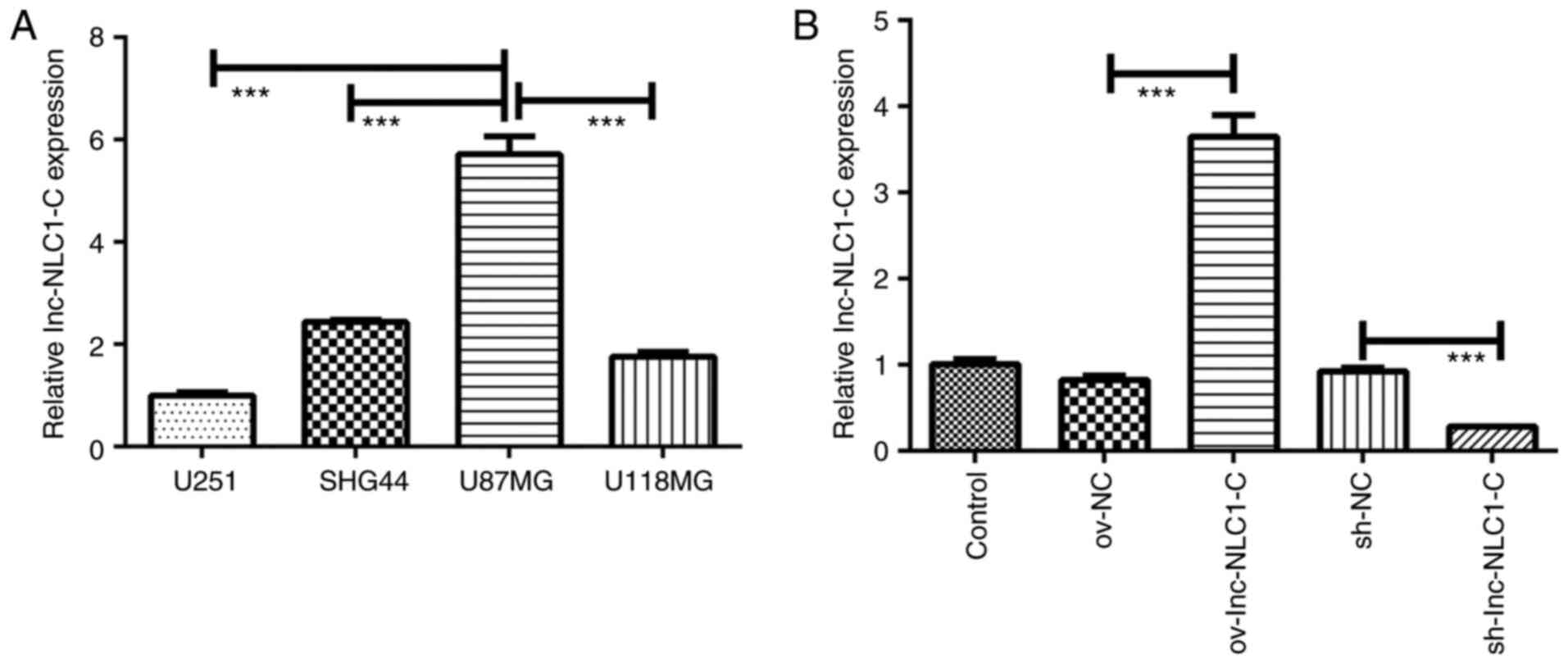
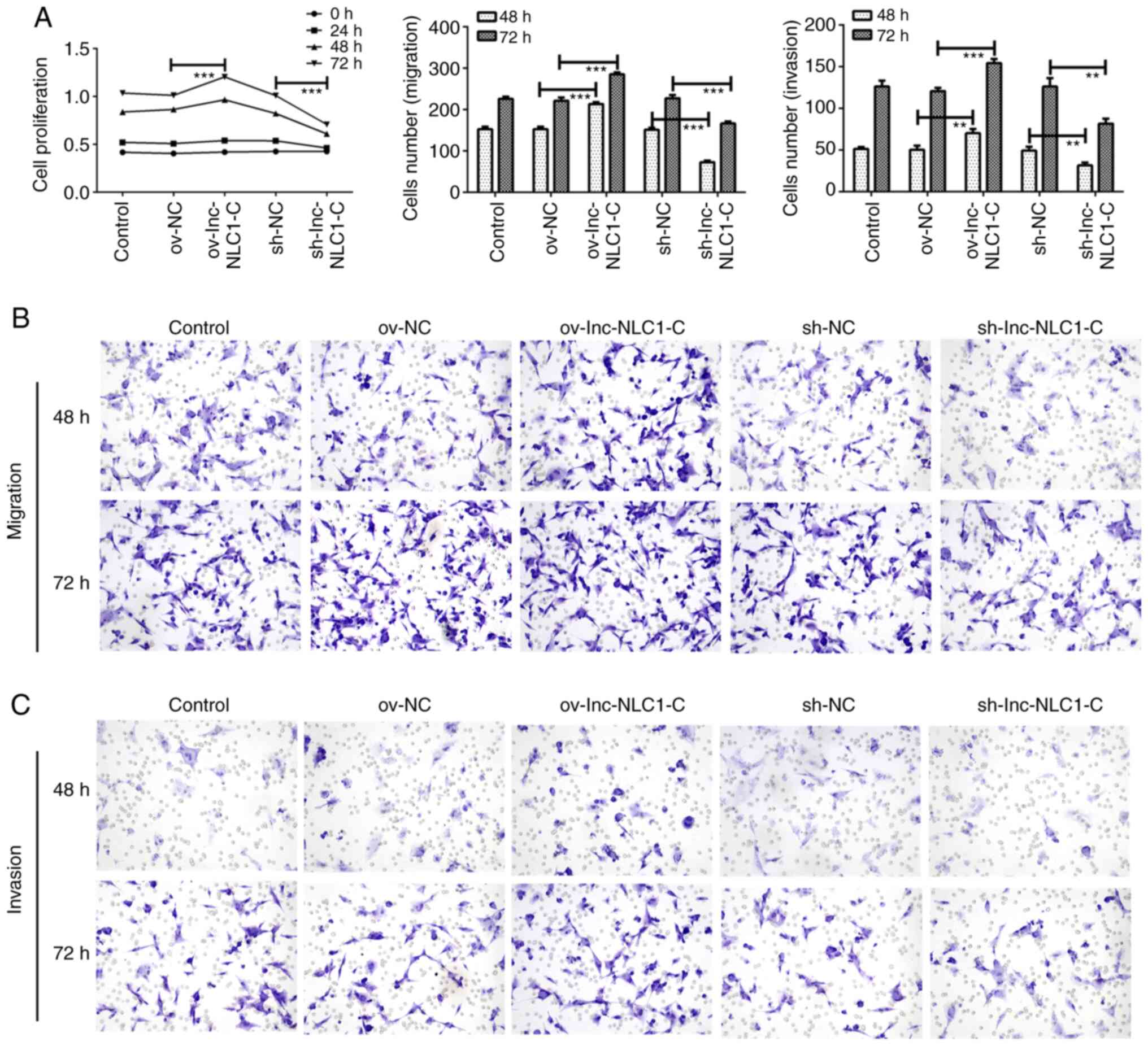
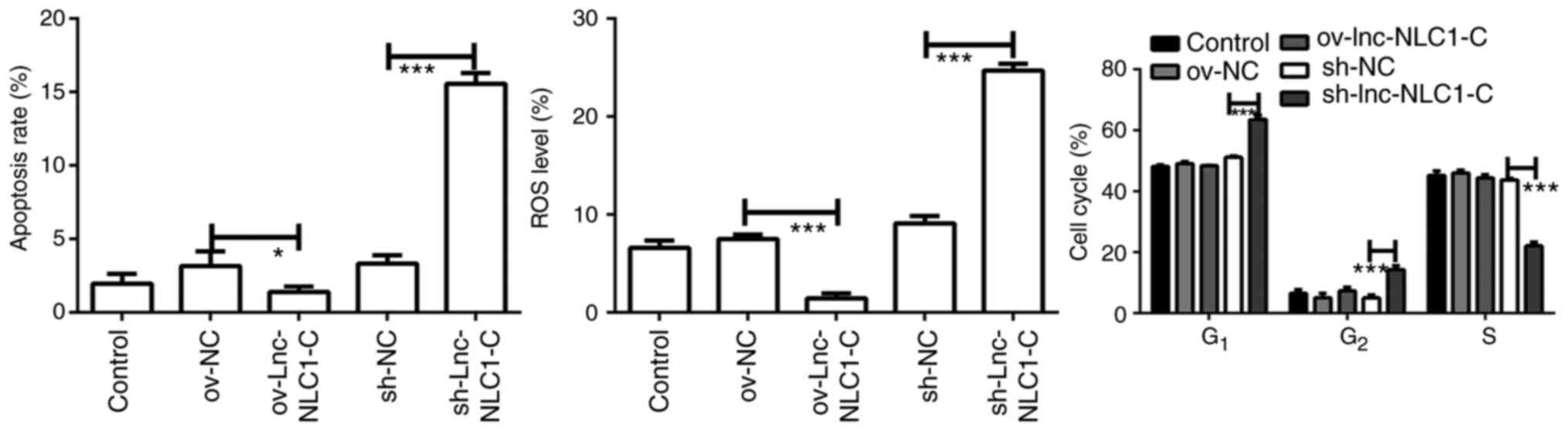
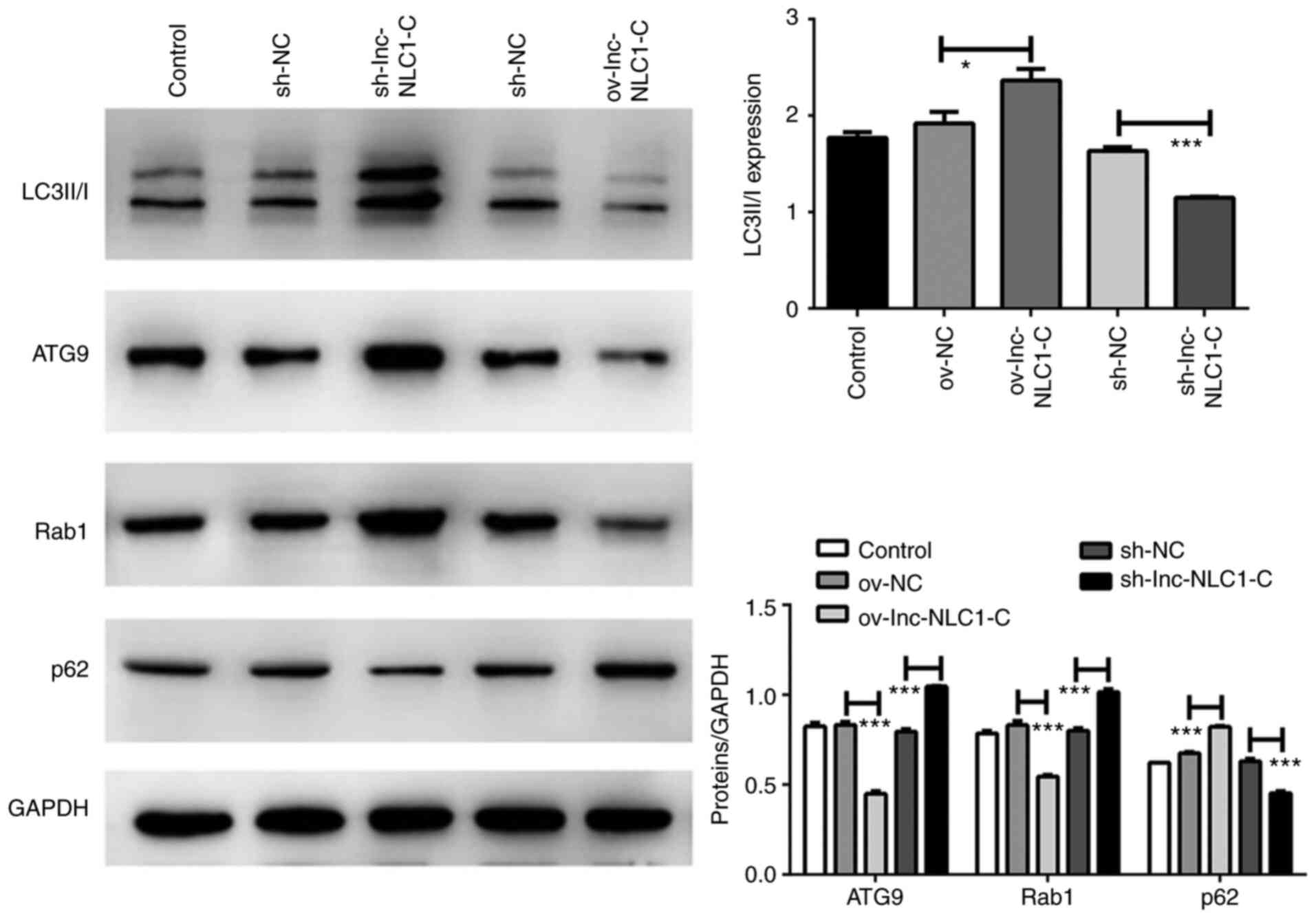
|
1
|
Lai NS, Wu DG, Fang XG, Lin YC, Chen SS,
Li ZB and Xu SS: Serum microRNA-210 as a potential noninvasive
biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of glioma. Br J Cancer.
112:1241–1246. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fabian C, Han M, Bjerkvig R and Niclou SP:
Novel facets of glioma invasion. Int Rev Cell Mol Bio. 360:33–64.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mansouri A, Mansouri S, Hachem LD,
Klironomos G, Vogelbaum MA, Bernstein M and Zadeh G: The role of
5-aminolevulinic acid in enhancing surgery for high-grade glioma,
its current boundaries, and future perspectives: A systematic
review. Cancer. 122:2469–2478. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moran VA, Perera RJ and Khalil AM:
Emerging functional and mechanistic paradigms of mammalian long
non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:6391–6400. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang L, Cho KB, Li Y, Tao G, Xie Z and Guo
B: Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-mediated competing endogenous RNA
networks provide novel potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets
for colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20:57582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wei GH and Wang X: LncRNA MEG3 inhibit
proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer via p53 signaling
pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:3850–3856. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu GJ, Sun Y, Zhang DW and Zhang P: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR functions as a competitive endogenous RNA to
regulate PRAF2 expression by sponging miR-326 in cutaneous squamous
cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 19:2702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang K, Luo Z, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Wu L,
Liu L, Yang J, Song X and Liu J: Circulating lncRNA H19 in plasma
as a novel biomarker for breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. 17:187–194.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Paraskevopoulou MD and Hatzigeorgiou AG:
Analyzing miRNA-lncRNA interactions. Methods Mol Biol.
1402:271–286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ballantyne MD, McDonald RA and Baker AH:
LncRNA/MicroRNA interactions in the vasculature. Clin Pharmacol
Ther. 99:494–501. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen L, Zhou Y and Li H: LncRNA, miRNA and
lncRNA-miRNA interaction in viral infection. Virus Res. 257:25–32.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wei L, Wang X, Lv L, Liu J, Xing H, Song
Y, Xie M, Lei T, Zhang N and Yang M: The emerging role of microRNAs
and long noncoding RNAs in drug resistance of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 18:1472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He Z, Cen D, Luo X, Li D, Li P, Liang L
and Meng Z: Downregulation of miR-383 promotes glioma cell invasion
by targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Med Oncol.
30:5572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kawashima M, Tamiya G, Oka A, Hohjoh H,
Juji T, Ebisawa T, Honda Y, Inoko H and Tokunaga K: Genomewide
association analysis of human narcolepsy and a new resistance gene.
Am J Hum Genet. 79:252–263. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mills JD, Kavanagh T, Kim WS, Chen BJ,
Kawahara Y, Halliday GM and Janitz M: Unique transcriptome patterns
of the white and grey matter corroborate structural and functional
heterogeneity in the human frontal lobe. PLoS One. 8:e784802013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zong L, Hattori N, Yasukawa Y, Kimura K,
Mori A, Seto Y and Ushijima T: LINC00162 confers sensitivity to
5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine via modulation of an RNA splicing protein,
HNRNPH1. Oncogene. 38:5281–5293. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lou X, Li J, Yu D, Wei YQ, Feng S and Sun
JJ: Comprehensive analysis of five long noncoding RNAs expression
as competing endogenous RNAs in regulating hepatoma carcinoma.
Cancer Med. 8:5735–5749. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Piipponen M, Nissinen L, Farshchian M,
Riihila P, Kivisaari A, Kallajoki M, Peltonen J, Peltonen S and
Kähäri VM: Long noncoding RNA PICSAR promotes growth of cutaneous
squamous cell carcinoma by regulating ERK1/2 activity. J Invest
Dermatol. 136:1701–1710. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu M, Tian H, Cao YX, He X, Chen L, Song
X, Ping P, Huang H and Sun F: Downregulation of
miR-320a/383-sponge-like long non-coding RNA NLC1-C (narcolepsy
candidate-region 1 genes) is associated with male infertility and
promotes testicular embryonal carcinoma cell proliferation. Cell
Death Dis. 6:e19602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morgan LL, Miller AB, Sasco A and Davis
DL: Mobile phone radiation causes brain tumors and should be
classified as a probable human carcinogen (2A) (review). Int J
Oncol. 46:1865–1871. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu W, Long H, Zhang M, Wang Y, Lu Q, Yuan
H, Qu Q and Qu J: Glutathione S-transferase genes variants and
glioma risk: A case-control and meta-analysis study. J Cancer.
10:4679–4688. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheng M and Liu L: MUC15 promotes growth
and invasion of glioma cells by activating Raf/MEK/ERK pathway.
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 47:1041–1048. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hu L, Zhao T, Wang J, Wang R, Bu H, Zheng
S, Li Y, Liu J and Wang S: Beauvericin inhibits the growth of U251
glioma cells and promotes apoptosis in vitro. J Biobased Materials
Bioenergy. 14:639–644. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hanaei S, Afshari K, Hirbod-Mobarakeh A,
Mohajer B, Amir Dastmalchi D and Rezaei N: Therapeutic efficacy of
specific immunotherapy for glioma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Rev The Neurosci. 29:443–461. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baumert BG, Hegi ME, van den Bent MJ, von
Deimling A, Gorlia T, Hoang-Xuan K, Brandes AA, Kantor G, Taphoorn
MJB, Hassel MB, et al: Temozolomide chemotherapy versus
radiotherapy in high-risk low-grade glioma (EORTC 22033–26033): A
randomised, open-label, phase 3 intergroup study. Lancet Oncol.
17:1521–1532. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jathar S, Kumar V, Srivastava J and
Tripathi V: Technological developments in lncRNA biology. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 1008:283–323. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kumar MM and Goyal R: LncRNA as a
therapeutic target for angiogenesis. Curr Top Med Chem.
17:1750–1757. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jarroux J, Morillon A and Pinskaya M:
History, discovery, and classification of lncRNAs. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1008:1–46. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Batista PJ and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell.
152:1298–1307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ren J, Zhang X, Cao J, Tian J, Luo J, Yu
Y, Wang F, Li J and Zhao Q: Radiosynthesis of a novel antisense
imaging probe targeting lncRNA HOTAIR in malignant glioma. Res Sq.
doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-152169/v1. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shi Y, Wang Y, Luan W, Wang P, Tao T,
Zhang J, Qian J, Liu N and You Y: Long Non-Coding RNA H19 promotes
glioma cell invasion by deriving miR-675. PLoS One. 9:e862952014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jing SY, Yang ZG, Cheng ZH, Fang JS and Li
X: Changes in expression levels of long-chain non-coding RNA CRNDE
in glioma and its association with clinical and pathological
characteristics. J Clin Neurosurgery. 16:11–16. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang D, Fu CW and Fan DQ: Participation of
tumor suppressors long non-coding RNA MEG3, microRNA-377 and PTEN
in glioma cell invasion and migration. Pathol Res Pract.
215:1525582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang JL, Ge HM, Yan ZJ and Yan H:
Correlativity between low expression level of long non-coding RNA
ADAMTS9-AS2 and poor prognosis in patients with gliomas. Chin J
Clin Neurosurgery. 24:278. 2019.
|
|
36
|
Luo Y, Morgan SL and Wang KC: PICSAR: Long
noncoding RNA in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Invest
Dermatol. 136:1541–1542. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li KK, Pang JC, Lau KM, Zhou L, Mao Y,
Wang Y, Poon WS and Ng HK: MiR-383 is downregulated in
medulloblastoma and targets peroxiredoxin 3 (PRDX3). Brain Pathol.
23:413–425. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tian S, Jiang H, Liu H, Cao X, Zhang D,
Mou SD and Li Z: The effects of miR-383 targeting PRDX3 on the
proliferation and invasion of HepG2 cells. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
29:1335–1340. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ng HK: Hsa-miR-383 and its Target
Peroxiredoxin 3 (PRDX3) Have Major Roles Controlling Cell Growth in
Medulloblastoma. Proceedings of the 88th Annual Meeting of the
American Association of Neuropathologists. AANP; Chicago, IL:
2012
|
|
40
|
Wang SZ, Gao ML and Hou JH: Regulation of
PRDX3 expression by miR383 and its effect on proliferation and
apoptosis of human medulloblastoma. Labeled Immunoassays Clin Med.
26:139–142. 2019.(In Chinese).
|
|
41
|
Li KK, Pang JC, Lau KM, Zhou L, Mao Y,
Wang Y, Poon WS and Ng HK: miR-383 is downregulated in
medulloblastoma and targets peroxiredoxin 3 (PRDX3). Brain Pathol.
23:413–425. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|