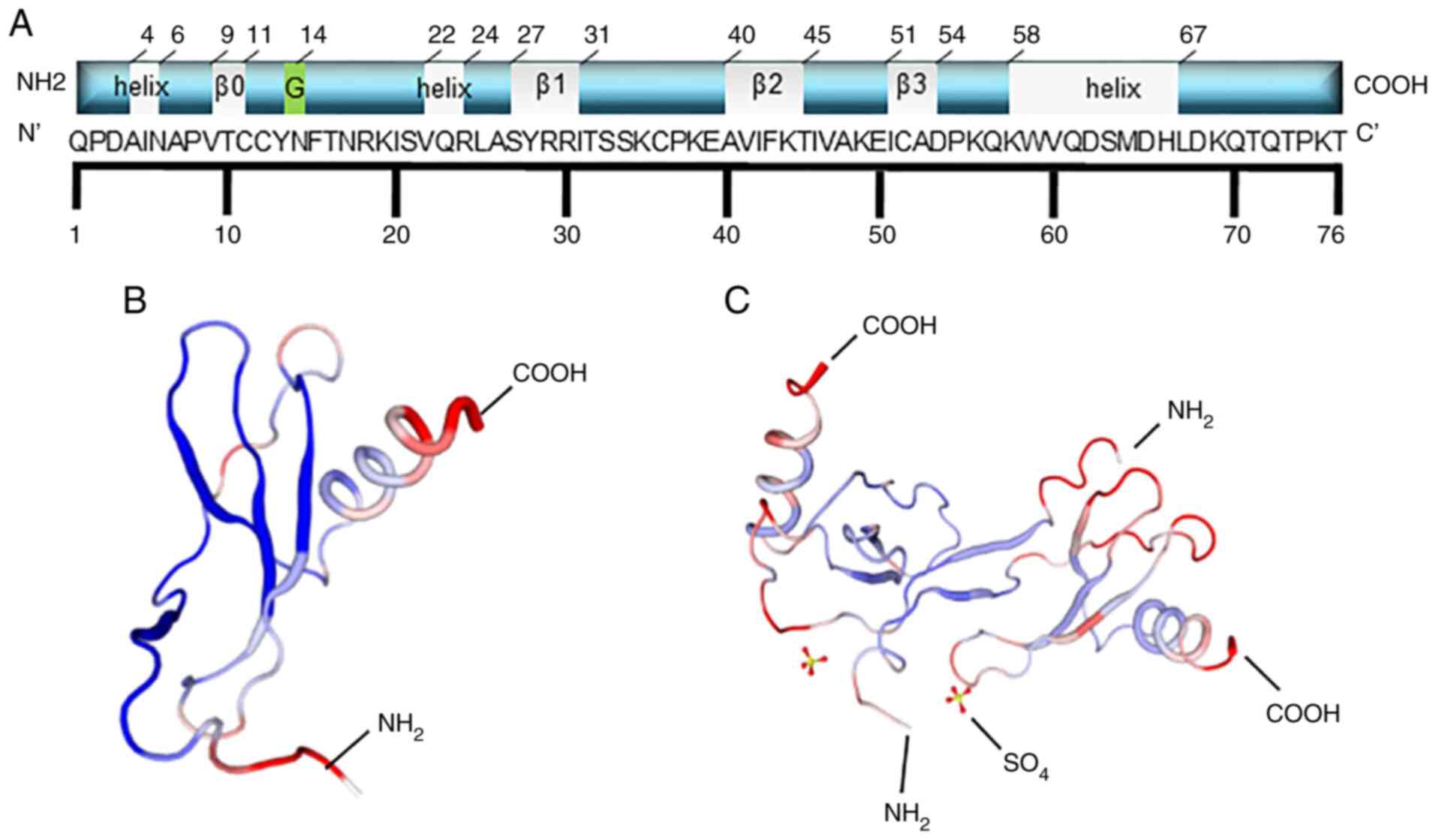
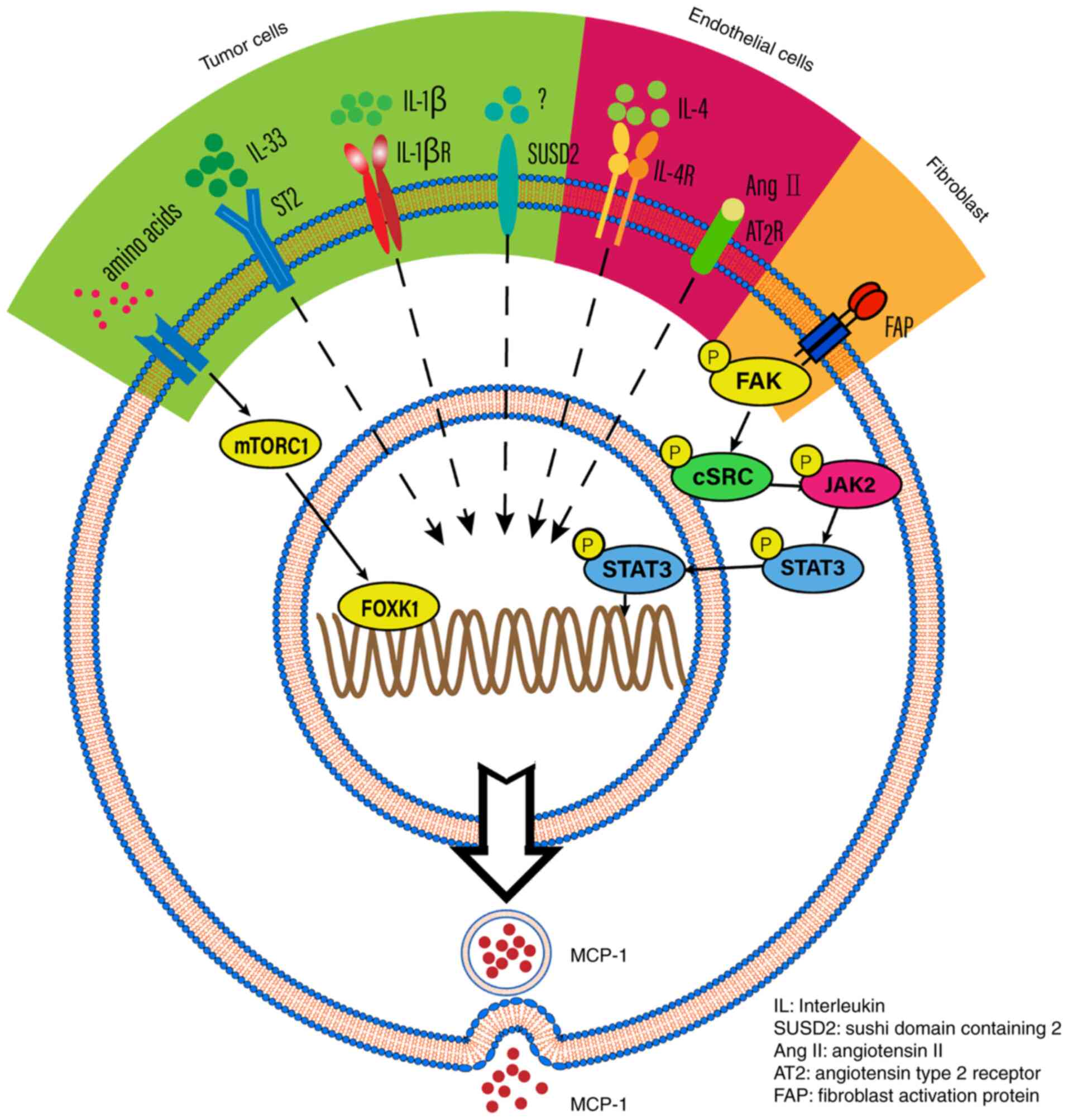
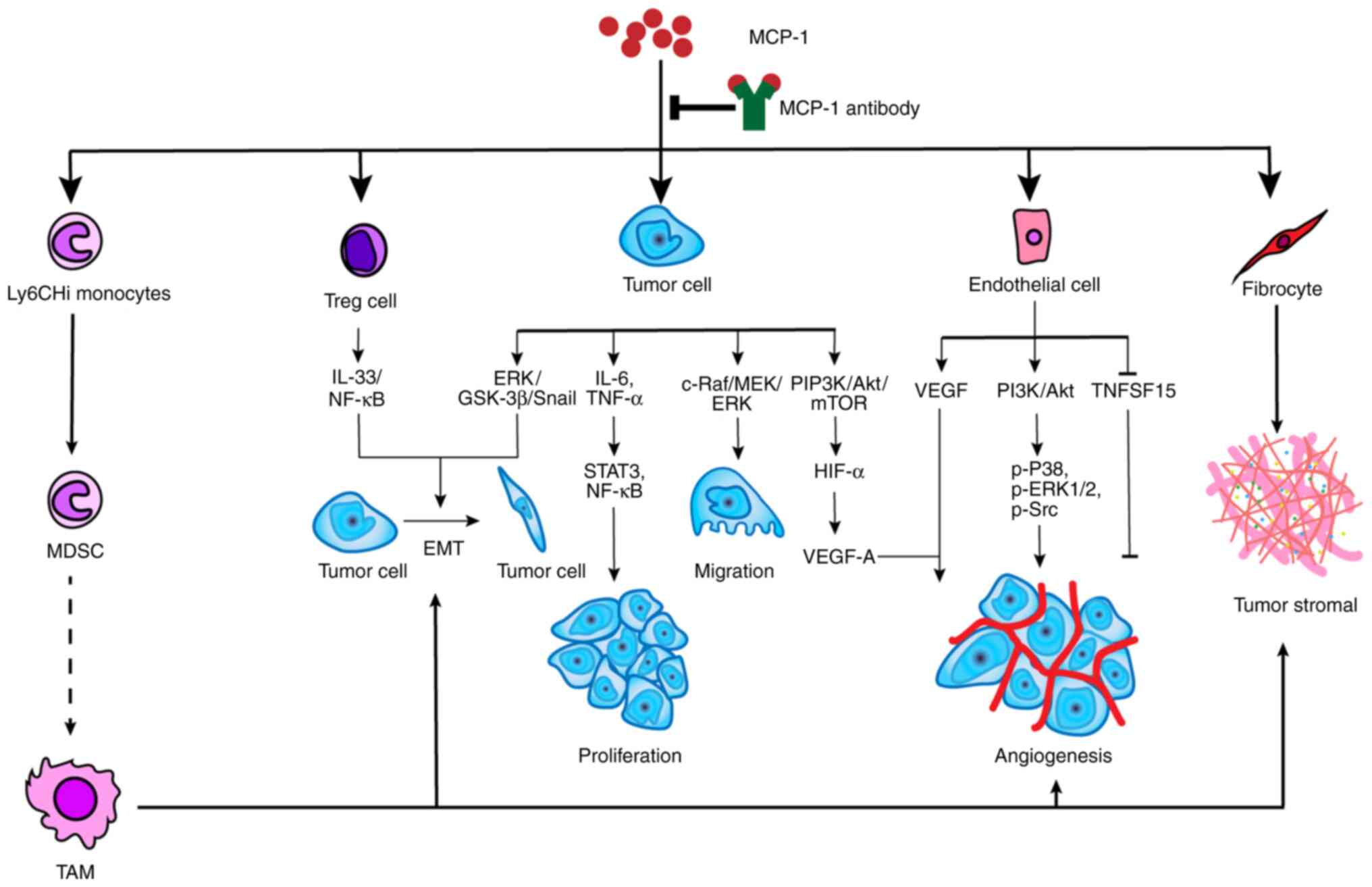
|
1
|
da Cunha Santos G, Shepherd FA and Tsao
MS: EGFR mutations and lung cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:49–69. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S,
Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et
al: EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical
response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 304:1497–1500. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Deshmane SL, Kremlev S, Amini S and Sawaya
BE: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 29:313–326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Blanpain CD, Migeotte I, Lee B, Vakili J,
Doranz BJ, Govaerts C, Vassart G, Doms RW and Parmentier M: CCR5
binds multiple CC-chemokines: MCP-3 acts as a natural antagonist.
Blood. 94:1899–1905. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bonini JA, Martin SK, Dralyuk F, Roe MW,
Philipson LH and Steiner DF: Cloning, expression, and chromosomal
mapping of a novel human CC-chemokine receptor (CCR10) that
displays high-affinity binding for MCP-1 and MCP-3. DNA Cell Biol.
16:1249–1256. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hemmerich S, Paavola C, Bloom A, Bhakta S,
Freedman R, Grunberger D, Krstenansky J, Lee S, McCarley D, Mulkins
M, et al: Identification of residues in the monocyte chemotactic
protein-1 that contact the MCP-1 receptor, CCR2. Biochemistry.
38:13013–13025. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kashiwazaki M, Tanaka T, Kanda H, Ebisuno
Y, Izawa D, Fukuma N, Akimitsu N, Sekimizu K, Monden M and Miyasaka
M: A high endothelial venule-expressing promiscuous chemokine
receptor DARC can bind inflammatory, but not lymphoid, chemokines
and is dispensable for lymphocyte homing under physiological
conditions. Int Immunol. 15:1219–1227. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schweickart VL, Epp A, Raport CJ and Gray
PW: CCR11 is a functional receptor for the monocyte chemoattractant
protein family of chemokines. J Biol Chem. 275:9550–9556. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Robinson EA, Yoshimura T, Leonard EJ,
Tanaka S, Griffin PR, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF and Appella E:
Complete amino acid sequence of a human monocyte chemoattractant, a
putative mediator of cellular immune reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 86:1850–1854. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoshimura T, Robinson EA, Tanaka S,
Appella E and Leonard EJ: Purification and amino acid analysis of
two human monocyte chemoattractants produced by
phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human blood mononuclear leukocytes. J
Immunol. 142:1956–1962. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yoshimura T, Yuhki N, Moore SK, Appella E,
Lerman MI and Leonard EJ: Human monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
(MCP-1). Full-length cDNA cloning, expression in mitogen-stimulated
blood mononuclear leukocytes, and sequence similarity to mouse
competence gene JE. FEBS Lett. 244:487–493. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bottazzi B, Colotta F, Sica A, Nobili N
and Mantovani A: A chemoattractant expressed in human sarcoma cells
(tumor-derived chemotactic factor, TDCF) is identical to monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1/monocyte chemotactic and activating
factor (MCP-1/MCAF). Int J Cancer. 45:795–797. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fujisaki K, Fujimoto H, Sangai T,
Nagashima T, Sakakibara M, Shiina N, Kuroda M, Aoyagi Y and
Miyazaki M: Cancer-mediated adipose reversion promotes cancer cell
migration via IL-6 and MCP-1. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 150:255–263.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu Q, Li B, Li Z, Li J and Sun S and Sun
S: Cancer-associated adipocytes: Key players in breast cancer
progression. J Hematol Oncol. 12:952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mehrabian M, Sparkes RS, Mohandas T,
Fogelman AM and Lusis AJ: Localization of monocyte chemotactic
protein-1 gene (SCYA2) to human chromosome 17q11.2-q21.1. Genomics.
9:200–203. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lubkowski J, Bujacz G, Boqué L, Domaille
PJ, Handel TM and Wlodawer A: The structure of MCP-1 in two crystal
forms provides a rare example of variable quaternary interactions.
Nat Struct Biol. 4:64–69. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang Y, Ernst CA and Rollins BJ: MCP-1:
Structure/activity analysis. Methods. 10:93–103. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Handel TM and Domaille PJ: Heteronuclear
(1H, 13C, 15N) NMR assignments and solution structure of the
monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) dimer. Biochemistry.
35:6569–6584. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Proost P, Struyf S, Couvreur M, Lenaerts
JP, Conings R, Menten P, Verhaert P, Wuyts A and Damme JV:
Posttranslational modifications affect the activity of the human
monocyte chemotactic proteins MCP-1 and MCP-2: Identification of
MCP-2(6–76) as a natural chemokine inhibitor. J Immunol.
160:4034–4041. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jung Y, Ahn SH, Park H, Park SH, Choi K,
Choi C, Kang JL and Choi YH: MCP-1 and MIP-3α secreted from
necrotic cell-treated glioblastoma cells promote
migration/infiltration of microglia. Cell Physiol Biochem.
48:1332–1346. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee CH, Hung PF, Lu SC, Chung HL, Chiang
SL, Wu CT, Chou WC and Sun CY: MCP-1/MCPIP-1 signaling modulates
the effects of IL-1β in renal cell carcinoma through ER
stress-mediated apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 20:61012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yue Y, Lian J, Wang T, Luo C, Yuan Y, Qin
G, Zhang B and Zhang Y: Interleukin-33-nuclear factor-κB-CCL2
signaling pathway promotes progression of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma by directing regulatory T cells. Cancer Sci. 111:795–806.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakatsumi H, Matsumoto M and Nakayama KI:
Noncanonical pathway for regulation of CCL2 expression by an
mTORC1-FOXK1 axis promotes recruitment of tumor-associated
macrophages. Cell Rep. 21:2471–2486. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen C, He W, Huang J, Wang B, Li H, Cai
Q, Su F, Bi J, Liu H, Zhang B, et al: LNMAT1 promotes lymphatic
metastasis of bladder cancer via CCL2 dependent macrophage
recruitment. Nat Commun. 9:38262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu S, Liu D, Zeng X, Wang J, Liu J, Cheng
J, Lei K, Bai H, Ji N, Zhou M, et al: PA28γ acts as a dual
regulator of IL-6 and CCL2 and contributes to tumor angiogenesis in
oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 428:192–200. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Castiñeiras-Landeira MI, Rodiño-Janeiro
BK, Paradela-Dobarro B, Batista-Oliveira AL, Raposeiras-Roubín S,
González-Peteiro M, González-Juanatey JR and Álvarez E: Change of
concept about the regulation of angiotensin II-induced monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 production in human endothelial cells.
Vascul Pharmacol. 80:20–34. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rollins BJ and Pober JS: Interleukin-4
induces the synthesis and secretion of MCP-1/JE by human
endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 138:1315–1319. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hembruff SL, Jokar I, Yang L and Cheng N:
Loss of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in mammary
fibroblasts enhances CCL2 secretion to promote mammary tumor
progression through macrophage-dependent and -independent
mechanisms. Neoplasia. 12:425–433. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kuper C, Beck FX and Neuhofer W: Autocrine
MCP-1/CCR2 signaling stimulates proliferation and migration of
renal carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 12:2201–2209. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu Y, Cai Z, Galson DL, Xiao G, Liu Y,
George DE, Melhem MF, Yao Z and Zhang J: Monocyte chemotactic
protein-1 (MCP-1) acts as a paracrine and autocrine factor for
prostate cancer growth and invasion. Prostate. 66:1311–1318. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mohamed HT, El-Ghonaimy EA, El-Shinawi M,
Hosney M, Götte M, Woodward WA, El-Mamlouk T and Mohamed MM: IL-8
and MCP-1/CCL2 regulate proteolytic activity in triple negative
inflammatory breast cancer a mechanism that might be modulated by
Src and Erk1/2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 401:1150922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fridlender ZG, Kapoor V, Buchlis G, Cheng
G, Sun J, Wang LC, Singhal S, Snyder LA and Albelda SM: Monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 blockade inhibits lung cancer tumor
growth by altering macrophage phenotype and activating CD8+ cells.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 44:230–237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Loberg RD, Ying C, Craig M, Yan L, Snyder
LA and Pienta KJ: CCL2 as an important mediator of prostate cancer
growth in vivo through the regulation of macrophage infiltration.
Neoplasia. 9:556–562. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qian BZ, Li J, Zhang H, Kitamura T, Zhang
J, Campion LR, Kaiser EA, Snyder LA and Pollard JW: CCL2 recruits
inflammatory monocytes to facilitate breast-tumour metastasis.
Nature. 475:222–225. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun C, Li X, Guo E, Li N, Zhou B, Lu H,
Huang J, Xia M, Shan W, Wang B, et al: MCP-1/CCR-2 axis in
adipocytes and cancer cell respectively facilitates ovarian cancer
peritoneal metastasis. Oncogene. 39:1681–1695. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Teng KY, Han J, Zhang X, Hsu SH, He S,
Wani NA, Barajas JM, Snyder LA, Frankel WL, Caligiuri MA, et al:
Blocking the CCL2-CCR2 axis using CCL2-neutralizing antibody is an
effective therapy for hepatocellular cancer in a mouse model. Mol
Cancer Ther. 16:312–322. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bakst RL, Xiong H, Chen CH, Deborde S,
Lyubchik A, Zhou Y, He S, McNamara W, Lee SY, Olson OC, et al:
Inflammatory monocytes promote perineural invasion via
CCL2-mediated recruitment and cathepsin B expression. Cancer Res.
77:6400–6414. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Salacz M, Kast RE, Saki N, Brüning A,
Karpel-Massler G and Halatsch ME: Toward a noncytotoxic
glioblastoma therapy: Blocking MCP-1 with the MTZ regimen. Onco
Targets Ther. 27:2535–2545. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ueno T, Toi M, Saji H, Muta M, Bando H,
Kuroi K, Koike M, Inadera H and Matsushima K: Significance of
macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 in macrophage recruitment,
angiogenesis, and survival in human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
6:3282–3289. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kuziel G, Thompson V, D'Amato JV and
Arendt LM: Stromal CCL2 signaling promotes mammary tumor fibrosis
through recruitment of myeloid-lineage cells. Cancers (Basel).
12:20832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cho HR, Kumari N, Vu HT, Kim H, Park CK
and Choi SH: Increased antiangiogenic effect by blocking
CCL2-dependent macrophages in a rodent glioblastoma model:
Correlation study with dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion
MRI. Sci Rep. 9:110852019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Guru SK, Pathania AS, Kumar S, Ramesh D,
Kumar M, Rana S, Kumar A, Malik F, Sharma PR, Chandan BK, et al:
Secalonic acid-D represses HIF1alpha/VEGF-mediated angiogenesis by
regulating the Akt/mTOR/p70S6K signaling cascade. Cancer Res.
75:2886–2896. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang J, Lu Y and Pienta KJ: Multiple
roles of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 in promoting prostate
cancer growth. J Natl Cancer Inst. 102:522–528. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen Q, Sun W, Liao Y, Zeng H, Shan L, Yin
F, Wang Z, Zhou Z, Hua Y and Cai Z: Monocyte chemotactic protein-1
promotes the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells and
upregulates the expression of AKT. Mol Med Rep. 12:219–225. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Loberg RD, Day LL, Harwood J, Ying C, John
LN, Giles R, Neeley CK and Pienta KJ: CCL2 is a potent regulator of
prostate cancer cell migration and proliferation. Neoplasia.
8:578–586. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu JF, Chen PC, Chang TM and Hou CH:
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 promotes cancer cell migration
via c-Raf/MAPK/AP-1 pathway and MMP-9 production in osteosarcoma. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:2542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
He S and Zhang X: The rs1024611 in the
CCL2 gene and risk of gynecological cancer in Asians: A
meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 16:342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ito Y, Ishiguro H, Kobayashi N, Hasumi H,
Watanabe M, Yao M and Uemura H: Adipocyte-derived monocyte
chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) promotes prostate cancer progression
through the induction of MMP-2 activity. Prostate. 75:1009–1019.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
An J, Xue Y, Long M, Zhang G, Zhang J and
Su H: Targeting CCR2 with its antagonist suppresses viability,
motility and invasion by downregulating MMP-9 expression in
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:39230–39240. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tang CH and Tsai CC: CCL2 increases MMP-9
expression and cell motility in human chondrosarcoma cells via the
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol.
83:335–344. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yang CQ, Li W, Li SQ, Li J, Li YW, Kong
SX, Liu RM, Wang SM and Lv WM: MCP-1 stimulates MMP-9 expression
via ERK 1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in human aortic smooth
muscle cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:266–276. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Orlichenko LS and Radisky DC: Matrix
metalloproteinases stimulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition
during tumor development. Clin Exp Metastasis. 25:593–600. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li S, Lu J, Chen Y, Xiong N, Li L, Zhang
J, Yang H, Wu C, Zeng H and Liu Y: MCP-1-induced ERK/GSK-3β/snail
signaling facilitates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
promotes the migration of MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells. Cell
Mol Immunol. 14:621–630. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu W, Wang L, Zhang J, Qiao L, Liu Y,
Yang X, Zhang J, Zheng W and Ma Z: Purification of recombinant
human chemokine CCL2 in E. coli and its function in ovarian
cancer. 3 Biotech. 11:82021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Salcedo R, Ponce ML, Young HA, Wasserman
K, Ward JM, Kleinman HK, Oppenheim JJ and Murphy WJ: Human
endothelial cells express CCR2 and respond to MCP-1: Direct role of
MCP-1 in angiogenesis and tumor progression. Blood. 96:34–40. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wang S, Xu M, Li F, Wang X, Bower KA,
Frank JA, Lu Y, Chen G, Zhang Z, Ke Z, et al: Ethanol promotes
mammary tumor growth and angiogenesis: The involvement of
chemoattractant factor MCP-1. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
133:1037–1048. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Deng W, Gu X, Lu Y, Gu C, Zheng Y, Zhang
Z, Chen L, Yao Z and Li LY: Down-modulation of TNFSF15 in ovarian
cancer by VEGF and MCP-1 is a pre-requisite for tumor
neovascularization. Angiogenesis. 15:71–85. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Arefieva TI, Kukhtina NB, Antonova OA and
Krasnikova TL: MCP-1-stimulated chemotaxis of monocytic and
endothelial cells is dependent on activation of different signaling
cascades. Cytokine. 31:439–446. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bronte V, Brandau S, Chen SH, Colombo MP,
Frey AB, Greten TF, Mandruzzato S, Murray PJ, Ochoa A,
Ostrand-Rosenberg S, et al: Recommendations for myeloid-derived
suppressor cell nomenclature and characterization standards. Nat
Commun. 7:121502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yang H, Zhang Q, Xu M, Wang L, Chen X,
Feng Y, Li Y, Zhang X, Cui W and Jia X: CCL2-CCR2 axis recruits
tumor associated macrophages to induce immune evasion through PD-1
signaling in esophageal carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer. 19:412020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Guilliams M, Mildner A and Yona S:
Developmental and functional heterogeneity of monocytes. Immunity.
49:595–613. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Shand FH, Ueha S, Otsuji M, Koid SS,
Shichino S, Tsukui T, Kosugi-Kanaya M, Abe J, Tomura M, Ziogas J
and Matsushima K: Tracking of intertissue migration reveals the
origins of tumor-infiltrating monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:7771–7776. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yang X, Lin Y, Shi Y, Li B, Liu W, Yin W,
Dang Y, Chu Y, Fan J and He R: FAP promotes immunosuppression by
cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment via
STAT3-CCL2 signaling. Cancer Res. 76:4124–4135. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Laviron M and Boissonnas A: Ontogeny of
tumor-associated macrophages. Front Immunol. 10:17992019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Li X, Yao W, Yuan Y, Chen P, Li B, Li J,
Chu R, Song H, Xie D, Jiang X, et al: Targeting of
tumour-infiltrating macrophages via CCL2/CCR2 signalling as a
therapeutic strategy against hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut.
66:157–167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cranford TL, Velázquez KT, Enos RT, Bader
JE, Carson MS, Chatzistamou L, Nagarkatti M and Murphy EA: Loss of
monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression delays mammary
tumorigenesis and reduces localized inflammation in the
C3(1)/SV40Tag triple negative breast cancer model. Cancer Biol
Ther. 18:85–93. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Li F, Kitajima S, Kohno S, Yoshida A,
Tange S, Sasaki S, Okada N, Nishimoto Y, Muranaka H, Nagatani N, et
al: Retinoblastoma inactivation induces a protumoral
microenvironment via enhanced CCL2 secretion. Cancer Res.
79:3903–3915. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zheng Y, Wang Z, Wei S, Liu Z and Chen G:
Epigenetic silencing of chemokine CCL2 represses macrophage
infiltration to potentiate tumor development in small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Lett. 499:148–163. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhu Z, Hou Q and Guo H: NT5DC2 knockdown
inhibits colorectal carcinoma progression by repressing metastasis,
angiogenesis and tumor-associated macrophage recruitment: A
mechanism involving VEGF signaling. Exp Cell Res. 397:1123112020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Sodhi A and Biswas SK: Monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1-induced activation of p42/44 MAPK and
c-Jun in murine peritoneal macrophages: A potential pathway for
macrophage activation. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 22:517–526. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Biswas SK and Sodhi A: Tyrosine
phosphorylation-mediated signal transduction in MCP-1-induced
macrophage activation: Role for receptor dimerization, focal
adhesion protein complex and JAK/STAT pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
2:1095–1107. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kuroda T, Kitadai Y, Tanaka S, Yang X,
Mukaida N, Yoshihara M and Chayama K: Monocyte chemoattractant
protein-1 transfection induces angiogenesis and tumorigenesis of
gastric carcinoma in nude mice via macrophage recruitment. Clin
Cancer Res. 11:7629–7636. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Chang AL, Miska J, Wainwright DA, Dey M,
Rivetta CV, Yu D, Kanojia D, Pituch KC, Qiao J, Pytel P, et al:
CCL2 produced by the glioma microenvironment is essential for the
recruitment of regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor
cells. Cancer Res. 76:5671–5682. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Mittal P, Wang L, Akimova T, Leach CA,
Clemente JC, Sender MR, Chen Y, Turunen BJ and Hancock WW: The
CCR2/MCP-1 chemokine pathway and lung adenocarcinoma. Cancers
(Basel). 12:37232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Sun W, Li WJ, Wei FQ, Wong TS, Lei WB, Zhu
XL, Li J and Wen WP: Blockade of MCP-1/CCR4 signaling-induced
recruitment of activated regulatory cells evokes an antitumor
immune response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 7:37714–37727. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Svensson S, Abrahamsson A, Rodriguez GV,
Olsson AK, Jensen L, Cao Y and Dabrosin C: CCL2 and CCL5 are novel
therapeutic targets for estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 21:3794–3805. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Yao M, Smart C, Hu Q and Cheng N:
Continuous delivery of neutralizing antibodies elevate CCL2 levels
in mice bearing MCF10CA1d breast tumor xenografts. Transl Oncol.
10:734–743. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wichmann G, Körner C, Boehm A, Mozet C and
Dietz A: Stimulation by monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
modulates the ex-vivo colony formation by head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 35:3917–3924. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Van Coillie E, Van Damme J and Opdenakker
G: The MCP/eotaxin subfamily of CC chemokines. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 10:61–86. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yoshimura T: The production of monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)/CCL2 in tumor microenvironments.
Cytokine. 98:71–78. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Laird BJA, Fallon M, Hjermstad MJ, Tuck S,
Kaasa S, Klepstad P and McMillan DC: Quality of life in patients
with advanced cancer: Differential association with performance
status and systemic inflammatory response. J Clin Oncol.
34:2769–2775. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Bonapace L, Coissieux MM, Wyckoff J, Mertz
KD, Varga Z, Junt T and Bentires-Alj M: Cessation of CCL2
inhibition accelerates breast cancer metastasis by promoting
angiogenesis. Nature. 515:130–133. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Shen C, Lie P, Miao T, Yu M, Lu Q, Feng T,
Li J, Zu T, Liu X and Li H: Conditioned medium from umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells induces migration and angiogenesis. Mol Med
Rep. 12:20–30. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Luo Y, Laning J, Hayashi M, Hancock PR,
Rollins B and Dorf ME: Serologic analysis of the mouse beta
chemokine JE/monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. J Immunol.
153:3708–3716. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Peri G, Milanese C, Matteucci C, Ruco L,
Zhou D, Sozzani S, Coletta I and Mantovani A: A new monoclonal
antibody (5D3-F7) which recognizes human monocyte-chemotactic
protein-1 but not related chemokines. Development of a sandwich
ELISA and in situ detection of producing cells. J Immunol Methods.
174:249–257. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhao C, Bu X, Wang W, Ma T and Ma H:
GEC-derived SFRP5 inhibits Wnt5a-induced macrophage chemotaxis and
activation. PLoS One. 9:e850582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Fujimoto H, Sangai T, Ishii G, Ikehara A,
Nagashima T, Miyazaki M and Ochiai A: Stromal MCP-1 in mammary
tumors induces tumor-associated macrophage infiltration and
contributes to tumor progression. Int J Cancer. 125:1276–1284.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Roy RM, Wuthrich M and Klein BS: Chitin
elicits CCL2 from airway epithelial cells and induces
CCR2-dependent innate allergic inflammation in the lung. J Immunol.
189:2545–2552. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Arakaki R, Yamasaki T, Kanno T, Shibasaki
N, Sakamoto H, Utsunomiya N, Sumiyoshi T, Shibuya S, Tsuruyama T,
Nakamura E, et al: CCL2 as a potential therapeutic target for clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 5:2920–2933. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Lai SW, Liu YS, Lu DY and Tsai CF:
Melatonin modulates the microenvironment of glioblastoma multiforme
by targeting sirtuin 1. Nutrients. 11:13432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhan Z, Xie X, Cao H, Zhou X, Zhang XD,
Fan H and Liu Z: Autophagy facilitates TLR4- and TLR3-triggered
migration and invasion of lung cancer cells through the promotion
of TRAF6 ubiquitination. Autophagy. 10:257–268. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Loberg RD, Ying C, Craig M, Day LL,
Sargent E, Neeley C, Wojno K, Snyder LA, Yan L and Pienta KJ:
Targeting CCL2 with systemic delivery of neutralizing antibodies
induces prostate cancer tumor regression in vivo. Cancer Res.
67:9417–9424. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|