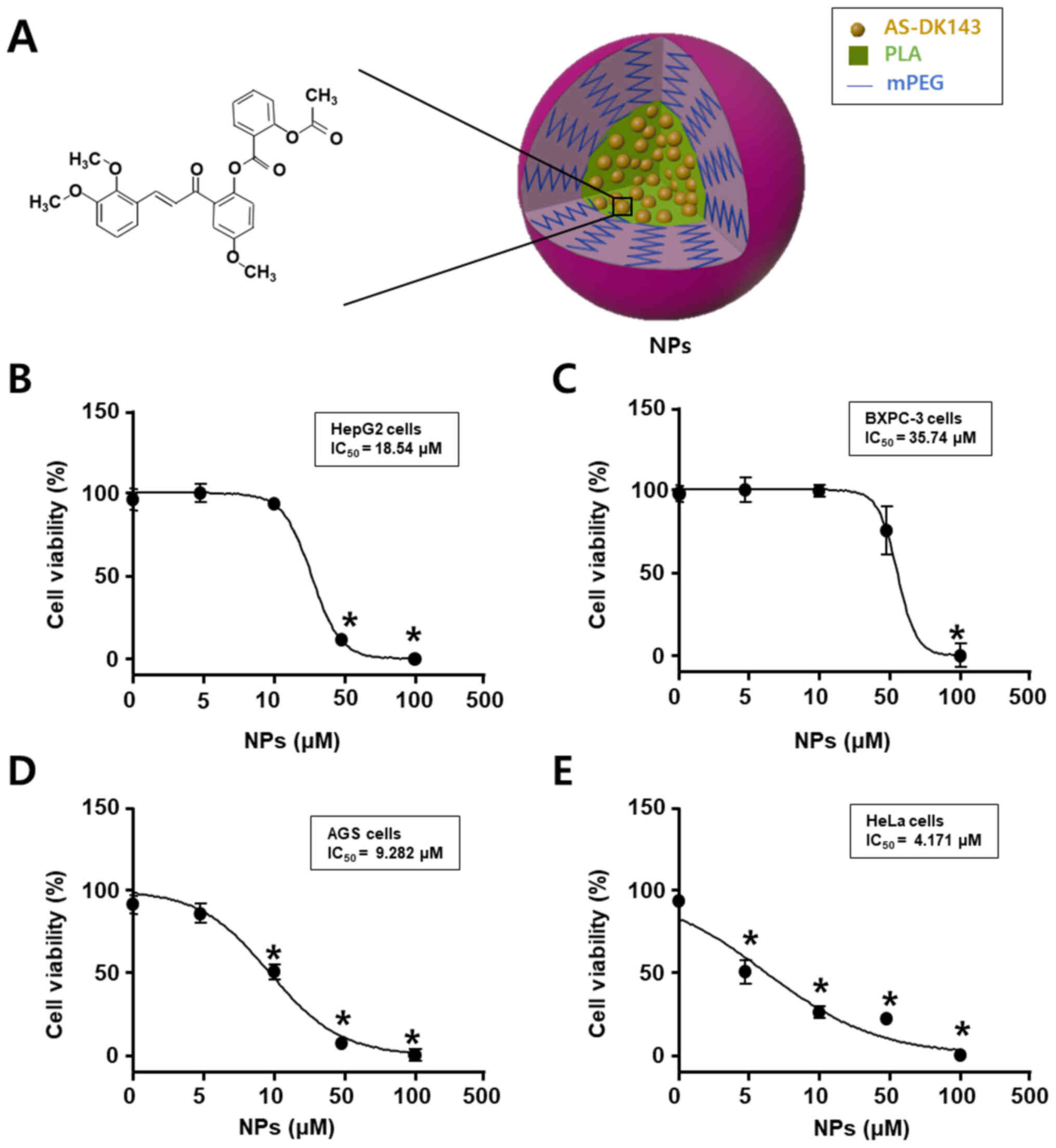
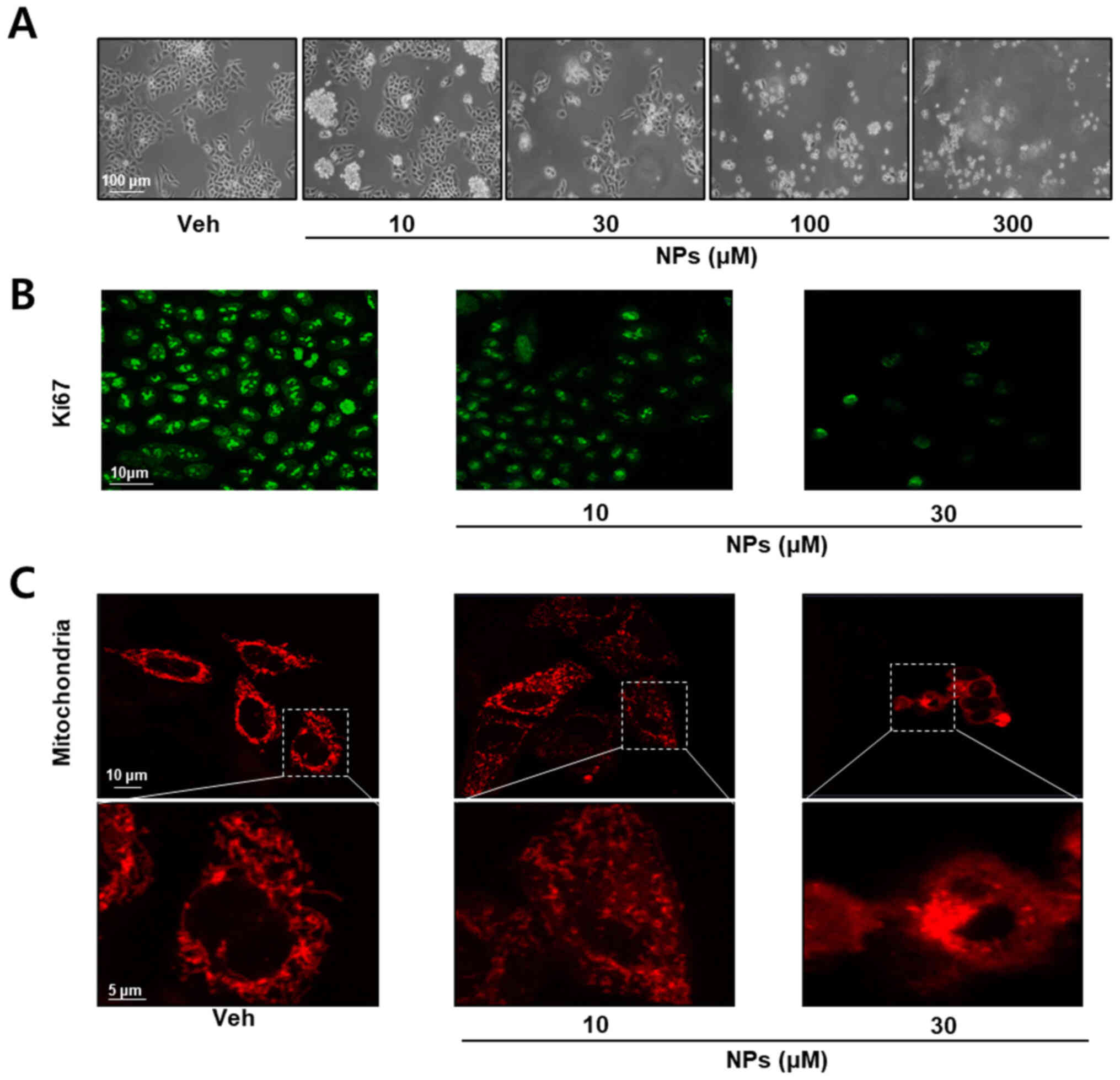
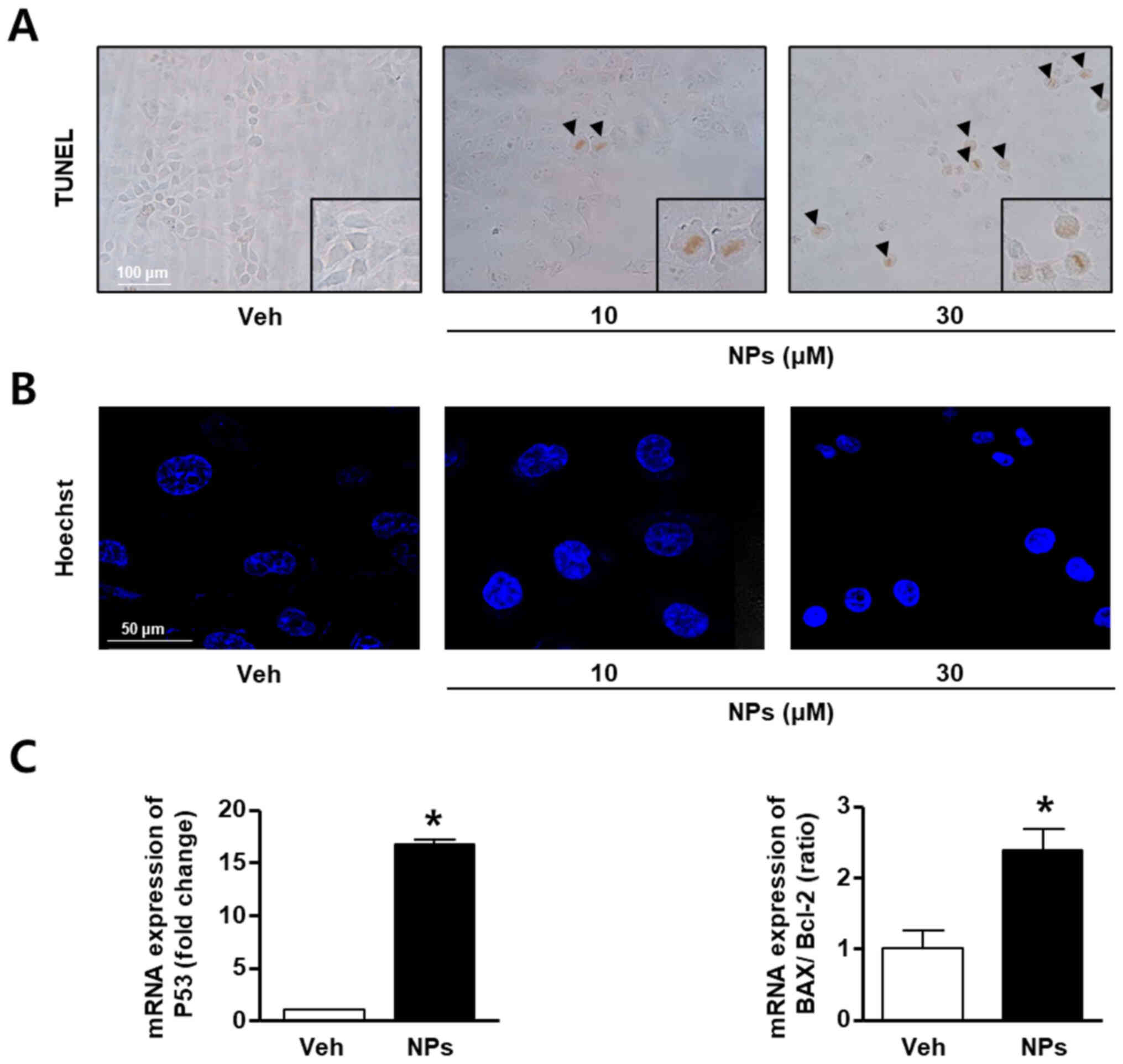
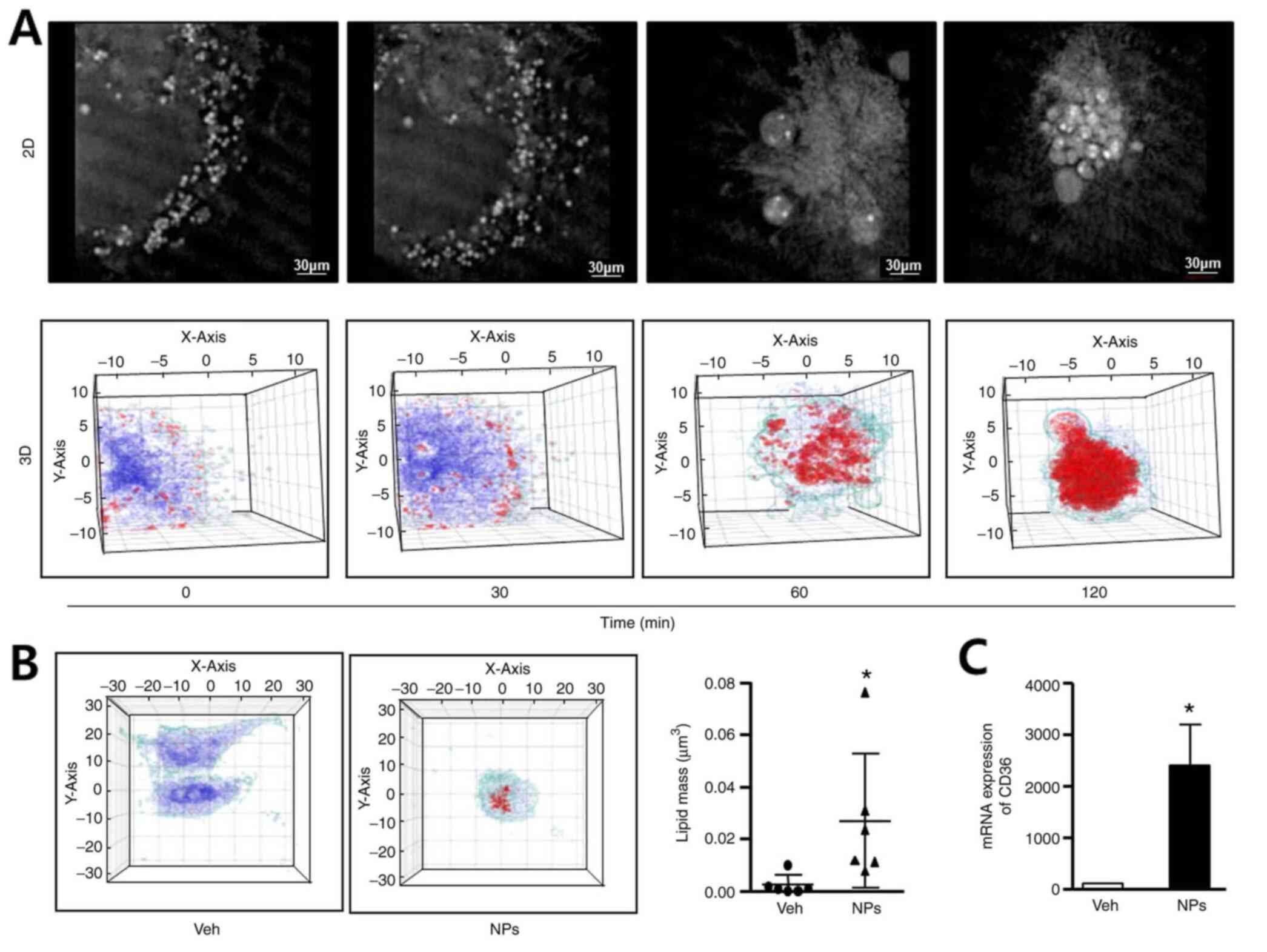
|
1
|
Arbyn M, Weiderpass E, Bruni L, de Sanjosé
S, Saraiya M, Ferlay J and Bray F: Estimates of incidence and
mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: A worldwide analysis. Lancet
Glob Health. 8:e191–e203. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maine D, Hurlburt S and Greeson D:
Cervical cancer prevention in the 21st century: Cost is not the
only issue. Am J Public Health. 101:1549–1555. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lowndes CM: Vaccines for cervical cancer.
Epidemiol Infect. 134:1–12. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burd EM: Human papillomavirus and cervical
cancer. Clin Microbiol Rev. 16:1–17. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yim EK and Park JS: The role of HPV E6 and
E7 oncoproteins in HPV-associated cervical carcinogenesis. Cancer
Res Treat. 37:319–324. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thomas M, Pim D and Banks L: The role of
the E6-p53 interaction in the molecular pathogenesis of HPV.
Oncogene. 18:7690–7700. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fischer M, Uxa S, Stanko C, Magin TM and
Engeland K: Human papilloma virus E7 oncoprotein abrogates the
p53-p21-DREAM pathway. Sci Rep. 7:26032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fan X, Liu Y and Chen JJ: Down-regulation
of p21 contributes to apoptosis induced by HPV E6 in human mammary
epithelial cells. Apoptosis. 10:63–73. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Photopulos GJ: Surgery or radiation for
early cervical cancer. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 33:872–882. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kumar L and Gupta S: Integrating
Chemotherapy in the Management of Cervical Cancer: A Critical
Appraisal. Oncology. 91 (Suppl 1):8–17. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hoffman MS, Roberts WS, Bryson SC,
Kavanagh JJ Jr, Cavanagh D and Lyman GH: Treatment of recurrent and
metastatic cervical cancer with cis-platin, doxorubicin, and
cyclophosphamide. Gynecol Oncol. 29:32–36. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu H, Luo H, Zhang W, Shen Z, Hu X and
Zhu X: Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance in cervical
cancer. Drug Des Devel Ther. 10:1885–1895. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Serkies K and Jassem J: Concurrent weekly
cisplatin and radiotherapy in routine management of cervical
cancer: A report on patient compliance and acute toxicity. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 60:814–821. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sarosiek KA, Ni Chonghaile T and Letai A:
Mitochondria: Gatekeepers of response to chemotherapy. Trends Cell
Biol. 23:612–619. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brunelle JK and Letai A: Control of
mitochondrial apoptosis by the Bcl-2 family. J Cell Sci.
122:437–441. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Willems PH, Rossignol R, Dieteren CE,
Murphy MP and Koopman WJ: Redox Homeostasis and Mitochondrial
Dynamics. Cell Metab. 22:207–218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jana BA, Chintamaneni PK, Krishnamurthy
PT, Wadhwani A and Mohankumar SK: Cytosolic lipid excess-induced
mitochondrial dysfunction is the cause or effect of high fat
diet-induced skeletal muscle insulin resistance: A molecular
insight. Mol Biol Rep. 46:957–963. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wong A, Chen S, Yang LK, Kanagasundaram Y
and Crasta K: Lipid accumulation facilitates mitotic
slippage-induced adaptation to anti-mitotic drug treatment. Cell
Death Discov. 4:1092018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang L, Zhu H, Liu D, Liang S, Xu H, Chen
J, Wang X and Xu Z: Aspirin suppresses growth of human gastric
carcinoma cell by inhibiting survivin expression. J Biomed Res.
25:246–253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sostres C, Gargallo CJ and Lanas A:
Aspirin, cyclooxygenase inhibition and colorectal cancer. World J
Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 5:40–49. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Johnson KE, Ceglowski JR, Roweth HG,
Forward JA, Tippy MD, El-Husayni S, Kulenthirarajan R, Malloy MW,
Machlus KR, Chen WY, et al: Aspirin inhibits platelets from
reprogramming breast tumor cells and promoting metastasis. Blood
Adv. 3:198–211. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee DY, Lee KP, Baek S, Park JS, Kim YJ,
Kim KN, Kim SR and Yoon MS: Anti-breast cancer activity of
aspirin-conjugated chalcone polymeric micelles. Macromol Res.
29:105–110. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reid Y, Storts D, Riss T and Minor L:
Authentication of Human Cell Lines by STR DNA Profiling Analysis.
In: Assay Guidance Manual. [Internet]. Markossian S, Grossman A,
Brimacombe K, Arkin M, Auld D, Austin CP, Baell J, Chang TDY,
Coussens NP, Dahlin JL, et al: Eli Lilly & Company and the
National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. (Bethesda,
MD). 2004.
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sarenac T and Mikov M: Cervical Cancer,
Different Treatments and Importance of Bile Acids as Therapeutic
Agents in This Disease. Front Pharmacol. 10:4842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cai F, Luis MAF, Lin X, Wang M, Cai L, Cen
C and Biskup E: Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity in the
chemotherapy treatment of breast cancer: Preventive strategies and
treatment. Mol Clin Oncol. 11:15–23. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vane JR and Botting RM: The mechanism of
action of aspirin. Thromb Res. 110:255–258. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ittaman SV, VanWormer JJ and Rezkalla SH:
The role of aspirin in the prevention of cardiovascular disease.
Clin Med Res. 12:147–154. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee DH, Jung Jung Y, Koh D, Lim Y, Lee YH
and Shin SY: A synthetic chalcone,
2′-hydroxy-2,3,5′-trimethoxychalcone triggers unfolded protein
response-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
372:1–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li LT, Jiang G, Chen Q and Zheng JN: Ki67
is a promising molecular target in the diagnosis of cancer
(review). Mol Med Rep. 11:1566–1572. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Indran IR, Tufo G, Pervaiz S and Brenner
C: Recent advances in apoptosis, mitochondria and drug resistance
in cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1807:735–745. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Khanzadeh T, Hagh MF, Talebi M, Yousefi B,
Azimi A, Hossein Pour Feizi AA and Baradaran B: Investigation of
BAX and BCL2 expression and apoptosis in a resveratrol- and
prednisolone-treated human T-ALL cell line, CCRF-CEM. Blood Res.
53:53–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Naseri MH, Mahdavi M, Davoodi J, Tackallou
SH, Goudarzvand M and Neishabouri SH: Up regulation of Bax and down
regulation of Bcl2 during 3-NC mediated apoptosis in human cancer
cells. Cancer Cell Int. 15:552015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Su LJ, Zhang JH, Gomez H, Murugan R, Hong
X, Xu D, Jiang F and Peng ZY: Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid
Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. October 13–2019.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1155/2019/5080843. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cruz ALS, Barreto EA, Fazolini NPB, Viola
JPB and Bozza PT: Lipid droplets: Platforms with multiple functions
in cancer hallmarks. Cell Death Dis. 11:1052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Frank AC, Ebersberger S, Fink AF, Lampe S,
Weigert A, Schmid T, Ebersberger I, Syed SN and Brüne B: Apoptotic
tumor cell-derived microRNA-375 uses CD36 to alter the
tumor-associated macrophage phenotype. Nat Commun. 10:11352019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|