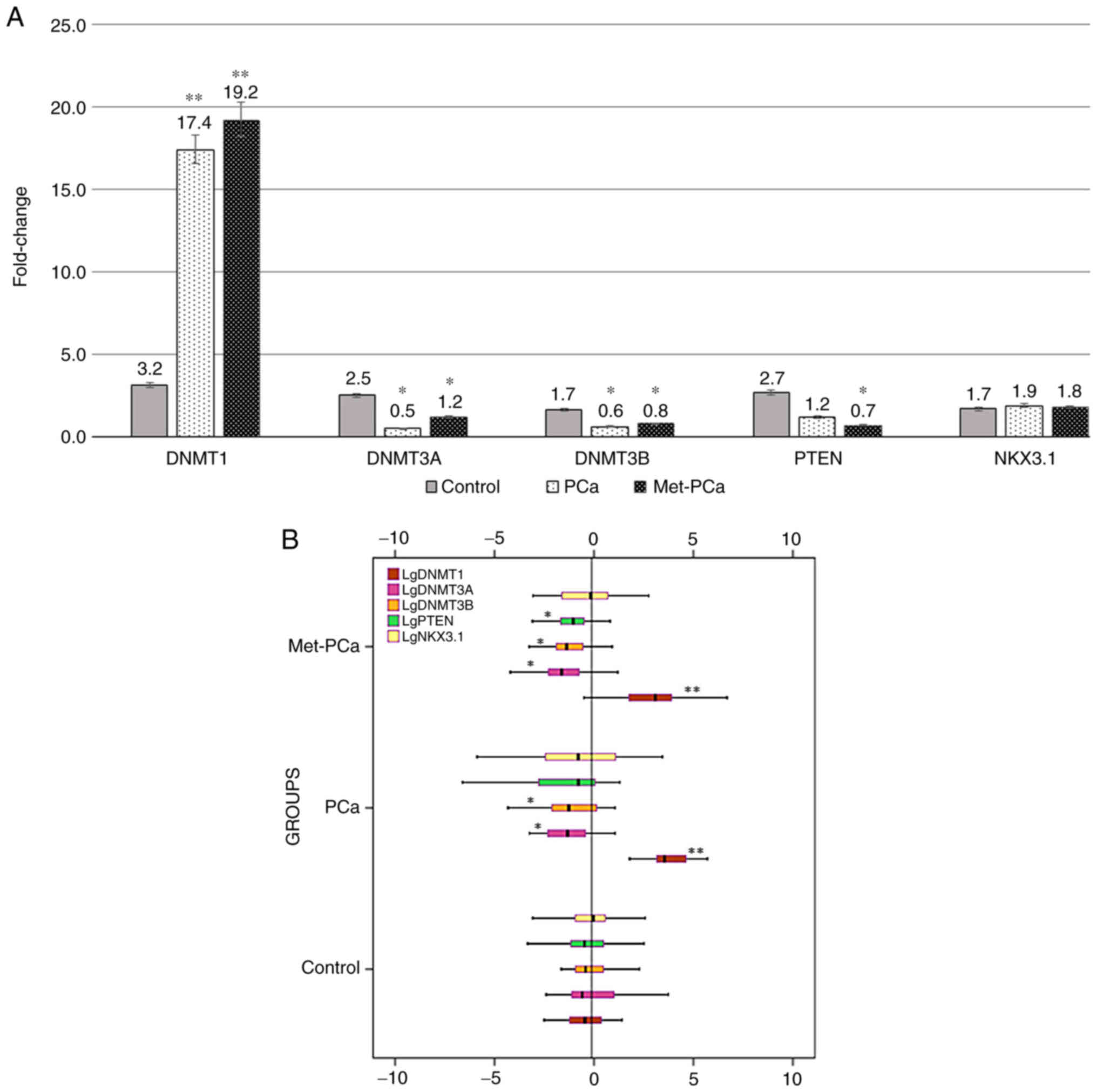
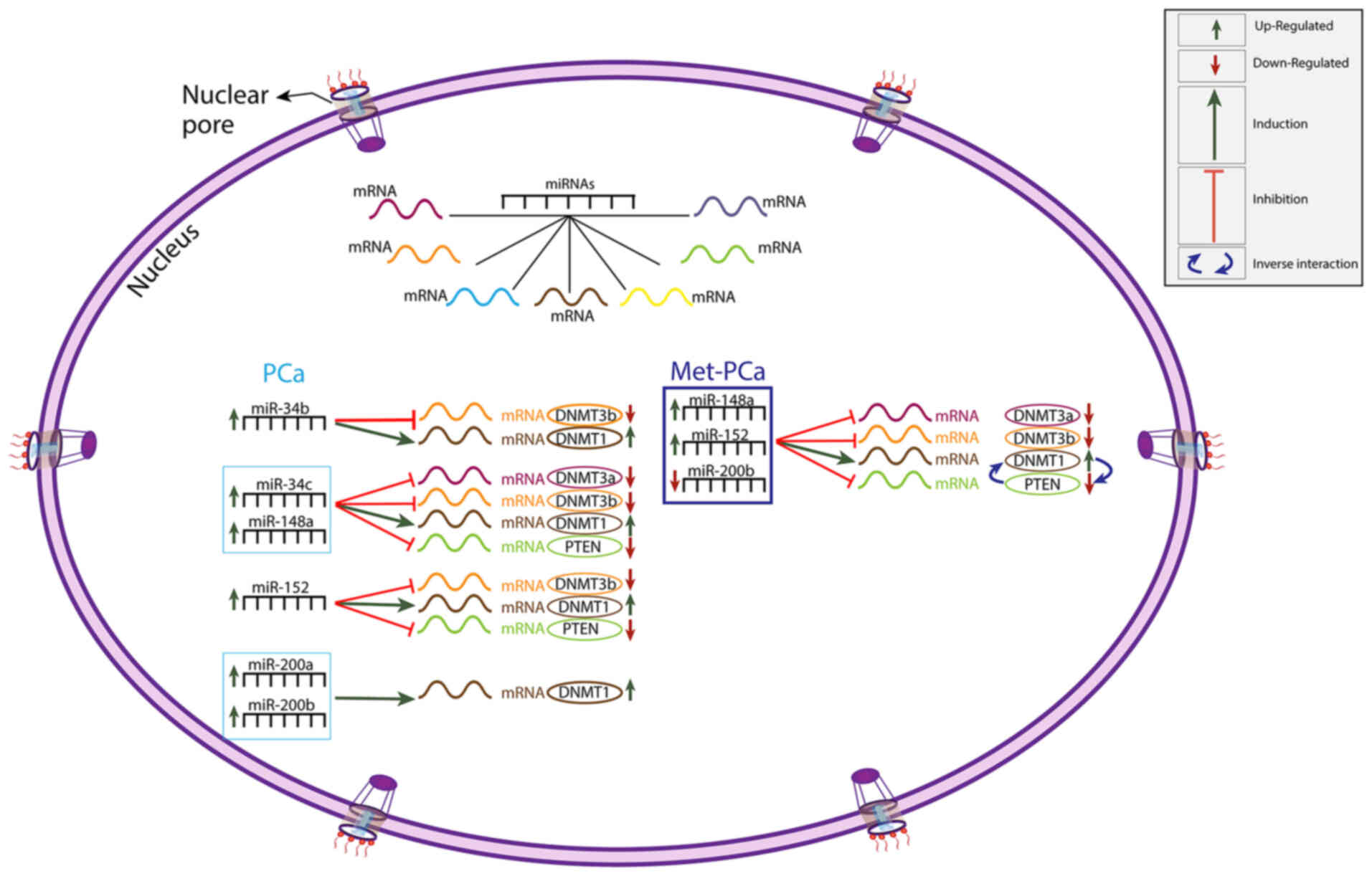
|
1
|
Stahl M, Kohrman N, Gore SD, Kim TK,
Zeidan AM and Prebet T: Epigenetics in cancer: A hematological
perspective. PLoS Genet. 12:e10061932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Malik SS, Batool R, Masood N and Yasmin A:
Risk factors for prostate cancer: A multifactorial case-control
study. Curr Probl Cancer. 42:337–343. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pandareesh MD, Kameshwar VH and Byrappa
KK: Prostate carcinogenesis: Insights in relation to epigenetics
and inflammation. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets.
21:253–267. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Prcic A, Begic E and Hiros M: Usefulness
of total PSA value in prostate diseases diagnosis. Acta Inform Med.
24:156–161. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bickers B and Aukim-Hastie C: New
molecular biomarkers for the prognosis and management of prostate
cancer-the post PSA era. Anticancer Res. 29:3289–3298.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Matin F, Jeet V, Moya L, Selth LA,
Chambers S; Australian Prostate Cancer BioResource, ; Clements JA
and Batra J: A plasma biomarker panel of four MicroRNAs for the
diagnosis of prostate cancer. Sci Rep. 8:66532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Filella X, Fernández-Galan E, Bonifacio RF
and Foj L: Emerging biomarkers in the diagnosis of prostate cancer.
Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 11:83–94. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sharma S, Kelly TK and Jones PA:
Epigenetics in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 31:27–36. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ramassone A, Pagotto S, Veronese A and
Visone R: Epigenetics and MicroRNAs in cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
19:4592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bosutti A, Zanconati F, Grassi G, Dapas B,
Passamonti S and Scaggiante B: Epigenetic and miRNAs dysregulation
in prostate cancer: The role of nutraceuticals. Anticancer Agents
Med Chem. 16:1385–1402. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lai X, Eberhardt M, Schmitz U and Vera J:
Systems biology-based investigation of cooperating microRNAs as
monotherapy or adjuvant therapy in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
47:7753–7766. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pesta M, Klecka J, Kulda V, Topolcan O,
Hora M, Eret V, Ludvikova M, Babjuk M, Novak K, Stolz J and Holubec
L: Importance of miR-20a expression in prostate cancer tissue.
Anticancer Res. 30:3579–3583. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brase JC, Johannes M, Schlomm T, Fälth M,
Haese A, Steuber T, Beissbarth T, Kuner R and Sültmann H:
Circulating miRNAs are correlated with tumor progression in
prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 128:608–616. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Watahiki A and Wang Y, Morris J, Dennis K,
O'Dwyer HM, Gleave M, Gout PW and Wang Y: MicroRNAs associated with
metastatic prostate cancer. PLoS One. 6:e249502011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Al-Kafaji G, Said HM, Alam MA and Al Naieb
ZT: Blood-based microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers to discriminate
localized prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia and
allow cancer-risk stratification. Oncol Lett. 16:1357–1365.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bhagirath D, Yang TL, Bucay N, Sekhon K,
Majid S, Shahryari V, Dahiya R, Tanaka Y and Saini S: microRNA-1246
is an exosomal biomarker for aggressive prostate cancer. Cancer
Res. 78:1833–1844. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Paziewska A, Mikula M, Dabrowska M,
Kulecka M, Goryca K, Antoniewicz A, Dobruch J, Borowka A, Rutkowski
P and Ostrowski J: Candidate diagnostic miRNAs that can detect
cancer in prostate biopsy. Prostate. 78:178–185. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang M, Wang F and Zhang X: miRNA-627
inhibits cell proliferation and cell migration, promotes cell
apoptosis in prostate cancer cells through upregulating MAP3K1,
PTPRK and SRA1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 11:255–261. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tu J, Peng Q, Shen Y, Hong Y, Zhu J, Feng
Z, Zhou P, Fan S, Zhu Y and Zhang Y: Identification of biomarker
microRNA-mRNA regulatory pairs for predicting the docetaxel
resistance in prostate cancer. J Cancer. 10:5469–5482. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bi CW, Zhang GY, Bai Y, Zhao B and Yang H:
Increased expression of miR-153 predicts poor prognosis for
patients with prostate cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e16705.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lynch SM, O'Neill KM, McKenna MM, Walsh CP
and McKenna DJ: Regulation of miR-200c and miR-141 by methylation
in prostate cancer. Prostate. 76:1146–1159. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Daniunaite K, Dubikaityte M, Gibas P,
Bakavicius A, Lazutka JM, Ulys A, Jankevicius F and Jarmalaite S:
Clinical significance of miRNA host gene promoter methylation in
prostate cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 26:2451–2461. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Torres-Ferreira J, Ramalho-Carvalho J,
Gomez A, Menezes FD, Freitas R, Oliveira J, Antunes L, Bento MJ,
Esteller M, Henrique R and Jerónimo C: miR-193b promoter
methylation accurately detects prostate cancer in urine sediments
and miR-34b/c or miR-129-2 promoter methylation define subsets of
clinically aggressive tumors. Mol Cancer. 16:262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barros-Silva D, Costa-Pinheiro P, Duarte
H, Sousa EJ, Evangelista AF, Graça I, Carneiro I, Martins AT,
Oliveira J, Carvalho AL, et al: MicroRNA-27a-5p regulation by
promoter methylation and MYC signaling in prostate carcinogenesis.
Cell Death Dis. 9:1672018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gurbuz V, Kiliccioglu I, Dikmen AU, Bilen
CY, Sozen S and Konac E: Comparative analysis of epi-miRNA
expression levels in local/locally advanced and metastatic prostate
cancer patients. Gene. 758:1449632020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lyko F: The DNA methyltransferase family:
A versatile toolkit for epigenetic regulation. Nat Rev Genet.
19:81–92. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Subramaniam D, Thombre R, Dhar A and Anant
S: DNA methyltransferases: A novel target for prevention and
therapy. Front Oncol. 4:802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang J, Yang C, Wu C, Cui W and Wang L:
DNA methyltransferases in cancer: Biology, paradox, aberrations,
and targeted therapy. Cancers (Basel). 12:21232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Maehama T, Taylor GS and Dixon JE: PTEN
and myotubularin: Novel phosphoinositide phosphatases. Annu Rev
Biochem. 70:247–279. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Robinson D, Van Allen EM, Wu YM, Schultz
N, Lonigro RJ, Mosquera JM, Montgomery B, Taplin ME, Pritchard CC,
Attard G, et al: Integrative clinical genomics of advanced prostate
cancer. Cell. 162:4542015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun J, Li S, Wang F, Fan C and Wang J:
Identification of key pathways and genes in PTEN mutation prostate
cancer by bioinformatics analysis. BMC Med Genet. 20:1912019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lei Q, Jiao J, Xin L, Chang CJ, Wang S,
Gao J, Gleave ME, Witte ON, Liu X and Wu H: NKX3.1 stabilizes p53,
inhibits AKT activation, and blocks prostate cancer initiation
caused by PTEN loss. Cancer Cell. 9:367–378. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bowen C, Ostrowski MC, Leone G and Gelmann
EP: Loss of PTEN accelerates NKX3.1 degradation to promote prostate
cancer progression. Cancer Res. 79:4124–4134. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gurel B, Ali TZ, Montgomery EA, Begum S,
Hicks J, Goggins M, Eberhart CG, Clark DP, Bieberich CJ, Epstein JI
and Marzo AM: NKX3.1 as a marker of prostatic origin in metastatic
tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 34:1097–1105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shivakumar M, Lee Y, Bang L, Garg T, Sohn
KA and Kim D: Identification of epigenetic interactions between
miRNA and DNA methylation associated with gene expression as
potential prognostic markers in bladder cancer. BMC Med Genomics.
10 (Suppl 1):S302017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Memari F, Joneidi Z, Taheri B, Aval SF,
Roointan A and Zarghami N: Epigenetics and Epi-miRNAs: Potential
markers/therapeutics in leukemia. Biomed Pharmacother.
106:1668–1677. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Arif K, Elliott E, Haupt L and Griffiths
L: Regulatory mechanisms of epigenetic miRNA relationships in human
cancer and potential as therapeutic targets. Cancers (Basel).
12:29222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fabbri M, Garzon R, Cimmino A, Liu Z,
Zanesi N, Callegari E, Liu S, Alder H, Costinean S,
Fernandez-Cymering C, et al: MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant
methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A
and 3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:15805–15810. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Reale E, Taverna D, Cantini L, Martignetti
L, Osella M, De Pittà C, Virga F, Orso F and Caselle M:
Investigating the epi-miRNome: Identification of epi-miRNAs using
transfection experiments. Epigenomics. 11:1581–1599. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Misso G, Di Martino MT, De Rosa G, Farooqi
AA, Lombardi A, Campani V, Zarone MR, Gullà A, Tagliaferri P,
Tassone P and Caraglia M: Mir-34: A new weapon against cancer? Mol
Ther Nucleic Acids. 3:e1942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tarasov V, Jung P, Verdoodt B, Lodygin D,
Epanchintsev A, Menssen A, Meister G and Hermeking H: Differential
regulation of microRNAs by p53 revealed by massively parallel
sequencing: MiR-34a is a p53 target that induces apoptosis and
G1-arrest. Cell Cycle. 6:1586–1593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, Shahryari V,
Arora S, Zaman MS, Chang I, Yamamura S, Tanaka Y, Chiyomaru T, et
al: miRNA-34b inhibits prostate cancer through demethylation,
active chromatin modifications, and AKT pathways. Clin Cancer Res.
19:73–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vogt M, Munding J, Grüner M, Liffers ST,
Verdoodt B, Hauk J, Steinstraesser L, Tannapfel A and Hermeking H:
Frequent concomitant inactivation of miR-34a and miR-34b/c by CpG
methylation in colorectal, pancreatic, mammary, ovarian,
urothelial, and renal cell carcinomas and soft tissue sarcomas.
Virchows Arch. 458:313–322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li Y, Deng X, Zeng X and Peng X: The role
of Mir-148a in cancer. J Cancer. 7:1233–1241. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hamilton MP, Rajapakshe KI, Bader DA,
Cerne JZ, Smith EA, Coarfa C, Hartig SM and McGuire SE: The
landscape of microRNA targeting in prostate cancer defined by
AGO-PAR-CLIP. Neoplasia. 18:356–370. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yu B, Lv X, Su L, Li J, Yu Y, Gu Q, Yan M,
Zhu Z and Liu B: MiR-148a functions as a tumor suppressor by
targeting CCK-BR via inactivating STAT3 and akt in human gastric
cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01589612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Guo SL, Peng Z, Yang X, Fan KJ, Ye H, Li
ZH, Wang Y, Xu XL, Li J, Wang YL, et al: miR-148a promoted cell
proliferation by targeting p27 in gastric cancer cells. Int J Biol
Sci. 7:567–574. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Walter BA, Valera VA, Pinto PA and Merino
MJ: Comprehensive microRNA profiling of prostate cancer. J Cancer.
4:350–357. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Porkka KP, Pfeiffer MJ, Waltering KK,
Vessella RL, Tammela TL and Visakorpi T: MicroRNA expression
profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 67:6130–6135. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kim J, Zhang Y, Skalski M, Hayes J, Kefas
B, Schiff D, Purow B, Parsons S, Lawler S and Abounader R:
microRNA-148a is a prognostic oncomiR that targets MIG6 and BIM to
regulate EGFR and apoptosis in glioblastoma. Cancer Res.
74:1541–1553. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Dybos SA, Flatberg A, Halgunset J, Viset
T, Rolfseng T, Kvam S and Skogseth H: Increased levels of serum
miR-148a-3p are associated with prostate cancer. APMIS.
126:722–731. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Szczyrba J, Löprich E, Wach S, Jung V,
Unteregger G, Barth S, Grobholz R, Wieland W, Stöhr R, Hartmann A,
et al: The MicroRNA profile of prostate carcinoma obtained by deep
sequencing. Mol Cancer Res. 8:529–538. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhu C, Li J, Ding Q, Cheng G, Zhou H, Tao
L, Cai H, Li P, Cao Q, Ju X, et al: miR-152 controls migration and
invasive potential by targeting TGFα in prostate cancer cell lines.
Prostate. 73:1082–1089. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Theodore SC, Davis M, Zhao F, Wang H, Chen
D, Rhim J, Dean-Colomb W, Turner T, Ji W, Zeng G, et al: MicroRNA
profiling of novel African American and Caucasian prostate cancer
cell lines reveals a reciprocal regulatory relationship of miR-152
and DNA methyltranferase 1. Oncotarget. 5:3512–3525. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li B, Xie Z and Li B: miR-152 functions as
a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer by targeting PIK3R3. Tumor
Biol. 37:10075–10084. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Braconi C, Huang N and Patel T:
MicroRNA-dependent regulation of DNA methyltransferase-1 and tumor
suppressor gene expression by interleukin-6 in human malignant
cholangiocytes. Hepatology. 51:881–890. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Huang S, Li X and Zhu H: MicroRNA-152
targets phosphatase and tensin homolog to inhibit apoptosis and
promote cell migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Med Sci
Monit. 22:4330–4337. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chen H, Liu H, Zou H, Chen R, Dou Y, Sheng
S, Dai S, Ai J, Melson J, Kittles RA, et al: Evaluation of plasma
miR-21 and miR-152 as diagnostic biomarkers for common types of
human cancers. J Cancer. 7:490–499. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Moya L, Meijer J, Schubert S, Matin F and
Batra J: Assessment of miR-98-5p, miR-152-3p, miR-326 and miR-4289
expression as biomarker for prostate cancer diagnosis. Int J Mol
Sci. 20:11542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Carter JV, O'Brien SJ, Burton JF, Oxford
BG, Stephen V, Hallion J, Bishop C, Galbraith NJ, Eichenberger MR,
Sarojini H, et al: The microRNA-200 family acts as an oncogene in
colorectal cancer by inhibiting the tumor suppressor RASSF2. Oncol
Lett. 18:3994–4007. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yang R, Xu J, Hua X, Tian Z, Xie Q, Li J,
Jiang G, Cohen M, Sun H and Huang C: Overexpressed miR-200a
promotes bladder cancer invasion through direct regulating
Dicer/miR-16/JNK2/MMP-2 axis. Oncogene. 39:1983–1996. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Schliekelman MJ, Gibbons DL, Faca VM,
Creighton CJ, Rizvi ZH, Zhang Q, Wong CH, Wang H, Ungewiss C, Ahn
YH, et al: Targets of the tumor suppressor miR-200 in regulation of
the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cancer Res.
71:7670–7682. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wong CM, Wei L, Au SL, Fan DN, Zhou Y,
Tsang FH, Law CT, Lee JM, He X, Shi J, et al: MiR-200b/200c/429
subfamily negatively regulates Rho/ROCK signaling pathway to
suppress hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Oncotarget.
6:13658–13670. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Osella M, Riba A, Testori A, Corà D and
Caselle M: Interplay of microRNA and epigenetic regulation in the
human regulatory network. Front Genet. 5:3452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Nakagawa T, Kanai Y, Ushijima S, Kitamura
T, Kakizoe T and Hirohashi S: DNA hypermethylation on multiple CpG
islands associated with increased DNA methyltransferase DNMT1
protein expression during multistage urothelial carcinogenesis. J
Urol. 173:1767–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Nakagawa T, Kanai YAE, Saito Y, Kitamura
T, Kakizoe T and Hirohashi S: Increased DNA methyltransferase 1
protein expression in human transitional cell carcinoma of the
bladder. J Urol. 170:2463–2466. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Patra SK, Patra A, Zhao H and Dahiya R:
DNA methyltransferase and demethylase in human prostate cancer. Mol
Carcinog. 33:163–171. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang W and Xu J: DNA methyltransferases
and their roles in tumorigenesis. Biomark Res. 5:12017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Qi D, Li J, Que B, Su J, Li M, Zhang C,
Yang M, Zhou G and Ji W: Long non-coding RNA DBCCR1-003 regulate
the expression of DBCCR1 via DNMT1 in bladder cancer. Cancer Cell
Int. 16:812016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Roscigno G, Quintavalle C, Donnarumma E,
Puoti I, Diaz-Lagares A, Iaboni M, Fiore D, Russo V, Todaro M,
Romano G, et al: MiR-221 promotes stemness of breast cancer cells
by targeting DNMT3b. Oncotarget. 7:580–592. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Pang Y, Liu J, Li X, Xiao G, Wang H, Yang
G, Li Y, Tang SC, Qin S, Du N, et al: MYC and DNMT3A-mediated DNA
methylation represses microRNA-200b in triple negative breast
cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 22:6262–6274. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ma HS, Wang EL, Xu WF, Yamada S, Yoshimoto
K, Qian ZR, Shi L, Liu LL and Li XH: Overexpression of DNA
(Cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) And DNA
(Cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3A (DNMT3A) is associated with
aggressive behavior and hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes
in human pituitary adenomas. Med Sci Monit. 24:4841–4850. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Li M, Wang Y, Song Y, Bu R, Yin B, Fei X,
Guo Q and Wu B: Aberrant DNA methyltransferase 1 expression in
clear cell renal cell carcinoma development and progression. Chin J
Cancer Res. 26:371–381. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Graça I, Sousa EJ, Costa-Pinheiro P,
Vieira FQ, Torres-Ferreira J, Martins MG, Henrique R and Jerónimo
C: Anti-neoplastic properties of hydralazine in prostate cancer.
Oncotarget. 5:5950–5964. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Jagadeesh S, Sinha S, Pal BC, Bhattacharya
S and Banerjee PP: Mahanine reverses an epigenetically silenced
tumor suppressor gene RASSF1A in human prostate cancer cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 362:212–217. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Agarwal S, Amin KS, Jagadeesh S, Baishay
G, Rao PG, Barua NC, Bhattacharya S and Banerjee PP: Mahanine
restores RASSF1A expression by down-regulating DNMT1 and DNMT3B in
prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 12:992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Le Magnen C, Virk RK, Dutta A, Kim JY,
Panja S, Lopez-Bujanda ZA, Califano A, Drake CG, Mitrofanova A and
Abate-Shen C: Cooperation of loss of NKX3.1 and inflammation in
prostate cancer initiation. Dis Model Mech. 11:dmm0351392018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Shiina M, Hashimoto Y, Kato T, Yamamura S,
Tanaka Y, Majid S, Saini S, Varahram S, Kulkarni P, Dasgupta P, et
al: Differential expression of miR-34b and androgen receptor
pathway regulate prostate cancer aggressiveness between
African-Americans and caucasians. Oncotarget. 8:8356–8368. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chamani F, Sadeghizadeh M, Masoumi M and
Babashah S: Evaluation of MiR-34 family and DNA methyltransferases
1, 3A, 3B gene expression levels in hepatocellular carcinoma
following treatment with dendrosomal nanocurcumin. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 17:219–224. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Sengupta D, Deb M and Patra SK:
Antagonistic activities of miR-148a and DNMT1: Ectopic expression
of miR-148a impairs DNMT1 mRNA and dwindle cell proliferation and
survival. Gene. 660:68–79. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Duursma AM, Kedde M, Schrier M, le Sage C
and Agami R: miR-148 targets human DNMT3b protein coding region.
RNA. 14:872–877. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Hua D, Mo F, Ding D, Li L, Han X, Zhao N,
Foltz G, Lin B, Lan Q and Huang Q: A catalogue of glioblastoma and
brain MicroRNAs identified by deep sequencing. OMICS. 16:690–699.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ma W, Zhang X, Chai J, Chen P, Ren P and
Gong M: Circulating miR-148a is a significant diagnostic and
prognostic biomarker for patients with osteosarcoma. Tumour Biol.
35:12467–12472. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhang H, Wang Y, Xu T, Li C, Wu J, He Q,
Wang G, Ding C, Liu K, Tang H and Ji F: Increased expression of
microRNA-148a in osteosarcoma promotes cancer cell growth by
targeting PTEN. Oncol Lett. 12:3208–3214. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Yuan K, Lian Z, Sun B, Clayton MM, Ng IOL
and Feitelson MA: Role of miR-148a in hepatitis B associated
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e353312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Ramalho-Carvalho J, Gonçalves CS, Graça I,
Bidarra D, Pereira-Silva E, Salta S, Godinho MI, Gomez A, Esteller
M, Costa BM, et al: A multiplatform approach identifies miR-152-3p
as a common epigenetically regulated onco-suppressor in prostate
cancer targeting TMEM97. Clin Epigenetics. 10:402018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Collino F, Deregibus MC, Bruno S, Sterpone
L, Aghemo G, Viltono L, Tetta C and Camussi G: Microvesicles
derived from adult human bone marrow and tissue specific
mesenchymal stem cells shuttle selected pattern of miRNAs. PLoS
One. 5:e118032010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Jiang X, Du L, Wang L, Li J, Liu Y, Zheng
G, Qu A, Zhang X, Pan H, Yang Y and Wang C: Serum microRNA
expression signatures as novel noninvasive biomarkers for
prediction and prognosis of muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:36733–36742. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Dudziec E, Miah S, Choudhry HM, Owen HC,
Blizard S, Glover M, Hamdy FC and Catto JW: Hypermethylation of CpG
islands and shores around specific microRNAs and mirtrons is
associated with the phenotype and presence of bladder cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:1287–1296. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Kim J, Yao F, Xiao Z, Sun Y and Ma L:
MicroRNAs and metastasis: Small RNAs play big roles. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 37:5–15. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Pan J, Ding M, Xu K, Yang C and Mao LJ:
Exosomes in diagnosis and therapy of prostate cancer. Oncotarget.
8:97693–97700. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Turchinovich A, Samatov T, Tonevitsky A
and Burwinkel B: Circulating miRNAs: Cell-cell communication
function? Front Genet. 4:1192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Pang Y, Young CY and Yuan H: MicroRNAs and
prostate cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 42:363–369.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Guo F, Kerrigan BC, Yang D, Hu L,
Shmulevich I, Sood AK, Xue F and Zhang W: Post-transcriptional
regulatory network of epithelial-to-mesenchymal and
mesenchymal-to-epithelial transitions. J Hematol Oncol. 7:192014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wu Q, Lu RL, Li JX and Rong LJ: MiR-200a
and miR-200b target PTEN to regulate the endometrial cancer cell
growth in vitro. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 10:498–502. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Yoneyama K, Ishibashi O, Kawase R, Kurose
K and Takeshita T: miR-200a, miR-200b and miR-429 are onco-miRs
that Target the PTEN gene in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 35:1401–1410. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Suo HB, Zhang KC and Zhao J: MiR-200a
promotes cell invasion and migration of ovarian carcinoma by
targeting PTEN. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:4080–4089.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Liu J, Zhang X, Huang Y, Zhang Q, Zhou J,
Zhang X and Wang X: miR-200b and miR-200c co-contribute to the
cisplatin sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells by targeting DNA
methyltransferases. Oncol Lett. 17:1453–1460. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zeng X, Qu X, Zhao C, Xu L, Hou K, Liu Y,
Zhang N, Feng J, Shi S, Zhang L, et al: FEN1 mediates miR-200a
methylation and promotes breast cancer cell growth via MET and EGFR
signaling. FASEB J. 33:10717–10730. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|